4/21/2021
1
BLUEBOOK &
THE CALIFORNIA
STYLE MANUAL
Do You Know the Difference?
Adrienne Brungess
Professor of Lawyering Skills
McGeorge School of Law
LSS - Day of Education
April 24, 2021
Purposes of Citation
1. To furnish the reader with legal support for an
assertion or argument:
a) provide information about the weight and persuasiveness of the
source;
b) convey the type and degree of support;
c) to demonstrate that a position is well supported and researched.
2. To inform the reader where to find the cited authority
if the reader wants to look it up.
Bluebook Parts of the Bluebook
1. Introduction: Overview of the BB
2. Bluepages: Provides guidance for the everyday citation needs of first-year law
students, summer associates, law clerks, practicing lawyers, and other legal
professionals. Includes Bluepages Tables.
Start in the Bluepages. Bluepages run from pp. 3-51.
3. Rules 1-21: Each rule in the Bluepages is a condensed, practitioner-focused version of
a rule from the white pages (pp. 53-214). Rules in the Bluepages may be incomplete
and may refer you to a rule(s) from the white pages for “more information” or “further
guidance.”
4. Tables (1-17): Includes tables T1 – T16. The two tables that you will consult most
often are T1 and T6. Tables are not rules themselves; rather, you consult them when
a relevant citation rule directs you to do so.
5. Index
6. Back Cover: Quick Reference
1 2
3 4
4/21/2021
2
Getting Familiar with the Bluebook
• Cases (B4)
• Statutes (B5)
• Books & Treatises (B8)
• Periodicals (B9)
Common rules include:Common rules include:
Basic Citation Forms
3 ways to
present a
citation
to legal
authority:
In the full citation format that is required when you cite to
a given authority for the first time in your document (e.g.,
Lambert v. Parrish
, 492 N.E.2d 289, 291 (Ind. 1986));
In a shortened version the second and subsequent times
that you cite to a given authority
(e.g.,
Lambert
, 492 N.E.2d at 291); and
In a general reference within your own sentence to an
authority that has already been discussed (e.g., “Unlike
the plaintiff in
Lambert
, Plotkin was injured while. . . .”).
Pinciting
Lambert v. Parrish
, 492 N.E.2d 289, 291 (Ind. 1986).
Lambert
, 492 N.E.2d at 291
These examples provide pinpoint references (“pincites”) to the exact
page on which the material being relied on appears (page 291 of an
opinion that begins on page 289 of volume 492 of the North Eastern
Reporter, 2d Series).
Some sources require pincites to page numbers; other sources require
pincites to section or paragraph numbers.
Pincites are important
Consider:
• A case that you need to cite could be several pages
long;
• A statute or regulation you need to cite could contain
numerous sections and subsections.
Don’t make the reader expend time searching for your
reference. Be specific.
5 6
7 8

4/21/2021
3
Pincites are important
Presume a pincite is needed in all citations.
Except: Two common situations where a pincite is
not
needed:
1. when appropriately using the short-form citation “
Id.”
to indicate
the same source and page number as a previous citation, and
2. when citing a particular authority for a proposition that is
supported by the entirety of the authority.
When to Cite
When quoting from the authority
When paraphrasing from the authority
When using ideas from the authority
When setting forth your own analysis or conclusion
that builds on the authority
When to Cite
When in doubt, cite.
It is less of a problem to
cite when you did not
need to than to not cite
when you did
.
Citing Cases
Formula:
• Name of case (first party v. second party), + volume
name and number + first page of case, + specific
page/paragraph or span of pages cited + (court date
of decision).
• Int’l Shoe v. Washington, 326 U.S. 310 (1945).
9 10
11 12
4/21/2021
4
Official & Unofficial Reporters
Federal system:
The official reporter for the Supreme Court is the
United States Reports (or U.S.).
Unofficial reporters are West’s Supreme Court Reports
(or S. Ct. ) or
United States Supreme Court Reports (Lawyer's
Edition) (L. Ed.).
Ex: Int’l Shoe v. Washington,
326 U.S. 310, 66 S. Ct. 154, 90 L. Ed. 95 (1945).
Federal Reporters
• United States Reports (official): U.S.
