
3 February 2022
ESMA50-165-1948
EU Alternative
Investment Funds
ESMA Annual Statistical Report 2022

ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 2
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds
2022
© European Securities and Markets Authority, Paris, 2022. All rights reserved. Brief excerpts may be reproduced or translated
provided the source is cited adequately. The reporting period of this document is 31 December 2020, unless indicated otherwise.
Legal reference of this report: Regulation (EU) No 1095/2010 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 24 November
2010 establishing a European Supervisory Authority (European Securities and Markets Authority), amending Decision
No 716/2009/EC and repealing Commission Decision 2009/77/EC, Article 32 ‘Assessment of market developments’, 1. ‘The
Authority shall monitor and assess market developments in the area of its competence and, where necessary, inform the
European Supervisory Authority (European Banking Authority), and the European Supervisory Authority (European Insurance
and Occupational Pensions Authority), the ESRB and the European Parliament, the Council and the Commission about the
relevant micro-prudential trends, potential risks and vulnerabilities. The Authority shall include in its assessments an economic
analysis of the markets in which financial market participants operate, and an assessment of the impact of potential market
developments on such financial market participants.’ This report contributes to ESMA’s risk assessment activities. The report and
its contents do not prejudice or impair ESMA’s regulatory, supervisory or convergence activities, nor the obligations of market
participants thereunder. Charts and analyses in this report are based on data provided by national competent authorities to ESMA
under the Alternative investment fund managers directive (AIFMD). ESMA uses these data in good faith and does not take
responsibility for their accuracy or completeness. ESMA is committed to constantly improving its data sources and reserves the
right to alter data sources at any time.
European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA)
Risk Analysis and Economics Department
201-203 rue de Bercy
FR–75012 Paris
risk.analysis@esma.europa.eu
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 3
Table of contents
Executive summary 4
Market monitoring 8
EU AIF market 9
Brexit implications for AIF statistics 16
Funds of Funds 19
Real Estate Funds 24
Hedge Funds 28
Private Equity Funds 32
Other AIFs 35
Non-EU AIFs (NPPR) 40
Statistics 45
EU AIF market 46
Funds of Funds 52
Real Estate Funds 55
Hedge Funds 59
Private Equity Funds 63
‘Other AIFs’ 67
Non-EU AIFs (NPPR) 71
Annex 75
EU AIFMD data reporting 76
Data inventory 78
List of abbreviations 80

ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 4
Executive summary
Market structure and developments
The EU Alternative Investment Funds (AIF) market: The size of the EU AIF universe (using data from
the 30 members of the European Economic Area, EEA30) continued to expand to reach EUR 5.9tn in
net asset value (NAV) at the end of 2020, an 8% increase from 2019. The growth of the AIF market
results from the launch of new AIFs in 2019 and positive valuation effects. Overall, AIFs accounted for
one-third of the EEA30 fund industry at the end of 2020. Among AIF types, Funds of Funds (FoFs)
account for 15% of the NAV, followed by Real Estate (RE) funds (13%), Private Equity (PE) funds (5%)
and Hedge Funds (HFs) (2%). The small share of HFs compared with 2019 is explained by the fact that
UK data have not been included (see editorial note for an explanation of Brexit implications for this
report), while in 2019 UK AIFs accounted for 75% of HFs NAV. The category of ‘other AIFs’ accounts
for 62% of the NAV, pointing to continued classification issues for Alternative Investment Fund
Managers (AIFMs). Professional investors own most of the shares of AIFs, yet retail investor share is
significant at 14% of the NAV, with more retail participation in RE funds (24%) and FoFs (19%). AIFs
invest predominantly in the EEA and across a broad range of asset classes (securities, derivatives and
funds). At the aggregate level, adjusted leverage declined to 128% of NAV (compared with 145% in
2019). Overall, there are signs of potential liquidity mismatch, as the liquidity offered to investors is
generally greater than the liquidity of the assets, especially for RE funds. While at aggregate level this
mismatch is unlikely to materialise, it indicates that AIFs with a liquidity deficit would face challenges if
large redemptions were to occur.
Funds of Funds: FoFs account for 15% of the NAV of EEA30 AIFs, at around EUR 0.9tn (+4% compared
with 2019). Among AIF types, FoFs have the second largest retail investor participation at 20% of NAV.
Open-ended FoFs remain exposed to significant liquidity mismatch across all time horizons, including
FoFs investing mainly in UCITS. The potential liquidity shortage for FoFs with a liquidity deficit is 16%
of their NAV in the short term (i.e. within one week).
Real Estate Funds: RE funds account for 13% of the NAV of EEA30 AIFs, at EUR 766bn. RE funds
continued to grow in 2020, albeit at a more moderate pace (+9% compared with 2019). The proportion
of retail investors has continued to grow to reach 24%, the highest among AIF types. While leverage
remains limited, liquidity risk in RE funds is a concern: around 54% are open-ended, and 40% of
Commercial Real Estate (CRE) funds by NAV offer daily liquidity to investors. At the aggregate level,
RE funds face liquidity mismatch across all time periods, an indication of a structural vulnerability as
the maturities of assets and liabilities are not aligned.
Hedge Funds: With the departure of the UK from the EU, the size of the EEA30 HF sector has
plummeted to only EUR 89bn (2% of the NAV of all AIFs), from EUR 354bn in 2019 (including the UK).
EEA30 HFs have widespread access to the EU passport and are mainly domiciled in Ireland and
Luxembourg. Leverage is very high, particularly for some strategies highly reliant on derivatives. HFs
using derivatives tend to maintain large, unencumbered cash positions, possibly to meet future margin
calls relating to derivatives positions. HFs are exposed to limited liquidity mismatch, as their assets can
be liquidated quickly to meet investor redemptions. However, HFs are exposed to financing risk, as for
some strategies more than half of their funding is overnight, implying potential rollover risk.
Private Equity Funds: PE funds account for 6% of the NAV of all EEA30 AIFs, or EUR 363bn. Among
AIF types, PE funds contributed remarkably to the growth of the AIF sector in 2020 (+29% compared
with 2019), together with ‘other AIFs’. They follow a range of strategies and are almost exclusively sold
to professional investors. PE funds invest mainly in illiquid securities (unlisted securities), but liquidity
risk is limited given that PE funds are overwhelmingly closed-ended.
Other AIFs: ‘Other AIFs’ account for 62% of the NAV of EEA30 AIFs, at around EUR 3,650bn (+4%
compared with 2019). This category of the AIFMD reporting regime covers a range of strategies, with
fixed income and equity strategies accounting for 68% of the NAV and an additional residual category
amounting to 28%. ‘Other AIFs’ are mainly sold to professional investors, although there is a significant
retail investor presence in the residual category. They make little use of financial or synthetic leverage.

ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 5
Although most types of ‘other AIFs’ have a limited liquidity risk at aggregate level, some funds in this
residual category may be subject to liquidity deficits.
AIFs managed by Non-EU AIFMs: EU Member States can allow non-EU asset managers to market
alternative funds at national level under the National Private Placement Regime (NPPR), even though
such funds cannot be passported to other EU Members States. The market for such non-EU funds is
comparatively large: The NAV of non-EU AIFs marketed under NPPR rules amounts to EUR 1.3tn, i.e.
more than one-fifth of the AIF market. NPPR fund marketing is concentrated in a small number of
Member States, and more than 99% of investors are professional investors. Hedge funds marketed
under the NPPR are predominantly domiciled in the Cayman Islands, while ‘other AIFs’ marketed under
the NPPR are predominantly US-based exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Overall, risk profiles for NPPR
funds are comparable to EEA30 AIFs. However, the geographical investment focus is different as NPPR
funds invest predominantly in non-EU areas.
Editorial note
Brexit implications for EU AIF statistics: The UK asset management industry was an important part of
the EU single financial market, and with that also of the EU AIF market. Statistics presented in this
report fall after the withdrawal of the United Kingdom from the EU on 31 January 2020. Although the
EU laws continued to apply to the UK until the end of the transition period on 31 December 2020, it was
not possible to collect data covering this period. Since this report uses end-year data, all the data used
were transmitted to ESMA during the course of 2021, i.e. after the departure of the UK from the EU,
making the transmission of UK data not feasible. Therefore, our statistics are constructed from data
reports provided by entities authorised or registered in the Member States of the EEA post-Brexit
(calculated on a constant perimeter of EEA30). Starting with this edition of this ASR series, we show
statistics of the EU AIF market after Brexit. All the data in this report refer to EEA30 (EU27 and Iceland,
Liechtenstein and Norway) and therefore exclude the UK, including for years before 2020. All time
series have been adjusted retroactively and the UK is counted out consistently over time. Comparisons
with statistics we had published in earlier editions are, therefore, limited. A dedicated section discusses
the implications of Brexit for AIF statistics.

ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 6
EEA30 AIFs: Essential statistics
Funds of
Funds
Real
Estate
Hedge
Funds
Private
Equity
Other
AIFs
Total
Size
Number of funds
(Absolute number)
5,362
3,978
930
4,992
14,324
30,035
Number of leveraged funds
(Absolute number)
250
1,439
345
136
2,124
4,345
Net Asset Value
(EUR bn)
873
766
89
363
3,652
5,899
Average fund size
(EUR mn per fund)
163
190
96
73
255
195
Proportion of total market
(NAV % of all AIFs)
15%
13%
2%
6%
62%
Distribution
EU passport
(% of total)
90%
84%
76%
51%
86%
80%
Retail participation
(% of total)
19%
23%
10%
6%
10%
13%
Exposures
Main exposures
(Asset type)
CIU
PA
IRD
S
S
DER
Main exposures
(% of exposures)
72%
69%
40%
84%
64%
24%
Leverage
Gross leverage
(% of NAV)
120%
141%
548%
117%
154%
151%
Adjusted leverage
(% of NAV)
119%
138%
327%
116%
141%
139%
Borrowing
(% of NAV)
9%
12%
250%
5%
22%
21%
Liquidity
Open ended AIFs
(% of total NAV)
69%
56%
76%
4%
78%
70%
Monthly portfolio liquidity
(% of NAV)
56%
3%
34%
2%
68%
55%
Monthly investor liquidity
(% of NAV)
70%
17%
37%
14%
72%
61%
Note: All values refer to AIFs managed and/or marketed by EEA30 AIFMs at the end of 2020, AIFs reported to ESMA by National Competent
Authorities (NCAs). AIFs sold under a National Private Placement Regime (NPPR) are excluded. Statistics for all EEA30 AIFs include 449 funds
with no predominant type, for which NAV amounts to EUR 155bn. Leveraged funds are identified using the AIF reporting code as specified in the
Annex 2 of ESMA guidelines on AIFMD reporting obligations. Open ended AIFs are funds that issue shares which are redeemable on demand by
investors. CIU=collective investment units; PA=Physical assets; IRD=Interest rate derivatives; S=Securities. DER=Derivatives. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.

ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 7
EEA30 AIFs: Gross notional exposures
Asset class
Asset type
2019
EUR bn
2020
EUR bn
Share
% of 2020 exposures
Securities
3,553
3,754
48%
Among which
Non-financial listed equities
777
847
11%
EU sovereign bonds
672
697
9%
IG financial bonds
336
341
4%
IG corporate bonds
311
301
4%
Loans
289
297
4%
Other cash and cash equivalent
274
295
4%
Unlisted equities
172
236
3%
Non-investment-grade financial bonds
86
130
2%
Financial listed equities
123
103
1%
Non-G10 sovereign bonds
101
101
1%
Deposits
73
83
1%
Leveraged loans
78
76
1%
G10 sovereign bonds
61
53
0.7%
Other structured products
41
47
0.6%
MBS
48
35
0.5%
Non-investment-grade corporate bonds
29
29
0.4%
Non-financial convertible bonds
17
20
0.3%
CDO/CLO
18
22
0.3%
Municipal bonds
20
21
0.3%
ABS
18
15
0.2%
Financial convertible bonds
8
4
0.1%
Derivatives
2,769
1,950
25%
Among which
Foreign exchange derivatives
618
686
9%
Interest rate derivatives
735
671
9%
Fixed income derivatives
241
223
3%
Equity derivatives
233
152
2%
Credit derivatives
117
124
2%
Other derivatives
785
58
0.8%
Commodity derivatives
40
36
0.5%
Collective Investment Undertakings
1,241
1,311
17%
Among which
Investment funds (excl. ETFs and
MMFs)
1102
1143
15%
ETFs
69
92
1%
MMFs
70
76
1%
Physical assets
547
641
8%
Among which
Physical real estate
539
629
8%
Other physical assets
9
12
0.2%
Other assets
96
134
2%
Total exposures
8,206
7,791
100%
Note: Gross notional exposures represent the gross market exposure of a fund which is calculated by summing the absolutes values of the notional
amounts of a fund’s derivatives and the value of the fund’s other investments. Exposures can be long (when an increase in price leads to an
increase in the NAV of the fund) or short (when an increase in price leads to a decrease in the NAV of the fund). Gross exposures measure the
investment funds’ absolute exposures (long and short). All values refer to AIFs managed and/or marketed by EEA30 AIFMs at the end of 2020,
AIFs reported to ESMA by National Competent Authorities (NCAs). AIFs sold under a National Private Placement Regime (NPPR) are excluded.
Statistics for all EEA30 AIFs include 449 funds for which no fund type has been specified by the AIFM, for a NAV of EUR 155bn. Data for the
EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 8
Market monitoring
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 9
EU AIF market
Summary
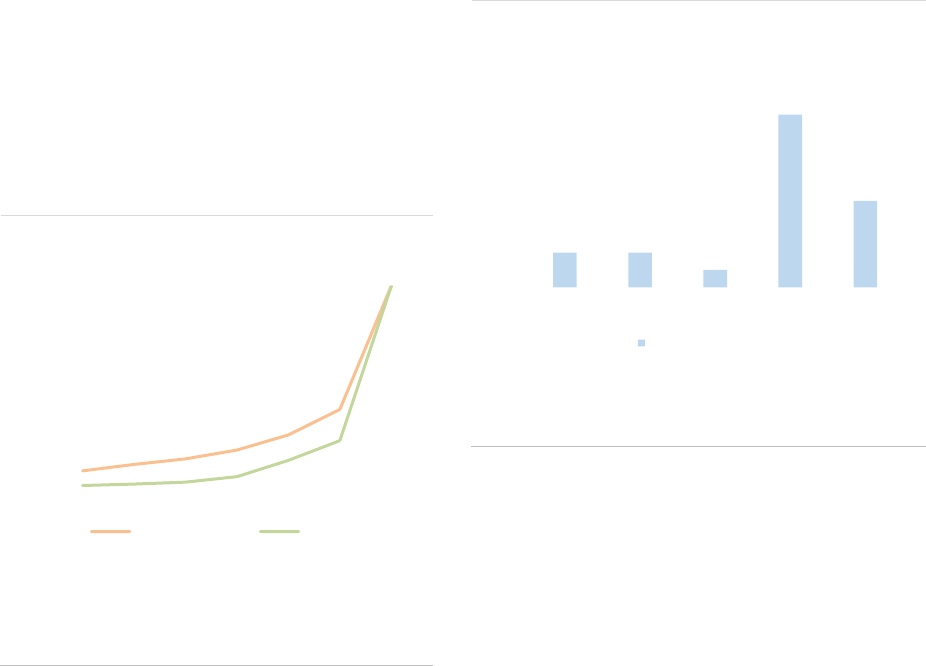
The size of the EU AIF universe (using data from the 30 members of the European Economic Area,
EEA30) continued to expand to reach EUR 5.9tn in net asset value (NAV) at the end of 2020, an 8%
increase from 2019. The growth of the AIF market results from the launch of new AIFs in 2019 and
positive valuation effects. Overall, AIFs accounted for one-third of the EEA30 fund industry at the end
of 2020. Among AIF types, Funds of Funds (FoFs) account for 15% of the NAV, followed by Real Estate
(RE) funds (13%), Private Equity (PE) funds (5%) and Hedge Funds (HFs) (2%). The small share of
HFs compared with 2019 is explained by the fact that UK data have not been included, while in 2019
UK AIFs accounted for 75% of HFs NAV. The category of ‘other AIFs’ accounts for 62% of the NAV,
pointing to continued classification issues for Alternative Investment Fund Managers (AIFMs).
Professional investors own most of the shares of AIFs, yet retail investor share is significant at 14% of
the NAV, with more retail participation in RE funds (24%) and FoFs (19%. AIFs invest predominantly in
the EEA and across a broad range of asset classes (securities, derivatives and funds). At the aggregate
level, adjusted leverage declined to 128% of NAV (compared with 145% in 2019). Overall, there are
signs of potential liquidity mismatch, as the liquidity offered to investors is generally greater than the
liquidity of the assets, especially for RE funds. While at aggregate level this mismatch is unlikely to
materialise, it indicates that AIFs with a liquidity deficit would face challenges if large redemptions were
to occur..
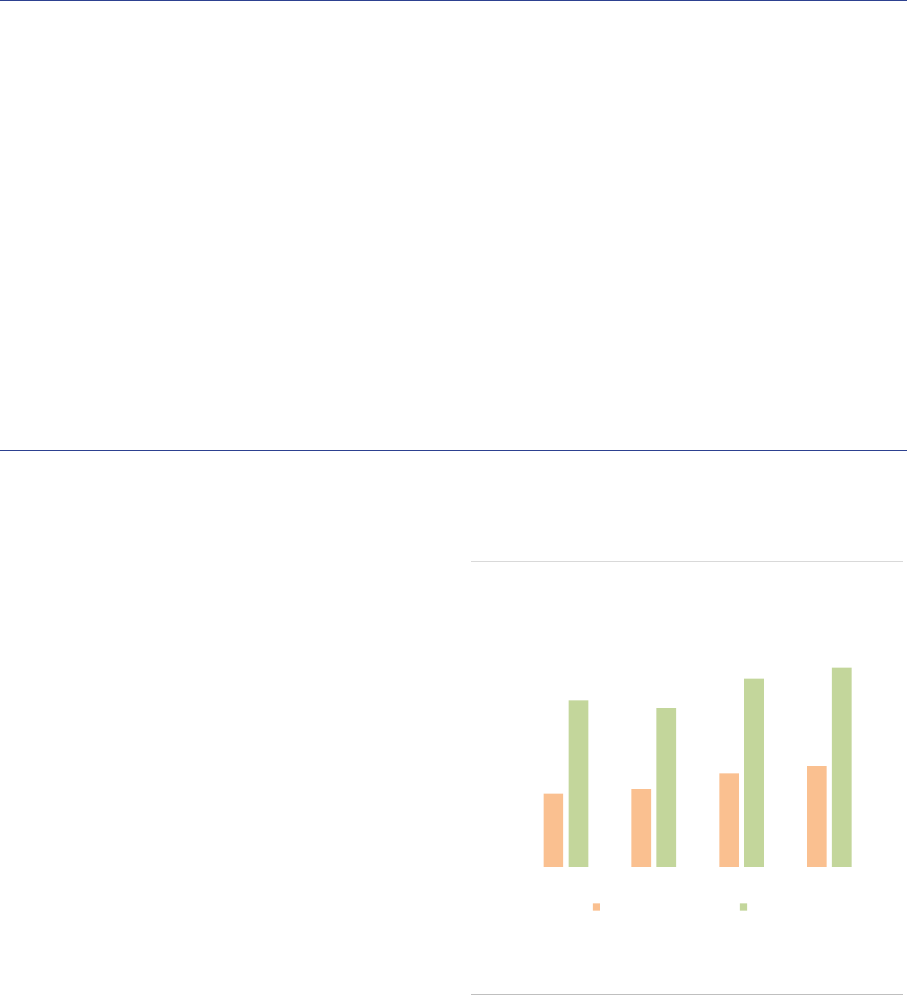
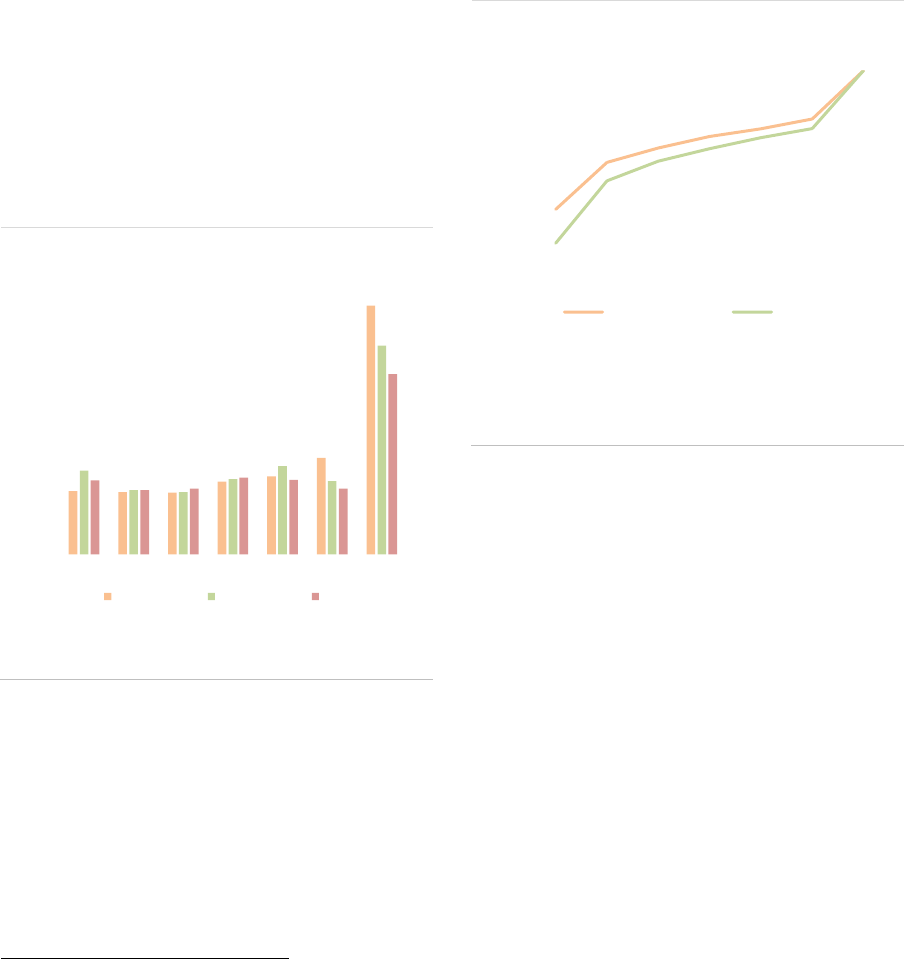
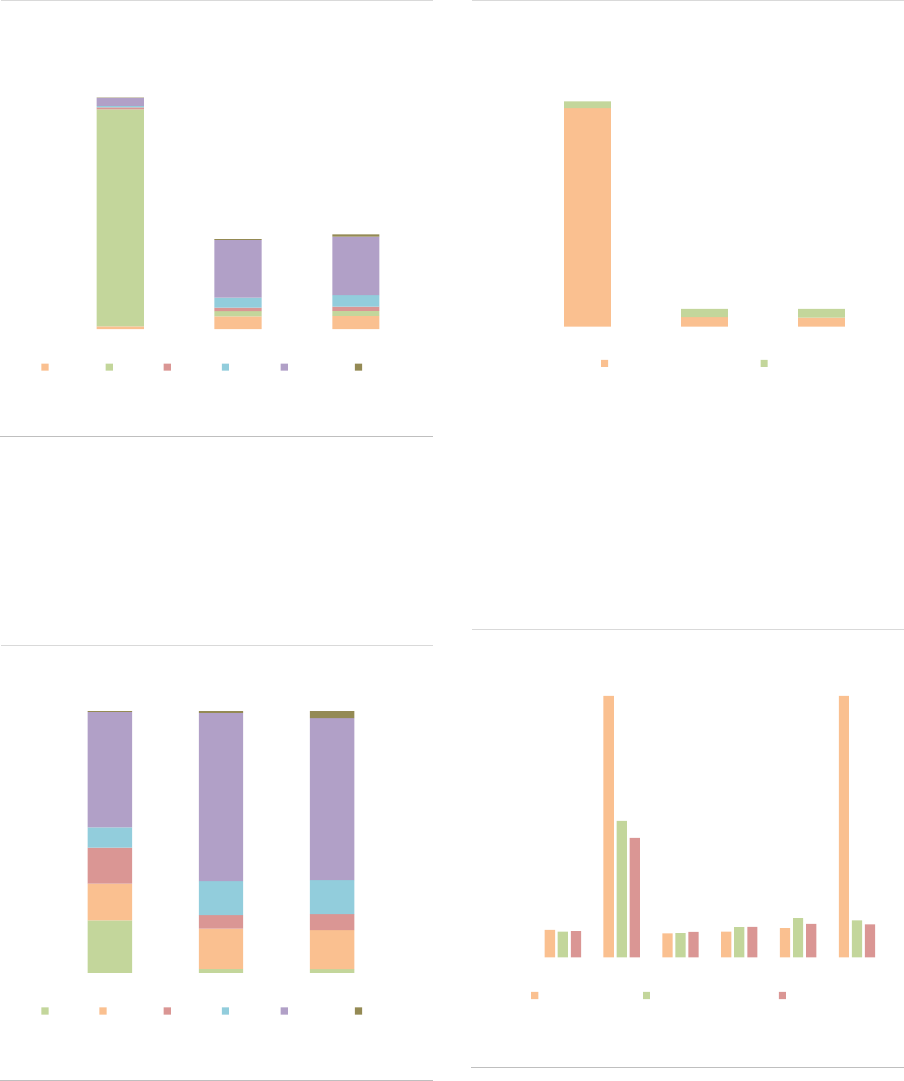
Market size and structure
All the data in this report refer to the EEA30
(EU27 and Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway),
hence UK data are excluded, also for years
before Brexit. The AIF industry continued to
expand in 2020 in the EEA30, with an 8%
increase from 2019, to reach a NAV of around
EUR 5.9tn at the end of 2020 (ASR-AIF.1). By
comparison, the NAV of Undertakings for the
Collective Investment in Transferable Securities
(UCITS) amounted to EUR 11.6tn at the end of
2020, according to the European Fund and Asset
Management Association (EFAMA). Overall,
AIFs therefore account for one-third of the EEA30
fund industry.
ASR-AIF.1
EEA30 fund industry
Significant growth in 2019
The growth in the EEA30 AIF market is
attributable to the launch of new AIFs in 2020
(EUR 514bn), and positive valuation and flow
effects (EUR 256bn), which compensated for the
decline of EUR 248bn related to the liquidation of
funds in 2020 (ASR-AIF.2).
4.3
4.6
5.5
5.9
9.7
9.3
11.0
11.6
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
2017 2018 2019 2020
AIFs UCITS
Note: NAV by type of AIF managed and/or marketed by authorized AIFMs and
sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions, in EUR bn.
Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, EFAMA, ESMA.
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 10
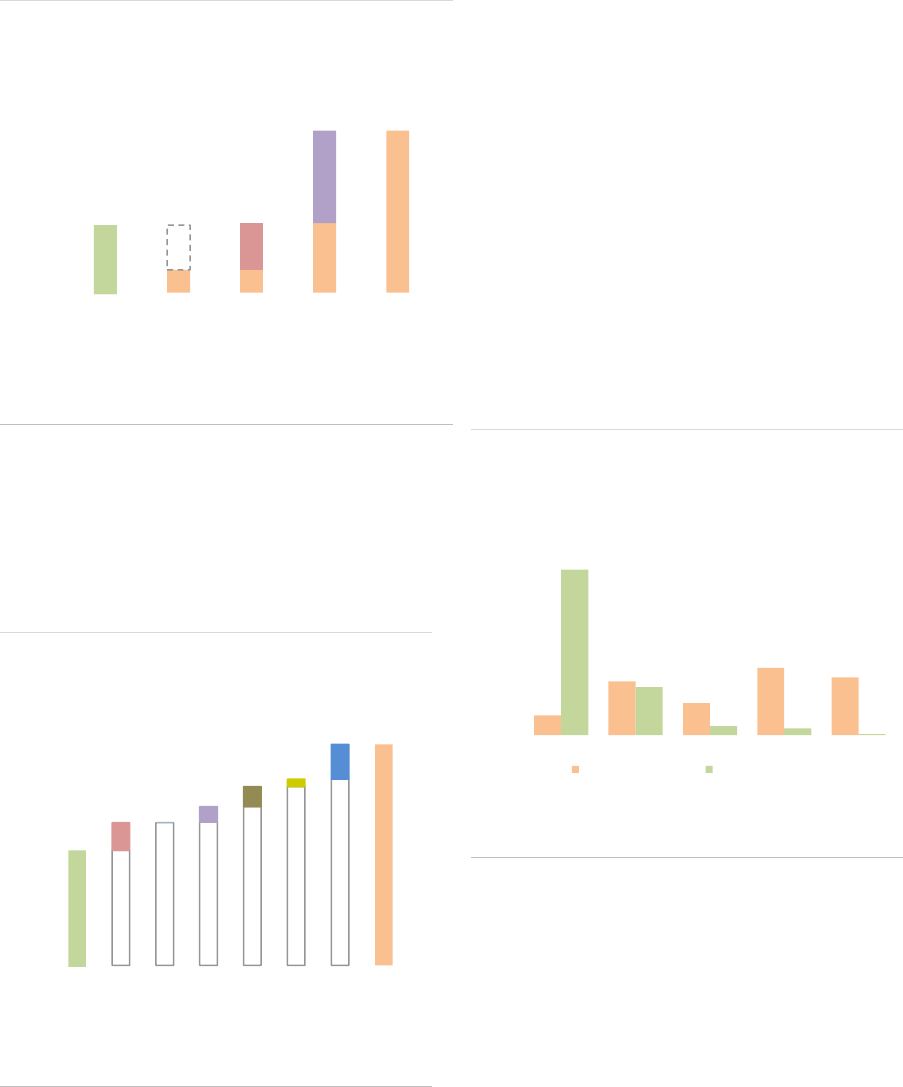
ASR-AIF.2
EEA30 AIFs growth decomposition
Growth owing to new AIFs, flows, valuation effects
By AIF types, ‘other AIFs’, PE and funds with no
predominant strategy (‘none’) contributed most to
the growth of the AIF sector (ASR-AIF.3). For the
AIFs with no predominant strategy, the rise in
NAV is explained by a change in classification for
one country: AIFs that were previously classified
as ‘Other AIFs’ changed to the ‘none’ category.
ASR-AIF.3
EEA30 AIF growth decomposition by types
Growth in ‘other AIFs’, PE, no predominant
strategy
AIF types: The composition of the AIF market by
type was broadly stable in 2020. FoFs account for
15% of the NAV (stable compared with 2019),
followed by RE funds (13%), PE funds (5%,
+1pp), funds with no predominant strategy (3%,
+2pp) and HFs (2%). The very small share of HFs
is related to Brexit, since UK AIFMs had
accounted for around 75% of the EU HF market
before the country left the EU. Finally, ‘other AIFs’
remain by far the largest type, accounting for 62%
of NAV (ASR-AIF.16). Within this category,
around 30% of NAV is attributed to a residual
category (which amounts to 17% of the NAV of all
AIFs), pointing to continued classification issues
for AIFMs, as detailed in the ‘Other AIF section’.
AIF size: The AIF market remains highly
concentrated, with a few large AIFs accounting
for most of the market. In 2020, AIFs with a NAV
larger than EUR 1bn accounted for less than 3%
of all AIFs but for 54% of the NAV (ASR-AIF.4).
Smaller AIFs (NAV lower than EUR 500mn)
account for 93% of all AIFs but only 32% of NAV.
The large concentration implies that by focusing
on the largest AIFs, one should be able to monitor
a dominant part of the market at a relatively high
frequency (as reporting requirements are
quarterly for funds from AIFMs with Assets under
management (AuM) above EUR 1bn).
ASR-AIF.4
Size and number of AIFs
High concentration among a few large AIFs
AIF domicile and distribution: In terms of
domicile of the AIFM, the AIF industry is
concentrated in a few countries, with the top five
accounting for 90% of the NAV (ASR-AIF.18). In
2020, Germany remained the country with the
largest AIF industry in the EEA30 (37%, +1pp),
followed by Luxembourg (16%, stable), the
Netherlands (15%, stable), France (13%, -1pp)
and Ireland (9%). Compared to 2019, the size of
the AIF industry expanded by 14% in
Luxembourg and 13% in Ireland, 8% in Germany,
5% in the Netherlands and 3% in France (ASR-
AIF.5).
5,899
5,374
514
5,000
5,300
5,600
5,900
6,200
2019 data Liquidated
after 2019
Valuation
and flow
effects
Newly
reported
AIFs
2020 data
Note: Decomposition of NAV by reporting and surviving AIFs, EUR bn. Newly
reported funds including AIFs incepted in 2020. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
-248
256
5,468
113
3
62
82
30
141
5,000
5,100
5,200
5,300
5,400
5,500
5,600
5,700
5,800
5,900
6,000
2019
data
None HF RE PE FoF Other 2020
data
Note:NAV by type of AIF managed and/or marketed by authorized AIFMs and
sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions, in EUR bn.
Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
5,899
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
<100mn 100-500mn 500mn-1bn 1-5bn >5bn
NAV Number of AIFs
Note: Share of AIFs by size, end of 2020, in %. AIFs managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national
jurisdictions. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 11
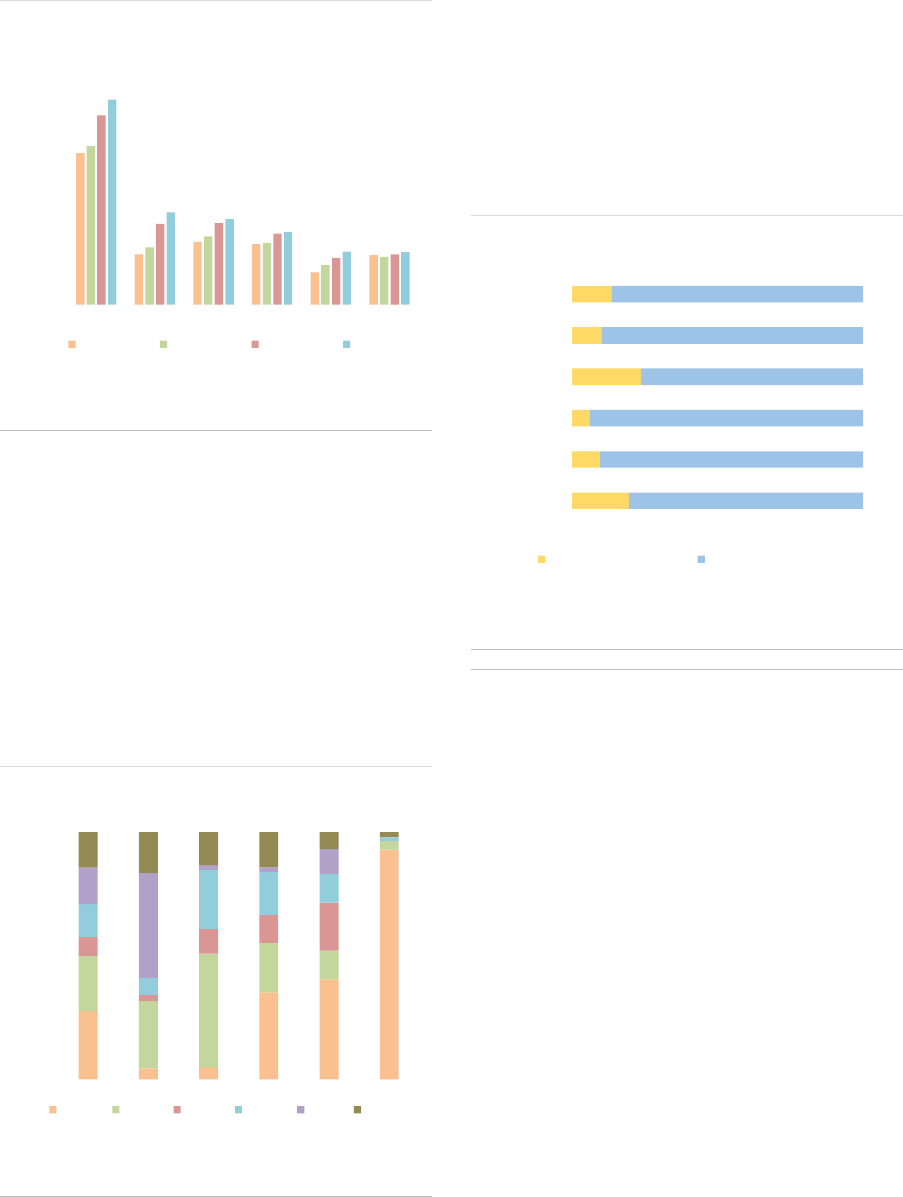
ASR-AIF.5
AIF size by country
More growth in LU and IE
FoFs are mainly domiciled in countries with a
large asset management industry such as
Germany, France, Ireland and Luxembourg, with
those four countries accounting for 78% of the
NAV (ASR-AIF.6). The HF industry is heavily
concentrated in Luxembourg and Ireland (70% of
NAV). Managers of PE funds are mainly
domiciled in Luxembourg and France (70% of
NAV). In contrast, RE funds and ‘other AIFs’ are
spread out across several countries. In most EU
Member States, ‘other AIFs’ account for the
majority of the NAV.
ASR-AIF.6
Country share by AIF type
Heterogeneity across AIF types
Most AIFs have access to the EU passport
(78%), allowing AIFs to be sold throughout the
EU (ASR-AIF.19).
AIF investors: The AIFMD provides the
regulatory framework for marketing AIFs primarily
to professional investors, rather than retail
investors. The marketing of AIFs to retail
investors remains at the discretion of each
Member State. Professional investors account for
around 86% of the NAV, and direct retail
investors’ participation is slightly declining but
remains significant at 14% of the NAV overall
(ASR-AIF.7), and amounts to 24% of NAV for RE.
Retail investor participation might be
underestimated since they could purchase
banking or insurance products that are invested
in AIFs.
ASR-AIF.7
AIF investors
Mainly professional investors
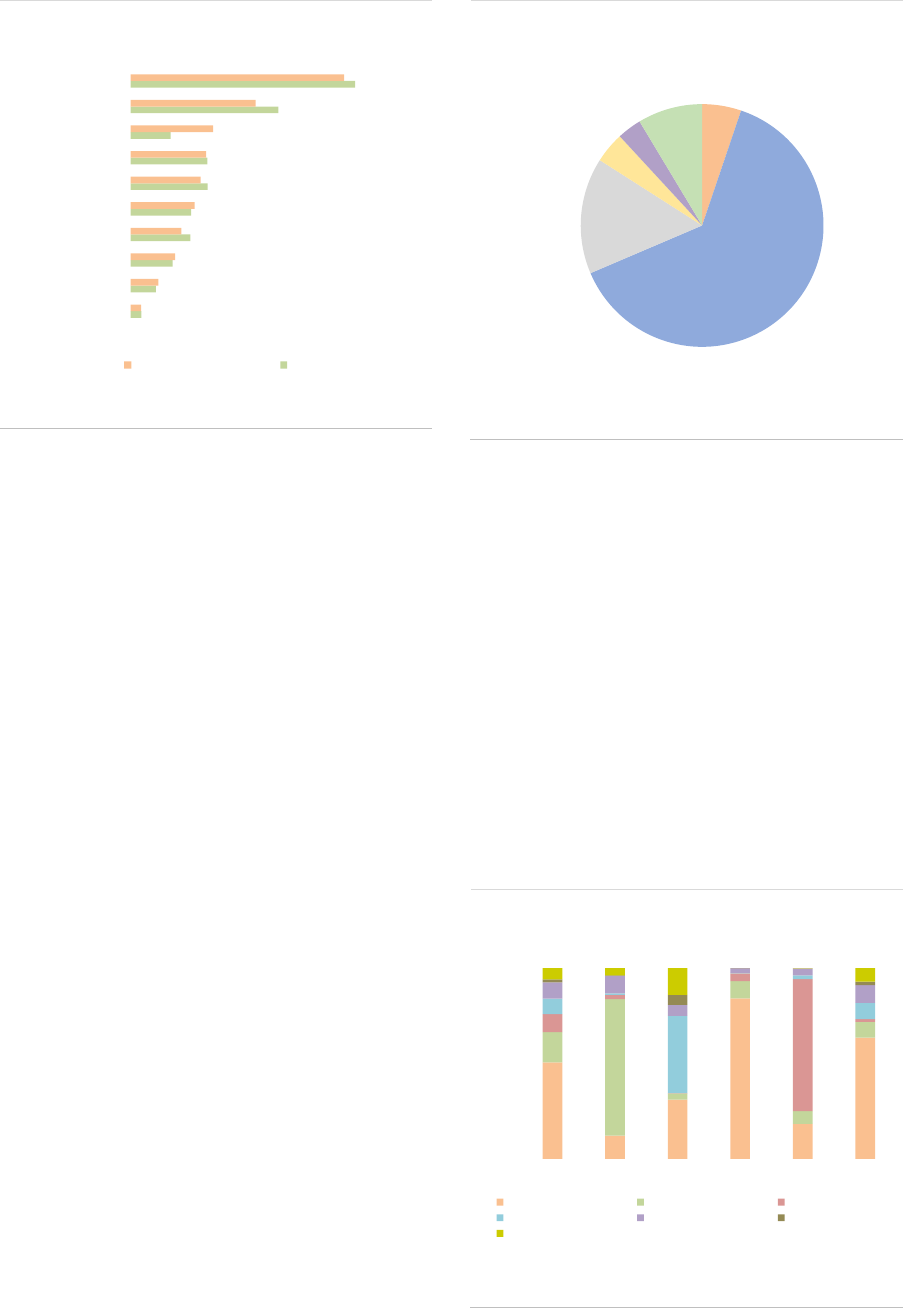
Among professional investors, unitholders are
diversified across AIF types (ASR-AIF.8).