• Supreme Court Reports: S. Ct.
• United States Supreme Court Reports (Lawyers’ Edition): L. Ed.
Supreme CourtSupreme Court
• Federal Reporter: F.2d
Federal Appeals CourtFederal Appeals Court
• Federal Supplement: F. Supp.
Federal District CourtFederal District Court
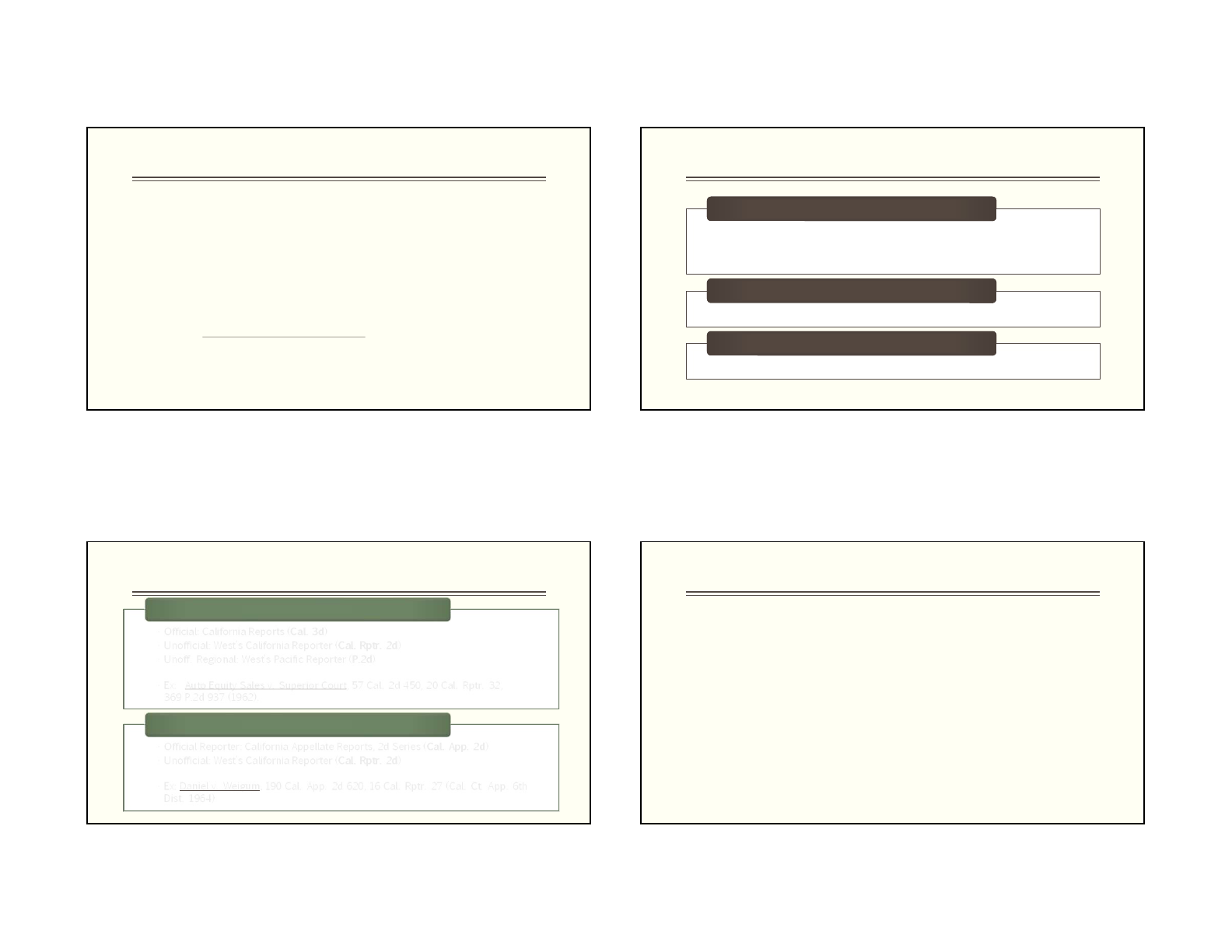
California Reporters
• Official: California Reports (Cal. 3d)
• Unofficial: West’s California Reporter (Cal. Rptr. 2d)
• Unoff. Regional: West’s Pacific Reporter (P.2d)
• Ex: Auto Equity Sales v. Superior Court, 57 Cal. 2d 450, 20 Cal. Rptr. 32,
369 P.2d 937 (1962).
• Official: California Reports (Cal. 3d)
• Unofficial: West’s California Reporter (Cal. Rptr. 2d)
• Unoff. Regional: West’s Pacific Reporter (P.2d)
• Ex: Auto Equity Sales v. Superior Court, 57 Cal. 2d 450, 20 Cal. Rptr. 32,
369 P.2d 937 (1962).
Supreme Court
• Official Reporter: California Appellate Reports, 2d Series (Cal. App. 2d)
• Unofficial: West’s California Reporter (Cal. Rptr. 2d)
• Ex: Daniel v. Weigum
,
190 Cal. App. 2d 620, 16 Cal. Rptr. 27 (Cal. Ct. App. 6th
Dist. 1964)
• Official Reporter: California Appellate Reports, 2d Series (Cal. App. 2d)
• Unofficial: West’s California Reporter (Cal. Rptr. 2d)
• Ex: Daniel v. Weigum
,
190 Cal. App. 2d 620, 16 Cal. Rptr. 27 (Cal. Ct. App. 6th
Dist. 1964)
Appellate Cases
Tips for Cases
Proper abbreviation for case names
Abbreviate ANY word in the case name that is listed in Table 6
Selection of the correct reporter
Find the correct jurisdiction in Table 1 of Bluebook
It will tell you which reporter to cite.
Proper numerical abbreviations –
R6.2 in Bluebook
“Second” = 2d NOT 2nd and “Third” = 3d NOT 3rd
Do NOT use superscript text in footnotes (ex: 1st not 1
st
)
Correct spacing for reporter names
– R6.1 in Bluebook
Close up adjacent single capitals (ex: S.D.N.Y.)
Individual numbers are treated as single capitals (ex: F.3d)
Do NOT close up single capitals w/ longer abbreviations (ex: D. Mass)
Insert a space adjacent to any abbreviation containing two or more letters
(ex: So. 2d and F. Supp. 2d)
13 14
15 16

4/21/2021
5
Citing Codes
Formula:
• Title number + abbreviated name of code +
section number + (publisher
if unofficial
&
year source was published).
• Ex: 35 U.S.C. § 271 (2006).
Official & Unofficial Codes
Federal system:
The official code is the United States Code
(U.S.C.).
Unofficial codes are published by West (U.S.C.A.)
and LexisNexis (U.S.C.S).
California system:
Deering’s and West’s both considered official.
Tips for Statutes
Section symbols
Always include a space between the section
symbol and the statute number (or other section
identification)
28 U.S.C. § 1291 (2000).
When citing to multiple sections in a statute, use
two section symbols
42 U.S.C. §§ 9601-9675 (2000).
Citing a Periodical (B9, R16)
5 Steps to Citing a Law Review or Journal Article
1. Author(s)
2. Title
3. Abbreviated name (Table T.13 in BB)
4. Pincite
5. (Year of publication)
Ex: Kenneth R. Feinberg,
Mediation – A
Preferred Method of Dispute Resolution
, 16
Pepp. L. Rev. 5, 14 (1989).
17 18
19 20
4/21/2021
6
Citing a Periodical, cont.
• Include the author’s entire name (as much as is known):
• Georgette C. Poindexter
• If two authors, include both, using “&”:
• A. Leo Levin & Meyer Kramer
• If more than two authors, either include all, or use just the first author and “et
al.”: Paul Butler et al.
Author(s)Author(s)
• Include the ENTIRE title as it appears on the title page
• Do not abbreviate words or omit articles in the title
• Underline
• Use Rule 8 for capitalization rules
TitleTitle
Citing a Periodical, cont.