Pension funds and insurance companies are the
main investors as they own close to 50% of the
NAV of AIFs (with 29% and 19% of the NAV
respectively). Banks account for 7%, other
financial institutions for 8%, and funds for 10%.
Non-profit organisations own 10% of the NAV,
and households 6%. The share of unknown
investors has declined from 11% to 5% of NAV,
indicating improvements in data reported. Still,
the relatively large proportion of banks might
indicate a lack of look-through approach by some
AIFMs, since they should report the ultimate
owners of the AIF shares.
-
500
1,000
1,500
2,000
2,500
DE LU NL FR IE Other
2017 2018 2019 2020
Note: NAV by type of AIF managed and/or marketed by authorized AIFMs and
sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions, in EUR bn.
Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
70%
80%
90%
100%
FoF HF PE RE Other None
DE LU NL FR IE Other
Note: Share of NAV by type of AIF managed and/or marketed by authorized
AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions, in
EUR bn. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100%
FoF
Hedge fund
Private equity
Real estate
Other AIF
Total EU
Retail investors Professional investors
Note: Clients of AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs and
sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions, end of 2020,
in % of NAV. FoF=Fund of funds. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 12
ASR-AIF.8
AIF investor types
Diversified investor base
AIF shares: The ownership of AIFs continues to
be highly concentrated: the top five investors
account for more than 75% of the NAV across AIF
types. More than 50% of all AIFs are entirely held
by their top five investors, as indicated by the
median of 100% for all AIF types (except PE
funds, where ownership is more diversified). The
high ownership concentration is explained by the
dominant role played by institutional investors. In
some cases, AIFs can be set up for a single
institutional investor that prefers to hold all of the
AIF shares, as the fund can be set up to fulfil its
specific investment objective.
AIF geographical investment focus: AIFs
invest mainly in the EEA (63%, +3pp), followed
by North America (15%) and supranational
issuers (9%), with the last category also including
investments without predominant geographical
focus. Other regions account for around 13% of
the NAV (ASR-AIF.9).
ASR-AIF.9
Regional investment focus
Most exposures towards the EEA
Leverage and liquidity risks
Gross exposures: AIFs are exposed to a wide
range of asset classes, with variation across AIF
types corresponding to their investment policies
(ASR-AIF.10). RE funds, PE funds and FoFs are
by construction heavily exposed to the underlying
assets (physical assets for RE funds, (unlisted)
securities for PE funds and collective investment
units for FoFs). HF exposures are
overwhelmingly biased towards interest rate
derivatives (IRDs), because exposures are
reported using gross notional values. The
exposures of ‘other AIFs’ are more diversified,
reflecting the range of strategies used in this
residual category.
ASR-AIF.10
Gross exposures
Diverse exposures by AIF type
Leverage: Leverage declined at the aggregate
level (ASR-AIF.20). Using the adjusted measure
(calculated as gross exposures to NAV excluding
IRDs and FX derivatives used for hedging
0% 5% 10% 15% 20% 25% 30% 35%
None
General gov.
Households
Banks
Oth. fin. institutions
Non-profit
Oth. CIU
Unknown
Insurances
Pension funds
2019 2020
Note: Ownership of units in AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised
AIFMs, in % of NAV. Data for the EEA30.
Asia
5%
EEA
63%
North
America
16%
Other
Europe
4%
Rest
3%
Supra National
9%
Note: Regional investment focus of AIFs managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national
jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Geo-focus determined according to
the domicile of investments, supra national category including investments
without predominant geo-focus. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Total EU FoF Hedge
fund
Private
equity
Real
estate
Other AIF
Securities CIUs Physical assets
IRDs FX CDS
Other derivatives
Note: NAV of AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorized AIFMs and sub-
threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions, in EUR bn. Data for
the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 13
purposes), leverage declined to 128% of NAV
compared with 145% in 2019. Similarly, leverage
measured by the ratio of AuM to NAV points to a
decline from 169% to 151%. Compared to
previous reports, both measures are relatively
close because HFs exposures, the main driver of
leverage at the aggregate level, plummeted. The
large decline in HFs exposures is explained by
the fact that UK data were not included in this
report, and that UK HFs accounted for 70% of all
AIFs exposures in 2019. Still, the aggregate
measure does not reflect important differences
across AIFs, with HF adjusted leverage at 312%
while for all other AIF types leverage is below
150% (ASR-AIF.11). The high leverage of HFs
stems mainly from the use of derivatives
(synthetic leverage) rather than outright
borrowing (financial leverage). In addition,
aggregate measures of leverage are upward
biased due to extreme outliers: the median
adjusted leverage for HFs remains around 120%,
while the 10% highest levered HFs have a
measure above 600%.
ASR-AIF.11
Adjusted leverage by AIF type
High leverage for HFs
Liquidity risk: Most AIFs are open-ended funds
(70% of NAV, +4pp compared with 2019), with
variation across types (ASR-AIF.21)
1
. Within
open-ended funds, around 68% offer daily
liquidity to investors, and 25% offer weekly to
monthly redemptions.
At the aggregate level, the liquidity profile of
AIFs points to potential liquidity risk at all
horizons: within a week, investors can redeem up
1
The flag for open or closed-ended structure of AIFs is not
a mandatory field for AIFMs. Around 72% of AIFs report
this information, accounting for 86% of NAV.
2
Since the new methodology is more conservative than the
previous one, liquidity indicators in this report cannot be
compared with previous reports.
to 54% of the NAV, whereas only 45% of the
assets can be liquidated within this time frame
(ASR-AIF.12). Compared with previous reports,
the liquidity mismatch is more pronounced due to
changes in methodologies (ASR-AIF.14)
2
. At the
aggregate level, this mismatch would materialise
only if very large redemptions were to take place
(higher than 45% of NAV). For funds with a
liquidity mismatch
3
, the liquidity shortage
amounts to around 20% of the NAV of all AIFs
over a one-day horizon (more than EUR 800bn,
ASR-AIF.13). Over longer time horizons, the
liquidity shortage declines significantly, edging
below 7% over one week.
ASR-AIF.12
Liquidity profile
Liquidity mismatch at aggregate level
3
While reflecting a structural misalignment in portfolio and
investor liquidity, the observed mismatch may be further
reduced through the imposition of notice periods to
investors for redeeming their shares.
0%
90%
180%
270%
360%
450%
All AIFs FoF Private
equity
Real
estate
Other
AIF
None Hedge
fund
2018 2019 2020
Note: Adjusted leverage by AIF tyoe in % of NAV. AIFs managed and/or
marketed by full scope AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only
in national jurisdictions. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
31%
54%
61%
67%
71%
76%
100%
14%
45%
55%
61%
67%
71%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day or
less
2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180 d 181-365
d
> 365 d
Investor Portfolio
Note: Portfolio and investor liquidity profiles of AIFs managed and/or marketed
by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020. Portfolio liquidity defined as the
percentage of the funds’ assets capable of being liquidated within each
specified period, investor liquidity defined as the shortest period for which
investors can redeem. EEA30 and non EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs
marketed, respectively, w/ and w/o passport. d= Days. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
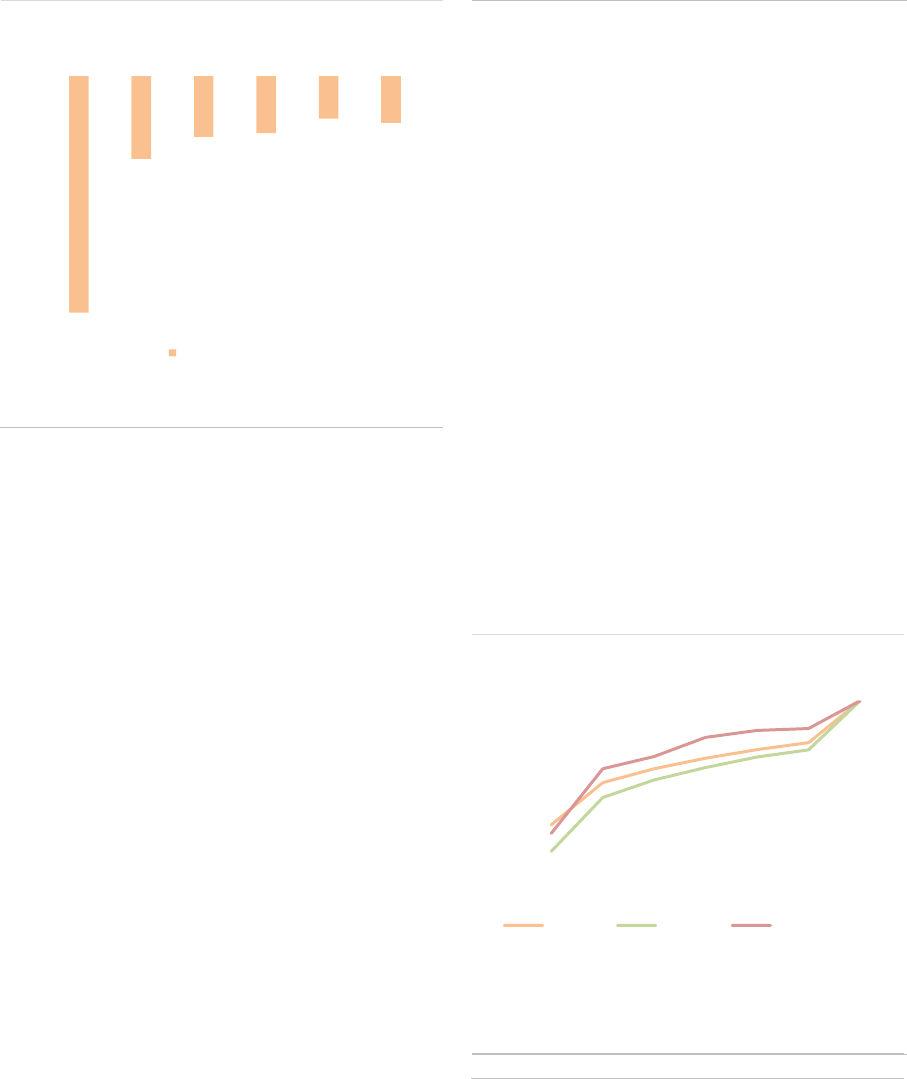
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 14
ASR-AIF.13
Liquidity shortage
Significant shortage at the short end
ASR-AIF.14
Liquidity profile
Comparing investor and portfolio liquidity
Aggregating liquidity profiles across funds is challenging. As
explained in the 2020 Annual Statistical Report (ESMA, 2020),
the method was revised to avoid having funds with excess
liquidity compensating for liquidity mismatch in other funds, i.e.
where the investor liquidity is higher than the portfolio liquidity.
Another challenge relates to the way portfolio and investor
liquidity are reported. Investor liquidity is reported in % of NAV
while portfolio liquidity is assessed for all assets, including
those acquired through the use of leverage which can bias
liquidity measures for AIFs . When leverage is used, the size
of the portfolio will be larger than the NAV, making the
comparison of investor and portfolio liquidity challenging.
In addition, the use of leverage entails that, in case of stress,
the fund might be in the position of using part of the portfolio
liquidity to satisfy borrowings and/or margin calls on
derivatives or securities financing transactions if no
unencumbered cash is at disposal. In that case, not all the
portfolio liquidity would be available to investors,
Therefore, a conservative approach is used whereby we
consider that the portfolio liquidity reported by AIFMs is
expressed in % of NAV and not AuM. This more conservative
approach is adopted here to assess potential liquidity
mismatch.
The chart below, using end-2019 data, shows the difference
between the two measures of portfolio liquidity: when using
AuM, AIFs would only show a liquidity mismatch at the very
short end (1 day or less), while when using NAV the liquidity
mismatch is visible over all time horizons.
ASR-AIF.15
Liquidity mismatch
Different liquidity profiles
-20
-15
-10
-5
0
1 day or
less
2-7
d
8-30
d
31-90
d
91-180
d
181-365
d
Liquidity shortage
Note: Liquidity shortage of AIFs, % of NAV. Liquidity shortage is defined as
the sum of liquidity deficits at the level of the funds, as non compensated by
liquidity surplus. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day or
less
2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180 d 181-365
d
> 365 d
Investor Portfolio Portfolio by AuM
Note: Portfolio and investor liquidity profiles of AIFs managed and/or
marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2019. Portfolio liquidity defined as the
percentage of the funds’ assets capable of being liquidated within each
specified period, investor liquidity defined as the shortest period for which
investors can redeem. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs
marketed, respectively, w/ and w/o passport. d= Days. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 15
ASR-AIF.16
ASR-AIF.17
Size of the AIF industry
AIF industry by type
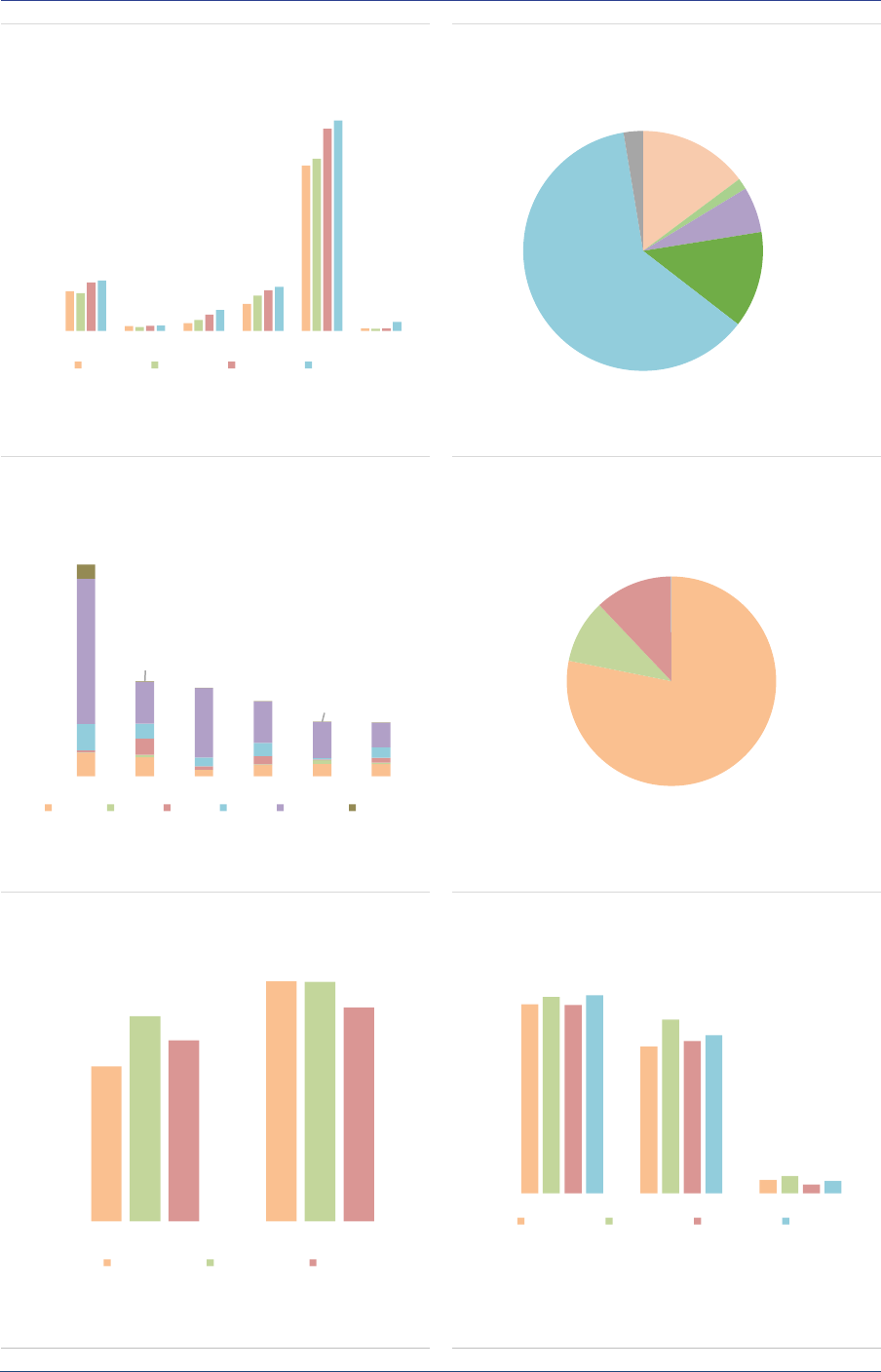
Growing market
‘Other AIFs’ largest type
ASR-AIF.18
ASR-AIF.19
Size of AIF by type and country
EU passport
Concentration in a few countries
Most AIFs can be passported
ASR-AIF.20
ASR-AIF.21
Leverage
Liquidity
Decline in leverage
Most AIFs open-ended
873
89
363
766
3,652
155
0
500
1,000
1,500
2,000
2,500
3,000
3,500
4,000
FoF HF PE RE Other None
2017 2018 2019 2020
Note: NAV by type of AIF managed and/or marketed by authorized AIFMs and
sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions, in EUR bn
and percent. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
FoF
15%
Hedge fund
1%
Private equity
6%
Real estate
13%
Other
62%
None
3%
Note: NAV by type of AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs and
sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions, end of 2020, in
%. FoF=Fund of funds, None=No predominant type. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
2,158
969
900
764
556
551
0
500
1,000
1,500
2,000
2,500
DE LU NL FR IE Other
FoF HF PE RE Other None
Note: NAV by type of AIF managed and/or marketed by authorized AIFMs and
sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions, in EUR bn.
Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
EU
passport
78%
EU w/o passport
10%
Non-EU w/o passport
12%
Non-EU not marketed
in EU
<1%
Note: NAV of AIFs by manager's access to AIFMD passport, end of 2020, in
%.
Authorised EEA30 AIFMs with access to AIFMD passport or marketing non-
EEA30 AIFs w/o passport, sub-threshold managers registered only in national
juridisdictions w/o passporting rights. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
125%
150%
175%
Adjusted leverage AuM/NAV
2018 2019 2020
Note: Leverage in% of NAV.AIFs managed and/or marketed by full scope
AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions.
Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
70%
80%
All AIFs RE PE
2017 2018 2019 2020
Note: Share of open-ended AIFs by type in % of NAV. AIFs managed and/or
marketed by full scope AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in
national jurisdictions. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 16
Brexit implications for AIF
statistics
Summary
The UK asset management industry was an important part of the EU single financial market, and with
that also of the EU AIF market. Statistics presented in this report fall after the withdrawal of the United
Kingdom from the EU on 31 January 2020. This section compares the size and structure of UK and
EEA30 AIF sector to discuss the implications of Brexit for AIF statistics.
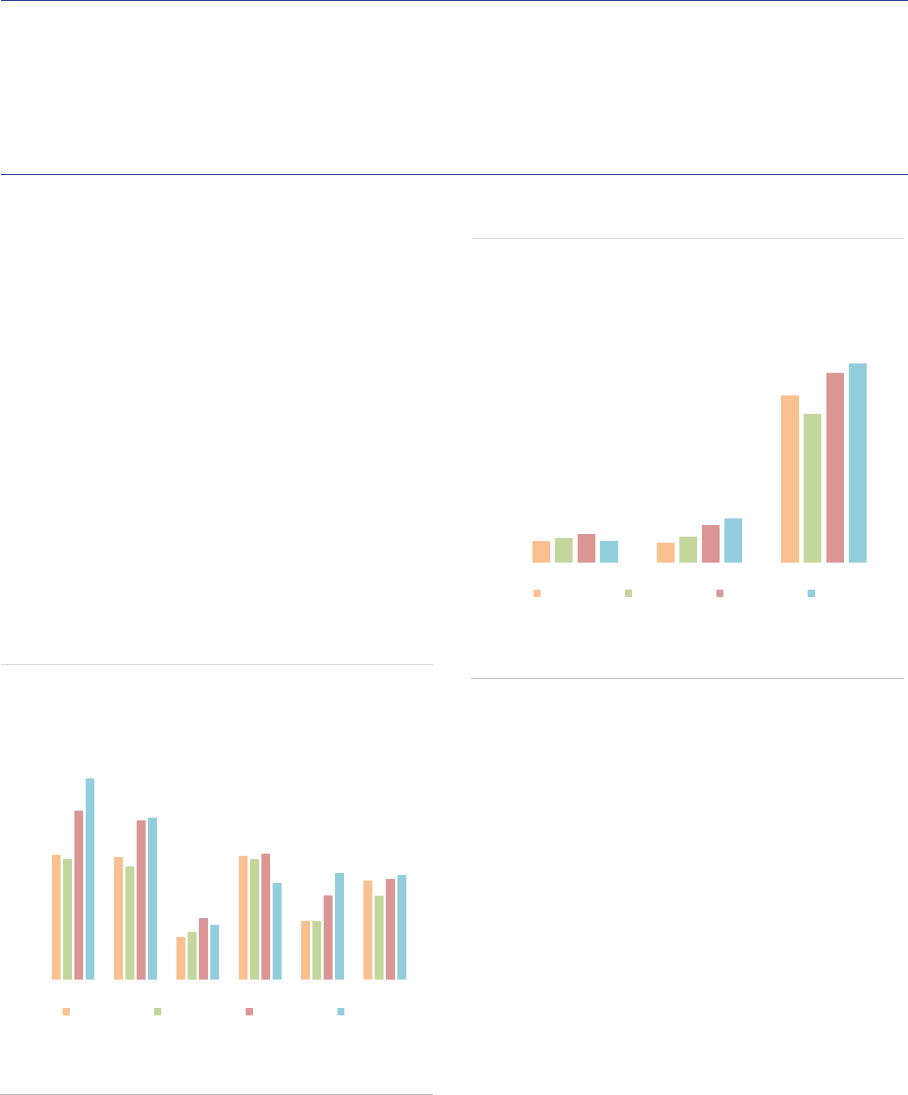
Comparative size of UK and
EEA30 AIFs
As a consequence of the withdrawal of the UK,
the composition and size of the EU AIF industry
has changed. While the UK withdrew from the EU
on 31 January 2020, EU law continued to apply
in the UK until the end of the transition period on
31 December 2020. However, this Annual
Statistical Report uses end-2020 data, which
were transmitted to ESMA in the course of 2021,
i.e. after the transition period, making ESMA
unable to collect data for the UK covering the year
2020.
Given these data constraints, this section uses
2019 data to illustrate the impact of Brexit on the
EEA30 AIF sector.
Size: In 2019, UK AIFs had a NAV of EUR
1,338bn compared with EUR 5,468bn for the
EEA30 (ASR-AIF.22). Therefore, the UK
accounted for 20% of the NAV of the EU sector
end-2019 (composed of EEA30 and the UK).
There were around 4,700 UK AIFs compared with
more than 28,000 for the EEA30.
ASR-AIF.22
AIFs managed by UK and EEA30 AIFMs
Sizeable share of UK AIFs
In terms of regulatory Asset under
Management (AuM), UK AIFs accounted for
70% of the combined AuM of the UK and the
EEA30 in 2019 (ASR-AIF.23). UK AIFs reported
around EUR 22trn in 2019 compared with EUR
8.5trn for the EEA30 in 2019 (and EUR 9trn in
2020). Hedge funds managed by UK AIFMs
account for the large share of AuM (mainly due to
the use of interest rate derivatives which are
reported in notional terms). Excluding HFs, UK
AIFs AuM amounted to EUR 1.3trn.
0
5,000
10,000
15,000
20,000
25,000
30,000
35,000
0
1,000
2,000
3,000
4,000
5,000
6,000
7,000
UK 2019 EEA30 2019 EEA30 2020
NAV Number of AIFs (rhs)
Note: NAV and number of AIFs managed by AIFMs domiciled in the UK and in
the EEA30, in EUR bn.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 17
ASR-AIF.23
Regulatory AuM
Larger size for the UK due to HFs
AIF type: The UK AIF sector has a different
composition compared with the EEA30, with a
larger role played by HFs and PE funds (ASR-
AIF.24). Other AIFs account for 44% of the NAV
in the UK (against 62% for the EEA30), followed
by HFs with 20% (2% for EEA30), FoFs with 14%
(15% in the EEA30), PE with 14% (5% for
EEA30), and RE with 8% (13% for the EEA30).
ASR-AIF.24
Structure of AIF sector
HFs and PE more important in the UK
Exposures: UK AIFs reported gross exposures
of EUR 21.4trn in 2019, mainly due to IRDs and
FX derivatives which account for 84% of
exposures (ASR-AIF.25). EEA30 reported gross
exposures of EUR 8.9trn, with IRDs and FX
derivatives accounting for only 15% of
exposures.
ASR-AIF.25
Gross exposures
Large exposures related to IRDs for UK AIFs
Leverage: UK AIFs report higher leverage than
EEA30 AIFs irrespective of the measure used.
The high leverage for UK AIFs is entirely driven
by the HF sector, while for other AIF types,
leverage measures are similar for UK and EEA30
AIFs. At the aggregate level, UK AIFs had a gross
leverage of 1,875% compared with 170% for
EEA30 AIFs (ASR-AIF.26).
ASR-AIF.26
Gross leverage
High leverage for UK AIFs due to HFs
Adjusted leverage indicators, when IRDs and FX
derivatives are excluded, show similar patterns
(ASR-AIF.27), with large values for UK HFs.
0
5,000
10,000
15,000
20,000
25,000
UK 2019 EEA30 2019 EEA30 2020
FoF HF PE RE Other None
Note: AuM of AIFs managed by AIFMs domiciled in the UK and in the EEA30,
in EUR bn.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
70%
80%
90%
100%
UK 2019 EEA30 2019 EEA30 2020
HF FoF PE RE Other None
Note: NAV by AIF type for AIFs managed by AIFMs domiciled in the UK and in
the EEA30, in %.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0
4,000
8,000
12,000
16,000
20,000
UK 2019 EEA30 2019 EEA 2020
IRDs FX
Note: Gross exposure to IRDs and FX derivatives, in EUR bn.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Comptent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
300%
600%
900%
1200%
FoF HF PE RE Other Total
UK 2019 EEA30 2019 EEA 2020
Note: Gross leverage, in % of NAV.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Comptent Authorities, ESMA.
UK HFs: 8402%
UK AIFs: 1875%

ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 18
ASR-AIF.27
Adjusted leverage
Higher for UK HFs compared to EEA30
Implications for AIF statistics
In terms of size and composition of the AIF
sector, Brexit had its largest impact on hedge
funds. HFs managed by UK AIFMs accounted
for more than 75% of the NAV of UK and EEA30
HFs and more than 97% of AuM. Since UK HFs
tend to be larger and use more leverage than
EEA30 AIFs, leverage measures have declined
when comparing EEA30 data for 2020 with the
2019 data published in the previous report (which
included the UK in the EU).
Private equity funds are also impacted, since
UK PEs accounted for 40% of the NAV of the
sector in 2019.
For other type of AIFs, the impact of Brexit on the
size of the sector is also significant, with
differences across types. UK AIFs accounted for
16% of FoFs in 2019 and around 12% for RE and
‘Other AIFs’.
0%
300%
600%
900%
1200%
FoF HF PE RE Other Total
UK 2019 EEA30 2019 EEA 2020
Note: Adjusted gross leverage, in % of NAV.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Comptent Authorities, ESMA.
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 19
Funds of Funds
Summary
FoFs account for 15% of the NAV of EEA30 AIFs, at around EUR 0.9tn (+4% compared with 2019).
Among AIF types, FoFs have the second largest retail investor participation at 20% of NAV. Open-ended
FoFs remain exposed to significant liquidity mismatch across all time horizons, including FoFs investing
mainly in UCITS. The potential liquidity shortage for FoFs with a liquidity deficit is 16% of their NAV short
term (within 1 week).
Market size and structure
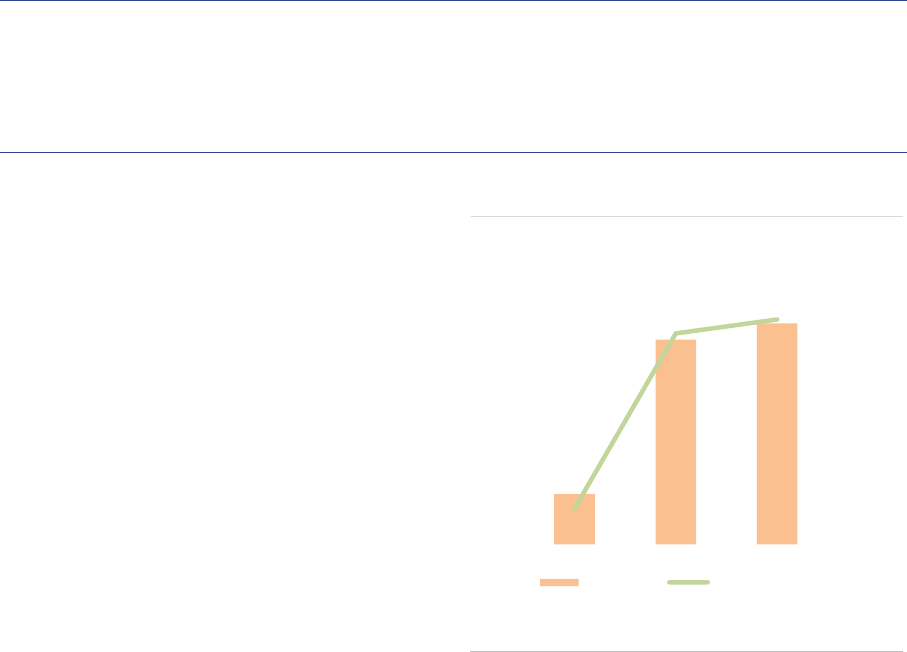
Size: As of the end of 2020, the NAV of FoFs sold
in the EEA30 by AIFMs domiciled in the EEA30
amounted to EUR 873bn, a 4% increase
(EUR 30bn) compared with 2019. FoFs account
for 15% of the NAV of all AIFs. The evolution of
FoFs has been very different among countries. A
few countries recorded high increase in NAV:
19% in Germany and 27% in Ireland (ASR-
AIF.28). In contrast, France and the Netherlands
experienced a sharp decline in NAV, with a 23%
and a 10% drop respectively. Luxembourg FoFs
remained stable (+1%). The top 5 EU jurisdictions
account for almost 90% of total EEA30 FoFs’
NAV.
ASR-AIF.28
Funds in FoFs’ portfolios
Spread across countries
Funds of funds strategies: Funds of funds
invest in underlying collective investment
undertakings and serve the purpose of
diversifying fund-specific risk, relieving burdens
for investors to perform due diligence on
individual fund managers. FoFs pursuing
strategies beyond PE funds or HFs have
registered a sustained growth since 2018 (+34pp)
and account for 75% of NAV (ASR-AIF.29).
ASR-AIF.29
FoF strategies
Mainly outside of PE funds and HFs
Information on the most traded instruments
provided by AIFMs on behalf of the managed
funds allows to classify the CIUs in which FoFs
invest and gain insights into their activity. For
FoFs investing in PE funds and HFs the top five
traded instruments account for around 60% for of
the portfolio, while the remaining FoFs have a
slightly more diversified portfolio (ASR-
AIF.30ASR-AIF.30).
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
DE LU NL FR IE Other
2017 2018 2019 2020
Note: NAV of FoFs managed and/or marketed by authorized AIFMs and sub-
threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions, in EUR bn. data
for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
Fund of HF Fund of PE Other FoF
2017 2018 2019 2020
Note: NAV of FoFs by strategy, in EUR bn.AIFs managed and/or marketed by
full scope AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national
jurisdictions. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2021 20
ASR-AIF.30
Main instruments
Concentrated portfolios
Distribution: Most FoFs have access to the EU
passport to a large extent, with 96% licensed to
be sold throughout the EU (ASR-AIF.39ASR-
AIF.39).
Funds of Fund investors: Among AIF types,
FoFs have the second largest proportion of retail
investors (20%), although they are sold mainly to
professional investors (80%) (ASR-AIF.31ASR-
AIF.31). FoFs are diversified and usually require
less initial investment than other types of
sophisticated vehicles, so are easier to access,
especially for retail investors. Nevertheless, retail
participation varies significantly between FoF
strategies — 3% for funds of PE funds and funds
of HFs, and around to 20 % for ‘other FoFs’.
Among professional investors, pension funds and
insurance companies are the main investors,
accounting for 25% (+6pp compared to 2019) and
9% of the NAV respectively. Around 10% of FoFs’
NAV is instead held by other CIUs, (ASR-AIF.40).
In particular pension funds and other CIUs have
a large participation in FoFs investing in PE and
HFs (~60%).
ASR-AIF.31
AIF investors
Relevant retail participation
Geographical investment focus: FoFs invest
primarily in the EEA (54%), followed by
supranational issuers (25%) and North America
(11%) (ASR-AIF.41ASR-AIF.41). Since the
supranational issuers category also covers
‘multiple regions’, FoFs may invest in
geographically diversified funds, rather than in
supranational issuers specifically.
Leverage and liquidity risks
Gross exposures: FoFs have a large proportion
of their fund holdings invested in funds from the
same manager (around 40% of the NAV including
Money Market Funds and ETFs by the same
AIFMs, ASR-AIF.32ASR-AIF.32).
ASR-AIF.32
Proportion of fund holdings for FoFs
Significant cross investment
This results also from the analysis of the main
traded instruments of FoFs investing in funds
different from PE funds and HFs. For this large
residual category of FoFs, 20% of total portfolio
exposure resulting from the top five instruments
60
58
46
0%
20%
40%
60%
Fund of HF Fund of PEQ Other FoF
Hundreds
Rank 1 Rank 2 Rank 3 Rank 4 Rank5
Note: Porfolio concentration of funds of funds, end of 2020, in % of AuM.
Portfolio concentration computed as the value of top 5 instruments traded with
respect to AuM. Data for EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100%
Other FoF
Fund of HF
Fund of
PE
Retail investors Professional investors
Note: Clients of funds of funds managed and/or marketed by authorised
AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictionsat,
end of 2020, in % of NAV. FoF=Fund of funds, PE= Private equity fund,
HF=Hedge fund. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
CIUs by
the AIFM
38%
CIUs by
others
54%
ETF by the
AIFM
1%
ETF by
others
5%
MMFs by
the AIFM
1%
MMFs by
others
1%
Note: Share of collective investment undertakings held by funds of funds in
4Q20. AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs.
CIUs=Collective Investment Undertakings. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2021 21
relates to cross investment. For funds of PE funds
and HFs the shares of CIUs managed by other
management companies is, respectively, above
40% and around 28%. Looking at the use of
derivatives, funds of HFs rely largely on FX
derivatives (ASR-AIF.33). The use of these
derivatives may serve to hedge the exposures
arising from foreign currency share classes held
in portfolio.
ASR-AIF.33
Main traded instruments
Instruments (%)
Funds of
HFs
Funds of
PE
Other
FoFs
Cash
3.0
1.8
2.0
Equities
0.9
3.4
1.5
Corporate bonds
0.0
0.0
0.1
Sovereign bonds
0.1
0.1
0.2
Convertible bonds
0.0
0.0
0.0
Loans
1.3
0.0
0.1
Structured products
0.0
0.0
0.1
CDS & equity derivatives
0.0
1.9
IRDs and FX
15.2
1.1
4.4
Other derivatives
0.0
0.0
0.5
Real assets
0.0
0.1
MMFs by other AIFMs
0.1
0.2
0.7
MMFs by the same AIFM
0.1
0.0
0.4
ETFs by other AIFMs
2.2
1.0
1.6
ETFs by the same AIFM
0.0
0.0
0.2
CIUs by other AIFMs
27.8
42.5
12.1
CIUs by the same AIFM
8.3
3.8
19.7
Other assets
0.4
3.6
0.8
Total
3.0
1.8
2.0
Note: Main traded instruments, end of 2020, % of total exposures.
Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities,
ESMA.
Leverage: FoFs display limited use of leverage:
regulatory AuM to NAV is 145% on aggregate,
with some variation by type (ASR-AIF.34ASR-
AIF.43). Relatively low leverage levels come from
limited exposures to derivatives and little use of
financial leverage (less than 1% of NAV).
Adjusted leverage appears stable over time and
even more limited in funds investing in PE funds
and in the large FoF residual category.
ASR-AIF.34
Adjusted leverage over time
Stable over time
Liquidity risk: Most FoFs are open-ended funds
(70% by NAV), with the exception of funds of PE
funds (ASR-AIF.42). Among open-ended FoFs,
most of funds investing in strategies beyond HFs
and PE funds offer daily liquidity to investors
(ASR-AIF.44). At the aggregate level, the
liquidity profile of FoFs points to a significant
and persisting liquidity mismatch over the
different time horizons. Within one day investors
can redeem up to 40% of the NAV, whereas 14%
of the assets can be liquidated within this time
frame. The liquidity gap reduced between three
and six months (ASR-AIF.35).
ASR-AIF.35
Liquidity profile
Significant liquidity mismatch
Most FoFs investing beyond HF and PE
strategies usually hold shares of UCITS, which
offer daily liquidity to investors. The observed
one-day liquidity gap implies that AIFMs might
consider their UCITS’ exposures subject to
liquidity risk over one day. One factor could be
that the AIFM might take into account the
0%
20%
40%
60%
80%
100%
120%
140%
Fund of HF Fund of PE Other FoF
2018 2019 2020
Note: Adjusted leverage of FoFs in % of NAV. AIFs managed and/or marketed by
full scope AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national
jurisdictions. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
40%
62%
70%
74%
78%
81%
100%
14%
56%
60%
73%
76%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day or
less
2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180 d 181-365
d
> 365 d
Investor Portfolio
Note: Portfolio and investor liquidity profiles of funds of funds managed and/or
marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020. Portfolio liquidity defined as the
percentage of the funds’ assets capable of being liquidated within each specified
period, investor liquidity defined as the shortest period for which investors can
redeem. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed,
respectively, w/ and w/o passport. d=Days. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
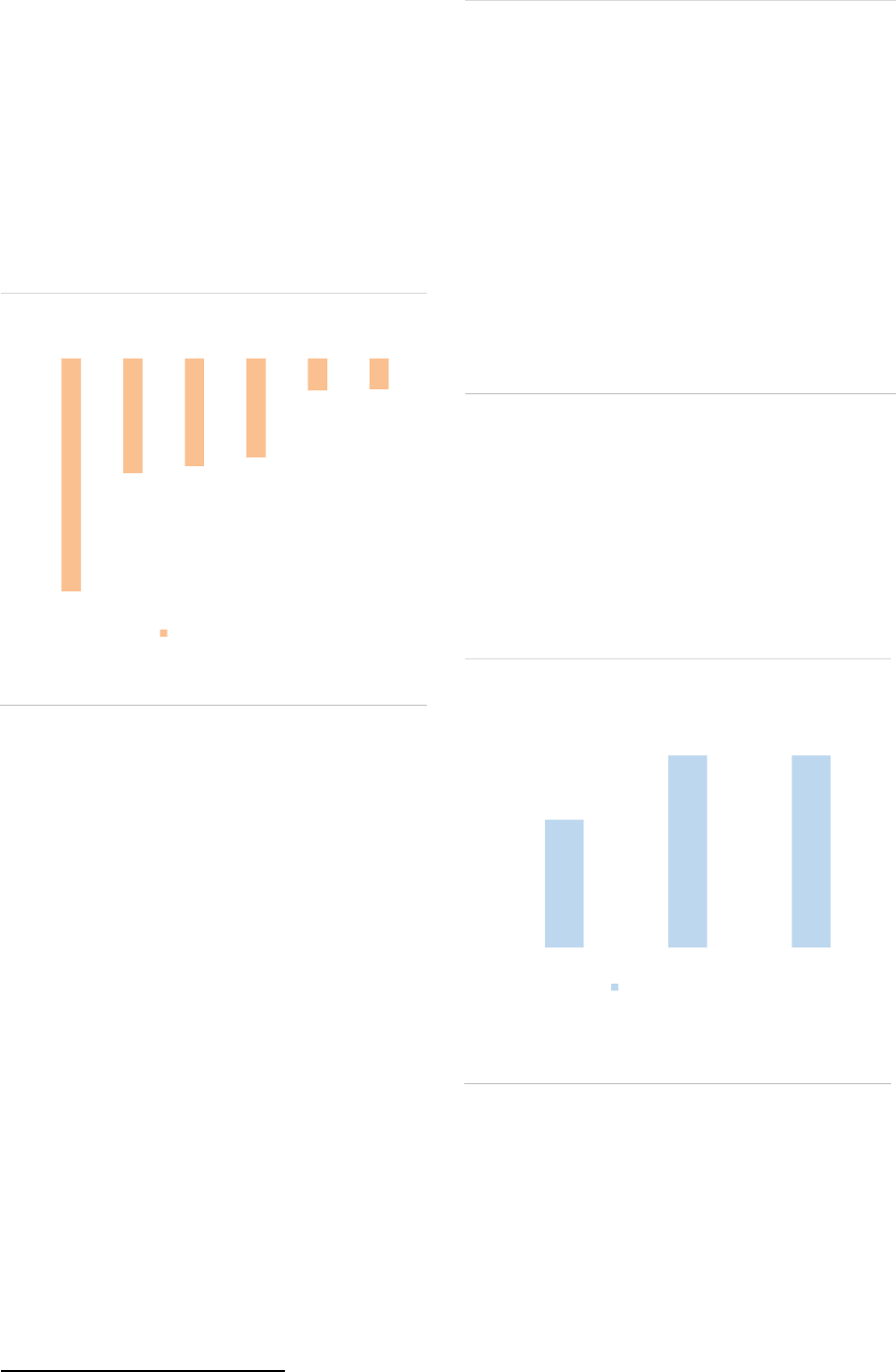
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2021 22
settlement period required by the underlying
funds (usually T+2). Alternatively, the manager
might report a liquidity mismatch based on its
internal liquidity risk assessment. FoFs might
hold a large portion of the shares of some UCITS.
Therefore, the manager would need more time to
sell its shares, to reduce the price impact of his
sales. When considering only FoFs with a
liquidity deficit, the potential liquidity shortage in
the very short term (within 1 day) is above 30% of
their NAV and it reduces significantly within the
six-months horizon (ASR-AIF.36).
ASR-AIF.36
Liquidity profile
Some liquidity mismatch
FoFs offering daily redemptions and not requiring
any notice period to investors for redeeming their
share represent one-third of the NAV. A notice
period ranging from 1 to 7 days for FoFs allowing
to redeem on a daily basis is instead more
commonly requested (40% of NAV). Overall,
more than 40% of FoFs by NAV do not require
any redemption notice to investors (Error!
Reference source not found.).
4
Unencumbered cash is an optional field for AIFMs to
report.
ASR-AIF.37
Redemption frequency and notice period
Majority of daily funds without any notice period
Redemption
Frequency
Notice Period
None
1D
1W
1M
>1M
Total
Daily
33.5
19.1
11.3
0.6
64.0
Weekly to
Monthly
8.6
7.3
4.4
13.9
3.1
29.1
Quarterly
0.6
0.1
0.1
0.3
0.1
4.3
Longer than
quarterly
0.3
0.1
0.8
1.4
Other
0.2
0.8
0.2
0.1
1.2
Total
43.3
26.5
16.7
15
4.0
100
Note: Funds of funds by redemption frequency and notice period
given to investors, in % of NAV, end of 2020. 1D= 1 day, 1W = 2 to
7 days, 1M = 8 to 30 days, >1M = more than 30 days’ notice period.
Data for the EEA30.
Source: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
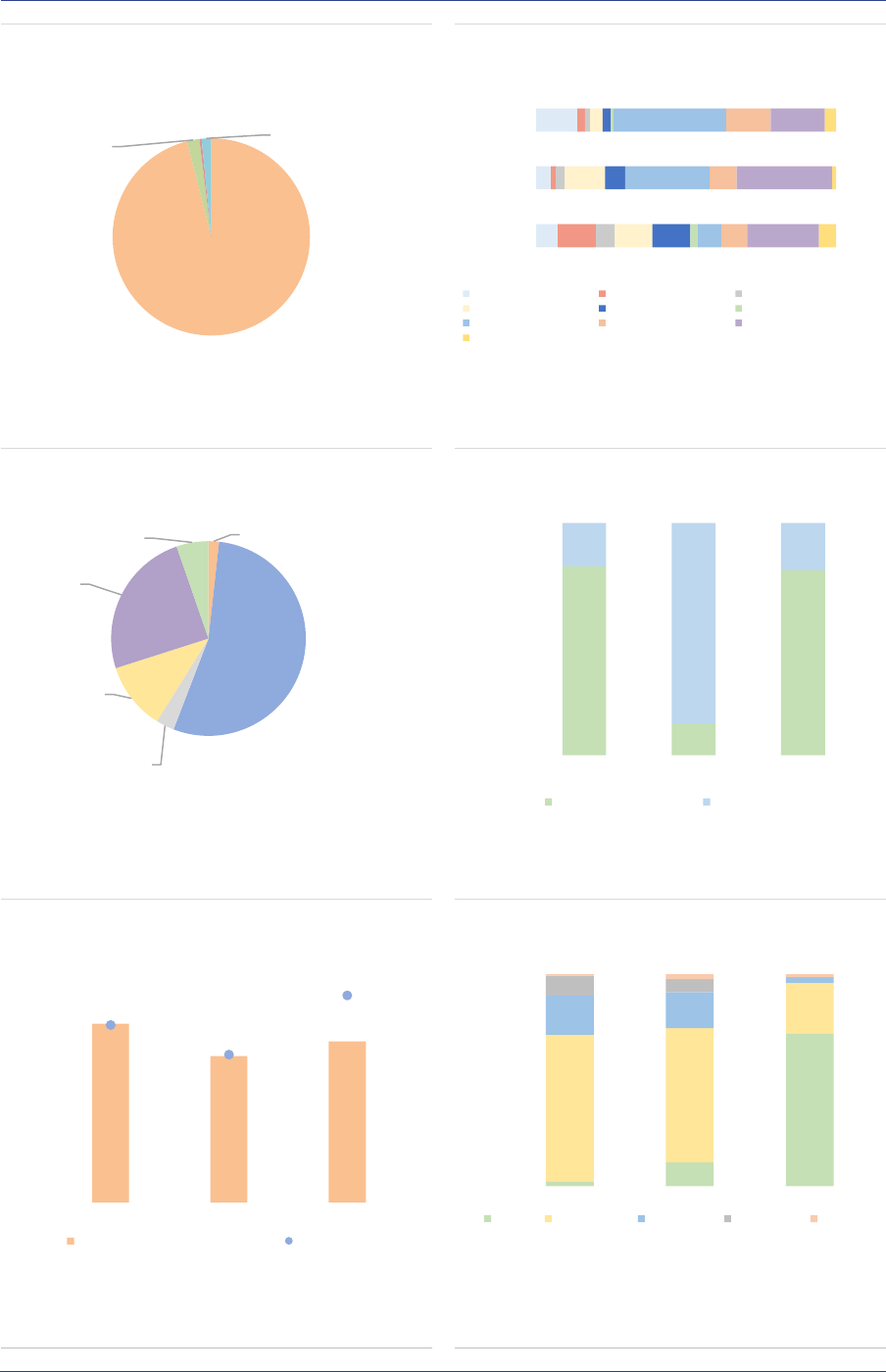
Unencumbered cash, i.e. a fund’s position in
cash or cash-like securities not subject to legal
claims by another party (e.g. from collateral
pledges or securities lending activities), is an
important indicator of a fund’s ability to mobilise
funds fast to meet redemption claims
4
. FoFs have
relatively low levels of unencumbered cash,
between 2% and 3% of the NAV across types
(ASR-AIF.38).
ASR-AIF.38
Unencumbered cash
Low cash buffers
-32
-24
-16
-8
0
1 day or
less
2-7
d
8-30
d
31-90
d
91-180
d
181-365
d
Liquidity shortage
Note: Liquidity shortage of funds of funds, % of NAV. Liquidity shortage is
defined as the sum of liquidity deficits at the level of the funds, as non
compensated by liquidity surplus. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
1%
2%
3%
Fund of HF Fund of PE Other FoF
Unencumbered cash
Note: Unencumbered cash held by funds of funds, end of 2020, in % of NAV.
EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed, respectively, w/
and w/o passport. FoF=Funds of funds, HF=Hedge fund, PE=Private equity
fund. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 23
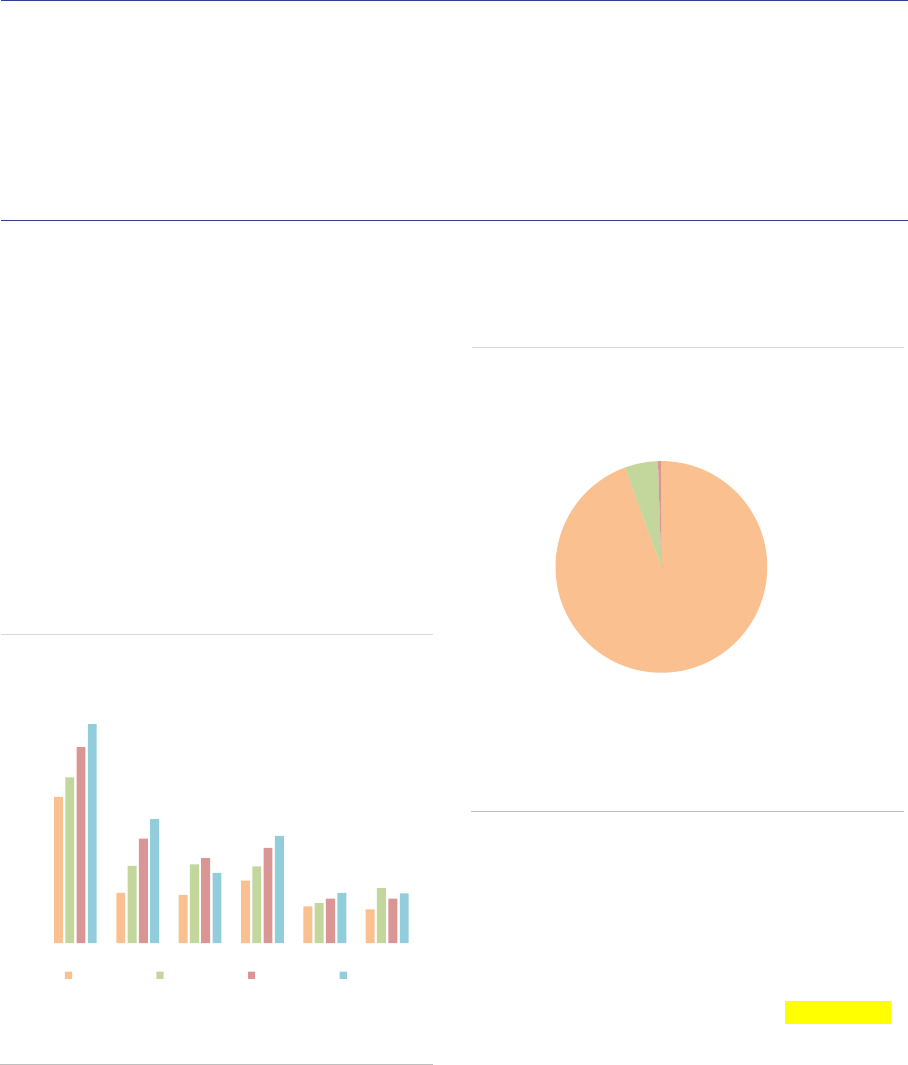
ASR-AIF.39
ASR-AIF.40
EU passport
FoF investors
Most FoFs can be passported
Mainly institutional investors
ASR-AIF.41
ASR-AIF.42
Regional investment focus
Investor rights
Mainly EEA
Funds of PE mostly closed
ASR-AIF.43
ASR-AIF.44
Leverage
Redemption frequencies
Limited leverage
Mostly daily and weekly
EU
passport
96%
EU w/o
passport
2%
Non-EU w/o passport
<1%
Non-EU not
marketed in
EU
2%
Note: NAV of funds of funds by manager's access to AIFMD passport, end of
2020, in %. Authorised EEA30 AIFMs with access to AIFMD passport or
marketing non-EEA30 AIFs w/o passport, sub-threshold managers are
registered only in national juridisdictions w/o passporting rights. Data for the
EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100%
Other FoF
Fund of PE
Fund of HF
Banks General government Household
Insurances Non-profit None
Other CIUs Oth. fin. institutions Pension funds
Unknown
Note: Ownership of units in funds of funds managed and/or marketed by authorised
AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. FoF=Fund of funds; PE=Private equity fund,
HF=Hedge fund. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
Asia
2%
EEA
54%
Other Europe
3%
North
America
11%
Supra
National
25%
Rest
5%
Note: Regional investment focus of funds of funds managed and/or marketed
by authorised AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national
jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Geo-focus determined according to the
domicile of investments and the supranational category including investments
without a predominant geo-focus. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Fund of HF Fund of PE Other FoF
Open-end Closed-end
Note: Redemption rights provided in the ordinary course to investors in funds
of funds managed and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of
NAV. HF=Hedge fund; PE=Private equity; FoF=Fund of funds, PE=Private
equity fund. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
40%
80%
120%
160%
Fund of HF Fund of PEQF Other FoF
Adjusted gross leverage AuM/NAV
Note: Adjusted gross leverage of funds of funds managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Adjusted gross leverage
computed as total exposure less IRDs with respect to NAV. FoF= Funds of
funds, PE=Private equity fund, HF=Hedge fund. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National competent authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Fund of HF Fund of PE Other FoF
Daily Weekly
to monthly
Quarterly Quarterly
to yearly
Other
Note: Investor redemption frequencies allowed by open-end funds of funds
managed and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV.
EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed, respectively, w/
and w/o passport. FoF=Fund of funds, PE=Private equity fund, HF=Hedge
Fund. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2021 24
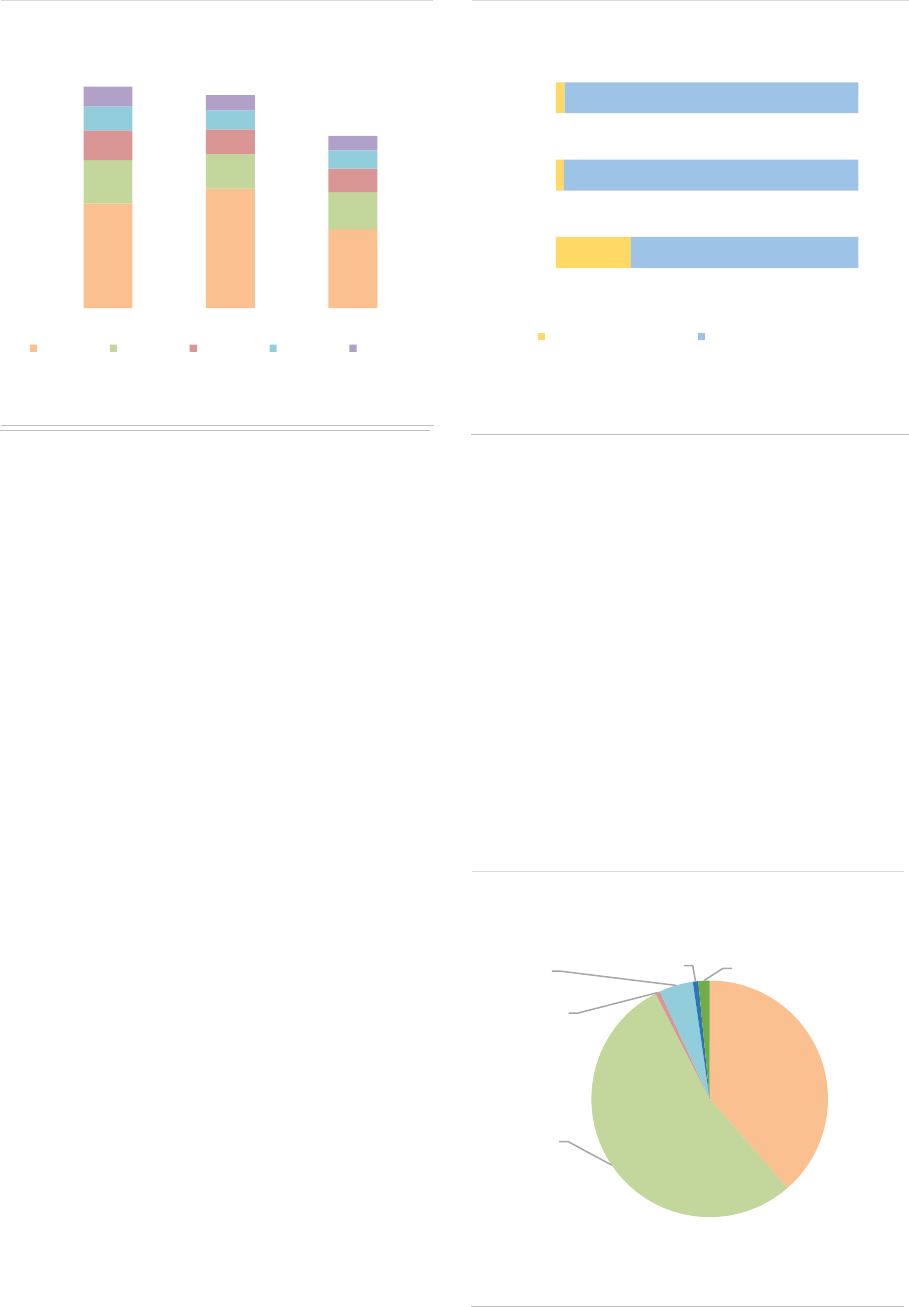
Real Estate Funds
Summary
RE funds account for 13% of the NAV of EEA30 AIFs, at EUR 766bn. RE funds continued to grow in
2020, albeit at a more moderate pace (+9% compared with 2019). The proportion of retail investors
has continued to grow to reach 24%, the highest among AIF types. While leverage remains limited,
liquidity risk in RE funds is a concern: around 54% are open-ended, and 40% of Commercial Real
Estate (CRE) funds by NAV offer daily liquidity to investors. At the aggregate level, RE funds face
liquidity mismatch across all time periods, an indication of a structural vulnerability as the maturities of
assets and liabilities are not aligned.
Market size and structure
Size: RE funds are the third-largest AIF type by
size, with a NAV of EUR 766bn, or 13% of all
EEA30 AIFs. The size of the RE fund industry
increased by 9% in 2020, a more moderate pace
compared to 2019 (15% increase), as the result
of positive developments in housing markets. The
RE fund industry remains concentrated in a few
countries (ASR-AIF.45), with the top five
accounting for 92% of the NAV. The NAV
increased in most countries with the largest RE
fund industry.
ASR-AIF.45
Size of RE funds
Concentration in a few countries
Real Estate fund types: RE investment
strategies continue to be dominated by CRE with
64% of the NAV (-2pp compared with 2018);
while exposure to residential markets remained
stable at 16% of NAV (+1pp, ASR-AIF.52ASR-
AIF.52).
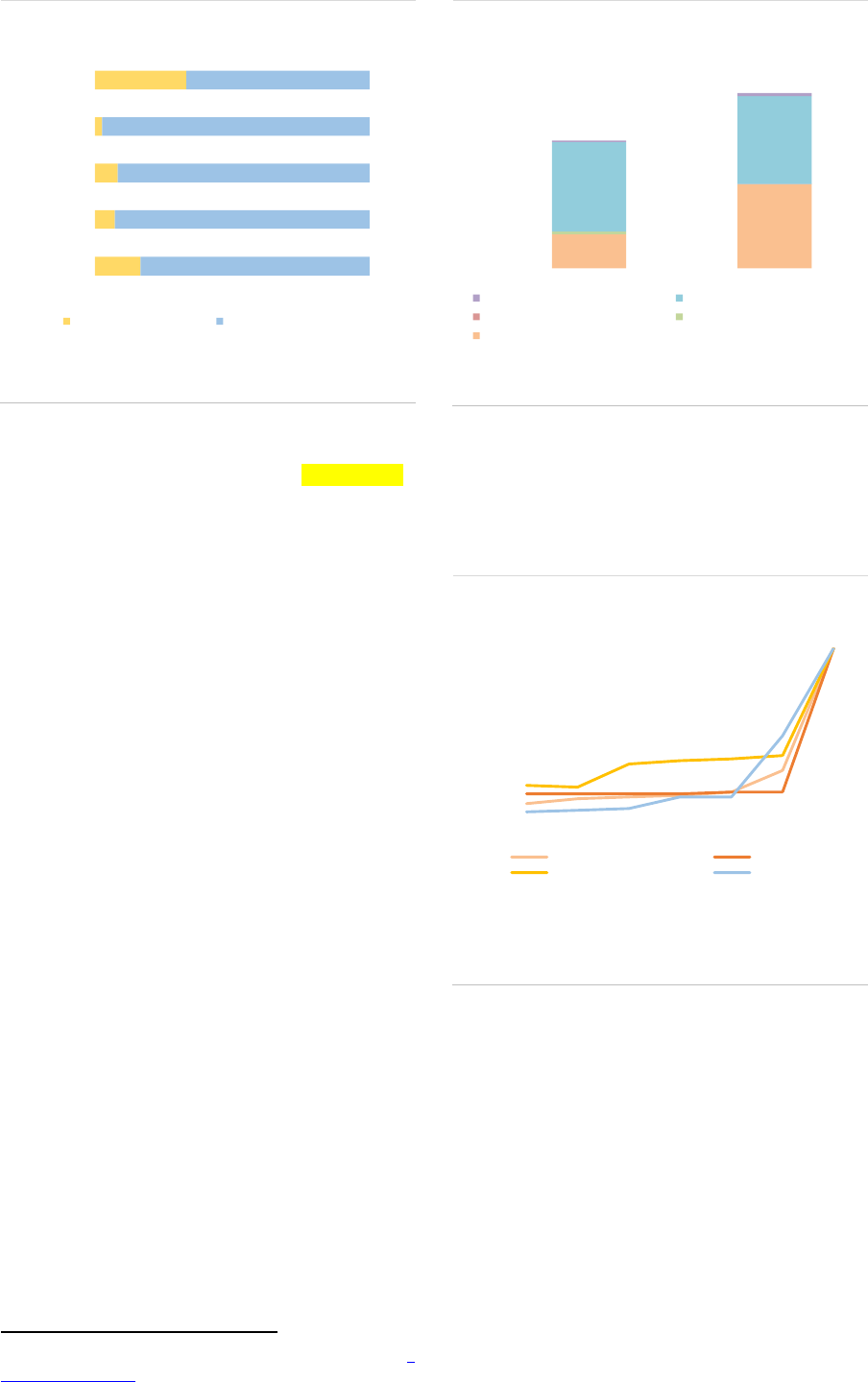
Distribution: Among AIFs, RE funds have an
extensive access to the EU passport, with 94%
able to be sold throughout the EU, a 3pp increase
from 2019 (ASR-AIF.46).
ASR-AIF.46
EU passport
High access to passport
Real Estate fund investors: RE funds are sold
mainly to professional investors (76%), with the
proportion of retail investors increasing by 3pp to
24% in 2020. The retail investor share is even
higher for CRE funds, at 33% of the NAV (+1pp)
while the share fell by 2pp to 17% for the
residential category (ASR-AIF.47ASR-AIF.47).
Among professional investors, pension funds and
insurance companies are the main investors,
accounting for 23% and 17% of the NAV
respectively (ASR-AIF.53). Households own 15%
of the NAV of RE, followed by other funds with
13% of the NAV. Banks have limited exposures
to RE funds, except for residential RE funds for
which banks hold 13% of NAV.
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
DE LU NL FR IT Other
2017 2018 2019 2020
Note: NAV of REs managed and/or marketed by authorized AIFMs and sub-
threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions, in EUR bn. data
for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
EU
passport
94%
EU w/o
passport
5%
Non-EU w/o passport
1%
Note: NAV of real estate AIFs by manager's access to AIFMD passport,
end of 2020, in %. Authorised EEA30 AIFMs with access to AIFMD
passport or marketing non-EEA30 AIFs w/o passport, sub-threshold
managers are registered only in national juridisdictions w/o passporting
rights. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2021 25
ASR-AIF.47
AIF investors
Large share of retail investors
Geographical investment focus: RE funds
invest overwhelmingly in the EEA (88%, +5pp
compared with 2019, ASR-AIF.54ASR-AIF.54).
RE funds have by far the largest exposures to
EEA countries compared with other AIF types.
Leverage and liquidity risks
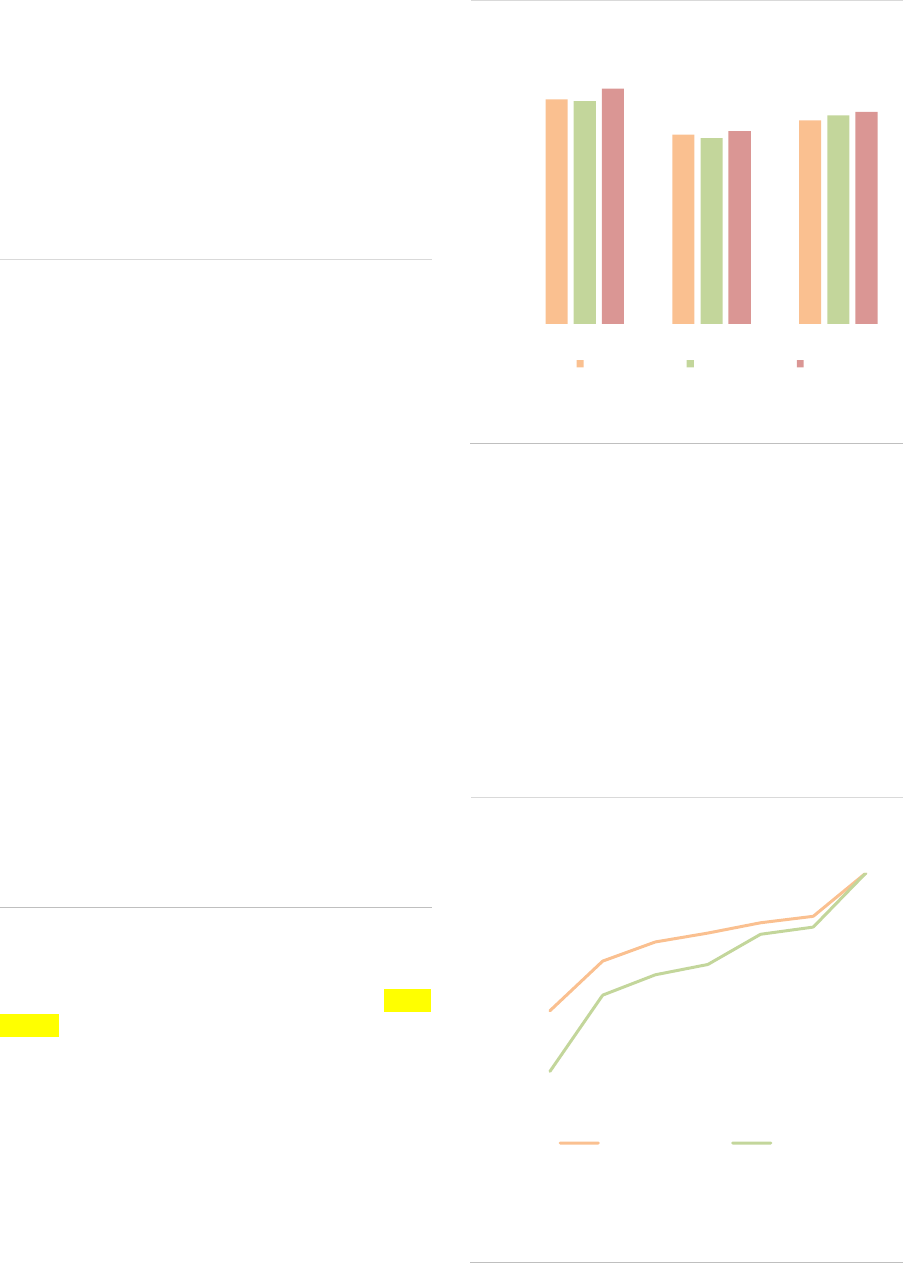
Gross exposures: RE gross exposures are
concentrated in physical assets (around 70% of
exposures, across most RE types), in line with the
strategy used (ASR-AIF.55).
Leverage: Specific limits to balance sheet
leverage in RE funds are established in most EU
jurisdictions to mitigate the risks related to
leverage and liquidity
5
. However, those
measures are not harmonized and can vary from
one country to another (ESRB, 2021). Regulatory
AuM to NAV is 138% on aggregate, as they have
limited exposures to derivatives, with low
dispersion across RE fund types (ASR-AIF.56).
However, RE funds do use financial leverage,
with outright borrowing amounting to 11% of the
NAV (+3pp compared with 2019, the second
largest by AIF type, after HFs (ASR-AIF.48ASR-
AIF.48). In 2020, the share of unsecured
borrowing jumped from 2% to 5% of NAV.
5
In 2021, the Central Bank of Ireland published a
Consultation Paper to introduce macroprudential limits on
leverage and liquidity mismatch (CBoI, 2021).
ASR-AIF.48
Financial leverage
Increase in unsecured borrowing
Financing liquidity risk for most RE funds appears
limited as most of the borrowing lines remain
available for relatively long periods. For ‘other’
RE funds, the reliance on overnight borrowing
increased by 6 pp since 2019 to amount to 17%
of financing liquidity (ASR-AIF.49).
ASR-AIF.49
Financing liquidity risk
Low short-term borrowings for most RE funds
Liquidity risk: In terms of NAV, 56% of RE funds
are open-ended funds (+2pp compared with
2019) and there is considerable heterogeneity
regarding redemption frequencies for open-
ended RE funds (ASR-AIF.57). The share of RE
funds offering daily to monthly liquidity remained
stable in 2020, accounting for 55% of the NAV.
However, 40%% of CRE funds still offer daily
liquidity to investors (-2pp). At the aggregate
level, the liquidity profile of RE fund points to
significant liquidity mismatch: within a month,
investors can redeem up to 14% of the NAV,
whereas only 2% of the assets can be liquidated
0% 50% 100%
Residential
Other
Multi-strategy
Industrial
Commercial
Retail investors Professional investors
Note: Clients of real estate funds managed and/or marketed by authorised
AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions,
end of 2020, in % of NAV. RE = Real estate. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
2%
4%
6%
8%
10%
12%
2019 2020
Short position borrowing sec. Secured via other
Reverse repo Secured via PB
Unsecured borrowing
Note: Share of cash and securities borrowed by RE funds, end of 2020, in % of
NAV. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed, respectively,
w/ and w/o passport. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
26%
17%
1%
47%
100%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day 2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180 d 181-365
d
> 365 d
Commercial Industrial
Other RE Residential
Note: Liquidity financing of real estate funds managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs, end of 2020. Aggregate amount of borrowing and cash
financing divided depending on longest period for which creditors are
contractually committed to provide such financing, Borrowing and cash financing
include drawn and undrawn, committed and uncommitted lines of credit as well as
any term financing. RE=Real estate. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2021 26
within this time frame. The liquidity mismatch
occurs across all time buckets within one year
and is most prevalent for the two main strategies
(CRE and residential) which account for 80% of
NAV (ASR-AIF.50). The aggregate level of
liquidity masks important differences across
Member States, as in some countries RE funds
can only be closed-ended.
ASR-AIF.50
Liquidity profile
Persisting significant liquidity mismatch
The liquidity mismatch at the short-end can be
mitigated by cash, albeit to a lesser extent:
unencumbered cash for RE funds remains
below 6% for commercial and residential RE
funds, the two largest strategies (ASR-
AIF.51ASR-AIF.51). Furthermore, cash buffers
are significantly lower than the potential liquidity
mismatch that could arise if investors were to
redeem over longer time horizons. In that context,
funds might have to rely on liquidity management
tools, provided that they were available at the
fund level. Around 70% of open-ended RE funds
require a notice period, which in most cases is at
least three months, and 21% have lock-up
periods.
ASR-AIF.51
Unencumbered cash
Cash buffers lower than liquidity gap
8%
11%
14%
18%
26%
38%
100%
1%
5%
13%
23%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day or
less
2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180 d 181-365
d
> 365 d
Investor Portfolio
Note: Portfolio and investor liquidity profiles of real estate funds managed
and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020. Portfolio liquidity defined
as the percentage of the funds’ assets capable of being liquidated within each
specified period, investor liquidity defined as the shortest period for which
investors can redeem. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs
marketed, respectively, w/ and w/o passport. d=Days. Data for the EEA30..
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
2%
4%
6%
8%
10%
12%
Commercial Industrial Multi-
strategy RE
Other RE Residential
Unencumbered cash
Note: Unencumbered cash held by real estate funds, end of 2020, in % of NAV.
EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed, respectively, w/ and
w/o passport. RE=Real estate. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
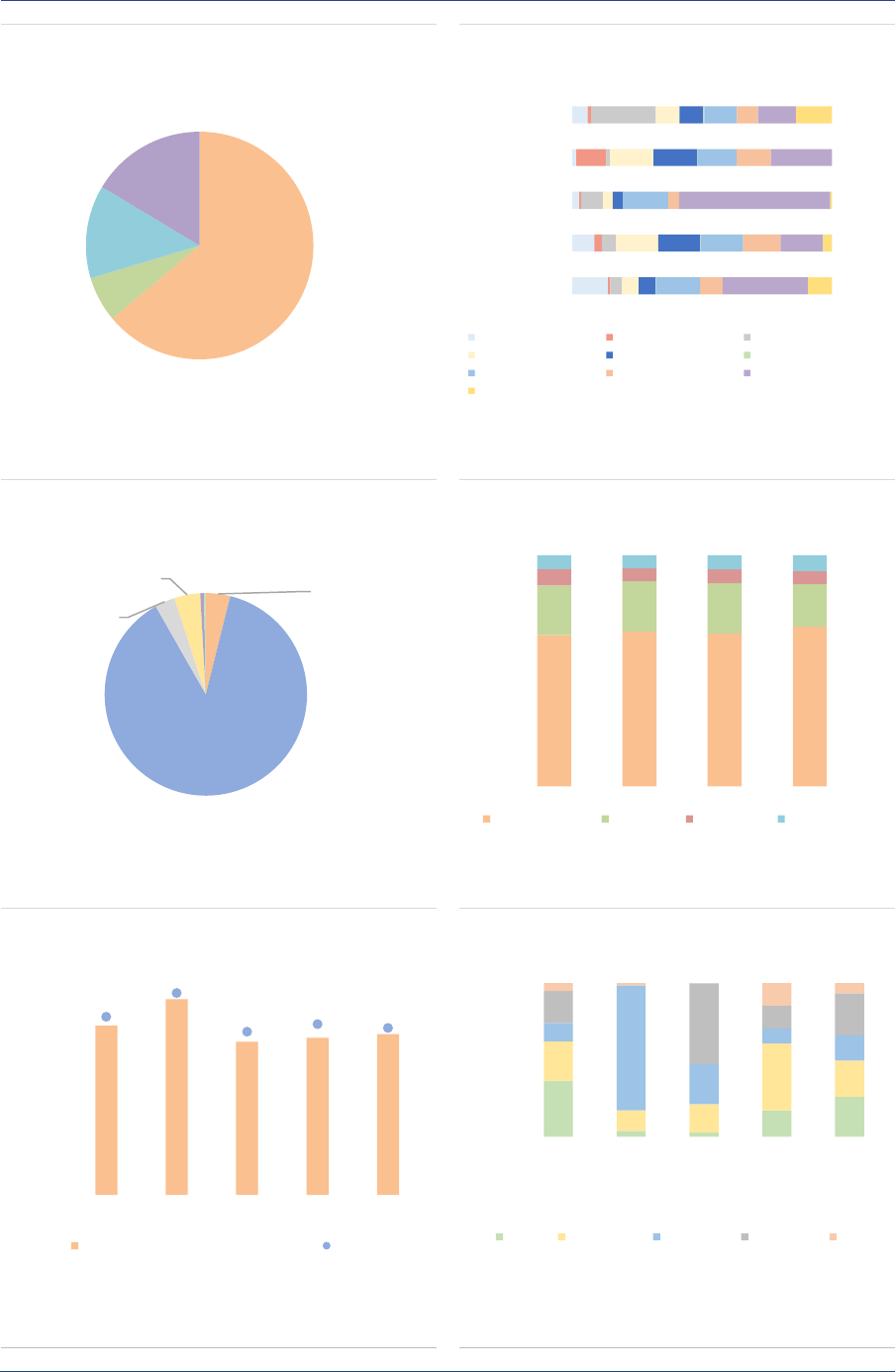
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2021 27
ASR-AIF.52
ASR-AIF.53
RE fund strategies
RE funds investors
Mainly CRE
Pension funds as largest investors
ASR-AIF.54
ASR-AIF.55
Regional investment focus
Gross exposures
Investments mainly in EEA
Mainly physical assets
ASR-AIF.56
ASR-AIF.57
Leverage
Redemption frequencies
Limited use of leverage
Large dispersion
Commercial
64%
Industrial
7%
Other RE
13%
Residential
16%
Note: Investment strategies of real estate funds, end of 2020, in % of NAV.
Real estate funds managed and/or marketed by full scope AIFMs and sub-
threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions. RE= Real estate.
Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100%
Residential
Other RE
Multi-strategy RE
Industrial
Commercial
Banks General government Household
Insurances Non-profit None
Other CIUs Oth. fin. institutions Pension funds
Unknown
Note: Ownership of units in real estate funds AIFs managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. RE=Real estate. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
Asia
4%
EEA
88%
Other Europe
3%
North America
4%
Rest
>1%
Note: Regional investment focus of real estate funds managed and/or
marketed by authorised AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in
national jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Geo-focus determined
according to the domicile of investments and the supranational category
including investments without a predominant geo-focus. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
70%
80%
90%
100%
2017 2018 2019 2020
Physical assets Securities Derivatives Other assets
Note: Share of exposures by RE funds, end of 2020, in % of total. AIFs
managed and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs. RE=Real estate. Data for the
EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
40%
80%
120%
160%
Comercial Industrial Multi-
strategy
RE
Other
RE
Residential
Median adjusted gross leverage AuM/NAV
Note: Adjusted gross leverage of real estate funds managed and/or marketed
by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Adjusted gross leverage
computed as total exposure less IRDs with respect to NAV. RE=Real estate.
Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National competent authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Commercial
Industrial
Multi-
strategy RE
Other RE
Residential
Daily Weekly
to monthly
Quarterly Quarterly
to yearly
Other
Note: Investor redemption frequencies allowed by open-end real estate funds
managed and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV.
EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed, respectively, w/
and w/o passport. RE=Real estate. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
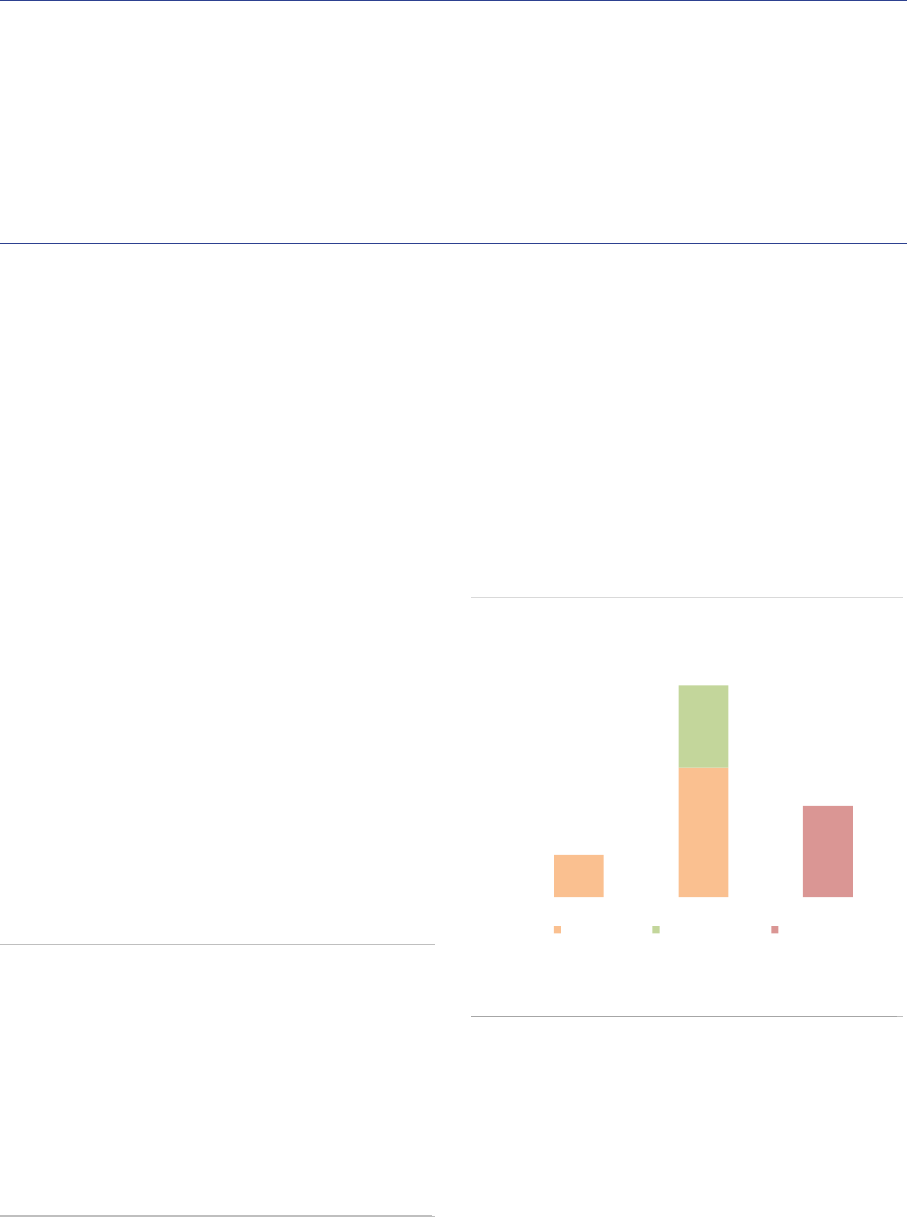
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2021 28
Hedge Funds
Summary
With the departure of the UK from the EU, the size of the EEA30 HF sector has plummeted to only EUR
89bn (2% of the NAV of all AIFs), from EUR 354bn in 2019 (including the UK). EEA30 HFs have
widespread access to the EU passport and are mainly domiciled in Ireland and Luxembourg. Leverage
is very high, particularly for some strategies highly reliant on derivatives. HFs using derivatives tend to
maintain large, unencumbered cash positions, possibly to meet future margin calls relating to derivatives
positions. HFs are exposed to limited liquidity mismatch, as their assets can be liquidated quickly to
meet investor redemptions. However, HFs are exposed to financing risk, as for some strategies more
than half of their funding is overnight, implying potential rollover risk.
Hedge Funds: market size and
structure
HFs are funds that employ complex strategies,
usually through the use of derivatives, and rely on
leverage to generate returns.