Journal
For a
consecutively paginated
journal (when the journal, for instance,
starts the 3rd issue of a volume on the page following the last page of the
2nd issue):
Identify the journal volume number
Look to Table T.13 for the journal abbreviation
Ex: David Rudovsky, Police Abuse: Can the Violence Be Contained?,
27 Harv. C.R.-C.L. L. Rev.
For a
non-consecutively paginated
journal (such as a magazine, where
each issue starts at page 1):
Include only the journal/magazine name, in small caps (BOLD for the
write on), and the date of issue
o Ex: Joan B. Kelly, Mediated and Adversarial Divorce: Respondents’
Perceptions of Their Processes and Outcomes, Mediation Q., Summer
1989.
Citing a Periodical, cont.
Pincite
Similar to a case, include the first page of the article after the
journal name, then a comma, and the specific page that contains
the material being cited:
Ex: David Rudovsky, Police Abuse: Can the Violence Be
Contained?, 27 Harv. C.R.-C.L. L. Rev. 465, 500.
For a magazine, include the word “at” and the first page of the
article:
Joan B. Kelly, Mediated and Adversarial Divorce: Respondents’
Perceptions of Their Processes and Outcomes, Mediation Q.,
Summer 1989, at 71.
Citing a Periodical, cont.
Date of Publication
For a consecutively paginated journal, at the end of
the citation, include the year of publication in
parentheses:
Ex: David Rudovsky, Police Abuse: Can the Violence Be
Contained?, 27 Harv. C.R.-C.L. L. Rev. 465, 500 (1992).
For a non-consecutively paginated journal, the year
will have already be included, so there is no need to
repeat it.
Ex: Joan B. Kelly, Mediated and Adversarial Divorce:
Respondents’ Perceptions of Their Processes and
Outcomes, Mediation Q., Summer 1989, at 71.
21 22
23 24
4/21/2021
7
Books & Treatises
Formula:
[Volume number (if multi-volume work)] + Author, +
Title
+
[at] Pinpoint reference + ([Editor name, ed.,] + [Publisher] +
[Edition number (other than 1st) ed.] + Year of publication).
Example:
7A Charles Alan Wright, Arthur R. Miller & Mary Kay Kane,
Federal
Practice and Procedure
§ 1758, 114–15 (3d ed. 2005).
Short Form: 7A Wright, § 1757.
Example:
1 Arthur Linton Corbin,
Corbin on Contracts
§ 4.14 (Joseph M.
Perillo ed., rev. ed. 1993).
California Style Manual
Style manual for California
courts
4th ed. (2000)
Published at irregular
intervals (every 15 years)
Available on Westlaw
(e.g.) CASTYLE s 1:1
Cal. State Court Citation Format
California Rules of Court Rule 1.200
Citations to authorities in all documents filed in the
California state courts must be in the style
established by either
California Style Manual
or
The Bluebook: A Uniform System of Citation
Party filing the document chooses the citation
manual.
Same style must be used consistently throughout
the document.
Cal. State Court Citation Format
• Advisory Committee Comment to
Cal. Rules of Court, Rule 8.204
Brief writers are encouraged
to follow the citation form of
the
California Style Manual
(4th ed., 2000).
Brief writers are encouraged
to follow the citation form of
the
California Style Manual
(4th ed., 2000).
• Cal. Rules of Court,
Rule 8.887(c)(1)
Opinions certified for
publication must comply to
the extent practicable with
the
California Style Manual
.
Opinions certified for
publication must comply to
the extent practicable with
the
California Style Manual
.
• Cal. Rules of Court,
Rule 3.1113(c)
A case citation must include
the official report volume
and page number and year
of decision.
A case citation must include
the official report volume
and page number and year
of decision.
25 26
27 28
4/21/2021
8
California Style Manual: Type Style
Use
italics
, not underlineUse
italics
, not underline
• Case names
• Cross reference words (
ante, ibid., id., infra, post, supra
)
• But, words denoting subsequent case history (revd., affd.) are
not usually italicized.
ItalicizeItalicize
Do not use underlining to signal italicsDo not use underlining to signal italics
California Style Manual: Placement of Citations
Use parentheses around a citation, whether it appears
within a sentence or at the end.
Use brackets [ ] to enclose any unofficial parallel citations.
(CSM §4:57)
Examples:
When statutory language is clear and unambiguous, there is no
need for construction and courts should not indulge in it. (
People
v. Overstreet
(1986) 42 Cal.3d 891, 895 [231 Cal.Rptr. 213, 726
P.2d 1288].)