Size: As of the end of 2020, the NAV of HFs sold
in the EEA30 by AIFMs domiciled in the EEA30
amounted to EUR 89bn, a 3% increase
compared with 2018. With the departure of the
UK from the EU, the size of the EEA30 HF
industry has shrunk considerably since HFs
managed by UK AIFMs accounted for 75% of the
NAV in 2019 (ESMA, 2021). Most of the EEA30
HF industry remains concentrated in two Member
States: Ireland and Luxembourg account for 58%
of the NAV (ASR-AIF.65).
Outside the AIFMD framework, definitions of
hedge funds have been put forward (ASR-
AIF.58). As a result, funds have been identified
that apply investment strategies comparable to
hedge funds, whose size has been found to be
significant.
ASR-AIF.58
Hedge funds
Definitions outside of the AIFMD framework
The ECB defines hedge funds as funds “which apply relatively
unconstrained investment strategies to achieve positive
absolute returns, and whose managers, in addition to
management fees, are remunerated in relation to the fund’s
performance’ (ECB, 2017).
In the US, the SEC defines a hedge fund as any private fund
whose managers are paid a performance fee, and that may
borrow in excess of 150% of its NAV or have a gross notional
exposure higher than 200% of its NAV or may sell securities
or other assets short (SEC, 2021).
For example, the ECB estimates the total size of
the euro area market for funds pursuing hedge-
fund style strategies to amount to EUR 408bn,
including EUR 250bn registered as AIFs, and
EUR 158bn of funds registered under the UCITS
framework (ASR-AIF.59). Most strikingly, the size
of AIF HFs cited by the ECB amounts to more
than three times the volume found under formal
AIF reporting. This represents a significant case
of reporting inconsistencies resulting from the AIF
categorisation. In the US, data from the
Securities and Exchange Commission indicate
that the NAV of HFs domiciled in two euro area
jurisdictions amount to EUR 176bn, two times
what is reported for euro area HFs in AIFMD.
ASR-AIF.59
Classification of euro area-domiciled hedge funds
Large reporting differences
There are also AIF HFs which are neither
domiciled nor managed in the EEA30 but are sold
in individual Members States under NPPR.
Those HFs had a NAV of EUR 1938bn at the end
of 2020. Most of HFs sold under NPPR are
domiciled in offshore centres such as the
Cayman Islands (53% of NAV) and the British
Virgin Islands (17%). Around 22% are domiciled
in the United States.
Hedge Fund types: HFs pursue a wide range of
strategies (ASR-AIF.66). Strategies relating to
82
408
176
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
AIFMD ECB SEC
AIF UCITS All types
Note: NAV of euro area domiciled hedge fund by regulatoty type and
definition, in EUR bn. SEC data only include HFs domiciled in Ireland and
Luxembourg.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ECB. SEC,
ESMA.
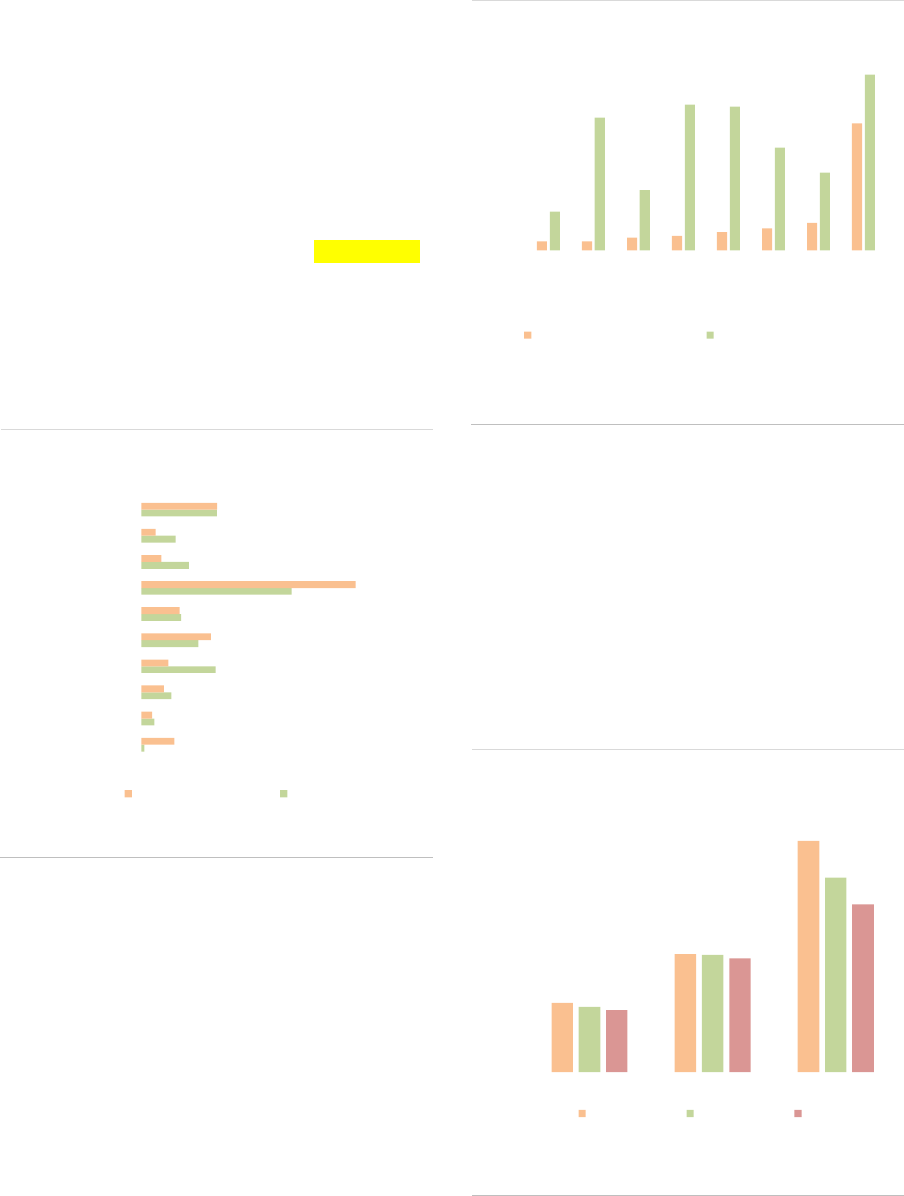
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2021 29
equities (such as long/short) remain dominant
(37%, +4pp), followed by other HF strategies
(25%) and credit (12%).
Distribution: EU HFs have an extensive access
to the EU passport, with 95% able to be sold
throughout the EU (+12pp compared with 2019).
This stands in sharp contrast with previous
reports when UK data were included, as UK HFs
were mainly domiciled outside the EU and hence
not eligible for passporting.
Hedge Fund investors: HFs are mainly owned
by professional investors, with retail investors
accounting for 10% of NAV. Among professional
investors, investment funds are the main holders
of HF shares at 29% (ASR-AIF.60ASR-AIF.60),
followed by pension funds (14%) and banks
(14%) and other financial institutions (11%,
+3pp). Similarly, for other types of AIFs, the
ownership of HF shares is highly concentrated,
with the top five holders accounting for around
80% of the NAV for HFs.
ASR-AIF.60
HF investors
Mainly funds and pension funds
Investment focus: HFs invest primarily in the
EEA (46%), and North America (36%, -4pp),
while exposures to Asia amount to 7% of NAV.
Leverage and liquidity risks
Gross exposures: Gross exposures of HFs are
diverse and heterogeneous across strategies
(ASR-AIF.67). Macro, CTA and relative value
HFs have high exposures relating to interest-rate
derivatives, while credit HFs are exposed mainly
to credit derivatives (47% of exposures).
Securities account for the main part of gross
exposures for event-driven and equity HFs (71%
and 60% respectively).
HFs have high levels of unencumbered cash
compared to other types of AIFs (11% for HFs
versus 5% for all AIFs). The highest levels of cash
are observed for CTA strategies which rely
heavily on derivatives (ASR-AIF.61). This
suggests that part of the unencumbered cash is
used to cover future margin calls.
ASR-AIF.61
Unencumbered cash
Cash correlated with derivatives exposures
Leverage: HFs are in general highly leveraged,
with adjusted leverage at around 330% of NAV
(ASR-AIF.62), although leverage has been
declining since 2018. The high levels of
aggregate leverage are driven by a few very large
outliers: half of HFs have a leverage below 130%,
as indicated by the median leverage which
remained stable at 121%. In addition, 3/4
th
of HFs
has a leverage below 220% (75
th
percentile).
Among HF strategies (ASR-AIF.68), CTAs have
the highest median leverage (at 640%), followed
by macro (435%) and relative value (230%).
ASR-AIF.62
Hedge fund leverage
High dispersion
Although most of the leverage is synthetic
leverage, i.e. due to the use of derivatives,
financial leverage is also significant for HFs
0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50%
None
General gov.
Households
Banks
Oth. fin. institutions
Non-profit
Oth. CIU
Unknown
Insurances
Pension funds
2019 2020
Note: Ownership of units in HFs managed and/or marketed by authorised
AIFMs, in % of NAV. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
20%
40%
60%
80%
100%
Event
driven
Rel. value
Equity
Macro
Multi-
strategy HF
Credit
Other
HF
CTA
Unencumbered cash Derivatives exposures
Note: Unencumbered cash in % of NAV and derivatives exposures in % of
gross exposures for hedge funds, end of 2020. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs
by authorised AIFMs marketed, respectively, w/ and w/o passport. HF=Hedge
fund. Data fror the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
50%
100%
150%
200%
250%
300%
350%
400%
450%
500%
Median 75th pc HF total
2018 2019 2020
Note: Adjusted leverage of HFs in% of NAV.AIFs managed and/or marketed
by full scope AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national
jurisdictions. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
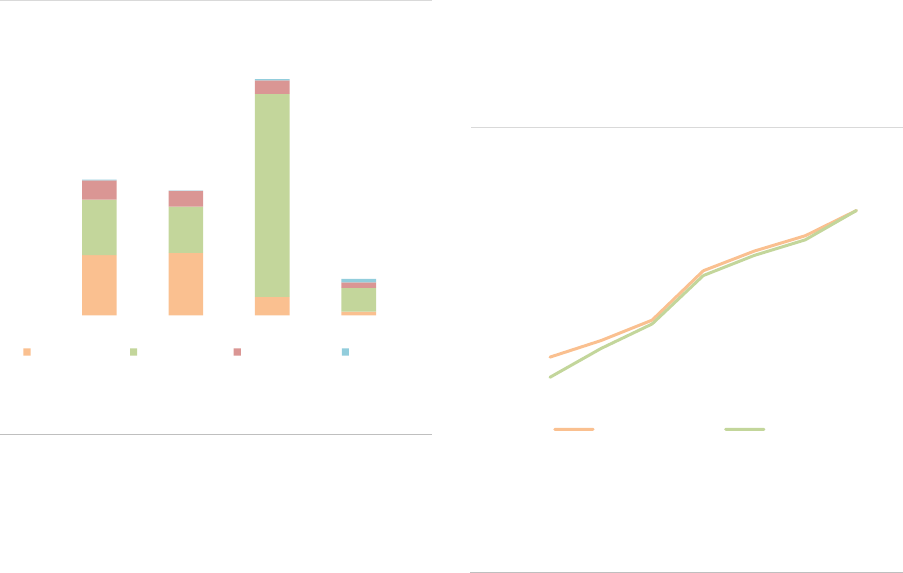
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2021 30
compared with other AIF types. However, in
2020, direct borrowings plummeted to 37% of
NAV compared with 225% in 2019 (ASR-AIF.63).
The drop is mainly driven by a sharp reduction in
repo: from 150% to 18% of NAV as well as lower
short positions (from 55% to 10% of NAV). In the
US, SEC reports also point to a decline in the use
of reverse repo by HFs, although by a much
smaller extent (from 40% to 34% of NAV).
ASR-AIF.63
Direct borrowing
Sharp drop in repo borrowing for EU HFs
Liquidity risk: HFs reliant on short-term
borrowings are exposed to financing liquidity
risk (ASR-AIF.70). The risk would crystallise if
HFs were to use most of their available financing,
and then their counterparts were to cut or reduce
their funding. For some strategies, such as CTA
and equity, borrowings are almost entirely
overnight (more than 90% for equity HFs),
exposing them to potential rollover risk.
Most HFs are open-ended funds (78% of NAV)
which offer weekly to monthly liquidity to
investors across strategies (ASR-AIF.69). HFs
offering daily liquidity account for only 8% of the
NAV. At the aggregate level, the liquidity profile
of HFs points to limited liquidity mismatch: within
one week, investors can redeem up to 25% of the
NAV, whereas 20% of the assets can be
liquidated within this time frame (ASR-AIF.64).
This pattern is evident across all HF strategies,
despite different levels of portfolio and investor
liquidity. In addition, among AIFs, HFs make the
most use of notice periods, which are on average
around one month.
ASR-AIF.64
Liquidity profile
Limited liquidity mismatch
0%
20%
40%
60%
80%
100%
120%
140%
160%
180%
2019 2020 2019 2020
Prime brokers Reverse repo Other secured Unsecured
Note: Cash and securities borrowed by hedge funds, end of 2019 and 2020, in
% of NAV. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed,
respectively, w/ and w/o passport. Data for the EEA30 and for the US.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, SEC, ESMA.
US
EU
25%
37%
65%
77%
85%
100%
4%
20%
34%
62%
74%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day or
less
2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180
d
181-365
d
> 365 d
Investor Portfolio
Note: Portfolio and investor liquidity profiles of hedge funds managed and/or
marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020. Portfolio liquidity defined as the
percentage of the funds’ assets capable of being liquidated within each
specified period, investor liquidity defined as the shortest period for which
investors can redeem. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs
marketed, respectively, w/ and w/o passport. d=Days. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
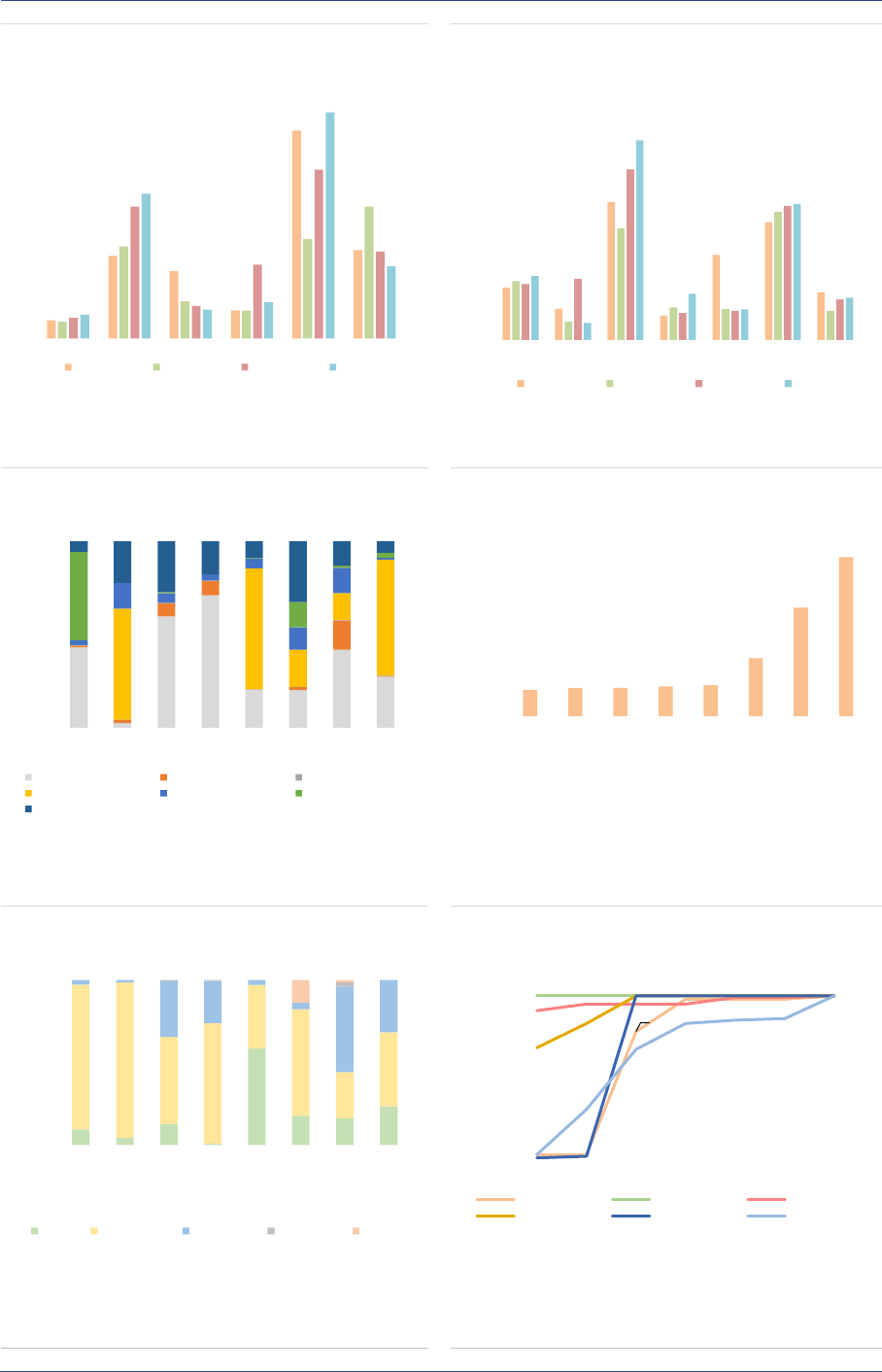
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2021 31
ASR-AIF.65
ASR-AIF.66
Size of HFs by country
HF strategies
Concentrated in two countries
Mainly equity strategies
ASR-AIF.67
ASR-AIF.68
Gross exposures
Leverage
Heterogeneity across HF strategies
Dispersion across HF strategies
ASR-AIF.69
ASR-AIF.70
Redemption profile
Liquidity financing
Mostly weekly to monthly frequency
Reliance on short-term funding
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
DE LU SE FR IE Other
2017 2018 2019 2020
Note: NAV of HFs of AIF managed and/or marketed by authorized AIFMs and
sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions, in EUR bn.
Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
Credit CTA Equity Event
Driven
Macro Other
HF
Relative
Value
2017 2018 2019 2020
Note: NAV of HFs by strategy, in EUR bn.AIFs managed and/or marketed by
full scope AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national
jurisdictions. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Credit CTA Equity Event
driven
Macro Multi-
strategy
HF
Other
HF
Rel.
value
Securities CIUs Physical assets
IRDs FX CDS
Other derivatives
Note: Share of exposures by hedge funds' investment strategies, end of 2020, in %
of total. AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs. HF=Hedge fund.
Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
100%
200%
300%
400%
500%
600%
700%
Event driven
Multistrategy HF
Other HF strategy
Equity
Credit
Relative value
Macro
CTA
Note: Median adjusted leverage of HFs in% of NAV, end of 2020.AIFs managed
and/or marketed by full scope AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered
only in national jurisdictions. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Credit
CTA
Equity
Event
driven
Macro
Multi-
strategy HF
Other
HF
Rel. value
Daily Weekly
to monthly
Quarterly Quarterly
to yearly
Other
Note: Investor redemption frequencies allowed by open-end hedge funds
managed and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV.
EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed, respectively, w/
and w/o passport. HF=Hedge fund. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
2%
78%
100%
91%
68%
83%
0%
1%
100%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day 8-30 d 91-180 d > 365 d
Credit CTA Equity
Event driven Macro Rel. value
Note: Liquidity financing of hedge funds managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs, end of 2020. Aggregate amount of borrowing and cash
financing divided depending on longest period for which creditors are
contractually committed to provide such financing, Borrowing and cash
financing include drawn and undrawn, committed and uncommitted lines of
credit as well as any term financing. HF=Hedge fund. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
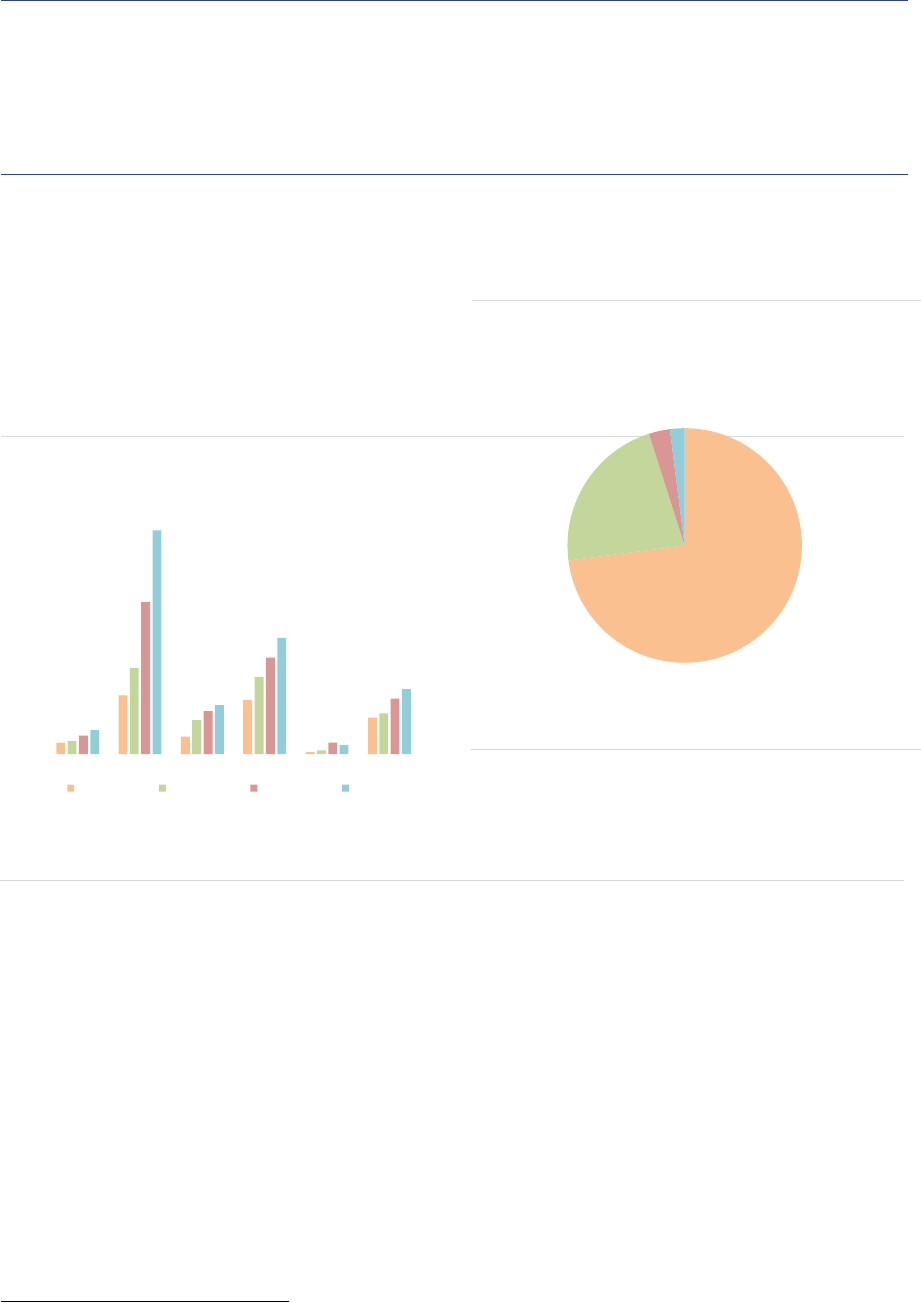
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2021 32
Private Equity Funds
Summary
PE funds account for 6% of the NAV of all EEA30 AIFs, or EUR 363bn. Among AIF types, PE funds
contributed remarkably to the growth of the AIF sector in 2020 (+29% compared with 2019), together
with ‘other AIFs’. They follow a range of strategies and are almost exclusively sold to professional
investors. PE funds invest mainly in illiquid securities (unlisted securities), but liquidity risk is limited
given that PE funds are overwhelmingly closed-ended.
Market size and structure
Size: PE funds have grown substantially (+29pp)
in 2020 reaching a total NAV of EUR 456bn, or
6% of all AIFs. The PE fund industry is
concentrated in a few countries (ASR-AIF.71),
with the top five accounting for 83% of the NAV.
ASR-AIF.71
Size of PE funds
Concentration in a few countries
Private Equity Fund types: PE investment
strategies are diversified, with 33% of the NAV
invested in growth capital, followed by venture
capital (16%) and mezzanine capital (6%). A
large part of the NAV (45%) is related to other
unspecified strategies (ASR-AIF.75). The large
residual category can be explained by
classification issues, as PE fund types do not
include leveraged buyouts, which account for a
significant proportion of the PE industry (around
60% of fundraising in 2019 according to Invest
Europe)
6
.
Distribution: As for other types of AIFs, the
majority of PE funds have access to the EU
6
See Invest Europe (2021).
passport, with 73% able to be sold throughout the
EU (ASR-AIF.72ASR-AIF.72).
ASR-AIF.72
EU passport
High access to passport
Private Equity Fund investors: Among AIFs,
PE funds have the lowest proportion of retail
investors (6%). Among PE fund types, venture
capital has a larger proportion of retail investors,
at 12% of the NAV (ASR-AIF.73ASR-AIF.73).
Among professional investors, no important shifts
in composition occurred in 2020. The main
investor type is other CIUs with 33% of the NAV
in 2020 (ASR-AIF.76), followed by other financial
institutions (17%) and non-profit funds (11%).
The distribution of the investors remains more or
less similar to the one of 2019.
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
180
DE LU NL FR IE Other
2017 2018 2019 2020
Note: NAV of PEs managed and/or marketed by authorized AIFMs and sub-
threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions, in EUR bn. Data
for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
EU
passport
73%
EU w/o
passport
22%
Non-EU w/o
passport
3%
Non-EU not marketed
in EU 2%
Note: NAV of private equity funds by manager's access to AIFMD passport,
end of 2020, in %. Authorised AIFMs with access to AIFMD passport,
subthreshold managers registered only in national juridisdictions w/o
passport. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
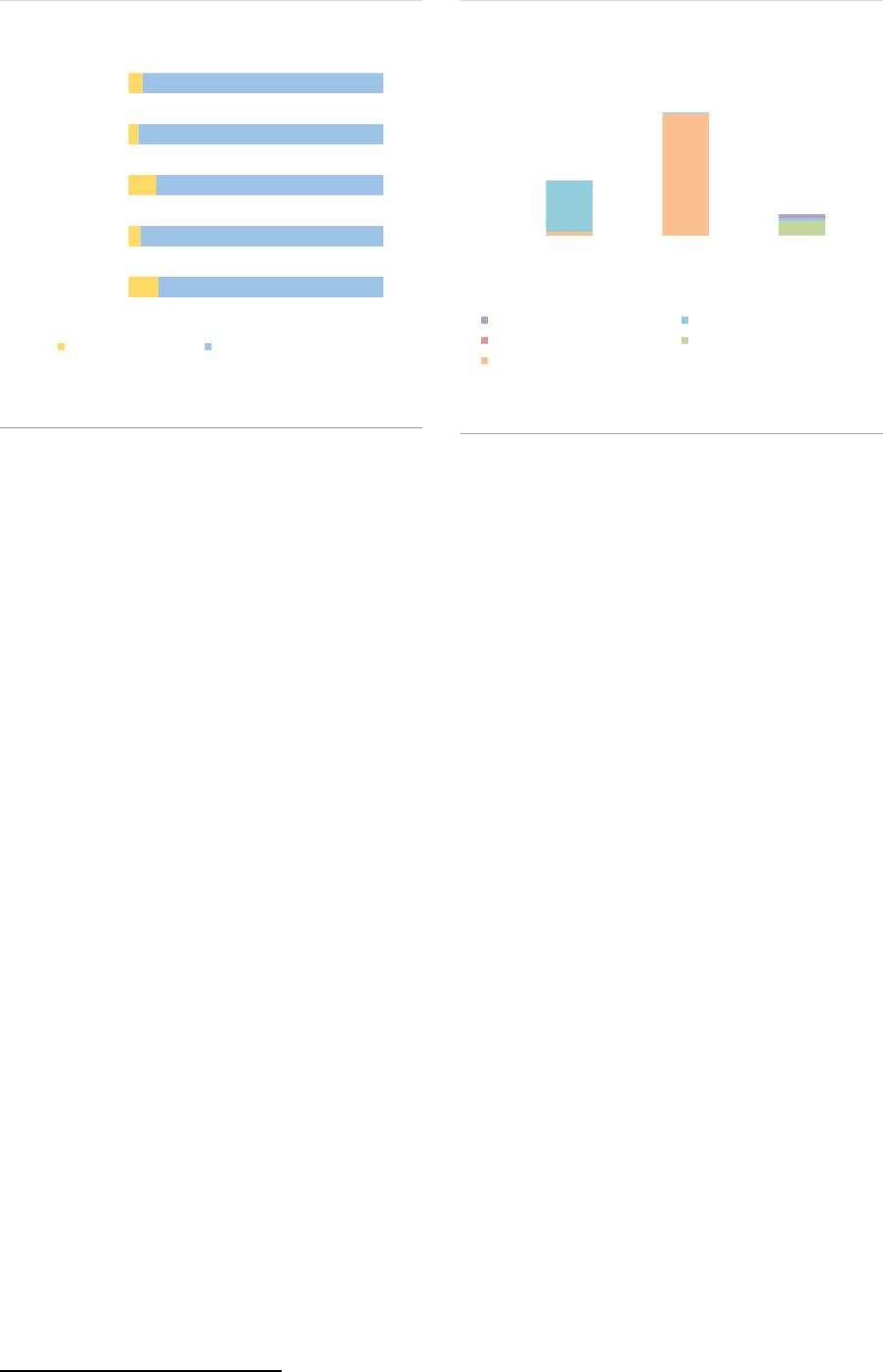
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2021 33
ASR-AIF.73
AIF investors
Predominantly professional investors
Geographical investment focus: PE funds
continue to invest mainly in the EEA (72% of NAV
(ASR-AIF.77ASR-AIF.77) and the relative share
remain more or less stable. The second region of
investments for PE funds is still North America
(17% of the NAV).
Leverage and liquidity risks
Leverage: PE funds make limited use of
leverage. The AuM-to-NAV ratio is at 115% on
aggregate, the lowest among AIF types, with low
dispersion across PE fund types (ASR-
AIF.79ASR-AIF.79). PE funds make limited use
of financial leverage, with outright borrowing
amounting to less than 2% of the NAV. The
borrowings are concentrated in Mezzanine
capital and other PE funds (ASR-AIF.74).
7
According to recital 78 of the AIFMD: “for private equity
and venture capital funds this means that leverage that
ASR-AIF.74
Financial leverage
Limited and concentrated borrowing
The low level of leverage is explained by the
structures used by PE funds. PE funds are not
usually leveraged but they invest in a portfolio
company that could be leveraged. According to
the AIFMD, leverage should not be reported by
the AIF at the portfolio company level.
7
Liquidity risk: Most PE funds are closed-ended
funds (96% of the NAV, ASR-AIF.80) and the
redemption frequency for open-ended PE funds
is usually weekly to monthly. Financing liquidity
risk for PE funds is limited in the very short-term
(only 1% of available financing is under a week),
but it increases substantially over one month, as
more than 70% of available financing expires
between 8 and 30 days (ASR-AIF.78). PE funds
have high levels of unencumbered cash
compared with 2019 at 6% of the NAV (+4pp) and
is almost entirely held by Other PE funds.
exists at the level of a portfolio company is not intended
to be included”.
0% 50% 100%
Venture Capital
Other PE
Multi-strategy PE
Mezzanine Capital
Growth Capital
Retail investors Professional investors
Note: Clients of private equity funds managed and/or marketed by authorised
AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions,
end of 2020, in % of NAV. PE = Private equity fund. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0.0%
2.5%
5.0%
7.5%
Growth Capital Mezzanine Capital Other private
equity fund
strategy
Short position borrowing sec. Secured via other
Reverse repo Secured via PB
Unsecured borrowing
Note: Cash and securities borrowed by PE, end of 2020, in % of NAV. EEA30
and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed, respectively, w/ and w/o
passport. RE=Real Estate. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD databse, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
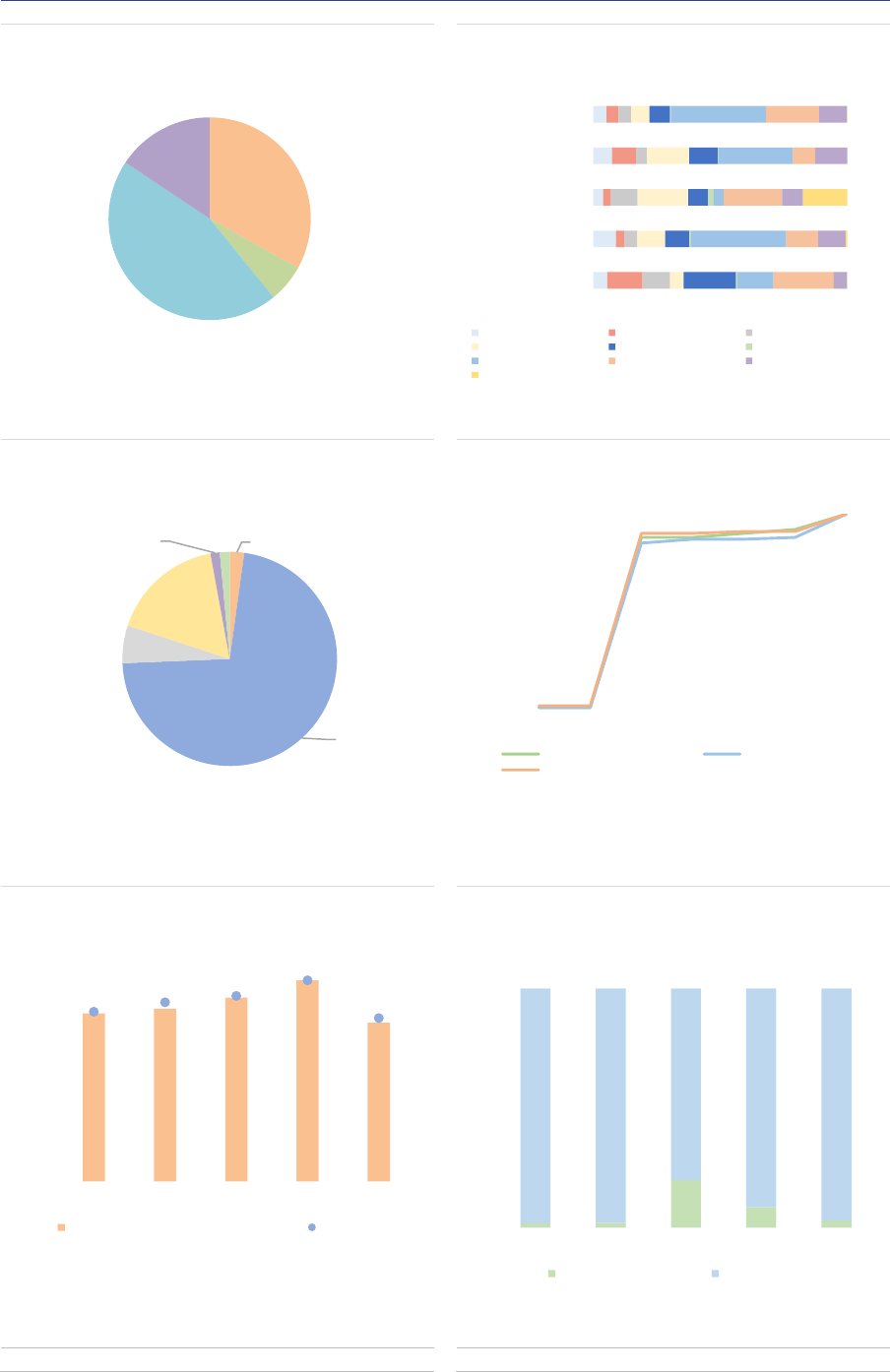
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 34
ASR-AIF.75
ASR-AIF.76
PE fund strategies
PE fund investors
Diversified strategies
Stable distribution of investors
ASR-AIF.77
ASR-AIF.78
Regional investment focus
Liquidity financing
Mostly EEA
High share of funding below one month
ASR-AIF.79
ASR-AIF.80
Leverage
Redemption rights
Limited use of leverage
Mainly closed-ended funds
Growth
Capital
33%
Mezzanine
Capital
6%
Other
private
equity
45%
Venture
Capital
16%
Note: Investment strategies of private equity funds, end of 2020, in % of
NAV. Private equity funds managed and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs
and sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions. Data for
the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100%
Venture Capital
Other PE
Multi-strategy PE
Mezzanine Capital
Growth Capital
Banks General government Household
Insurances Non-profit None
Other CIUs Oth. fin. institutions Pension funds
Unknown
Note: Ownership of units in private equity funds managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. PE=Private equity fund. Data for the
EEA30..
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
Asia
2%
EEA
72%
Other Europe
6%
North America
17%
Supra National
1%
Rest
2%
Note: Regional investment focus of private equity funds managed and/or
marketed by authorised AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in
national jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Geo-focus determined
according to the domicile of investments, and the supranational category
including investments without a predominant geo-focus. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
85%
1
1%
90%
91%
100%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day 2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180
d
181-365
d
> 365 d
Growth Capital Mezzanine Capital
Venture Capital
Note: Liquidity financing of private equity funds managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs, end of 2020. Aggregate amount of borrowing and cash
financing divided depending on longest period for which creditors are
contractually committed to provide such financing, Borrowing and cash financing
include drawn and undrawn, committed and uncommitted lines of credit as well
as any term financing. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
30%
60%
90%
120%
Growth
capital
Mezzanine
capital
Multi-
strategy
Other PE Venture
capital
Median adjusted gross leverage AuM/NAV
Note: Adjusted gross leverage of private equity funds managed and/or
marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Adjusted gross
leverage computed as total exposure less IRDs with respect to NAV.
PE=Private equity fund. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National competent authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Growth
Capital
Mezzanine
Capital
Multi-
strategy
Other PE Venture
Capital
Open-end Closed-end
Note: Redemption rights provided in the ordinary course to investors in private
equity funds managed and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of
NAV. PE=Private equity fund.Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
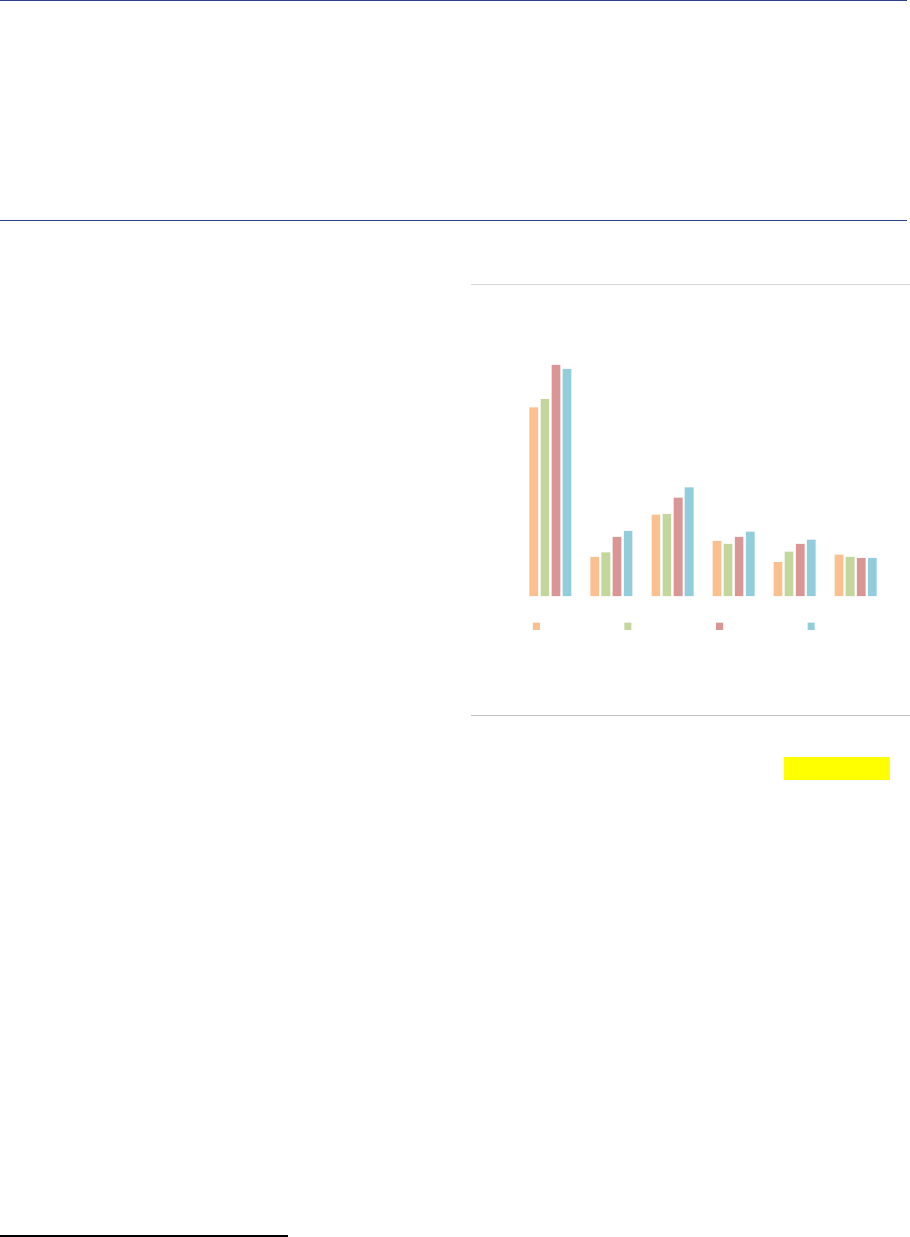
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2021 35
Other AIFs
Summary
‘Other AIFs’ account for 62% of the NAV of EEA30 AIFs, at around EUR 3,650bn (+4% compared with
2019). This category of the AIFMD reporting regime covers a range of strategies, with fixed income and
equity strategies accounting for 68% of the NAV and an additional residual category amounting to 28%.