Unlike the Fourth Amendment, which proscribes “unreasonable”
government seizures, (
Graham v. Connor
(1989) 490 U.S. 386,
394), the Eight Amendment only protects ….
California Style Manual: Placement of Citations
If the citation forms an integral part of the
sentence, do not use parentheses.
Use brackets around any parallel citations.
Example:
In
American Academy of Pediatrics v. Lungren
(1997) 16
Cal.4th 307 [66 Cal.Rptr.2d 210, 940 P.2d 797], the
California Supreme Court considered this very question.
California Style Manual: Introductory Signals
• Signals appear in ordinary roman type
A signal informs the
reader about the
relationship between the
idea stated in the text
and the cited source.
• See
• See also
• Cf. or e.g.
• But see
• Contra
Examples of signals:
29 30
31 32
4/21/2021
9
California Style Manual: California Code Citations
If the code cite is at the end of a sentence, the
citation must be placed inside parentheses.
The period at the end of the cite is inside the
parentheses
Do not use “Cal.” before code names
A comma comes after the code name
Only includes publisher and year only if citing to
publisher-added materials
There is not a provision for code cites to Westlaw or
Lexis
California Style Manual:
California Code Citations Examples
(Bus. & Prof. Code, § 16700 et seq.)
(Code Civ. Proc., § 564, subd. (a).)
(Pen. Code, § 331.)
(Civ. Code, §§ 1810.2-1812.12.)
(Pen. Code, §§ 118, 118a, 126.)
(Prob. Code, §§ 610 et seq., 670 et seq.)
(Evid. Code, § 700; see Pen. Code, § 1321.)
California Style Manual: California Code Citations
For code sections within the text of a
sentence:
use unabbreviated code names
spell out "section" before the code section
number
insert a comma after subdivisions
California Style Manual: California Code Citations
Example of citations outside parentheses:
Civil Code section 1000 et seq.
Civil Code sections 1006 et seq., and 1013 et seq.
Section 844 of the Penal Code
Section 1203.1 b of the Penal Code
Probate Code section 233, subdivision (a)
33 34
35 36
4/21/2021
10
California Style Manual: California Code Citations
Short form:
Code name may be omitted after initial cite if a
footnote or parenthetical explains that
undesignated section references are to that code.
Only one code designation may be omitted in
each document.
California Style Manual: California Code Citations
Example of how to use a footnote to indicate the omitted
code name:
Code of Civil Procedure section 631
1
provides that a jury trial may be waived by
written consent filed with the clerk.
______________________________
1. All further unspecified statutory references are to the Code of Civil Procedure.
California Style Manual: California Code Citations
• case name
• no comma after the case name
• year and court
• reporter with volume and page
• the complete cite is in parenthesis
• the period is at the end of the cite but inside the parentheses
Elements of a Case Law CitationElements of a Case Law Citation
• (
Smiley v. Citibank
(1995) 11 Cal.4th 138.)
Example:Example:
California Style Manual: Case Law Citations
Case names
Italicize
case names (including the v.)
Year and court
Always include the year
Only include the court if it cannot be determined by cite to reporter
Reporter
Provide cite to the official reporter.
CSM recommends a parallel cite to an unofficial reporter in [ ].
Pincites are not needed for parallel cites.
Example
(
Smith v. Williams
(1966) 65 Cal.2d 263, 265 [54 Cal.Rptr.2d 370].)
37 38
39 40
4/21/2021
11
California Style Manual: Case Law Citations
(
People v. Marshall
(1997) 15 Cal.4th 1.)
(
California v. Romero
(1983) 463 U.S. 992.)
(
Spurgeon v. Mission State Bank
(8th Cir. 1945)
151 F.2d 702.)
(
Mcinnis v. Shapiro
(ND.Ill. 1968) 293 F.Supp. 327)
(
Gressler v. New York Life Ins. Co.
(Utah 1945)
163 P.2d 324.)
(
English v. State
(Okla.Crim.App. 1969) 462 P.2d 275.)