‘Other AIFs’ are mainly sold to professional investors, although there is a significant retail investor
presence in the residual category. They make little use of financial or synthetic leverage. Although most
types of ‘other AIFs’ have a limited liquidity risk at aggregate level, some funds in this residual category
may be subject to liquidity deficit.
Market size and structure
Size: At the end of 2020, the size of the ‘other
AIFs’ amounted to EUR 3,650bn (+4% compared
with 2019), concentrated in a few countries (ASR-
AIF.81ASR-AIF.81). According to the AIFMD
fund classification the category of ‘other AIFs’ is
a residual category. However, almost half of the
reported AIFs, accounting for 62% of total NAV,
fall in this category that comprehend a
heterogeneous group of strategies.
8
In relative
terms, ‘other AIFs’ constitutes the main AIF type
in most EEA30 countries, accounting for around
80% of the NAV in the Netherlands and Poland,
around 70% in Germany, Spain, Ireland and
between 40% and 60% in France, Luxembourg,
Austria and Sweden.
8
The transparency obligations established by the AIFMD
require AIFMs to make available to investors and NCAs a
description of the fund strategy and the type of assets in
which it may invest. For a detailed description of this
category and a discussion of the related potential
ASR-AIF.81
Size of ‘other AIFs’
Main AIF type in most countries
‘Other AIF’ types: ‘other AIFs’ can use very
different strategies (ASR-AIF.82ASR-AIF.82).
The main strategies are related to fixed income
(44% of the NAV) — which includes a few money-
market funds operating under the AIFMD
framework — and equity (24%).
classification issues, see the section “AIFMD fund
classification – shedding light on ‘other AIFs’ in ESMA
(2020b).
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
1600
DE LU NL FR IE Other
2017 2018 2019 2020
Note: NAV of 'Other AIFs' managed and/or marketed by authorized AIFMs and
sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions, in EUR bn.
data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.

ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2021 36
ASR-AIF.82
‘Other’ AIFs strategies admitted under AIFMD
Diversified set of strategies
Real estate
strategies
Number of
AIFs (%)
NAV
(EUR bn)
Equity
21
893
Fixed income
28
1594
Infrastructure
2
91
Commodity
2
35
Other-other
46
1,037
Total ‘other AIFs’
15,419 AIFs
3,650
Note: AIFs classified as ‘‘other AIFs’’ under the AIFMD, end of
2020. Strategies identified according to the fund primary strategy.
Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities,
ESMA.
Within ‘other AIFs’ there is an additional residual
fund category, the so-called ‘other-other’ AIFs,
accounting for a significant portion of the NAV
(28%) which cannot be fully identified as
managers did not refer to a specified strategy.
Benchmarking the strategies self-reported under
the AIFMD with the information collected by the
ECB allows to clarify the characteristics of the
investment policies of those AIFs classified in
residual categories.
9
A relevant portion of ‘other
AIFs’ with an undefined strategy could be largely
described as mixed funds, that is investing in both
equity and bonds with no prevalence of one
instrument, while one third remain still
unidentified (ASR-AIF.83).
ASR-AIF.83
‘Other AIFs’ mapped into ECB investment policy
Mainly captured by bond and mixed strategies
Traded instruments and portfolio
characteristics: Commodity and infrastructure
AIFs appear highly concentrated with the top-five
9
The ECB publishes the list of European investment funds
based on information provided regularly by all members
of the ESCB. Funds domiciled in Denmark and Norway
are not covered. MMFs and Pension funds are excluded
from the definition of investment fund adopted for ESCB
assets representing on average respectively
more than 50% and 60% of their total
investments. (ASR-AIF.84ASR-AIF.84). Equity
AIFs have around 17% of their long-position
assets invested in their five largest positions.
Similarly, the typical fixed income AIFs appear
moderately diversified, with the top five positions
representing almost 20% of total assets. Mixed
funds and unidentified ‘other-other’ AIFs show
instead a higher degree of asset concentration,
implying that the returns of these AIFs depend on
the performance of a smaller number of key
assets. For all strategies, the largest asset to
which AIFs are exposed (highest ranked asset)
accounts for half of the main instruments in which
AIFs are trading.
ASR-AIF.84
Size of ‘other AIFs’
Low concentration for Equity and Fixed income
For AIFs reclassified as mixed funds, the top five
instruments show sizable shares of CIUs (6.5%
of total investments), while 'other-other’ AIFs
have on average the largest footprint in sovereign
bonds (6.8%). Looking at the use of derivatives,
these AIFs rely to some extent on IRDs, FX
derivatives and CDS (ASR-AIF.85ASR-AIF.85).
Derivatives may be used by funds engaging into
bond trading as risk management tool
10
or as a
flexible and less capital-intensive alternative to
other assets to enhance the risk-return profile of
the fund through leverage.
data collection. MMFs would then be still classified as
fixed income AIFs.
10
For example, managers investing in debt securities could
use derivatives to adjust exposures to interest rate, credit,
and currency risk
0
600
1200
1800
Commodity Equity Fixed
income
Infra-
structure
Other
fund
Bonds Equities Hedge Mixed
Other Real estate Not mapped
Note: NAV of AIFs classified as Other under AIFMD mapped into the ECB
investment policy classification, end of 2020, EUR bn. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA, ECB.
56
17
19
67
28
27
0
12
24
36
48
60
72
Com-
modity
Equity Fixed
income
Infra-
structure
Mixed Other
funds
Rank 1 Rank 2 Rank 3 Rank 4 Rank5
Note: Porfolio concentration of AIF, end of 2020, in % of AuM. Portfolio
concentration computed as the value of top 5 instruments traded with respect
to AuM. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.

ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2021 37
ASR-AIF.85
Main traded instruments
Instruments (%)
Commodity
Infra-
structure
Equity
Cash
38.5
2.0
0.4
Equities
0.1
27.3
10.1
Corporate bonds
0.0
3.6
0.1
Sovereign bonds
1.1
0.0
0.1
Convertible bonds
2.2
0.0
Loans
0.1
12.3
0.0
Structured products
0.2
0.1
0.0
CDS & equity
derivatives
0.0
1.1
IRDs and FX
0.2
1.0
3.0
Commodity and other
derivatives
13.4
0.0
0.3
Real assets
1.6
3.7
0.0
MMFs
0.4
0.6
0.1
ETFs
0.0
0.0
0.5
Other CIUs
0.1
13.4
1.2
Other assets
0.0
1.4
0.3
Total
55.7
67.5
17.3
Instruments (%)
Fixed
income
Mixed
other-
Other
Cash
1.8
2.3
1.1
Equities
0.4
2.0
3.0
Corporate bonds
1.0
1.5
0.5
Sovereign bonds
3.5
2.5
6.8
Convertible bonds
0.0
0.0
0.0
Loans
0.5
1.4
2.2
Structured products
0.1
0.4
0.4
CDS & equity derivatives
2.4
3.1
1.5
IRDs and FX
5.4
5.8
4.5
Commodity and other
derivatives
0.2
0.6
0.7
Real assets
0.0
0.3
0.2
MMFs
0.5
0.2
1.0
ETFs
0.1
0.8
0.4
Other CIUs
2.3
6.5
2.3
Other assets
0.1
1.1
2.4
Total
18.6
28.3
26.8
Note: Main traded instruments, end of 2020, % of total
exposures. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities,
ESMA.
Distribution: Like most types of AIF, ‘‘other AIFs’
have access to the EU passport to a large extent,
with 93% (+8pp) able to be sold throughout the
EU (ASR-AIF.91).
‘Other AIF’ investors: ‘other AIFs’ are sold
mainly to professional investors (88%, +2pp),
although retail investor presence is higher for the
residual category (‘other-other’), accounting for
11
Pension funds in Netherlands hold the majority of the NAV
of AIFs, typically investing in equity and fixed income
AIFs, partially explaining the higher proportion of pension
funds in ‘other AIFs’ at European level. A large share of
19% of the NAV (ASR-AIF.86ASR-AIF.86).
Overall, retail clients participate in ‘other AIFs’ for
EUR 480bn. Among professional investors,
pension funds and insurance companies are the
main investors, accounting for 31% and 21% of
the NAV respectively. However, there are large
differences by strategy with insurances holding
one-third of fixed income AIFs’ NAV and pension
funds highly exposed also to equity and
infrastructure funds (ASR-AIF.92). The high
proportion of pension funds might be partly
explained by country-specific factors.
11
ASR-AIF.86
AIF investors
Predominantly professional investors
Geographical investment focus: ‘other AIFs’
are primarily exposed to securities issued in the
EEA (61%), with a significant geo-focus also on
North America (18%) and Asia (6%) (ASR-
AIF.93).
Leverage and liquidity risks
Leverage: ‘Other AIFs’ display limited use of
leverage: regulatory AuM to NAV is 153% on
aggregate as their exposures to derivatives is
limited to 18% of the total exposure (ASR-AIF.94)
and is accompanied by a limited use of financial
leverage (around 5% of the NAV).
Liquidity risk: The vast majority of ‘other AIFs’
are open-ended, representing around 80% of the
NAV of this segment. Infrastructure funds have
instead mostly a closed structure with only 8% of
their NAV redeemable by investors, mostly on
over a monthly horizon. Overall, open-ended
other AIFs offer mainly daily liquidity (75%) or
weekly and monthly liquidity (24%; ASR-AIF.87).
German ‘Spezialfonds’ are also classified in this category.
For a detail discussion see ESMA (2020b).
0% 50% 100%
Other
Infrastructure
Fixed income
Equity
Commodity
Retail investors Professional investors
Note: Clients of AIFs classified as Other AIFs managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national
jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD databse, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
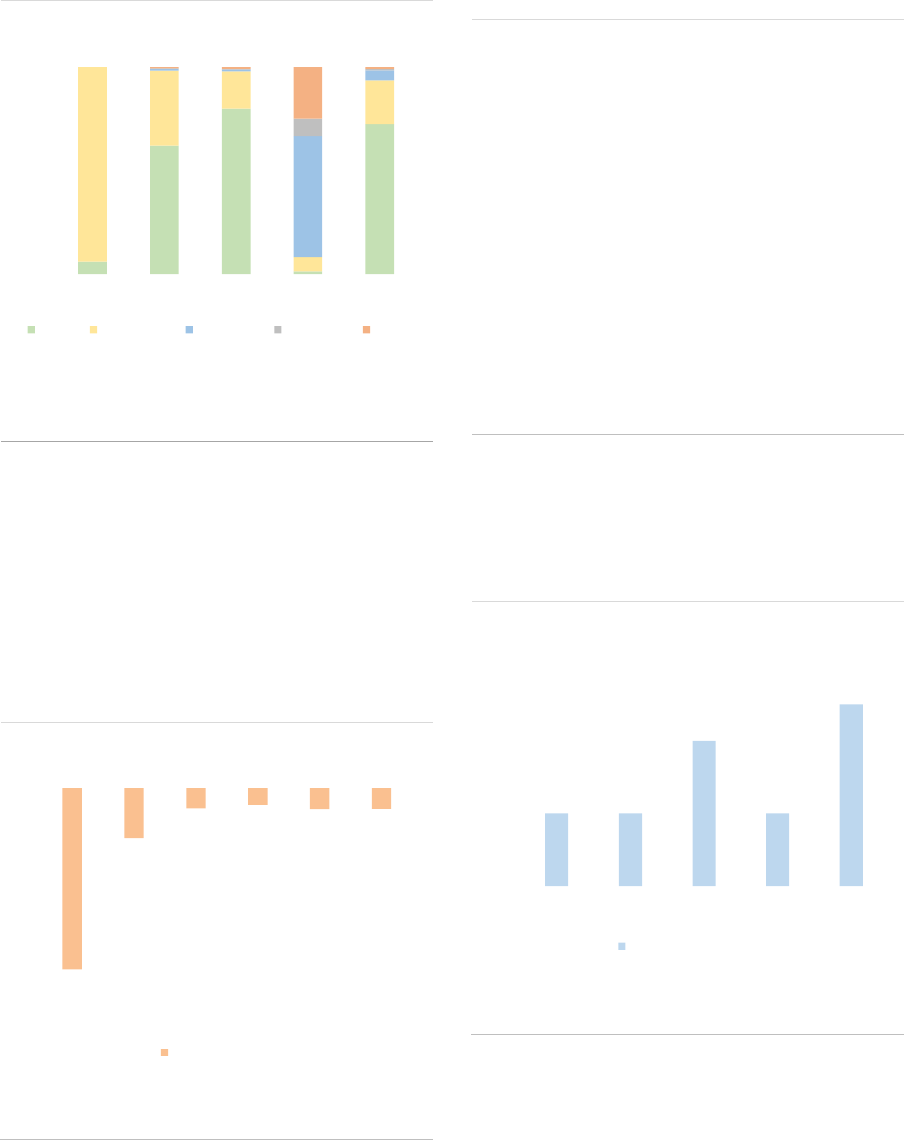
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2021 38
ASR-AIF.87
Redemption frequency
Mainly daily to monthly frequency
At the aggregate level, the liquidity profile of
‘other AIFs’ indicates that within one week,
investors can redeem up to 63% of the NAV,
whereas 55% of the assets can be liquidated
within this time frame. The liquidity shortage of
those funds with a liquidity deficit is 17% of the
NAV in the very short term (within 1 day) and it
reduces to 5% within one week (ASR-
AIF.88ASR-AIF.88).
ASR-AIF.88
Liquidity profile
Some liquidity mismatch
The majority of AIFs in the broad ‘other’ category
that offer to investors the possibility to redeem on
a daily basis do not require any notice period
(40% of the NAV). A minimum notice period
ranging from 1 to 7 days is requested only by
Other AIFs representing one-third of the total
NAV. Overall, around 43% by NAV of ‘other-AIFs’
do not require any redemption notice to investors.
(ASR-AIF.89ASR-AIF.89).
ASR-AIF.89
Redemption frequency and notice period
Notice period often not imposed
Redemption
Frequency
Notice Period
None
1D
1W
1M
>1M
Total
Daily
39.5
22.2
10.6
0.6
0.2
72.9
Weekly to
Monthly
3.7
3.2
1.6
13.9
1.3
23.8
Quarterly
0.3
0.5
0.2
0.3
0.9
2.1
Longer than
quarterly
0.1
0.0
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
Other
0.1
0.2
0.1
0.2
0.2
0.8
Total
43.7
26.2
12.5
15
2.7
100
Note: AIFs classified as ‘other’ by redemption frequency and notice
period given to investors, in % of NAV, end of 2020. 1D= 1 day, 1W
= 2 to 7 days, 1M = 8 to 30 days, >1M = more than 30 days’ notice
period. Data for the EEA30.
Source: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities,
ESMA.
Levels of unencumbered cash (ASR-AIF.90)
are higher for ‘other-Other’ and fixed income
AIFs, accounting respectively for 5% and 4% of
the NAV. This level of cash is in line with their
reliance on IRDs and FX derivatives.
ASR-AIF.90
Unencumbered cash
Sizeable buffers for commodity funds
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Commodity Equity Fixed
income
Infra-
structure
Other
funds
Daily Weekly
to monthly
Quarterly Quarterly
to yearly
Other
Note: Investor redemption frequencies allowed by open-end AIFs classified as
Othe rmanaged and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of
NAV. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised EU AIFMs marketed,
respectively, w/ and w/o passport. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
-20
-15
-10
-5
0
1 day or
less
2-7
d
8-30
d
31-90
d
91-180
d
181-365
d
Liquidity shortage
Note: Liquidity shortgage of AIFs classified as Other, % of NAV, end of 2020.
Liquidity shortage is defined as the sum of liquidity deficits at the level of the
funds, as non compensated by liquidity surplus. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
2%
4%
6%
Commodity Equity Fixed
income
Infra-
structure
Other
funds
Unencumbered cash
Note: Unencumbered cash held by AIFs classified as Other, end of 2020, in %
of NAV. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed,
respectively, w/ and w/o passport. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
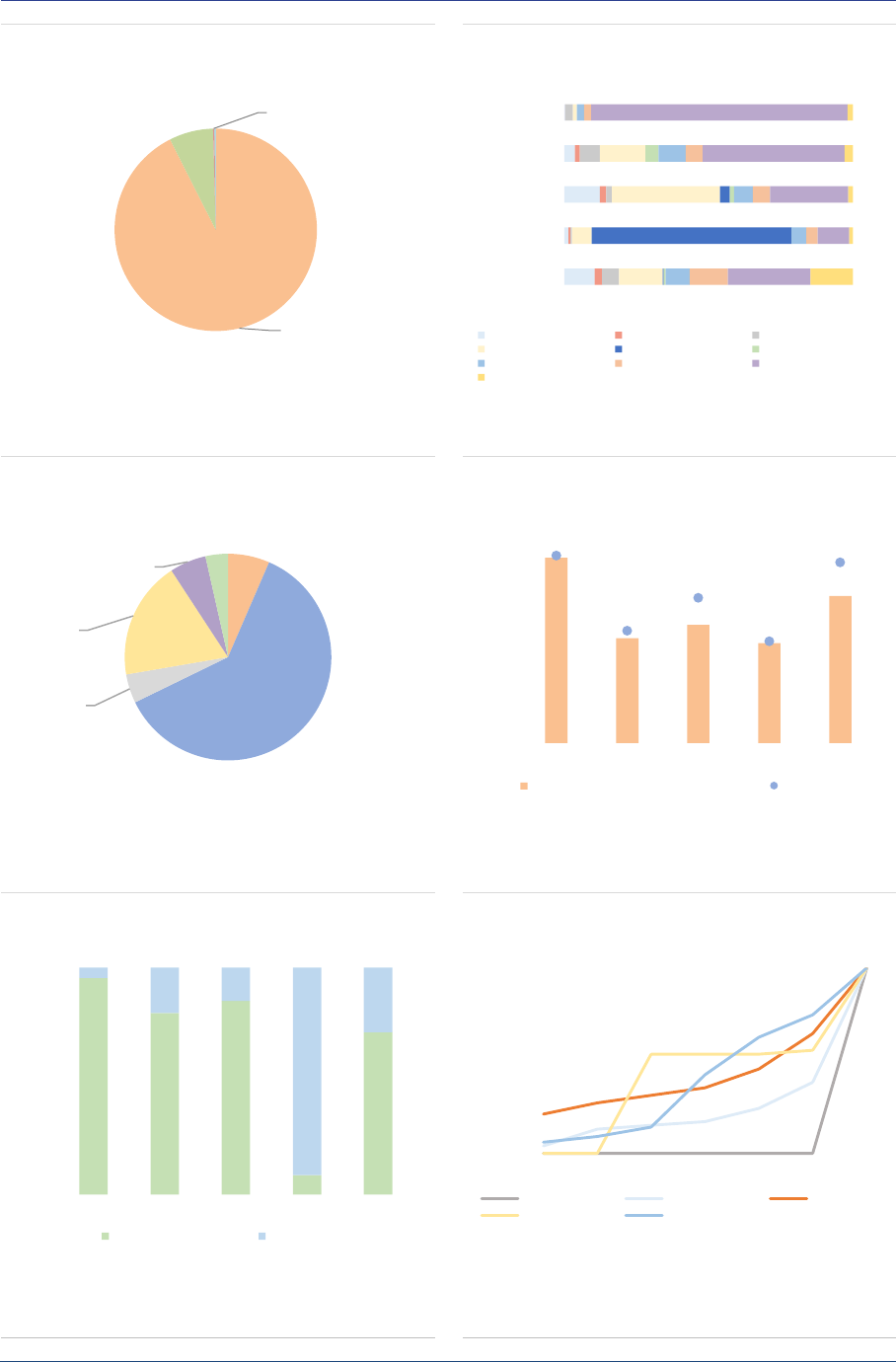
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 39
ASR-AIF.91
ASR-AIF.92
EU passport
‘Other AIFs’ investor types
Most ‘other AIFs’ can be passported
Mainly pension funds
ASR-AIF.93
ASR-AIF.94
Regional investment focus
Leverage
Mostly EEA
Limited use of leverage
ASR-AIF.95
ASR-AIF.96
Redemption rights
Financial leverage
Mostly open-ended
High short-term funding for bond funds
EU passport
93%
EU w/o
passport
7%
Non-EU w/o
passport
<1%
Note: NAV of AIFs classified as Other by manager's access to AIFMD
passport, end of 2020, in %. Authorised EEA30 AIFMs with access to AIFMD
passport or marketing non-EEA30 AIFs w/o passport, sub-threshold
managers registered only in national juridisdictions w/o passporting rights.
Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100%
Other
Infrastructure
Fixed income
Equity
Commodity
Banks General gov. Households
Insurances Non-profit None
Oth. CIUs Oth. fin. institutions Pension funds
Unknown
Note: Ownership of units in AIFs classified as Other AIFs managed and/or
marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. CIUs=Collective
investment undertakings. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
Asia
6%
EEA
61%
Other
Europe
5%
North
America
18%
Supra National
6%
Rest
4%
Note: Regional investment focus of EU AIFs classified as Other, managed
and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered
only in national jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Geo-focus determined
according to the domicile of investments and the supranational category
including investments without a predominant geo-focus. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
40%
80%
120%
160%
200%
Commodity Equity Fixed
income
Infra-
structure
Other
funds
Median adjusted gross leverage AuM/NAV
Note: Adjusted gross leverage of funds of funds managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Adjusted gross leverage
computed as total exposure less IRDs with respect to NAV. FoF= Funds of
funds, PE=Private equity fund, HF=Hedge fund. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National competent authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Commodity Equity Fixed
income
Infra-
structure
Other
funds
Open-end Closed-end
Note: Redemption rights provided in the ordinary course to investors in AIFs
classified as Other managed and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of
2020, in % of NAV. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
100%
22%
100%
1%
54%
56%
100%
7%
100%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day 2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180 d 181-365
d
> 365 d
Commodity Equity Fixed income
Infrastructure Other
Note: Liquidity financing of AIFs classified as Other managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs, end of 2020. Aggregate amount of borrowing and cash financing
divided depending on longest period for which creditors are contractually committed
to provide such financing, Borrowing and cash financing include drawn and undrawn,
committed and uncommitted lines of credit as well as any term financing. Data for the
EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
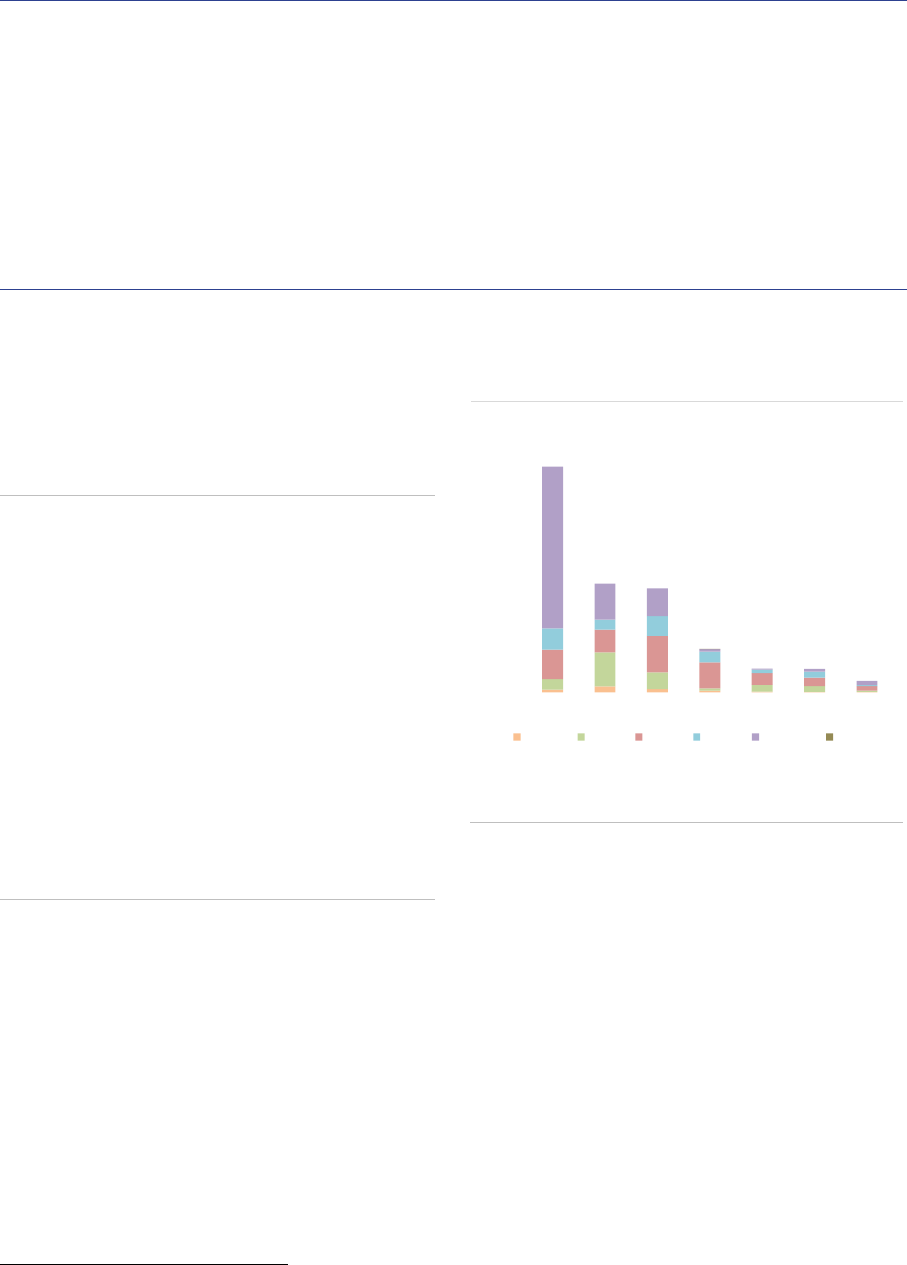
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 40
Non-EU AIFs (NPPR)
Summary
EU Member States can allow non-EU asset managers to market alternative funds at national level under
the National Private Placement Regime (NPPR), even though such funds cannot be passported to other
EU Members States. The market for such non-EU funds is comparatively large: The NAV of non-EU
AIFs marketed under NPPR rules amounts to EUR 1.3tn, i.e. more than one-fifth of the AIF market.
NPPR fund marketing is concentrated in a small number of Member States, and more than 99% of
investors are professional investors. Hedge funds marketed under the NPPR are predominantly
domiciled in the Cayman Islands, while ‘other AIFs’ marketed under the NPPR are predominantly US-
based exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Overall, risk profiles for NPPR funds are comparable to EEA30
AIFs. However, the geographical investment focus is different as NPPR funds invest predominantly in
non-EU areas.
Market size and structure
AIF size: At a minimum estimated EUR 1.3tn
NAV, the NPPR market is equivalent to more than
one-fifth of the EEA30 AIF market.
ASR-AIF.97
ART. 42 AIFMD
Non-EU AIFMs under National Private Placement
The NPPR is a mechanism to allow non-EU managers to
market investment funds that are not allowed to be marketed
under the AIFMD domestic marketing or passporting regimes.
This principally relates to the marketing of non-EU AIFs by
non-EU AIFMs. NPPRs are not a form of cross-border
distributions and NPPRs’ rules vary significantly across
jurisdictions. Non-EU AIFMs are subject to reporting under the
AIFMD in each jurisdiction in which they are authorised to
market their products. Because under the NPPR rules the
same AIFs can be marketed under different jurisdictions, the
full assessment of the non-EU AIF market in terms of size,
composition and risks for financial stability depends on the
possibility of uniquely identifying AIFs. International identifiers
(i.e. Legal Entity Identifiers (LEIs) or International Securities
Identification Numbers (ISINs)) are used to analyse this
segment of the AIF industry to avoid overestimating market
shares for funds reporting in different countries.
AIF domicile and EEA30 jurisdictions:
According to data reported by National
Competent Authorities, non-EU AIFs are
marketed in 9 EU Member States. A total of 508
non-EU AIFs marketed under the NPPR can be
uniquely identified.
12
The total regulatory AuM of
these uniquely identified AIFs reach EUR 3tn for
the NPPR market. The difference between the
regulatory AuM and the NAV is due to the large
exposure of offshore HFs to IRDs. In terms of
cross-country distribution, the AIF industry is
concentrated in 6 countries, with FI as the largest
hub of non-EU AIFs (ASR-AIF.98ASR-AIF.98).
12
Around 1,500 AIFs marketed under NPPR in different
EU jurisdictions cannot be uniquely identified owing to
the lack of international identifiers.
As in 2019, FI, LU and IE remain the top three
countries in terms of access from non-EU AIFs
13
.
ASR-AIF.98
NPPR market by country
Non-EU AIF markets across jurisdictions
In terms of NAV, the NPPR segment is dominated
by US ETFs (mostly equity) that are classified as
‘other AIFs’ (ASR-AIF.99ASR-AIF.99).
The AIF market regulated by Article 42 of the
AIFMD appears extremely concentrated: 9% of
NPPR AIFs have a NAV higher than EUR 5bn —
these funds represent 72% of the NPPR NAV.
13
In 2019, the UK was the largest EU country in terms of
NPPR market, with close to EUR 2trn (ESMA, 2021).
0
400
800
1,200
FI IE LU DE BE NO Other
FoF HF PE RE Other None
Note: NAV by authorising EEA30 country of AIFs marketed by non-EEA30
AIFMs w/o passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2020, in EUR bn.
AIFs identified via international standard identifiers (LEIs, ISIN, Cusip).
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
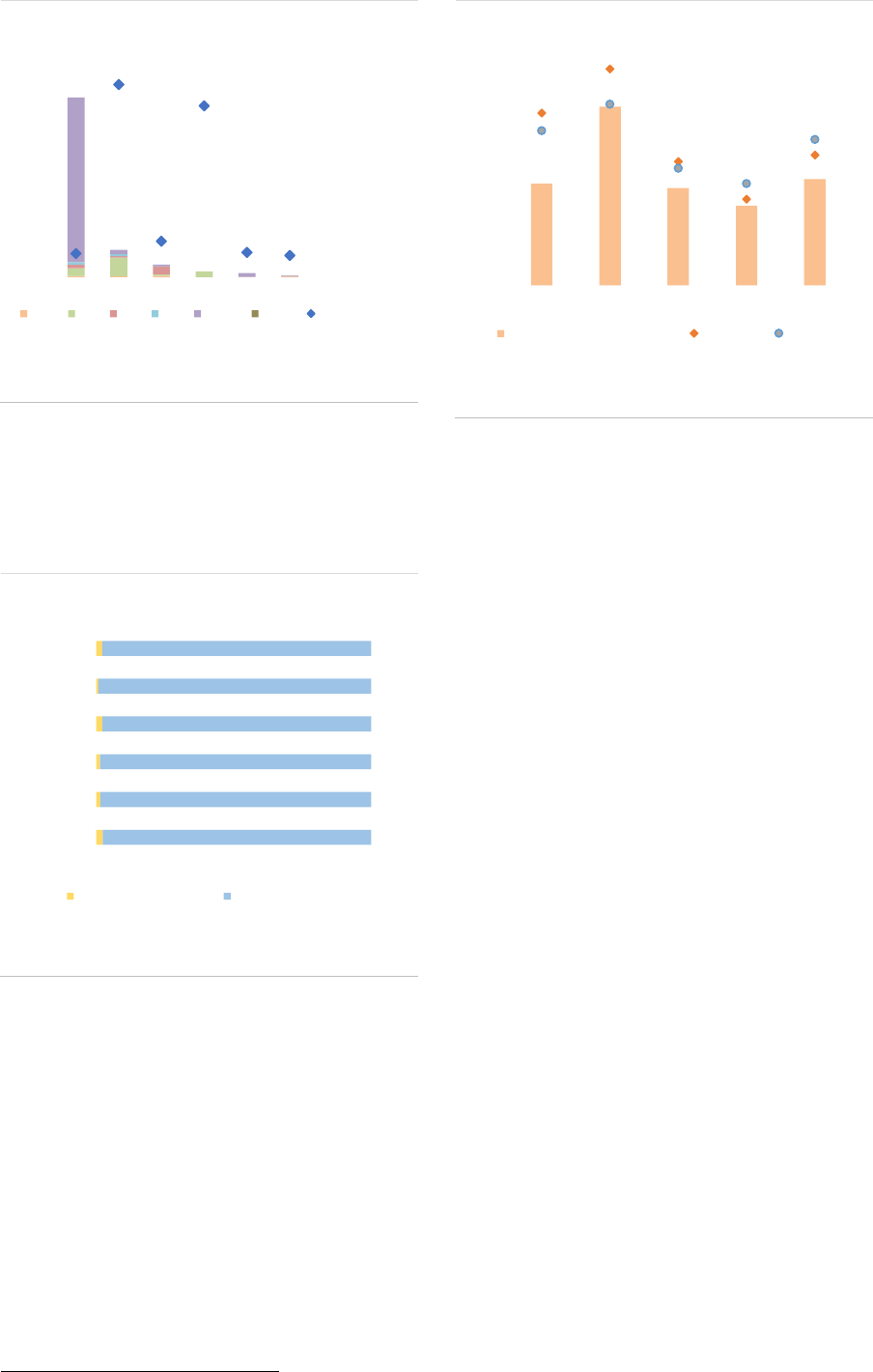
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2021 41
ASR-AIF.99
Domicile of AIFs marketed under NPPR (Article 42)
Large presence of US AIFs and off-shore HFs
Non-EU AIF investors: All the AIF types
marketed under the NPPR by non-EU AIFMs see
a retail participation of less than 3% (ASR-
AIF.100ASR-AIF.100). Overall non-EU AIFs sold
by non-EU AIFMs are owned almost entirely by
professional investors (99%).
ASR-AIF.100
AIF investors
Predominantly professional investors
On average, the top-5 holders of US ETFs
account for more than 75% of the NAV (ASR-
AIF.101). Other AIF types display a less
concentrated ownership (above 40% NAV). A
large proportion of NPPR investors cannot be
identified (25% of the NAV). Banks, pension
funds and insurance companies have only a
limited exposure, amounting to 6% of NAV (ASR-
AIF.107Error! Reference source not found.).
14
This includes 104 HFs uniquely identified.
ASR-AIF.101
Investor concentration
Less concentrated than EU AIFs
Geographical investment focus: non-EU funds
appear not to be focused on EU assets. Their
investments are domiciled mostly in North
America (65%) and Asia (15%) (ASR-AIF.109).
This result is driven by the high number of US
domiciled ETFs identified through their ISINs.
Leverage and liquidity risks
Gross exposures: The asset exposure of non-
EU AIFs is similar to that of EU-domiciled funds
with RE funds exposed to physical assets, FoFs
investing in collective investment schemes and
hedge funds heavily exposed to interest rate
derivatives (ASR-AIF.110).
Leverage: With the exception of HFs, non-EU
funds make limited use of leverage. Regulatory
AuM to NAV is 161% on aggregate when
excluding HFs, as the exposures to derivatives
are limited. When the effect of IRDs is netted,
HFs leverage declines from 870% to 560% (ASR-
AIF.102). The ratio of regulatory AuM to NAV
reaches 1,090% for HFs domiciled offshore
(Cayman Islands, Virgin Islands, Bahamas,
Bermuda)
14
.
0%
200%
400%
600%
800%
1000%
0
200
400
600
800
1,000
1,200
US KY GG VI CH UK
FoF HF PE RE Other None Leverage (rhs)
Note: NAV by domicile of AIFs marketed by non-EEA30 AIFMs w/o
passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2020, in EUR bn. AIFs identified
via international standard identifiers (LEIs, ISIN, Cusip). in EUR bn.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0% 50% 100%
FoF
Hedge fund
Private equity
Real estate
Other AIF
Total NPPR
Retail investors Professional investors
Note: Clients of AIFs marketed by non-EEA30 AIFMs w/o passporting rights
(art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2209, in % of NAV. AIFs identified via international
standard identifiers (LEIs, ISIN, Cusip). FoF=Fund of Funds
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
FoF Hedge
fund
Private
equity
Real estate Other AIF
Top 5 beneficial investors Median Average
Note: Investor concentration of AIFs marketed by non-EU AIFMs w/o
passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2020, in % of NAV. Investor
concentration computed as share of AIF equity beneficially owned by the 5
largest investors. FoF=Fund of funds.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
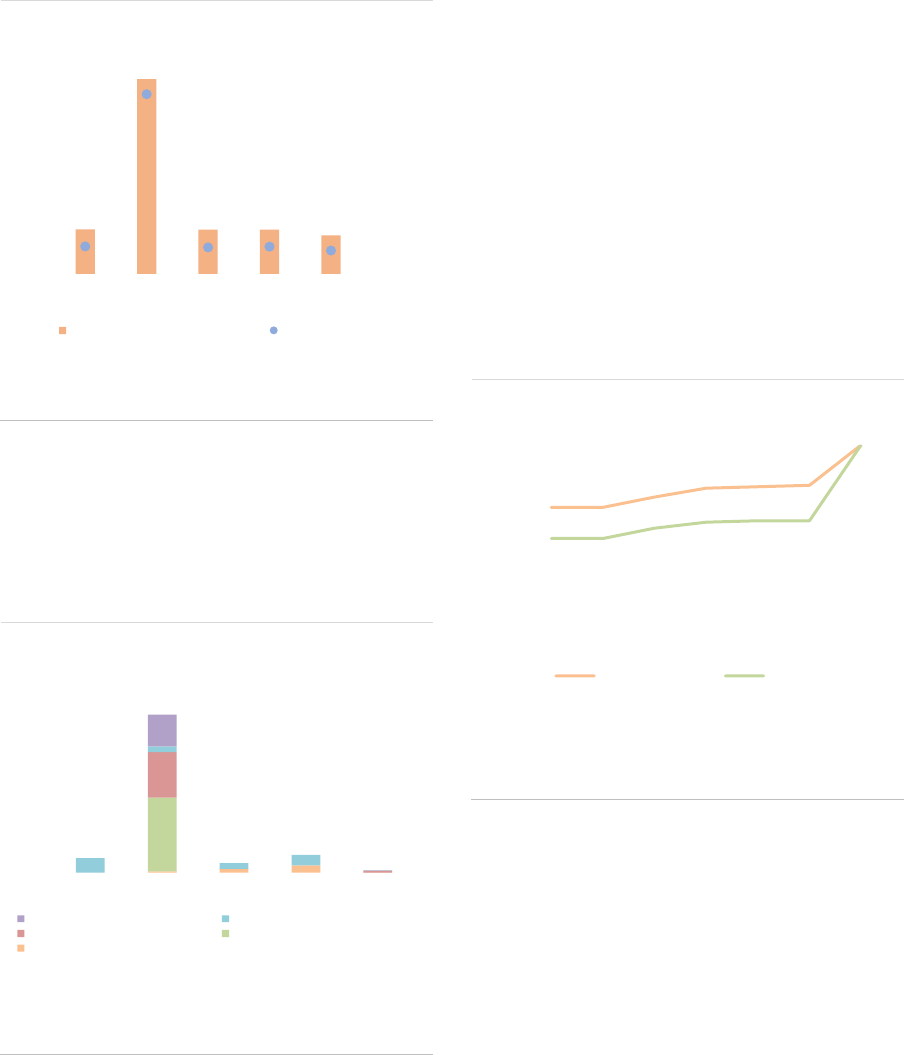
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2021 42
ASR-AIF.102
Leverage
Limited except for hedge funds
Non-EU HFs borrowings stand at 137% of their
NAV (ASR-AIF.103). Whereas EU HFs increase
their financial leverage by engaging in repo
trades, non-EU HFs borrow comparatively more
from their prime broker (64% of NAV). Other non-
EU funds do not use financial leverage
extensively.
ASR-AIF.103
Financial leverage
Sizeable secured borrowing by HFs
Liquidity risk: In absolute terms, 57% of non-EU
AIFs uniquely identified are open-ended. Around
85% of NAV of AIFs regulated by art. 42 AIFMD
is held by open-ended funds, with variation
across fund types.
The vast majority offer daily or weekly liquidity to
their investors. In the case of other AIFs with non-
EU AIFs, 96% of their NAV is redeemable on a
daily basis (ASR-AIF.108). At the aggregate
level, the liquidity profile of non-EU AIFs points to
a liquidity risk for all time horizons. within a day,
investors can redeem up to 58% of the NAV,
whereas only 37% of the assets can be liquidated
within this time frame. The liquidity gap is
increasing to 24% for the long end (ASR-
AIF.104ASR-AIF.104).
ASR-AIF.104
Liquidity profile
Moderate liquidity mismatch
0%
200%
400%
600%
800%
1000%
0%
200%
400%
600%
FoF Hedge
fund
Private
equity
Real
estate
Other AIF
Adjusted gross leverage AuM/NAV (rhs)
Note: Adjusted gross leverage of AIFs AIFs marketed by non-EEA30 AIFMs
w/o passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2020, in % of NAV. Adjusted
gross leverage does not include IRDs. FoF= Fund of funds,
Sources: AIFMD database, National competent authorities, ESMA.
0%
40%
80%
120%
160%
FoF Hedge
fund
Private
equity
Real estate Other AIF
Short position borrowing sec. Secured via other
Reverse repo Secured via PB
Unsecured borrowing
Note: Cash and securities borrowed, end of 2020, in % of NAV. marketed by
non-EEA30 AIFMs w/o passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD) in EUR bn. AIFs
identified via international standard identifiers (LEIs, ISIN, Cusip
FoF=Funds of Funds,
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
58%
65%
71%
72%
73%
100%
37%
44%
48%
49%
49%
-25%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 d or
less
2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180 d 181-365
d
> 365 d
Investor Portfolio
Note: Portfolio and investors liquidity profiles of AIFs marketed by non-EEA30
AIFMs w/o passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2020. AIFs identified
via international standard identifiers (LEIs, ISIN, Cusip). Portfolio liquidity
defined as the percentage of the funds’ assets capable of being liquidated
within each specified period, investor liquidity defined as the shortest period
for which investors can redeem. d= Days.
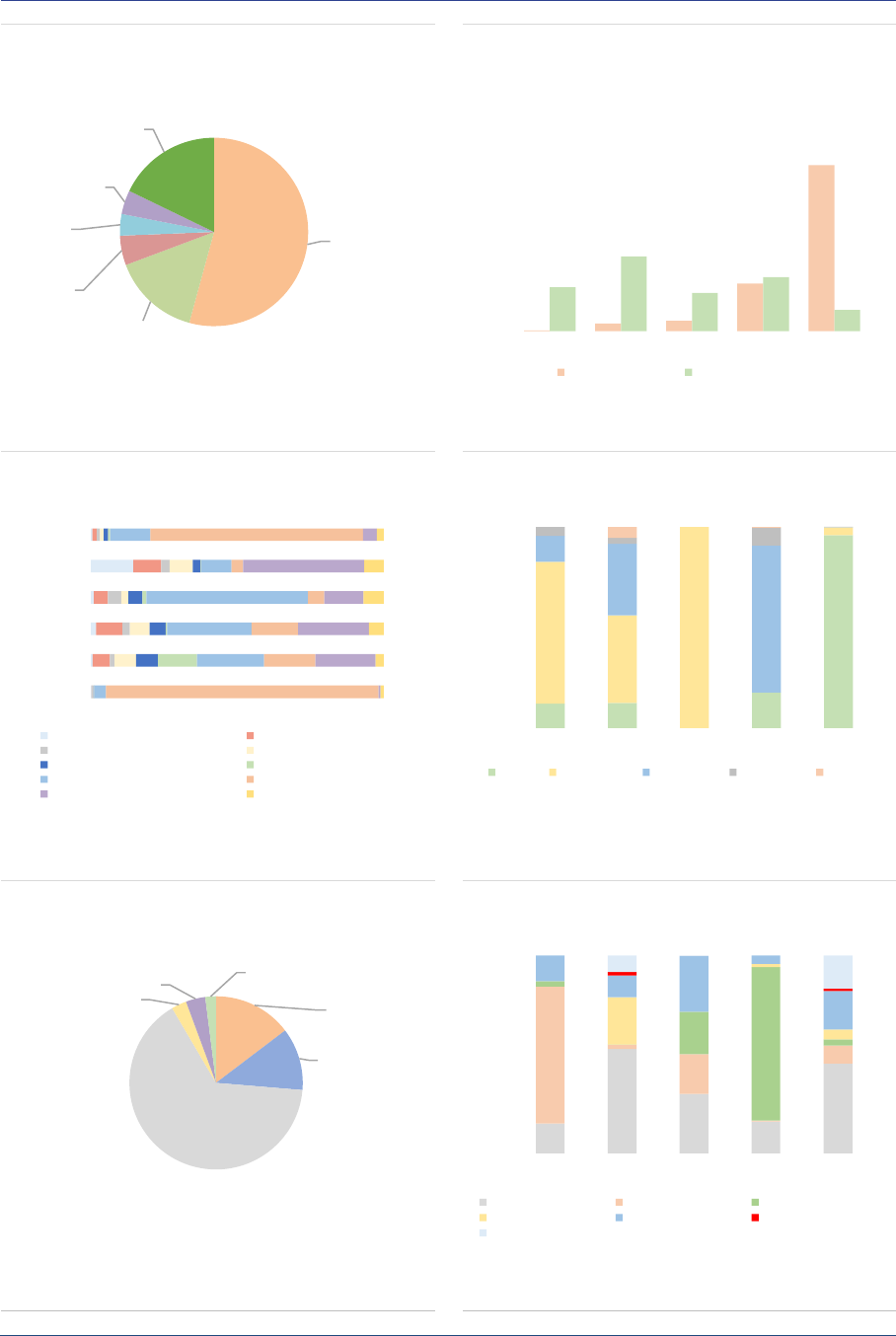
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 43
ASR-AIF.105
ASR-AIF.106
NPPR strategies
Size distribution
US ETFs dominant in terms of NAV
Large funds dominating the segment
ASR-AIF.107
ASR-AIF.108
NPPR investor types
Redemption frequency
Large proportion of ownership unidentified
Mainly daily to monthly frequency
ASR-AIF.109
ASR-AIF.110
Regional investment focus
Exposures
Mostly North America
Use of derivatives limited to HFs
Equity
54%
Fixed
income
15%
Other HF
5%
Other PE
4%
Other fund
4%
Remaining
strategies
18%
Note: Investment strategies of AIFs marketed by non-EEA30 AIFMs w/o
passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2020, in % of NAV. AIFs
identified via international standard identifiers (LEIs, ISIN, Cusip).
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
<100mn 100-
500mn
500mn-
1bn
1-5bn >5bn
NAV Number of AIFs
Note: Share of AIFs marketed by non-EEA30 AIFMs w/o passporting rights
(art. 42 of AIFMD) by size, end of 2020. In %. AIFs identified via international
standard identifiers (LEI, ISIN, Cusip).
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100%
Other AIFs
RE
PE
HF
FoF
Total 2020
Banks General gov.
Households Insurances
Non-profit None
Oth. CIU Oth. fin. institutions
Pension funds Unknown
Note: Ownership of units in AIFs marketed by non-EEA30 AIFMs w/o
passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2020, in % of NAV. AIFs
identified via international standard identifiers (LEIs, ISIN, Cusip). FoF=Fund
of Funds;
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
FoF Hedge fund Private
equity
Real estate Other AIF
Daily Weekly
to monthly
Quarterly Quarterly
to yearly
Other
Note: Investor redemption frequencies allowed by open-end AIFs marketed by
non-EEA30 AIFMs w/o passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2020, in
% of NAV. AIFs identified via international standard identifiers (LEIs, ISIN,
Cusip).
Asia
15%
EEA
12%
North
America
65%
Other
Europe
3%
Rest
3%
Supra National
2%
Note: Regional investment focus of AIFs marketed by non-EEA30 AIFMs w/o
passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2020, in EUR bn. AIFs identified
via international standard identifiers (LEIs, ISIN, Cusip). in EUR bn. Geo-focus
determined according to the domicile of investments, supra national category
including investments without predominant geo-focus.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
FoF Hedge fund Private
equity
Real estate Other AIF
Securities CIUs Physical assets
IRDs FX CDS
Other derivatives
Note: Share of gross exposures by AIF type, end of 2020, in % of total. AIFs
managed and/or marketed by authorised EEA30 AIFMs. FoF=Fund of funds,
None=No predominant type.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.

ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 44
References
Central Bank of Ireland, (2021), “Macroprudential
measures for the property fund sector”,
Consultation Paper 145, November.
European Central Bank, (2017), “Manual on
investment fund statistics”, December.
European Securities and Markets Authority,
(2020), “Annual Statistical Report on EU
Alternative Investment Funds”, March.
European Securities and Markets Authority,
(2021), “Annual Statistical Report on EU
Alternative Investment Funds”, April.
European Systemic Risk Board, (2021), “EU
Non-bank Financial Intermediation Risk Monitor
2021”, July.
Invest Europe, (2021), “Investing in Europe:
Private Equity Activity 2020”, May.
Securities and Exchange Commission, (2021),
“Reporting Form for Investment Advisers to
Private Funds and Certain Commodity Pool
Operators and Commodity Trading Advisors”.
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 45
Statistics
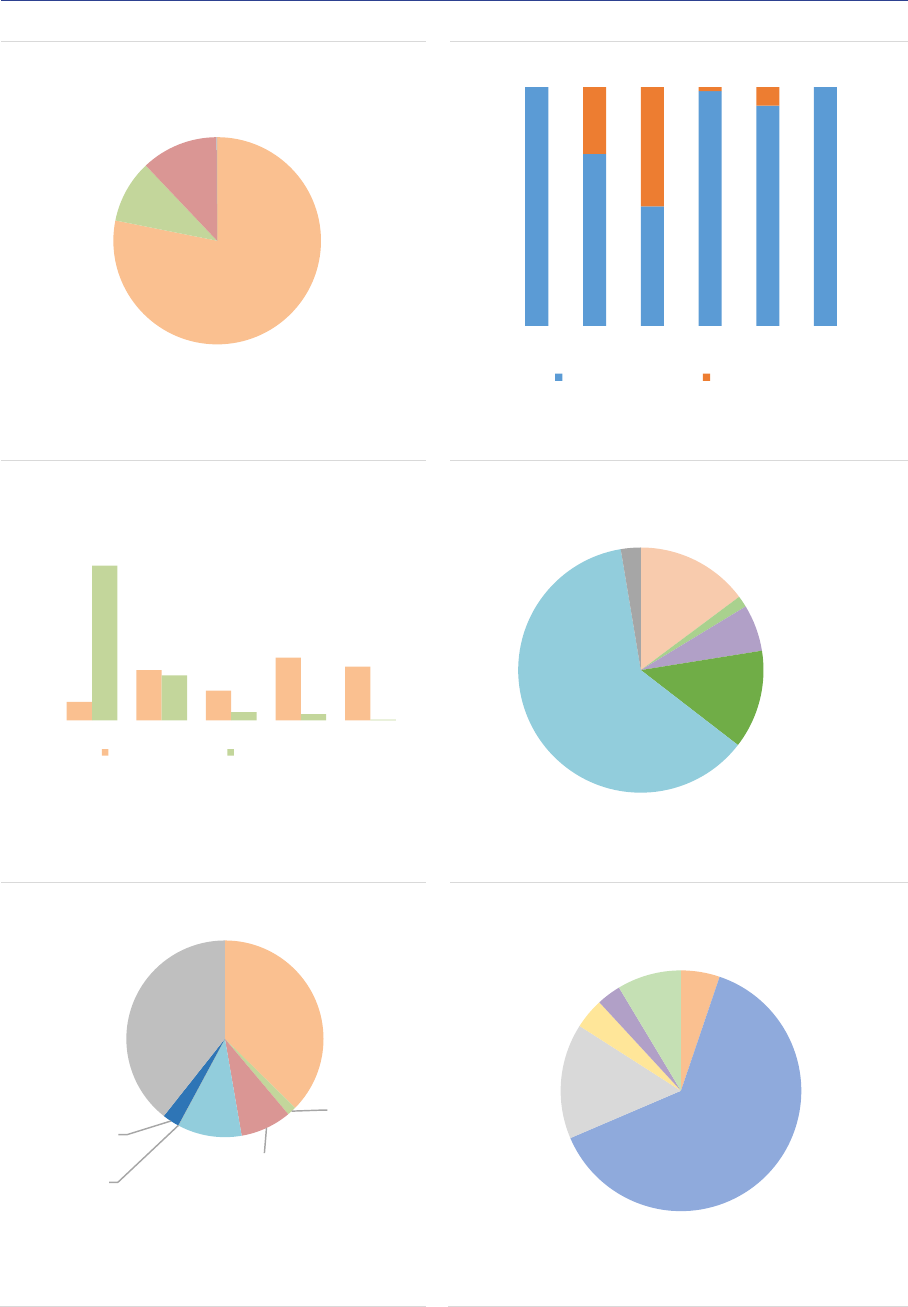
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 46
EU AIF market
AIF characteristics
ASR-AIF-S.1
ASR-AIF-S.2
AIFMD passport
EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs
ASR-AIF-S.3
ASR-AIF-S.4
AIF distribution by size
AIF types
ASR-AIF-S.5
ASR-AIF-S.6
AIF strategies
Investment regions
EU
passport
78%
EU w/o passport
10%
Non-EU w/o passport
12%
Non-EU not marketed
in EU
<1%
Note: NAV of AIFs by manager's access to AIFMD passport, end of 2020, in
%.
Authorised EEA30 AIFMs with access to AIFMD passport or marketing non-
EEA30 AIFs w/o passport, sub-threshold managers registered only in national
juridisdictions w/o passporting rights. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
FoF Hedge
fund
Private
equity
Real
estate
Other None
EEA30 Non-EEA30
Note: Share of EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national
jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % on NAV. Non-EEA30 AIFs marketed w/o
passport. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
<100mn 100-500mn 500mn-1bn 1-5bn >5bn
NAV Number of AIFs
Note: Share of AIFs by size, end of 2020, in %. AIFs managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national
jurisdictions. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
FoF
15%
Hedge fund
1%
Private equity
6%
Real
estate
13%
Other
62%
None
3%
Note: NAV by type of AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs
and sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions, end of
2020, in %. FoF=Fund of funds, None=No predominant type. Data for the
EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
Commercial
RE 37%
Equity
2%
Fixed
income
8%
Other FoF
11%
Other PE
<1%
Other RE
<1%
Other-other
3%
All
remaining
strategies
39%
Note: Investment strategy of AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised
AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions,
end of 2020, in % of NAV. FoF=Fund of funds, PE=Private equity funds,
RE=Real estate. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
Asia
5%
EEA
63%
North
America
16%
Other
Europe
4%
Rest
3%
Supra National
9%
Note: Regional investment focus of AIFs managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national
jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Geo-focus determined according to
the domicile of investments, supra national category including investments
without predominant geo-focus. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
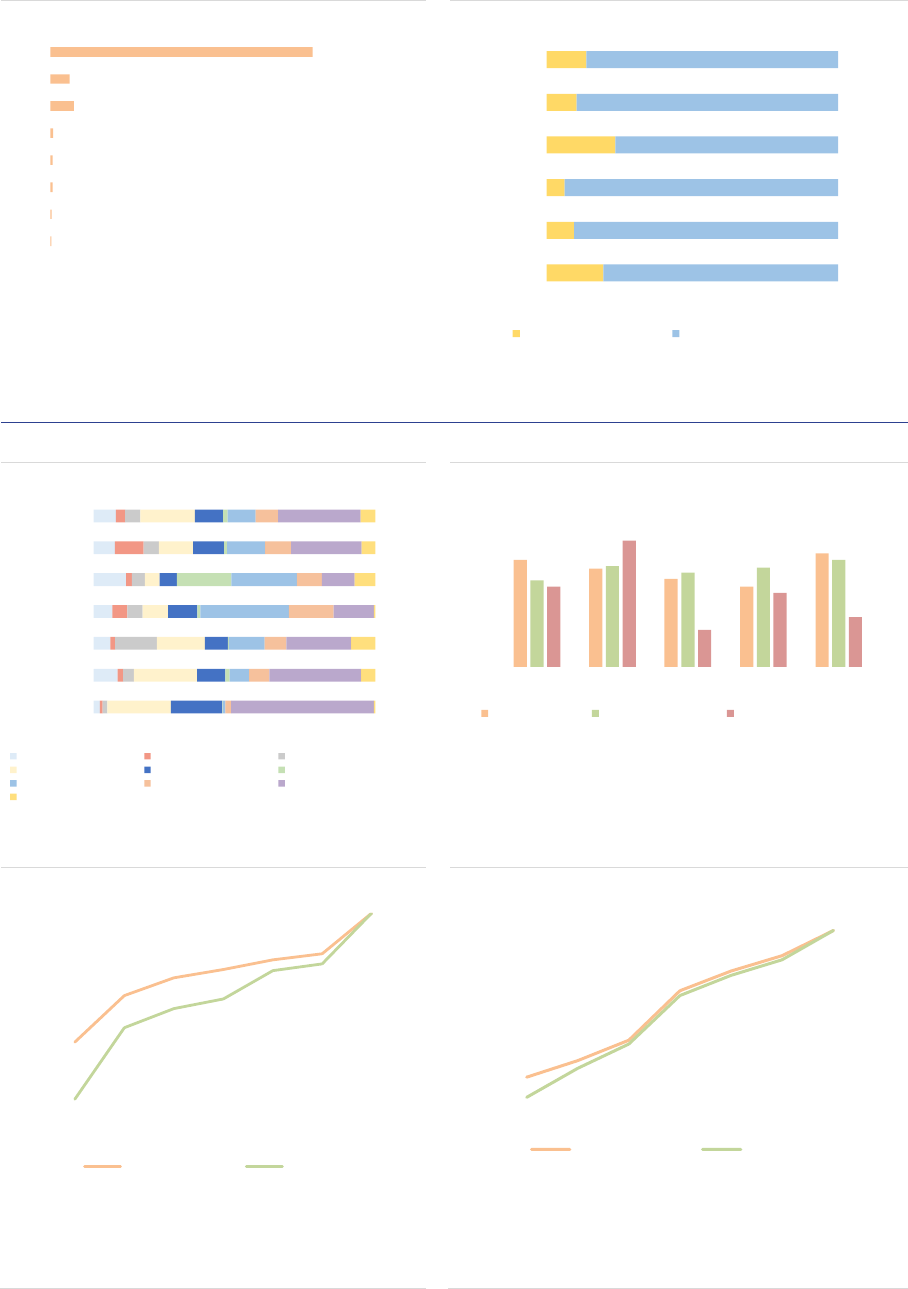
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 47
ASR-AIF-S.7
ASR-AIF-S.8
Base currencies
Clients
Liquidity and counterparty risk profile
ASR-AIF-S.9
ASR-AIF-S.10
Ownership of AIF
Top 5 beneficial owners
ASR-AIF-S.11
ASR-AIF-S.12
FoFs: Liquidity profile
HFs: Liquidity profile
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100%
CZK
NOK
PLN
JPY
SEK
USD
GBP
EUR
Note: Base currency managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs and
sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions, end of 2020,
in % of NAV. Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities,
ESMA. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100%
FoF
Hedge fund
Private equity
Real estate
Other AIF
Total EU
Retail investors Professional investors
Note: Clients of AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs and
sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions, end of 2020,
in % of NAV. FoF=Fund of funds. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100%
None
Other AIF
Real estate
Private equity
Hedge fund
FoF
Total EU
Banks General gov. Households
Insurances Non-profit None
Oth. CIU Oth. fin. institutions Pension funds
Unknown
Note: Ownership of units in AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised EU
AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. FoF=Fund of funds; None=No predominant type.
Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
125%
FoF Hedge fund Private
equity
Real estate Other
AIF
EU passport EU w/o passport Non-EU w/o passport
Note: Investor concentration of AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised EU
AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Investor concentration computed as share of AIF
equity beneficially owned by the 5 largest investors. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
40%
62%
70%
74%
78%
81%
100%
14%
56%
60%
73%
76%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day or
less
2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180 d 181-365
d
> 365 d
Investor Portfolio
Note: Portfolio and investor liquidity profiles of funds of funds managed and/or
marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020. Portfolio liquidity defined as the
percentage of the funds’ assets capable of being liquidated within each specified
period, investor liquidity defined as the shortest period for which investors can
redeem. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed,
respectively, w/ and w/o passport. d=Days. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
25%
37%
65%
77%
85%
100%
4%
20%
34%
62%
74%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day or
less
2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180
d
181-365
d
> 365 d
Investor Portfolio
Note: Portfolio and investor liquidity profiles of hedge funds managed and/or
marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020. Portfolio liquidity defined as the
percentage of the funds’ assets capable of being liquidated within each
specified period, investor liquidity defined as the shortest period for which
investors can redeem. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs
marketed, respectively, w/ and w/o passport. d=Days. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
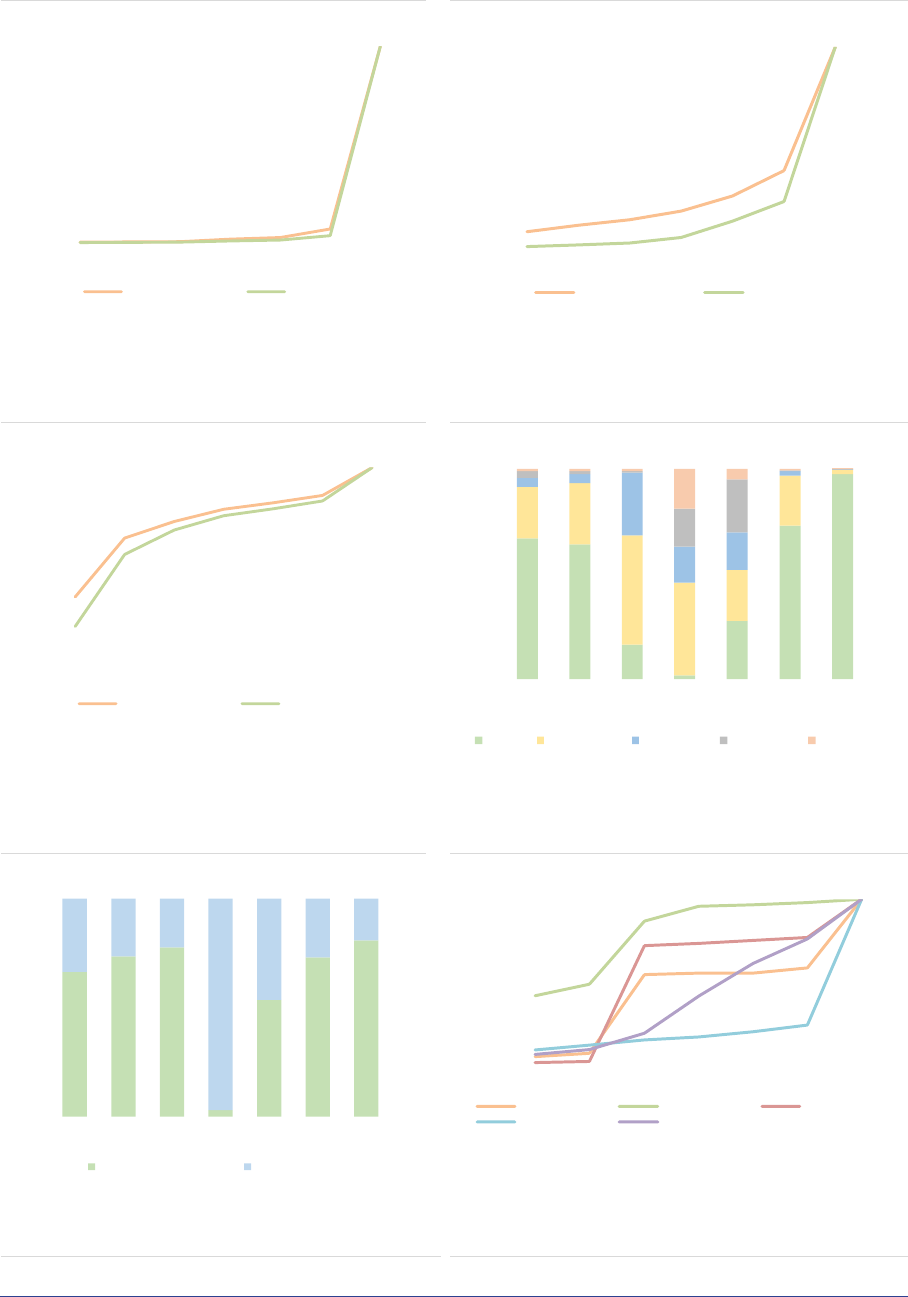
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 48
ASR-AIF-S.13
ASR-AIF-S.14
PE funds: Liquidity profile
RE funds: Liquidity profile
ASR-AIF-S.15
ASR-AIF-S.16
Funds classified as ‘Other’: Liquidity profile
Liquidity financing
ASR-AIF-S.17
ASR-AIF-S.18
Redemption rights to investors
Liquidity financing
0%
1%
1%
2%
7%
100%
2%
4%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day or
less
2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180 d 181-365
d
> 365 d
Investor Portfolio
Note: Portfolio and investor liquidity profiles of private equity funds managed
and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020. Portfolio liquidity defined
as the percentage of the funds’ assets capable of being liquidated within each
specified period, investor liquidity defined as the shortest period for which
investors can redeem. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs
marketed, respectively, w/ and w/o passport. d=Days. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
8%
11%
14%
18%
26%
38%
100%
1%
5%
13%
23%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day or
less
2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180 d 181-365
d
> 365 d
Investor Portfolio
Note: Portfolio and investor liquidity profiles of real estate funds managed
and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020. Portfolio liquidity defined
as the percentage of the funds’ assets capable of being liquidated within each
specified period, investor liquidity defined as the shortest period for which
investors can redeem. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs
marketed, respectively, w/ and w/o passport. d=Days. Data for the EEA30..
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
33%
63%
72%
78%
82%
100%
18%
55%
68%
75%
79%
83%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day or
less
2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180 d 181-365
d
> 365 d
Investor Portfolio
Note: Portfolio and investor liquidity profiles of AIFs classified as Other
managed and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020. Portfolio
liquidity defined as the percentage of the funds’ assets capable of being
liquidated within each specified period, investor liquidity defined as the
shortest period for which investors can redeem. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs
by authorised AIFMs marketed, respectively, w/ and w/o passport. d=Days.
Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Total
EU
FoF Hedge
fund
Private
equity
Real
estate
Other
AIF
None
Daily Weekly
to monthly
Quarterly Quarterly
to yearly
Other
Note: Investor redemption frequencies allowed by open-end AIFs managed
and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. EEA30 and
non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed, respectively, w/ and w/o
passport. FoF=Fund of Funds, None=No Predominant Type. Data for the
EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Total
EU
FoF Hedge
fund
Private
equity
Real
estate
Other
AIF
None
Open-end Closed-end
Note: Redemption rights provided in the ordinary course to investors in AIFs
managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of
NAV. FoF=Fund of funds, None=No predominant type. Data for 28 EEA
countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day 2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180 d181-365
d
> 365 d
FoF Hedge fund Private equity
Real estate Other AIF
Note: Liquidity financing of AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs,
end of 2020. Aggregate amount of borrowing and cash financing divided
depending on longest period for which creditors are contractually committed to
provide such financing, Borrowing and cash financing include drawn and
undrawn, committed and uncommitted lines of credit as well as any term
financing. FoF=Fund of funds, None=No Predominant type. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
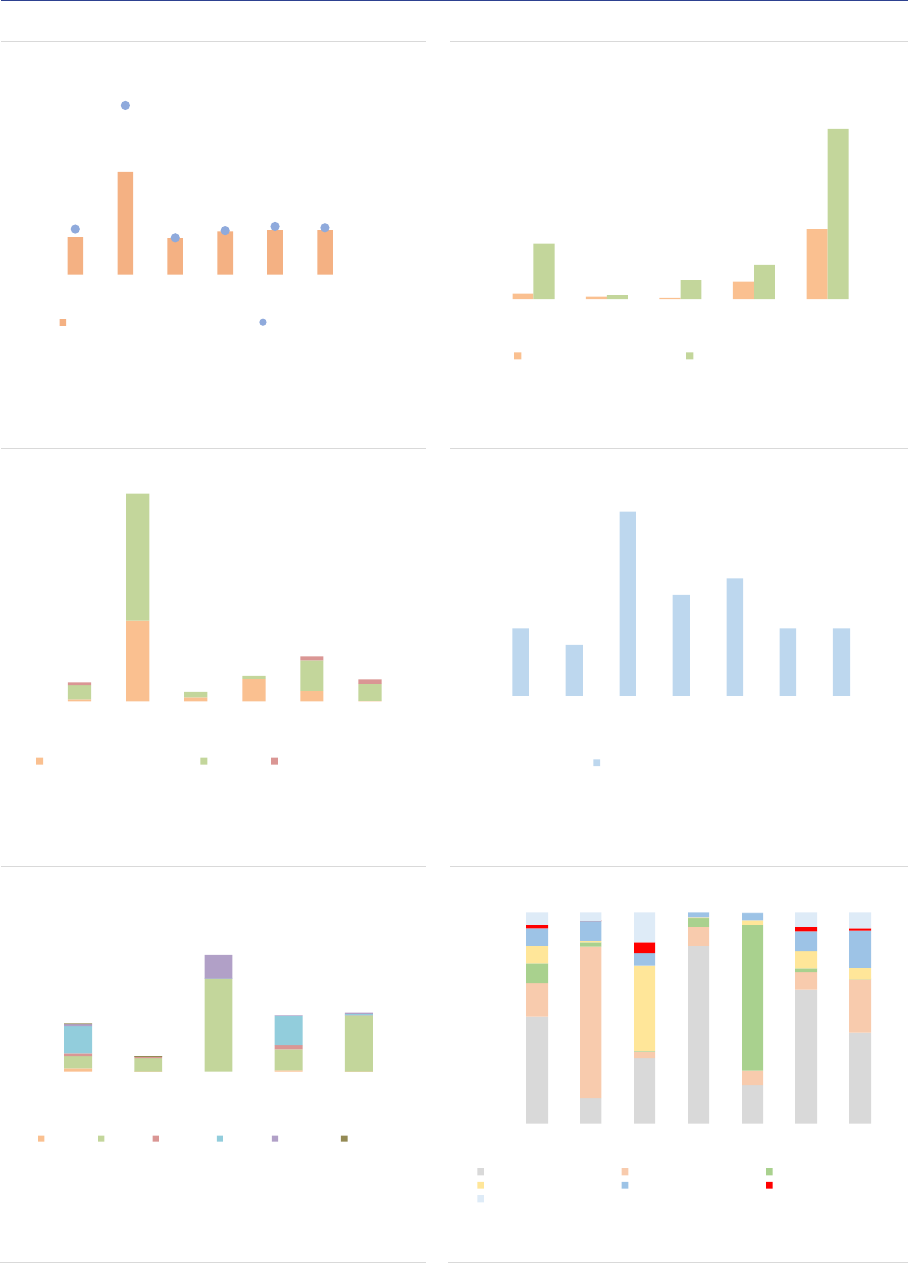
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 49
Leverage and exposure
ASR-AIF-S.19
ASR-AIF-S.20
Adjusted gross leverage
Leverage and unleveraged AIFs
ASR-AIF-S.21
ASR-AIF-S.22
Borrowing embedded in financial instruments
Unencumbered cash
ASR-AIF-S.23
ASR-AIF-S.24
Financial leverage
Decomposition of exposures
0%
150%
300%
450%
600%
FoF Hedge
fund
Private
equity
Real
estate
Other
AIF
None
Adjusted gross leverage AuM/NAV (rhs)
Note: Adjusted gross leverage of AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised
AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Adjusted gross leverage does not include IRDs.
FoF= Fund of funds, None=No predominant type. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National competent authorities, ESMA.
0
1000
2000
3000
FoF Hedge fund Private
equity
Real
estate
Other AIF
Leveraged AIFs Unleveraged AIFs
Note: Leveraged and unleveraged AIFs managed and/or marketed by
authorised EU AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national
jurisdictions, end of 2020, EUR bn. Leveraged funds identified using the AIF
reporting code as specified in Annex 2 of ESMA guidelines on AIFMD
reporting obligations. FoF=Fund of funds. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Comptent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
FoF Hedge
fund
Private
equity
Real
estate
Other
AIF
None
Cash and securities OTC Exhange-traded
Note: Borrowing of cash and securities or embedded in derivatives, end of
2020, in % of total exposure. AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised
AIFMs. OTC and exchange-traded deriatives net of margins. FoF=Fund of
funds, None=No predominant type. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
3%
6%
9%
12%
Total
EU
FoF Hedge
fund
Private
equity
Real
estate
Other
AIF
None
Unencumbered cash
Note: Unencumbered cash, end of 2020, in % of NAV. EEA30 and non-EEA30
AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed, respectively, w/ and w/o passport.
FoF=Fund of funds, None=No predominant type. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
10%
20%
30%
Unsecured
borrowing
Secured via
PB
Reverse
repo
Secured via
other
Short
position
borrowing
sec.
FoF HF PEQ RE Other
AIF
None
Note: Cash and securities borrowed, end of 2020, in % of NAV. EEA30 and non-
EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed, respectively, w/ and w/o passport.
FoF=Funds of Funds, None=No predominant type
FoF=Funds of Funds, Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD databse, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Total EU FoF Hedge
fund
Private
equity
Real
estate
Other
AIF
None
Securities CIUs Physical assets
IRDs FX CDS
Other derivatives
Note: Share of gross exposures by AIF type, end of 2020, in % of total. AIFs
managed and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs. FoF=Fund of funds, None=No
predominant type. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
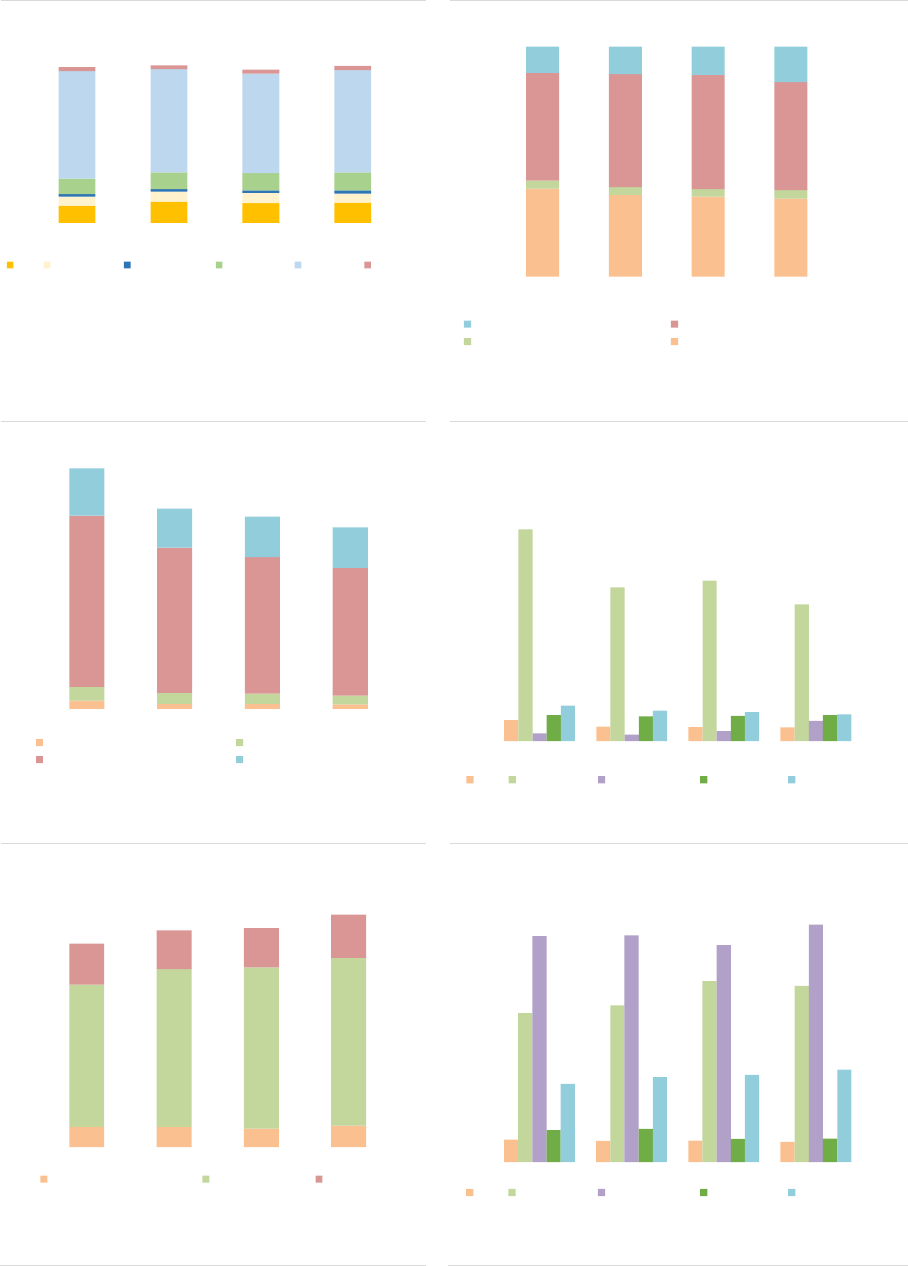
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 50
ASR-AIF-S.25
ASR-AIF-S.26
Total exposures
Corporate bond quality
ASR-AIF-S.27
ASR-AIF-S.28
Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents by AIF type
ASR-AIF-S.29
ASR-AIF-S.30
Equities
Equities by AIF type
0
3
6
9
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
FoF Hedge fund Private equity Real estate Other AIF None
Note: Exposures of AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs, funds
quarterly reported, EUR tn. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs
marketed, respectively, w/ and w/o passport. FoF=Fund of funds, None=No
predominant type. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
70%
80%
90%
100%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Non-IG corp bonds by non-fin IG corp bonds by non-fin inst
Corp bonds nonIG by fin Corp bonds IG by fin inst
Note: Corporate bonds exposure, funds reported quarterly, in % of NAV. AIFs
managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs. Data for 28 EEA
countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
2%
4%
6%
8%
10%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Hundreds
Certificates of deposit Commercial papers
Other cash equivalent Other deposits
Note: Cash and cash equivalents exposure, funds reported quarterly, in % of
NAV. Government bonds excluded from other cash equivalents. Data for 28
EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD databse, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
20%
40%
60%
80%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Hundreds
FoF Hedge fund Private equity Real estate Other AIFs
Note: Cash and cash equivalents exposure by AIF type, funds quarterly
reported, in % of NAV. Data for 28 EEA countries. FoF=Funds of funds.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
5%
10%
15%
20%
25%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Hundreds
Listed financial inst. Other listed Unlisted
Note: Exposure to equities, funds quarterly reported, in % of NAV. AIFs
managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs. Data for 28 EEA
countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
20%
40%
60%
80%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Hundreds
FoF Hedge fund Private equity Real estate Other AIFs
Note: Equities exposure by AIF type, funds quarterly reported, in % of NAV.
AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs. Data for 28 EEA
countries.FoF=Funds of Funds.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
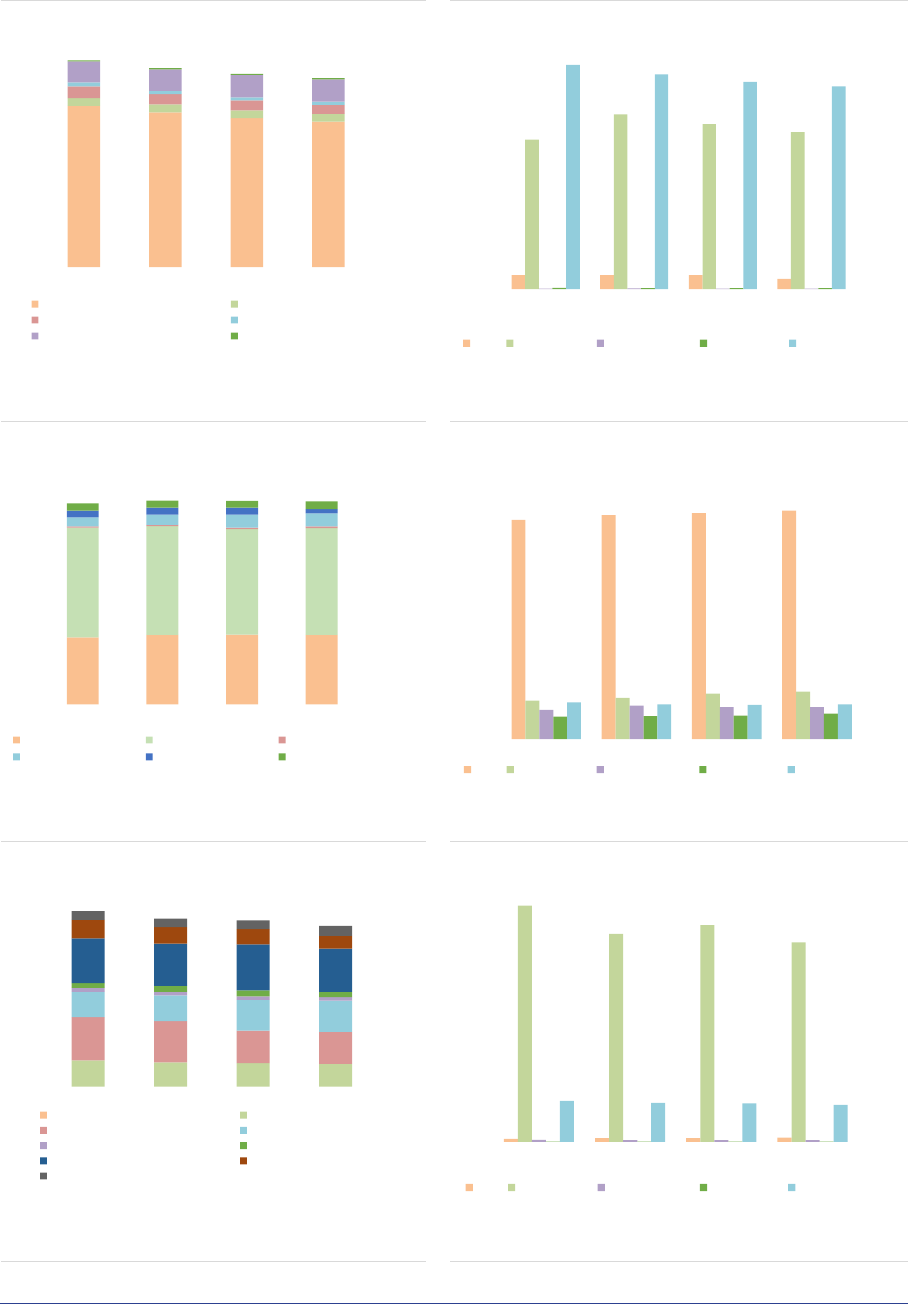
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 51
ASR-AIF-S.31
ASR-AIF-S.32
Sovereign bonds
Sovereign bonds by AIF type
ASR-AIF-S.33
ASR-AIF-S.34
CIUs
CIUs by AIF type
ASR-AIF-S.35
ASR-AIF-S.36
Structured products
Structured products by AIF type
0%
4%
8%
12%
16%
20%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Hundreds
EU Sov >1Y TM EU Sov up 1Y TM
G10 Sov >1Y TM G10 Sov up 1Y TM
Non-G10 Sov >1Y TM Non-G10 Sov up 1Y TM
Note: Sovereign bonds exposure, funds reported quarterly, in % of NAV. AIFs
managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs. Sov=Sovereign bonds,
TM=Time to Maturity. Data for 27 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
5%
10%
15%
20%
25%
30%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
FoF Hedge fund Private equity Real estate Other AIFs
Note: Sovereign bonds exposure by AIF type, funds reported quarterly, in % of
NAV. AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs. FoF=Funds of
Funds. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
7%
14%
21%
28%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Hundreds
CIUs by the AIFM CIUs by others ETF by the AIFM
ETF by others MMFs by the AIFM MMFs by others
Note: Collective investment undertakings exposure, funds reported quaterly,
in % of NAV. AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs.