California Style Manual: Case Law Citations
There are no spaces between the reporters
and the edition:
Cal.App.3d
Cal.3d
F.Supp.4th
F.3d
Main differences from Bluebook
Italics
not
underline and no
choice
Italics
not
underline and no
choice
(The entire citation
is in parentheses.)
(The entire citation
is in parentheses.)
(Ending period is
placed inside the
parentheses.)
(Ending period is
placed inside the
parentheses.)
There is no comma
after the case
name
There is no comma
after the case
name
The date comes
immediately after
the case name
The date comes
immediately after
the case name
Parallel cites are
recommended and
put in []
Parallel cites are
recommended and
put in []
The spacing for the
reporter
abbreviations may
be different
The spacing for the
reporter
abbreviations may
be different
California Style Manual: Short Form
After an opinion is first cited in a document, it is not
cited in full again.
Short cite format depends on whether the subsequent
reference is
1. In the same paragraph (intervening authority / no intervening
authority) or
2. In a different paragraph
41 42
43 44
4/21/2021
12
California Style Manual: Short Form
Once an opinion is cited in full, the first reference in
any subsequent paragraph must include the case
name,
supra
, the reporter, and the volume and page
numbers.
Note: per Bluebook – you cannot use supra to refer to primary
authority.
California Style Manual: Short Form
If the first subsequent reference is to a point page
within the opinion, either provide the inception page for
the opinion plus the point page
OR use "at page" (or "at p." in parentheses) without the
inception page.
California Style Manual: Short Form
(
Silacci v. Abramson, supra,
45 Cal.App.4th 558.)
(
Silacci v. Abramson, supra,
45 Cal.App.4th 558, 562.)
(
Silacci v. Abramson, supra,
45 Cal.App.4th at p. 562.)
California Style Manual: Short Form
To repeat an identical citation to an opinion within the same
paragraph,
ibid.
may be used when no intervening authority is cited
.
To repeat a citation to an opinion with a different point page,
id.
may be used.
Ibid.
and
id.
are used only to refer to the immediately preceding
citation in the same paragraph.
Note: there is no “ibid” in Bluebook
45 46
47 48
4/21/2021
13
California Style Manual: Short Form
The conduct of the plaintiff in
Khawar v. Globe Internet, Inc.
(1998) 19 Cal.4th 254, 267 [79 Cal.Rptr. 178] did not make
him a public figure. His role in the underlying controversy
was "trivial at best." (
Ibid.
)
The California Supreme Court declined to characterize the
plaintiff as a public figure in
Khawar v. Globe Internet, Inc.
(1998) 19 Cal.4th 254, 267 [79 Cal.Rptr. 178]. The court
also declined to adopt a neutral reportage privilege in that
case. (
Id.
at p. 273.)
California Style Manual: Short Form
Burglary is not committed by placing a stolen check in
a bank's window chute, based on the court's decision
in
People v. Davis
(1998) 18 Cal.4th 712, 724
(disapproving
People v. Ravenscroft
(1988) 198
Cal.App.3d 639). However, burglary "may be
committed by using an instrument to enter a
building." (
People v. Davis, supra,
at p. 717.)
California Style Manual: Short Form
A shortened case name followed by a point page reference is
also sufficient for second and subsequent references within the
same paragraph, whether or not there is intervening authority.
• A penalty provision is separate from the underlying offense.
(
People v. Wolcott
(1992) 10 Cal.App.4th 1584, 1596,1598;
People v. Bryant
(1983) 34 Cal.3d 92, 101.) The jury does not
consider the penalty allegation until it first reaches a verdict
on the substantive offense. (
Bryant,
at p. 101.)
• Note: this form is NOT compliant with Bluebook
California Style Manual: Short Form
Same paragraph, no intervening
authority
Same paragraph, intervening
authority
Different paragraph
Use ibid. for identical cite
Use id. at p. __ for change in
page number
1) case name
2) supra (optional)
3) page
(People v. Davis, supra,
at p. 718.)
or
1) shortened case name
2) page
(Davis, at p. 1097.)
1) case name
2) supra
3) reporter with volume
and
page
(Smith v. Williams, supra,
45 Cal.App.4th at p. 562.)
49 50
51 52