CIUs=Collective Investment Undertakings. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Hundreds
FoF Hedge fund Private equity Real estate Other AIFs
Note: Collective investment undertakings exposure by AIF type, funds
reported quarterly, in % of NAV. AIFs managed and/or marketed by
authorised EU AIFMs. FoF=Funds of Funds. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0.0%
0.6%
1.2%
1.8%
2.4%
3.0%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Hundreds
ABCP ABS
Agency MBS CDO/CLO
CMBS ETP
Other RMBS
Structured certificate
Note: Structured products exposure, funds reported quarterly, in % of NAV.
AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs. Data for 28 EEA
countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
5%
10%
15%
20%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Hundreds
FoF Hedge fund Private equity Real estate Other AIFs
Note: Structured products exposure by AIF type, funds reported quarterly, in
% of NAV. AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs.
FoF=Funds of funds. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
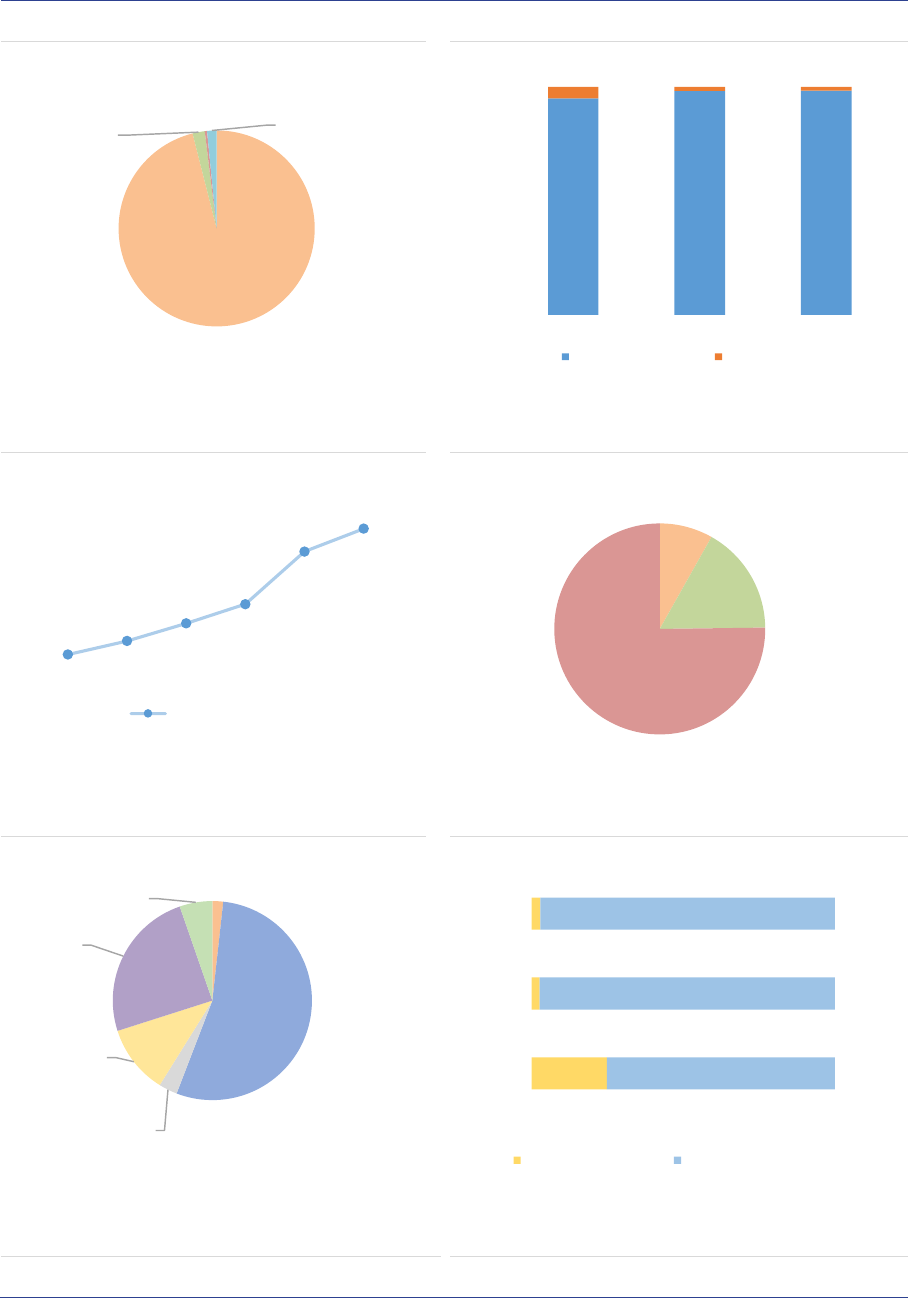
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 52
Funds of Funds
AIF characteristics
ASR-AIF-S.37
ASR-AIF-S.38
AIFMD passport
EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs
ASR-AIF-S.39
ASR-AIF-S.40
Market concentration
Investment strategies by NAV
ASR-AIF-S.41
ASR-AIF-S.42
Investment regions by NAV
Investor type
EU
passport
96%
EU w/o
passport
2%
Non-EU w/o passport
<1%
Non-EU not
marketed in
EU
2%
Note: NAV of funds of funds by manager's access to AIFMD passport, end of
2020, in %. Authorised EEA30 AIFMs with access to AIFMD passport or
marketing non-EEA30 AIFs w/o passport, sub-threshold managers are
registered only in national juridisdictions w/o passporting rights. Data for the
EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Fund of HF Fund of PE Other FoF
EEA30 Non-EEA30
Note: Share of EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national
jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % on NAV. Non-EEA30 AIFs marketed w/o
passport. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0
25
50
75
100
top 10 top 20 top 50 top 100 top 500 top 1,000
Market concentration
Note: Market concentration of the largest 10-to-1,000 funds of funds managed
and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered
only in national jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD databse, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
Fund of HF
8%
Fund of PE
17%
Other FoF
75%
Note: Investment strategies of funds of funds, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Funds of
funds managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs and sub-threshold
managers registered only in national jurisdictions. FoF=Fund of funds, PE=Private
equity fund, HF=Hedge fund. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD databaseNational Competent Authorities, ESMA.
Asia
2%
EEA
54%
Other Europe
3%
North
America
11%
Supra
National
25%
Rest
5%
Note: Regional investment focus of funds of funds managed and/or marketed
by authorised AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national
jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Geo-focus determined according to
the domicile of investments and the supranational category including
investments without a predominant geo-focus. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100%
Other FoF
Fund of HF
Fund of
PE
Retail investors Professional investors
Note: Clients of funds of funds managed and/or marketed by authorised EU
AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictionsat,
end of 2020, in % of NAV. FoF=Fund of funds, PE= Private equity fund,
HF=Hedge fund. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
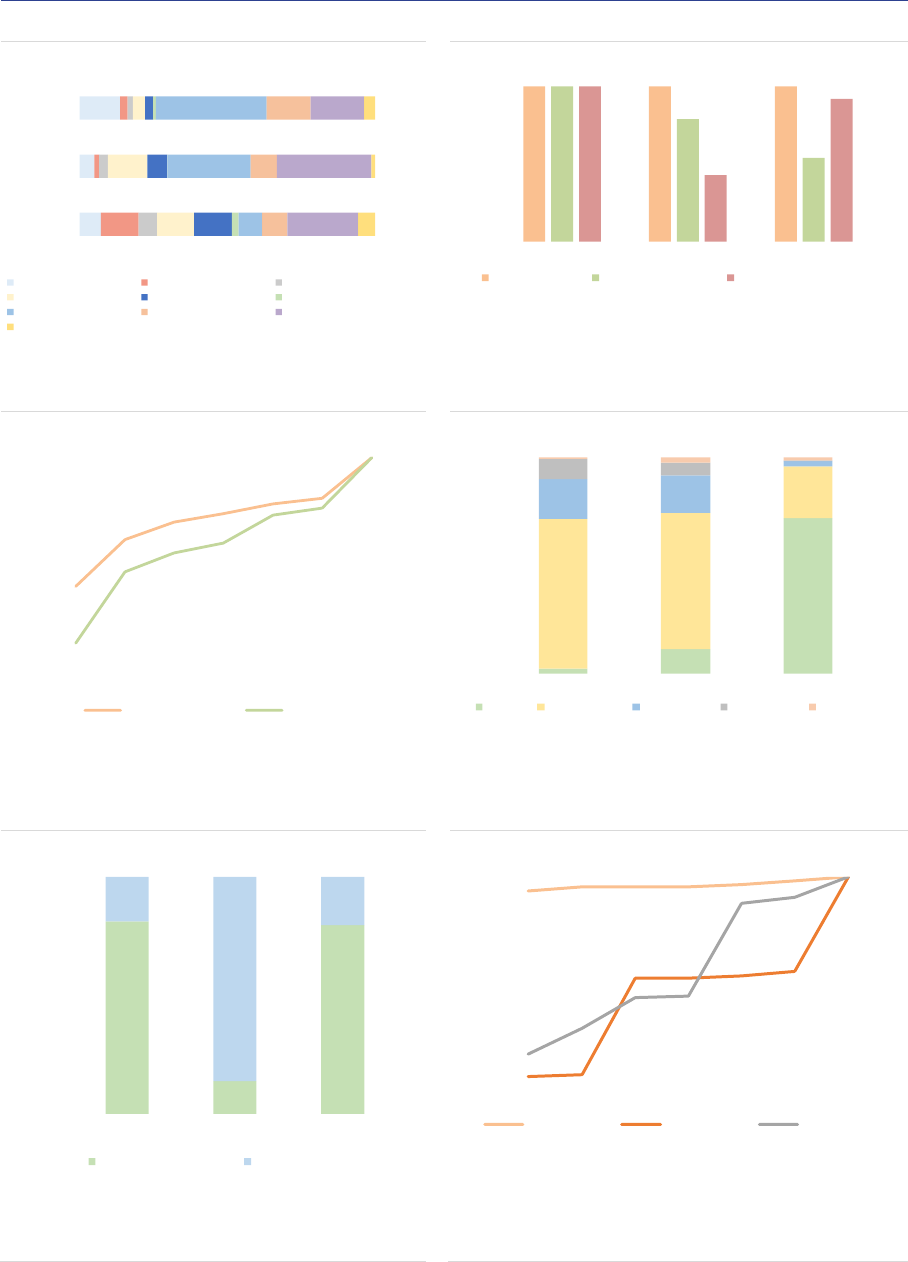
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 53
Liquidity and counterparty risk profile
ASR-AIF-S.43
ASR-AIF-S.44
Ownership of AIFs
Top five beneficial owners
ASR-AIF-S.45
ASR-AIF-S.46
FoFs: liquidity profile
Redemption frequencies
ASR-AIF-S.47
ASR-AIF-S.48
Redemption rights to investors
Liquidity financing
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100%
Other FoF
Fund of PE
Fund of HF
Banks General government Household
Insurances Non-profit None
Other CIUs Oth. fin. institutions Pension funds
Unknown
Note: Ownership of units in funds of funds managed and/or marketed by authorised
EU AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. FoF=Fund of funds; PE=Private equity fund,
HF=Hedge fund. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
EU passport EU w/o passport Non-EU w/o passport
Note: Investor concentration of funds of funds managed and/or marketed by
authorised EU AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Investor concentration computed
as share of AIF equity beneficially owned by the 5 largest investors. FoF=Fund of
Funds, PEQF=Private Equity Fund, HF=Hedge Fund.Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
40%
62%
70%
74%
78%
81%
100%
14%
56%
60%
73%
76%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day or
less
2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180 d 181-365
d
> 365 d
Investor Portfolio
Note: Portfolio and investor liquidity profiles of funds of funds managed and/or
marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020. Portfolio liquidity defined as the
percentage of the funds’ assets capable of being liquidated within each specified
period, investor liquidit y defined as the shortest period for which investors can
redeem. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed,
respectively, w/ and w/o passport. d=Days. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Fund of HF Fund of PE Other FoF
Daily Weekly
to monthly
Quarterly Quarterly
to yearly
Other
Note: Investor redemption frequencies allowed by open-end funds of funds
managed and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV.
EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed, respectively, w/
and w/o passport. FoF=Fund of funds, PE=Private equity fund, HF=Hedge
Fund. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Fund of HF Fund of PE Other FoF
Open-end Closed-end
Note: Redemption rights provided in the ordinary course to investors in funds
of funds managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs, end of 2020, in
% of NAV. HF=Hedge fund; PE=Private equity; FoF=Fund of funds,
PE=Private equity fund. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
2%
53%
100%
41%
87%
100%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day 2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180
d
181-365
d
> 365 d
Fund of HF Fund of PE Other FoF
Note: Liquidity financing of funds of funds managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs, end of 2020. Aggregate amount of borrowing and cash
financing divided depending on longest period for which creditors are
contractually committed to provide such financing, Borrowing and cash financing
include drawn and undrawn, committed and uncommitted lines of credit as well
as any term financing. Data for the EEA30. FoF=Fund of funds, PE=Private
equity fund, HF=Hedge fund.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
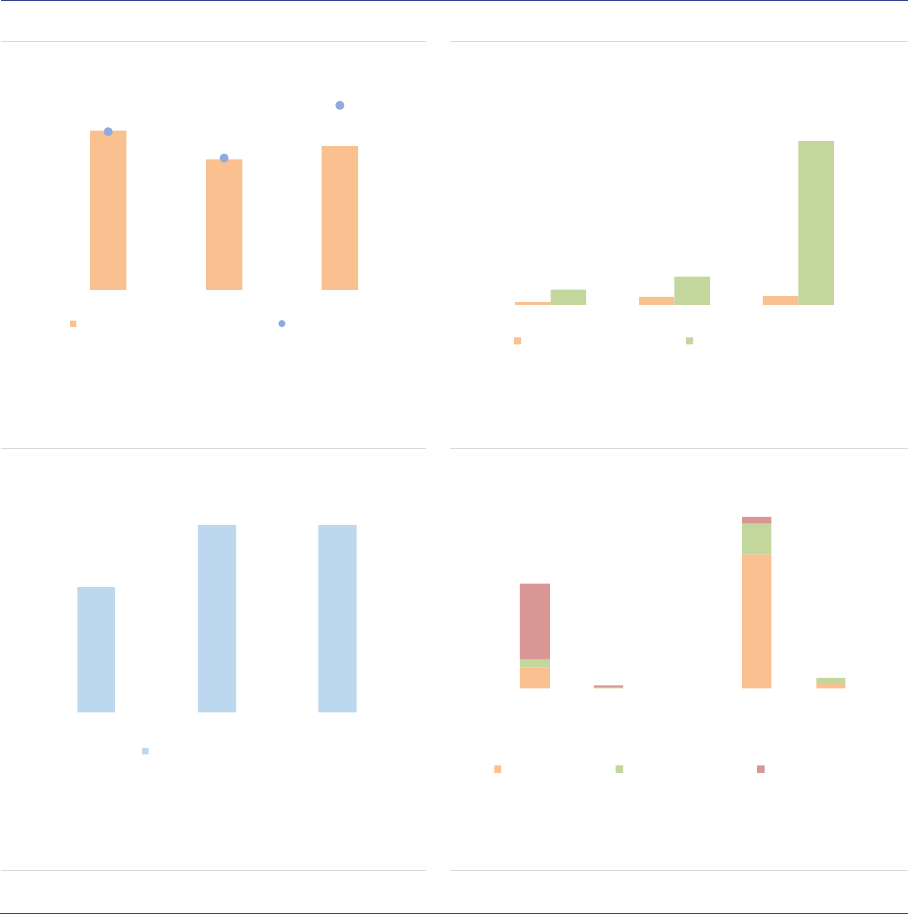
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 54
Leverage and exposure
ASR-AIF-S.49
ASR-AIF-S.50
Adjusted gross leverage
Leveraged and unleveraged AIFs
ASR-AIF-S.51
ASR-AIF-S.52
Unencumbered cash
Financial leverage
0%
40%
80%
120%
160%
Fund of HF Fund of PEQF Other FoF
Adjusted gross leverage AuM/NAV
Note: Adjusted gross leverage of funds of funds managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Adjusted gross leverage computed as
total exposure less IRDs with respect to NAV. FoF= Funds of funds, PE=Private
equity fund, HF=Hedge fund. Data for the EEA30.
0
200
400
600
800
Fund of HF Fund of PEQ Other FoF
Leveraged AIFs Unleveraged AIFs
Note: Leveraged and unleveraged funds of funds managed and/or marketed
by authorised EU AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in
national jurisdictions, end of 2019, EUR bn. Leveraged funds identified using
the AIF reporting code as specified in Annex 2 of ESMA guidelines on AIFMD
reporting obligations FoF=Funds of funds, HF=Hedge funds, PEQ=Private
equity funds. Data for 27 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Comptent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
1%
2%
3%
Fund of HF Fund of PE Other FoF
Unencumbered cash
Note: Unencumbered cash held by funds of funds, end of 2020, in % of NAV.
EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed, respectively, w/
and w/o passport. FoF=Funds of funds, HF=Hedge fund, PE=Private equity
fund. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0.0%
0.4%
0.8%
1.2%
1.6%
2.0%
Unsecured
borrowing
Secured via
PB
Reverse
repo
Secured via
other
Short
position
borrowing
sec.
Fund of HF Fund of PEQF Other FoF
Note: Cash and securities borrowed by funds of funds, end of 2020, in % of
NAV. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed,
respectively, w/ and w/o passport. FoF=Funds of Funds, PEQF= Private
Equity Fund. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD databse, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
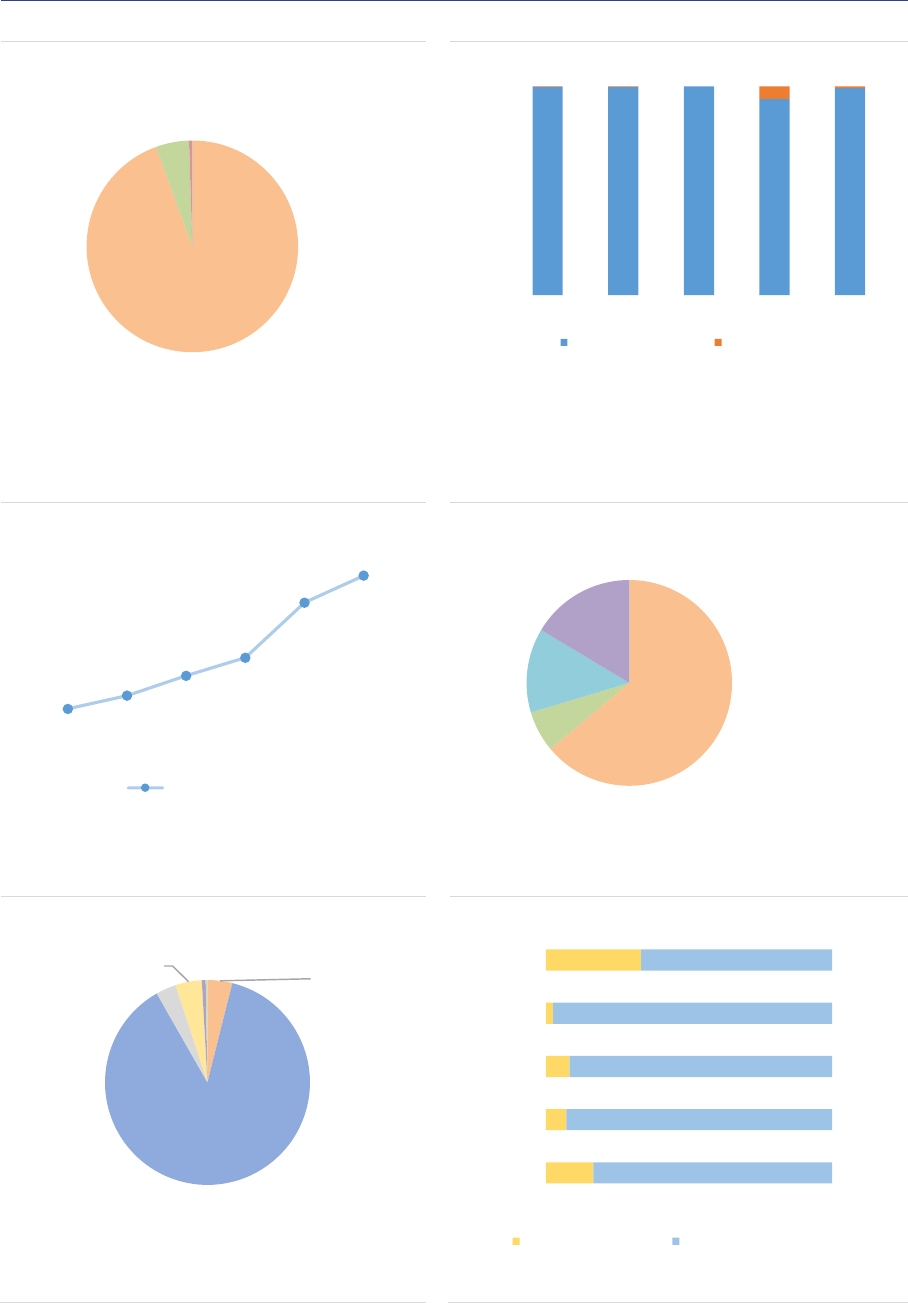
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 55
Real Estate Funds
AIF characteristics
ASR-AIF-S.53
ASR-AIF-S.54
AIFMD passport
EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs
ASR-AIF-S.55
ASR-AIF-S.56
Market concentration
Investment strategies by NAV
ASR-AIF-S.57
ASR-AIF-S.58
Investment regions by NAV
Investor type
EU
passport
94%
EU w/o
passport
5%
Non-EU w/o passport
1%
Note: NAV of real estate AIFs by manager's access to AIFMD passport,
end of 2020, in %. Authorised EEA30 AIFMs with access to AIFMD
passport or marketing non-EEA30 AIFs w/o passport, sub-threshold
managers are registered only in national juridisdictions w/o passporting
rights. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Commercial Industrial Multi-
strategy
Other RE Residential
EEA30 Non-EEA30
Note: Share of EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national
jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % on NAV. Non-EEA30 AIFs marketed w/o
passport. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0
25
50
75
100
top 10 top 20 top 50 top 100 top 500 top 1,000
Market concentration
Note: Market concentration of the largest 10-to-1,000 real estate funds managed
and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs accessing AIFMD passport and sub-
threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % of
NAV. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Commercial
64%
Industrial
7%
Other RE
13%
Residential
16%
Note: Investment strategies of real estate funds, end of 2020, in % of NAV.
Real estate funds managed and/or marketed by full scope EU AIFMs and
sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions. RE= Real
estate. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
Asia
4%
EEA
88%
Other Europe
3%
North America
4%
Rest
>1%
Note: Regional investment focus of real estate funds managed and/or
marketed by authorised AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in
national jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Geo-focus determined
according to the domicile of investments and the supranational category
including investments without a predominant geo-focus. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100%
Residential
Other
Multi-strategy
Industrial
Commercial
Retail investors Professional investors
Note: Clients of real estate funds managed and/or marketed by authorised EU
AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions,
end of 2020, in % of NAV. RE = Real estate. Data for 28 EEA countries.
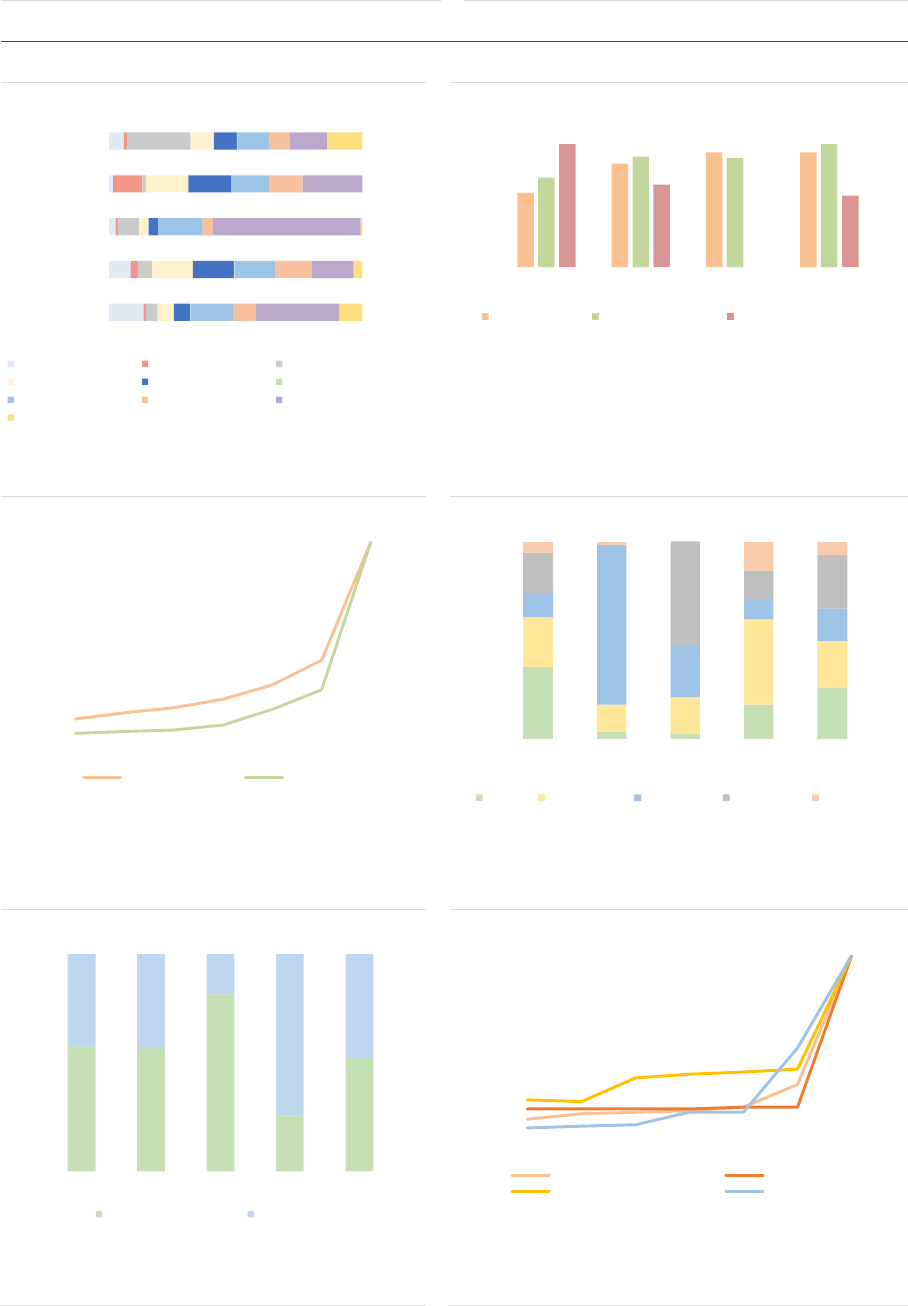
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 56
Liquidity and counterparty risk profile
ASR-AIF-S.59
ASR-AIF-S.60
Ownership of RE funds
Top five beneficial owners
ASR-AIF-S.61
ASR-AIF-S.62
RE: liquidity profile
Redemption frequencies
ASR-AIF-S.63
ASR-AIF-S.64
Redemption rights to investors
Liquidity financing
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100%
Residential
Other RE
Multi-strategy RE
Industrial
Commercial
Banks General government Household
Insurances Non-profit None
Other CIUs Oth. fin. institutions Pension funds
Unknown
Note: Ownership of units in real estate funds AIFs managed and/or marketed by
authorised EU AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. RE=Real estate. Data for 28 EEA
countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Industrial Multi-
strategy RE
Other RE Residential
EU passport EU w/o passport Non-EU w/o passport
Note: Investor concentration of real estate managed and/or marketed by authorised
EU AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Investor concentration computed as share of
AIF equity beneficially owned by the 5 largest investors. RE=Real estate. Data for
28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
8%
11%
14%
18%
26%
38%
100%
1%
5%
13%
23%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day or
less
2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180 d 181-365
d
> 365 d
Investor Portfolio
Note: Portfolio and investor liquidity profiles of real estate funds managed
and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020. Portfolio liquidity defined
as the percentage of the funds’ assets capable of being liquidated within each
specified period, investor liquidity defined as the shortest period for which
investors can redeem. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs
marketed, respectively, w/ and w/o passport. d=Days. Data for the EEA30..
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Commercial Multi-
strategy RE
Residential
Daily Weekly
to monthly
Quarterly Quarterly
to yearly
Other
Note: Investor redemption frequencies allowed by open-end real estate funds
managed and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV.
EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed, respectively, w/
and w/o passport. RE=Real estate. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Commercial Industrial Multi-
strategy RE
Other RE Residential
Open-end Closed-end
Note: Redemption rights provided in the ordinary course to investors in real estate
funds managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of
NAV. RE=Real estate. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
26%
17%
1%
47%
100%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day 2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180 d 181-365
d
> 365 d
Commercial Industrial
Other RE Residential
Note: Liquidity financing of real estate funds managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs, end of 2020. Aggregate amount of borrowing and cash
financing divided depending on longest period for which creditors are
contractually committed to provide such financing, Borrowing and cash financing
include drawn and undrawn, committed and uncommitted lines of credit as well as
any term financing. RE=Real estate. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
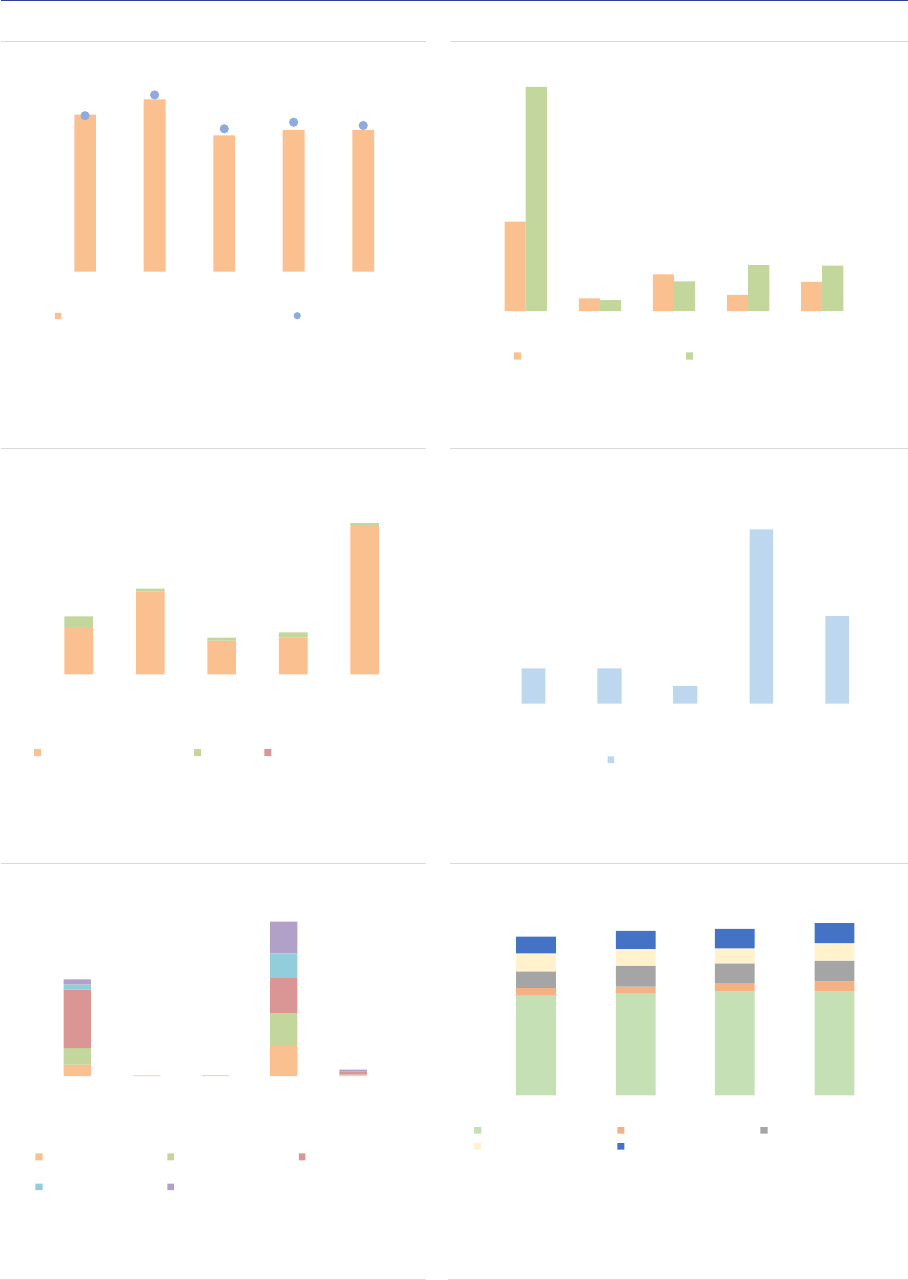
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 57
Leverage and exposure
ASR-AIF-S.65
ASR-AIF-S.66
Adjusted gross leverage
Leveraged and unleveraged AIFs
ASR-AIF-S.67
ASR-AIF-S.68
Borrowings embedded in derivatives
Unencumbered cash
ASR-AIF-S.69
ASR-AIF-S.70
Financial leverage
Total exposures
0%
40%
80%
120%
160%
Comercial Industrial Multi-
strategy RE
Other
RE
Residential
Median adjusted gross leverage AuM/NAV
Note: Adjusted gross leverage of real estate funds managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Adjusted gross leverage computed
as total exposure less IRDs with respect to NAV. RE=Real estate. Data for the
EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National competent authorities, ESMA.
0
70
140
210
280
Commercial Industrial Multi-
strategy
Other RE Residential
Leveraged AIFs Unleveraged AIFs
Note: Leveraged and unleveraged real estate AIFs managed and/or
marketed by authorised EU AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered
only in national jurisdictions, end of 2018, EUR bn. Leveraged funds identified
using the AIF reporting code as specified in Annex 2 of ESMA guidelines on
AIFMD reporting obligations Data for 27 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Comptent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
6%
12%
18%
24%
Commercial Industrial Multi-
strategy RE
Other
RE
Residential
Cash and securities OTC Exchange-traded
Note: Borrowing of cash and securities or embedded in derivatives by real
estate funds, end of 2020, in % of total exposure. AIFs managed and/or
marketed by authorised AIFMs marketed. OTC and exchange-traded
deriatives net of margins. RE=Real estate. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA
0%
2%
4%
6%
8%
10%
12%
Commercial Industrial Multi-
strategy RE
Other RE Residential
Unencumbered cash
Note: Unencumbered cash held by real estate funds, end of 2020, in % of NAV.
EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed, respectively, w/ and
w/o passport. RE=Real estate. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
5%
10%
15%
20%
25%
30%
Unsecured
borrowing
Secured
via PB
Reverse
repo
Secured
via other
Short
position
borrowing
sec.
Commercial Industrial Multi
-strategy RE
Other RE Residential
Note: Cash and securities borrowed by real estate funds, end of 2020, in % of
NAV. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed,
respectively, w/ and w/o passport. RE=Real Estate. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD databse, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Commercial RE Industrial RE Multi-strategy RE
Other RE Residential RE
Note: Exposure of real estate funds managed and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs,
funds quarterly reported, EUR tn. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs
marketed, respectively, w/ and w/o passport. RE=Real estate. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
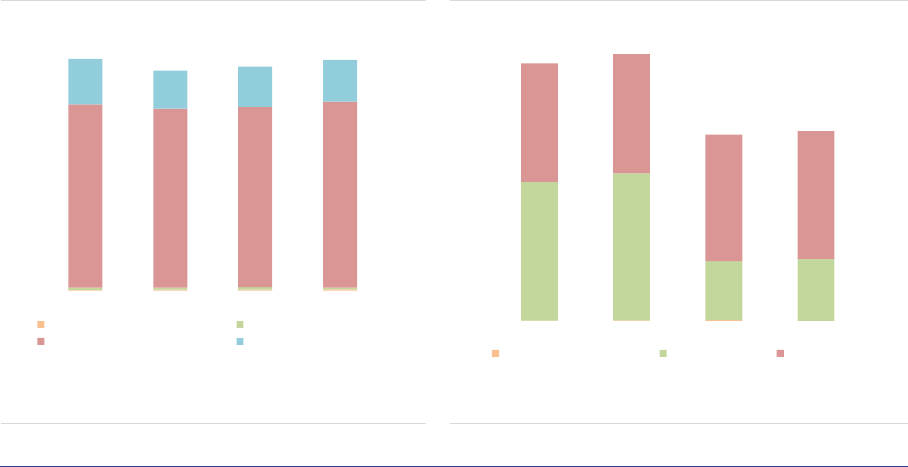
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 58
ASR-AIF-S.71
ASR-AIF-S.72
Cash and cash equivalents
Equities
0%
2%
4%
6%
8%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Hundreds
Certificates of deposit Commercial papers
Other cash equivalent Other deposits
Note: Cash and cash equivalents exposure of real estate funds, AIFs reported
quarterly, in % of NAV. Government bonds excluded from other cash
equivalents. Data for 28 EEA countries;
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
2%
4%
6%
8%
10%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Hundreds
Listed financial inst. Other listed Unlisted
Note: Real estate funds' exposure to equity, AIFs reported quarterly, in % of
NAV. AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs. Data for 28
EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
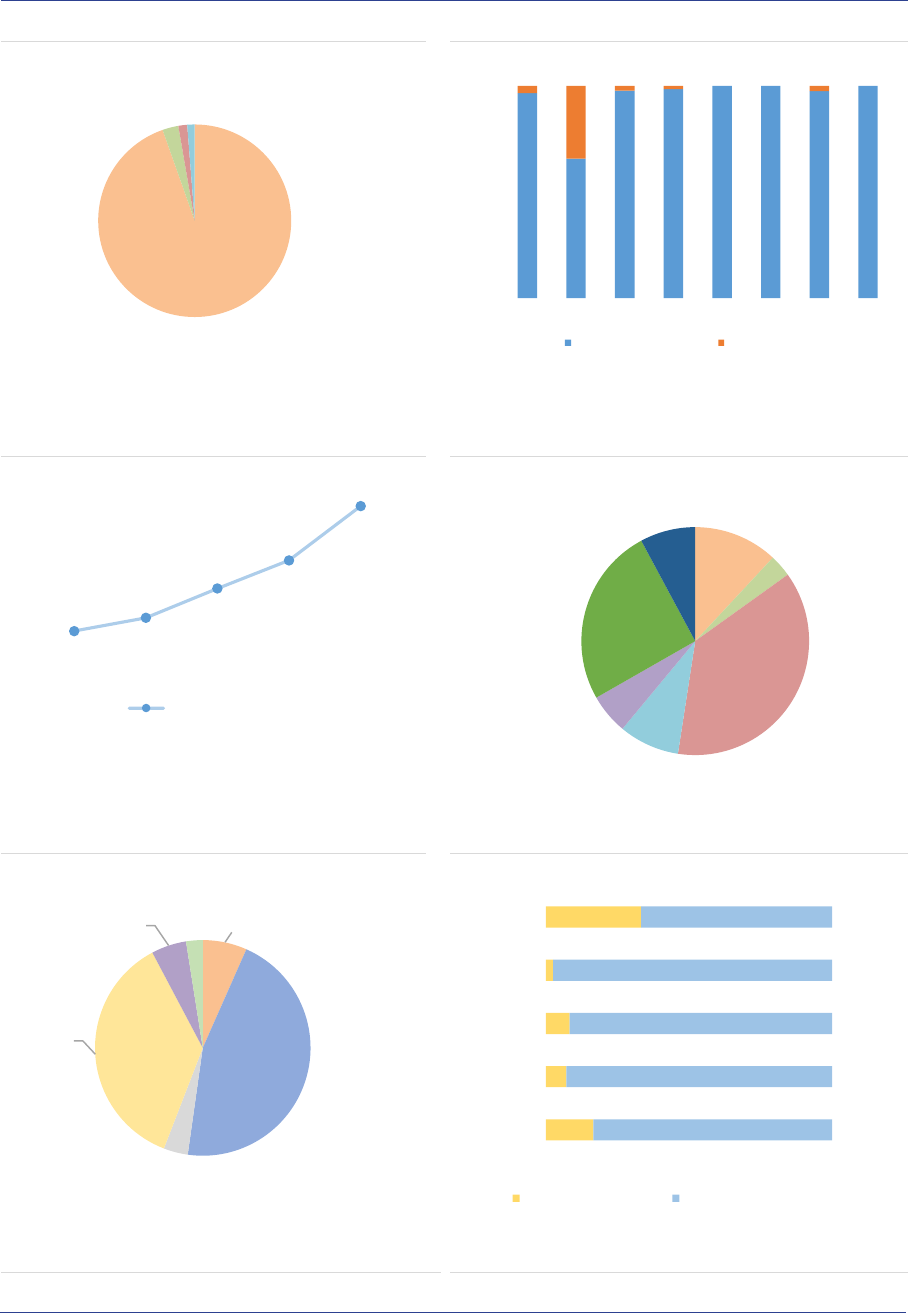
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 59
Hedge Funds
AIF characteristics
ASR-AIF-S.73
ASR-AIF-S.74
AIFMD passport
EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs
ASR-AIF-S.75
ASR-AIF-S.76
Market concentration
Investment strategies by NAV
ASR-AIF-S.77
ASR-AIF-S.78
Investment regions by NAV
Investor type
EU passport
95%
EU w/o
passport
3%
Non-EU w/o
passport
1%
Non-EU not
marketed in EU 1%
Note: NAV of hedge funds by manager's access to AIFMD passport, end of
2020, in %. Authorised EEA30 AIFMs with access AIFMD passport or
marketing non-EEA30 AIFs w/o passport, subthreshold managers are
registered only in national juridisdictions w/o passporting rights. Data for the
EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Credit CTA Equity Event Macro Multi-
strategy
HF
Other
HF
Rel.
value
EEA30 Non-EEA30
Note: Share of EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national
jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % on NAV. Non-EEA30 AIFs marketed w/o
passport. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0
25
50
75
100
top 10 top 20 top 50 top 100 top 500
Market concentration
Note: Market concentration of the largest 10-to-500 hedge funds managed and/or
marketed by authorised EU AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in
national jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
Credit
12%
CTA
3%
Equity
37%
Event Driven
9%
Macro
6%
Multi-
strategy
25%
Other HF
8%
Note: Investment strategies of hedge funds, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Hedge
funds managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs and sub-threshold
managers registered only in national jurisdictions. HF=Hedge fund. Data for 28
EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
Asia
7%
EEA
46%
Other Europe
4%
North
America
36%
Supra
National
5%
Rest
2%
Note: Regional investment focus of hedge funds managed and/or marketed
by authorised AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national
jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Geo-focus determined according to
the domicile of investments, and the supranational category including
investments without a predominant geo-focus. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100%
Residential
Other
Multi-strategy
Industrial
Commercial
Retail investors Professional investors
Note: Clients of real estate funds managed and/or marketed by authorised EU
AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions,
end of 2020, in % of NAV. RE = Real estate. Data for 28 EEA countries.

ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 60
Liquidity and counterparty risk profile
ASR-AIF-S.79
ASR-AIF-S.80
Ownership of AIFs
Top five beneficial owners
ASR-AIF-S.81
ASR-AIF-S.82
HFs: liquidity profile
Redemption frequencies
ASR-AIF-S.83
ASR-AIF-S.84
Redemption rights to investors
Liquidity financing
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100%
Relative Value
Other HF
Multi-strategy HF
Macro
Event Driven
Equity
CTA
Credit
Banks General government
Household Insurances
Non-profit None
Other CIUs Oth. fin. institutions
Note: Ownership of units in hedge funds managed and/or marketed by authorised
EU AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. HF=Hedge fund. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Credit CTA Equity Event
driven
Macro Multi-
strategy
HF
Other
HF
Rel.
value
EU passport EU w/o passport Non-EU w/o passport
Note: Investor concentration of hedge funds managed and/or marketed by authorised EU
AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Investor concentration computed as share of AIF equity
beneficially owned by the 5 largest investors. HF=Hedge Fund. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
25%
37%
65%
77%
85%
100%
4%
20%
34%
62%
74%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day or
less
2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180
d
181-365
d
> 365 d
Investor Portfolio
Note: Portfolio and investor liquidity profiles of hedge funds managed and/or
marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020. Portfolio liquidity defined as the
percentage of the funds’ assets capable of being liquidated within each
specified period, investor liquidity defined as the shortest period for which
investors can redeem. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs
marketed, respectively, w/ and w/o passport. d=Days. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Credit
CTA
Equity
Event
driven
Macro
Multi-
strategy HF
Other
HF
Rel. value
Daily Weekly
to monthly
Quarterly Quarterly
to yearly
Other
Note: Investor redemption frequencies allowed by open-end hedge funds
managed and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV.
EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed, respectively, w/
and w/o passport. HF=Hedge fund. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Credit CTA Equity Event
Driven
Macro Multi-
strategy
Other
HF
Rel.
Value
Open-end Closed-end
Note: Redemption rights provided in the ordinary course to investors in hedge funds
managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAF.
HF=Hedge fund. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
2%
78%
100%
91%
68%
83%
0%
1%
100%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day 8-30 d 91-180 d > 365 d
Credit CTA Equity
Event driven Macro Rel. value
Note: Liquidity financing of hedge funds managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs, end of 2020. Aggregate amount of borrowing and cash
financing divided depending on longest period for which creditors are
contractually committed to provide such financing, Borrowing and cash
financing include drawn and undrawn, committed and uncommitted lines of
credit as well as any term financing. HF=Hedge fund. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
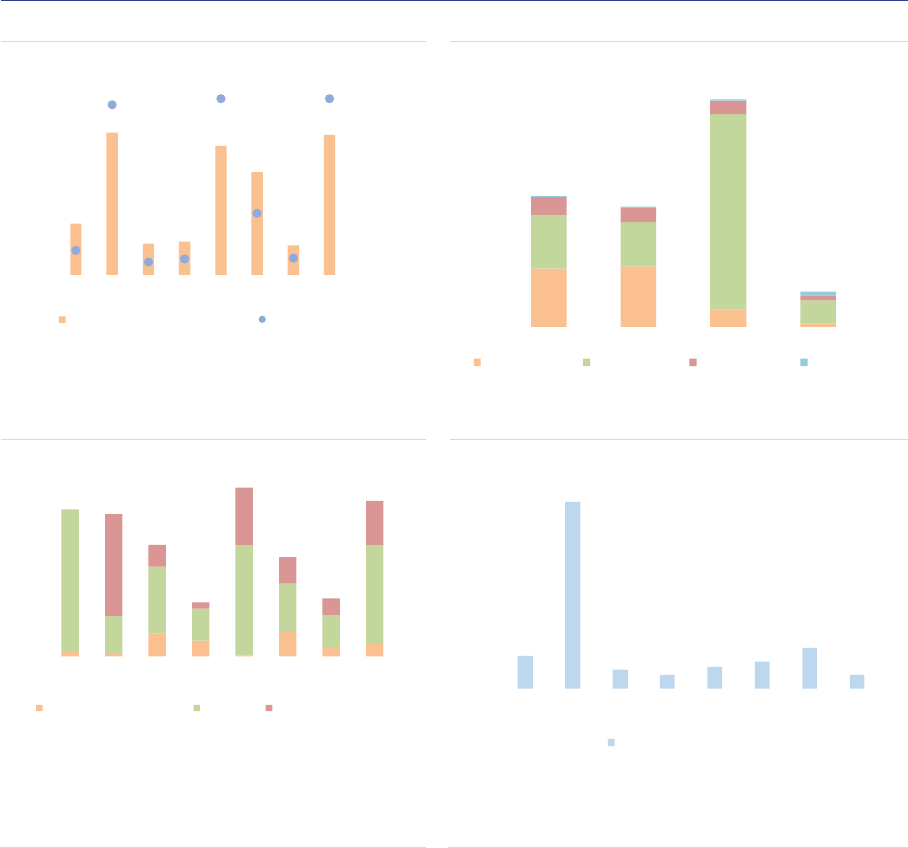
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 61
Leverage and exposure
ASR-AIF-S.85
ASR-AIF-S.86
Adjusted gross leverage
Borrowing activity
ASR-AIF-S.87
ASR-AIF-S.88
Borrowing embedded in financial instruments
Unencumbered cash
0%
800%
1600%
2400%
0%
300%
600%
900%
1200%
Credit
CTA
Equity
Event
driven
Macro
Multi-
strats
Other
HF
Rel.
value
Adjusted gross leverage AuM/NAV (rhs)
Note: Adjusted gross leverage of funds of funds managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Adjusted gross leverage computed
as total exposure less IRDs with respect to NAV. FoF= Funds of funds, PE=Private
equity fund, HF=Hedge fund. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National competent authorities, ESMA.
0%
20%
40%
60%
80%
100%
120%
140%
160%
180%
2019 2020 2019 2020
Prime brokers Reverse repo Other secured Unsecured
Note: Cash and securities borrowed by hedge funds, end of 2019 and 2020, in %
of NAV. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed, respectively,
w/ and w/o passport. Data for the EEA30 and for the US.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, SEC, ESMA.
US
EU
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Credit CTA Equity Event
driven
Macro Multi-
strategy
Other
HF
Rel.
value
Cash and securities OTC Exchange-traded
Note: Borrowing of cash and securities or embedded in derivatives by hedge
funds, end of 2020, in % of total exposure. AIFs managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs. OTC and exchange-traded deriatives net of margins.
HF=Hedge fund. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
15%
30%
45%
60%
75%
Credit CTA Equity Event
driven
Macro Multi-
strategy
HF
Other
HF
Rel.
value
Unencumbered cash
Note: Unencumbered cash held by hedge funds, end of 2020, in % of NAV. EEA30
and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed, respectively, w/ and w/o
passport. HF=Hedge fund. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
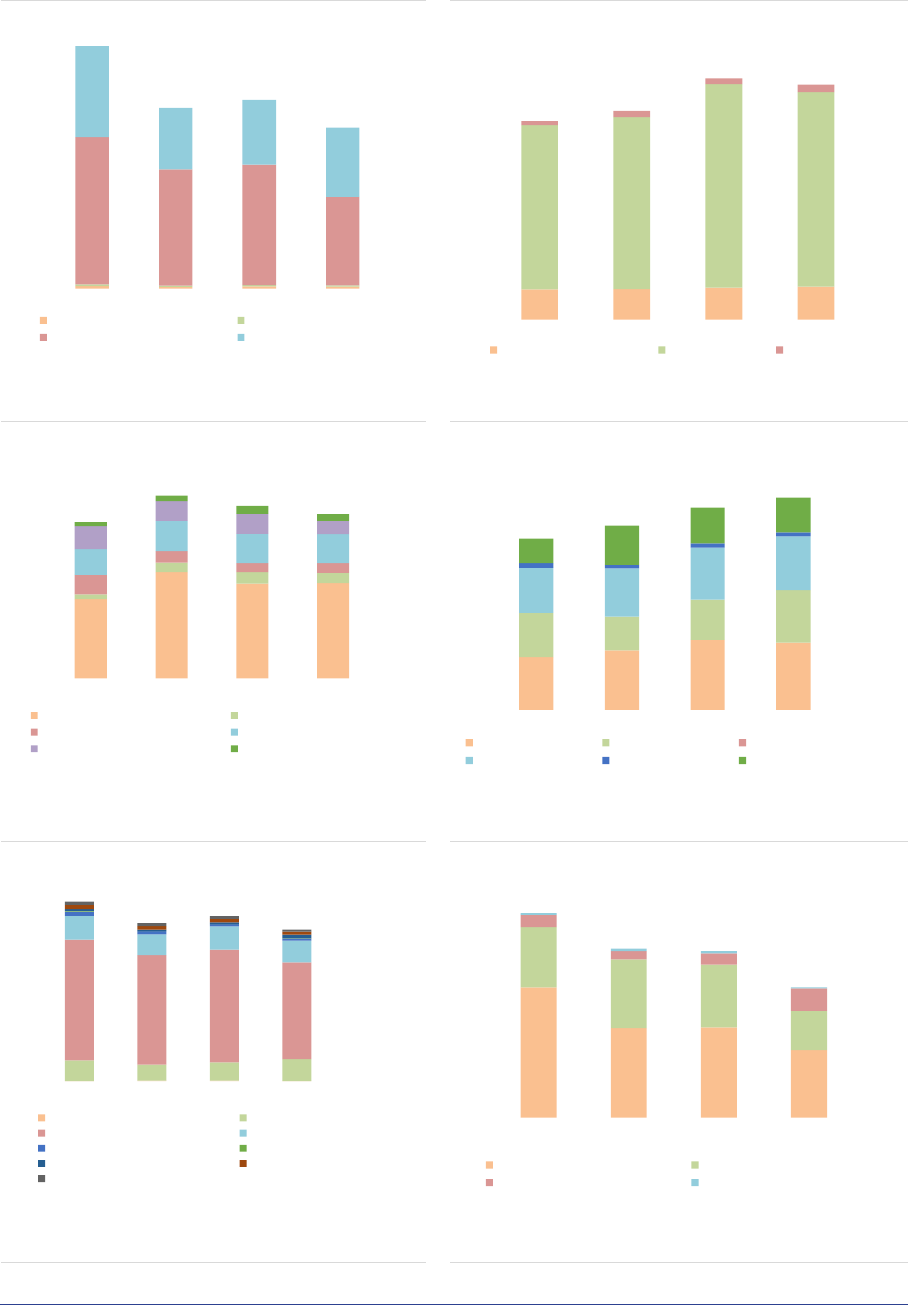
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 62
ASR-AIF-S.89
ASR-AIF-S.90
Cash and cash equivalents
Equities
ASR-AIF-S.91
ASR-AIF-S.92
Sovereign bonds
Collective investment undertakings
ASR-AIF-S.93
ASR-AIF-S.94
Structured products
Corporate bond quality
0%
20%
40%
60%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Certificates of deposit Commercial papers
Other cash equivalent Other deposits
Note: Cash and cash equivalents exposure of hedge funds, AIFs reported
quarterly, in % of NAV. Government bonds excluded from the other cash
equivalents. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
15%
30%
45%
60%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Hundreds
Listed financial inst. Other listed Unlisted
Note: Hedge funds' exposure to equity, AIFs reported quarterly, in % of NAV.
AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs. Data for 28 EEA
countries;
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
5%
10%
15%
20%
25%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
EU Sov >1Y TM EU Sov up 1Y TM
G10 Sov >1Y TM G10 Sov up 1Y TM
Non-G10 Sov >1Y TM Non-G10 Sov up 1Y TM
Note: Sovereign bonds exposure exposure of hedge funds, AIFs reported
quarterly, in % of NAV. AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised EU
AIFMs. Sov=Sovereign bonds, TM=Time to Maturity. Data for 28 EEA
countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
5%
10%
15%
20%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Hundreds
CIUs by the AIFM CIUs by others ETF by the AIFM
ETF by others MMFs by the AIFM MMFs by others
Note: Collective investment undertakings exposure of hedge funds, AIFs
reported quarterly, in % of NAV. AIFs managed and/or marketed by
authorised EU AIFMs. CIUs=Collective Investment Undertakings. Data for 28
EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
5%
10%
15%
20%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Hundreds
ABCP ABS
Agency MBS CDO/CLO
CMBS ETP
Other RMBS
Structured certificate
Note: Structured and securitised products exposure of hedge funds, AIFs
reported quarterly, in % of NAV. AIFs managed and/or markted by authorised.
Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
10%
20%
30%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Hundreds
IG by fin. inst. IG by non-fin. inst.
Non-IG by fin. inst. Non-IG by non-fin. inst.
Note: Corporate bonds exposure of hedge funds, AIFs reported quarterly, in
% of NAV. AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs. Data for
28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
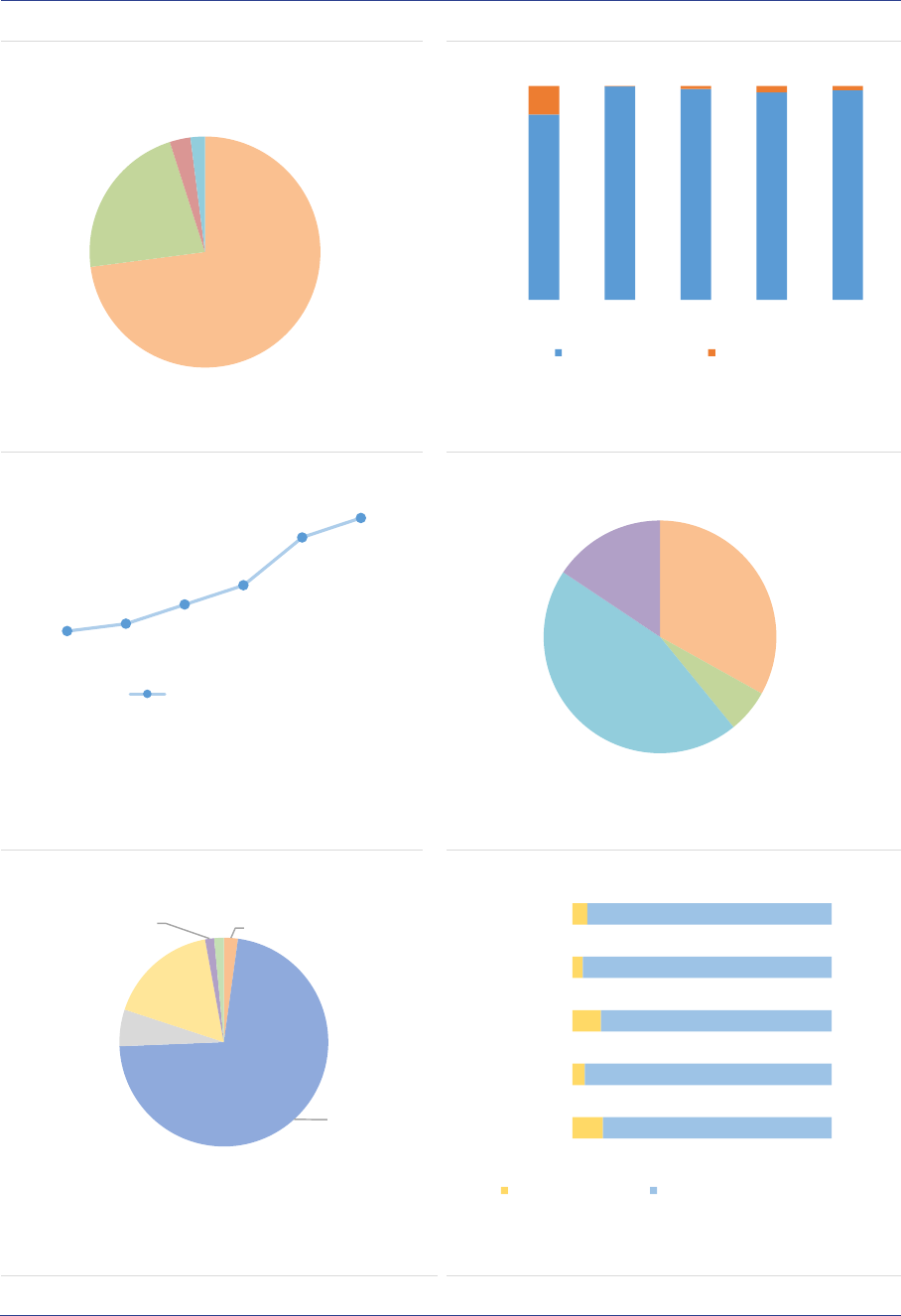
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 63
Private Equity Funds
AIF characteristics
ASR-AIF-S.95
ASR-AIF-S.96
AIFMD passport
EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs
ASR-AIF-S.97
ASR-AIF-S.98
Market concentration
Investment strategies by NAV
ASR-AIF-S.99
ASR-AIF-S.100
Investment regions by NAV
Investor type
EU
passport
73%
EU w/o
passport
22%
Non-EU w/o
passport
3%
Non-EU not marketed
in EU 2%
Note: NAV of private equity funds by manager's access to AIFMD passport,
end of 2020, in %. Authorised AIFMs with access to AIFMD passport,
subthreshold managers registered only in national juridisdictions w/o passport.
Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Growth
Capital
Mezzanine
Capital
Multi-
strategy
Other PE Venture
Capital
EEA30 Non-EEA30
Note: Share of EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national
jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % on NAV. Non-EEA30 AIFs marketed w/o
passport. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0
25
50
75
100
top 10 top 20 top 50 top 100 top 500 top 1,000
Market concentration
Note: Market concentration of the largest 10-to-1,000 private equity funds
managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs accessing AIFMD passport
and sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions, end of 2020,
in % of NAV. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
Growth
Capital
33%
Mezzanine Capital
6%
Other
private
equity
45%
Venture
Capital
16%
Note: Investment strategies of private equity funds, end of 2020, in % of NAV.
Private equity funds managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs and
sub-threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions. Data for 28
EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
Asia
2%
EEA
72%
Other Europe
6%
North America
17%
Supra National
1%
Rest
2%
Note: Regional investment focus of private equity funds managed and/or
marketed by authorised AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only
in national jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Geo-focus determined
according to the domicile of investments, and the supranational category
including investments without a predominant geo-focus. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0% 50% 100%
Venture Capital
Other PE
Multi-strategy PE
Mezzanine Capital
Growth Capital
Retail investors Professional investors
Note: Clients of private equity funds managed and/or marketed by authorised
EU AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national
jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % of NAV. PE = Private equity fund. Data for 28
EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
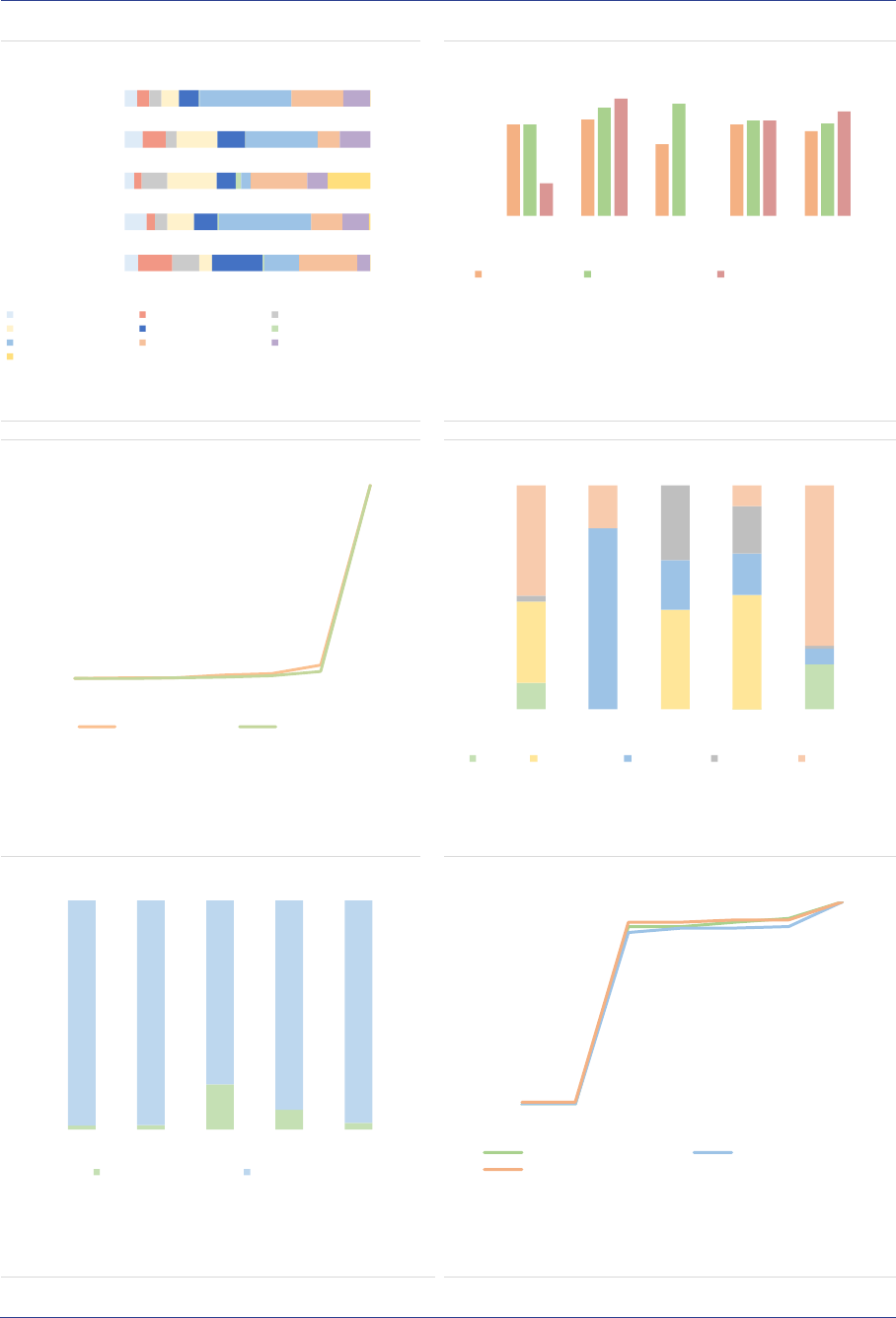
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 64
Liquidity and counterparty risk profile
ASR-AIF-S.101
ASR-AIF-S.102
Ownership of PE funds
Top five beneficial owners
ASR-AIF-S.103
ASR-AIF-S.104
Multi-strategy PE funds: liquidity profile
Redemption frequency
ASR-AIF-S.105
ASR-AIF-S.106
Redemption rights to investors
Liquidity financing
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100%
Venture Capital
Other PE
Multi-strategy PE
Mezzanine Capital
Growth Capital
Banks General government Household
Insurances Non-profit None
Other CIUs Oth. fin. institutions Pension funds
Unknown
Note: Ownership of units in private equity funds managed and/or marketed by
authorised EU AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. PE=Private equity fund. Data for
28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Growth
capital
Mezzanine
capital
Multi-
strategy
PEQF
Other
PEQF
Venture
capital
EU passport EU w/o passport Non-EU w/o passport
Note: Investor concentration of private equity funds managed and/or marketed by
authorised EU AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Investor concentration computed
as share of AIF equity beneficially owned by the 5 largest investors. PE=Private
equity fund. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
1%
1%
2%
7%
100%
2%
4%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day or
less
2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180 d 181-365
d
> 365 d
Investor Portfolio
Note: Portfolio and investor liquidity profiles of private equity funds managed
and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020. Portfolio liquidity defined
as the percentage of the funds’ assets capable of being liquidated within each
specified period, investor liquidit y defined as the shortest period for which
investors can redeem. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs
marketed, respectively, w/ and w/o passport. d=Days. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Growth
capital
Mezzanine
capital
Multi-
strategy
Other PE Venture
capital
Daily Weekly
to monthly
Quarterly Quarterly
to yearly
Other
Note: Investor redemption frequencies allowed by open-end private equity
funds managed and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of
NAV. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed,
respectively, w/ and w/o passport. PEQF=Private Equity Fund. Data for the
EEA30.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Growth
Capital
Mezzanine
Capital
Multi-
strategy
Other PE Venture
Capital
Open-end Closed-end
Note: Redemption rights provided in the ordinary course to investors in private
equity funds managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs, end of 2020, in
% of NAV. PE=Private equity fund.Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
85%
1
1%
90%
91%
100%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day 2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180
d
181-365
d
> 365 d
Growth Capital Mezzanine Capital
Venture Capital
Note: Liquidity financing of private equity funds managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs, end of 2020. Aggregate amount of borrowing and cash
financing divided depending on longest period for which creditors are
contractually committed to provide such financing, Borrowing and cash financing
include drawn and undrawn, committed and uncommitted lines of credit as well
as any term financing. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
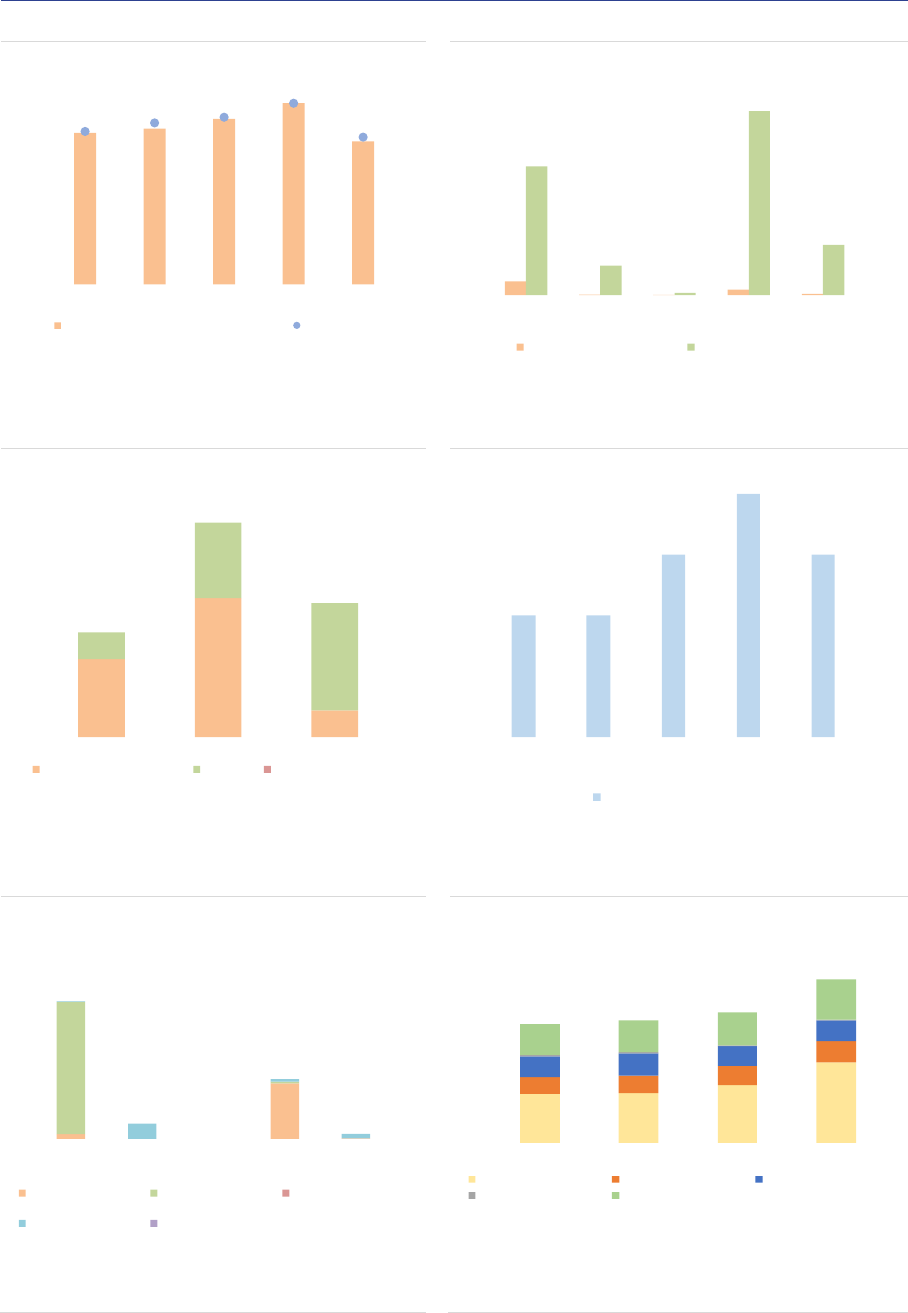
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 65
Leverage and exposure
ASR-AIF-S.107
ASR-AIF-S.108
Adjusted gross leverage
Adjusted gross leverage
ASR-AIF-S.109
ASR-AIF-S.110
Borrowing embedded in financial instruments
Unencumbered cash
ASR-AIF-S.111
ASR-AIF-S.112
Financial leverage
Total exposures
0%
30%
60%
90%
120%
Growth
capital
Mezzanine
capital
Multi-
strategy
Other PE Venture
capital
Median adjusted gross leverage AuM/NAV
Note: Adjusted gross leverage of private equity funds managed and/or marketed
by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Adjusted gross leverage
computed as total exposure less IRDs with respect to NAV. PE=Private equity
fund. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National competent authorities, ESMA.
0
35
70
105
140
Growth Mezzanine Multi-
strategy
Other PEQ Venture
Capital
Leveraged AIFs Unleveraged AIFs
Note: Leveraged and unleveraged private equity funds managed and/or
marketed by authorised EU AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered
only in national jurisdictions, end of 2019, EUR bn. Leveraged funds identified
using the AIF reporting code as specified in Annex 2 of ESMA guidelines on
AIFMD reporting obligations Data for 27 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Comptent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
2%
4%
6%
8%
10%
Growth Capital Mezzanine Capital Other PE
Cash and securities OTC Exchange-traded
Note: Borrowing of cash and securities or embedded in derivatives by private
equity funds, end of 2020, in % of total exposure. AIFs managed and/or
marketed by authorised AIFMs marketed. OTC and exchange-traded
deriatives net of margins. PE=Private equity fund. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
1%
2%
3%
4%
Growth
capital
Mezzanine
capital
Multi-
strategy
PE
Other
PE
Venture
Capital
Unencumbered cash
Note: Unencumbered cash held by private equity funds, end of 2020, in % of
NAV. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed,
respectively, w/ and w/o passport. PE=Private equity fund. Data for the
EEA30.
0%
4%
8%
Unsecured
borrowing
Secured
via PB
Reverse
repo
Secured
via other
Short
position
borrowing
sec.
Growth capital Mezzanine capital Multi
-strategy PEQF
Other PEQF Venture Capital
Note: Cash and securities borrowed by private equity funds, end of 2020, in %
of NAV. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed,
respectively, w/ and w/o passport. PEQF=Private Equity Fund. Data for the
EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD databse, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0
50
100
150
200
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Other PE Mezzanine Capital Venture Capital
Multi-strategy Growth Capital
Note: Exposure of private equity funds managed and/or marketed by authorised
AIFMs, funds quarterly reported, EUR tn. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by
authorised AIFMs marketed, respectively, w/ and w/o passport. PE=Private equity
fund. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
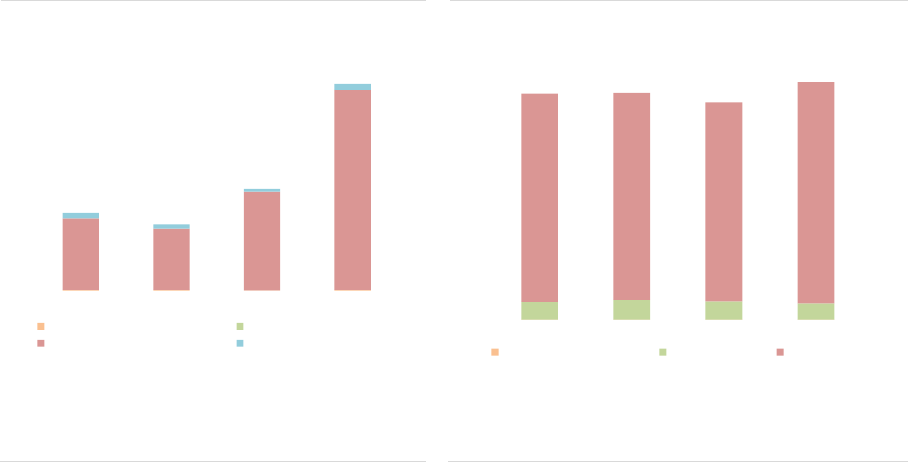
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 66
ASR-AIF-S.113
ASR-AIF-S.114
Cash and cash equivalents
Equities
0%
2%
4%
6%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Hundreds
Certificates of deposit Commercial papers
Other cash equivalent Other deposits
Note: Cash and cash equivalents exposure of private equity funds, AIFs
reported quarterly, in % of NAV. Government bonds excluded from other cash
equivalents. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
20%
40%
60%
80%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Hundreds
Listed financial inst. Other listed Unlisted
Note: Private equity funds' exposure to equity, AIFs reported quarterly, in % of
NAV. AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs. Data for 28
EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
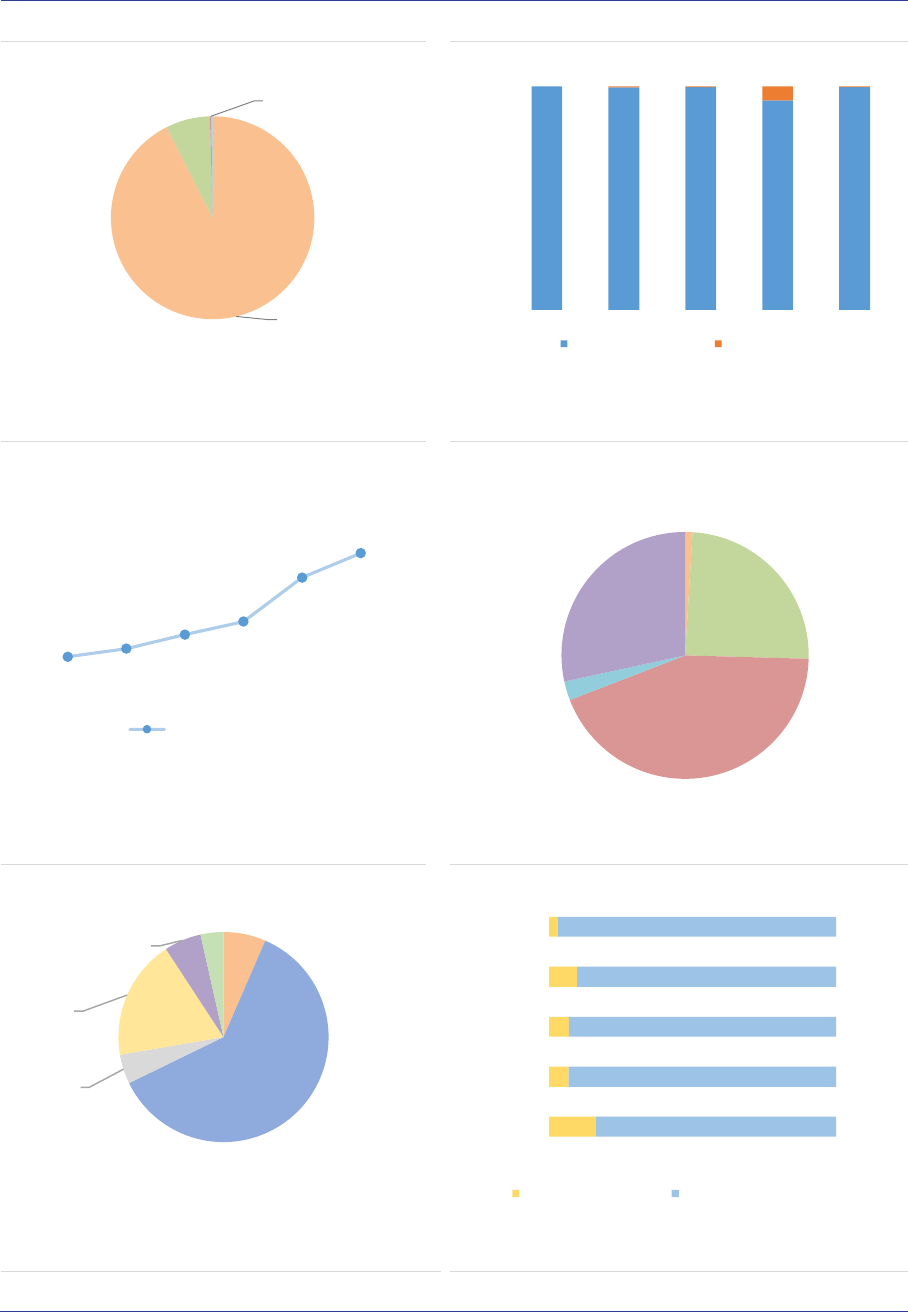
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 67
‘Other AIFs’
AIF characteristics
ASR-AIF-S.115
ASR-AIF-S.116
AIFMD passport
EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs
ASR-AIF-S.117
ASR-AIF-S.118
Market concentration
Investment strategy by NAV
ASR-AIF-S.119
ASR-AIF-S.120
Investment regions by NAV
Investor type
EU passport
93%
EU w/o
passport
7%
Non-EU w/o
passport
<1%
Note: NAV of AIFs classified as Other by manager's access to AIFMD
passport, end of 2020, in %. Authorised EEA30 AIFMs with access to AIFMD
passport or marketing non-EEA30 AIFs w/o passport, sub-threshold
managers registered only in national juridisdictions w/o passporting rights.
Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Commodity Equity Fixed
income
Infrastructure Other
EEA30 Non-EEA30
Note: Share of EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national
jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % on NAV. Non-EEA30 AIFs marketed w/o
passport. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0
25
50
75
100
top 10 top 20 top 50 top 100 top 500 top 1,000
Market concentration
Note: Market concentration of the largest 10-to-1,000 AIFs classified as Other
managed and/or marketed by authorised EU and sub-threshold managers
registered only in national jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Data for 28 EEA
countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
Commodity
1%
Equity
24%
Fixed
income
44%
Infrastructure
3%
Other
28%
Note: Investment strategies of AIFs classified as Other, end of 2020, in % of
NAV. AIFs managed and/or marketed by full scope EU AIFMs and sub-
threshold managers registered only in national jurisdictions. Data for 28 EEA
countries.
Sources: National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
Asia
6%
EEA
61%
Other
Europe
5%
North
America
18%
Supra National
6%
Rest
4%
Note: Regional investment focus of EU AIFs classified as Other, managed
and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs and sub-threshold managers
registered only in national jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Geo-focus
determined according to the domicile of investments and the supranational
category including investments without a predominant geo-focus. Data for the
EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0% 50% 100%
Other
Infrastructure
Fixed income
Equity
Commodity
Retail investors Professional investors
Note: Clients of AIFs classified as Other AIFs managed and/or marketed by
authorised EU AIFMs and sub-threshold managers registered only in national
jurisdictions, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD databse, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
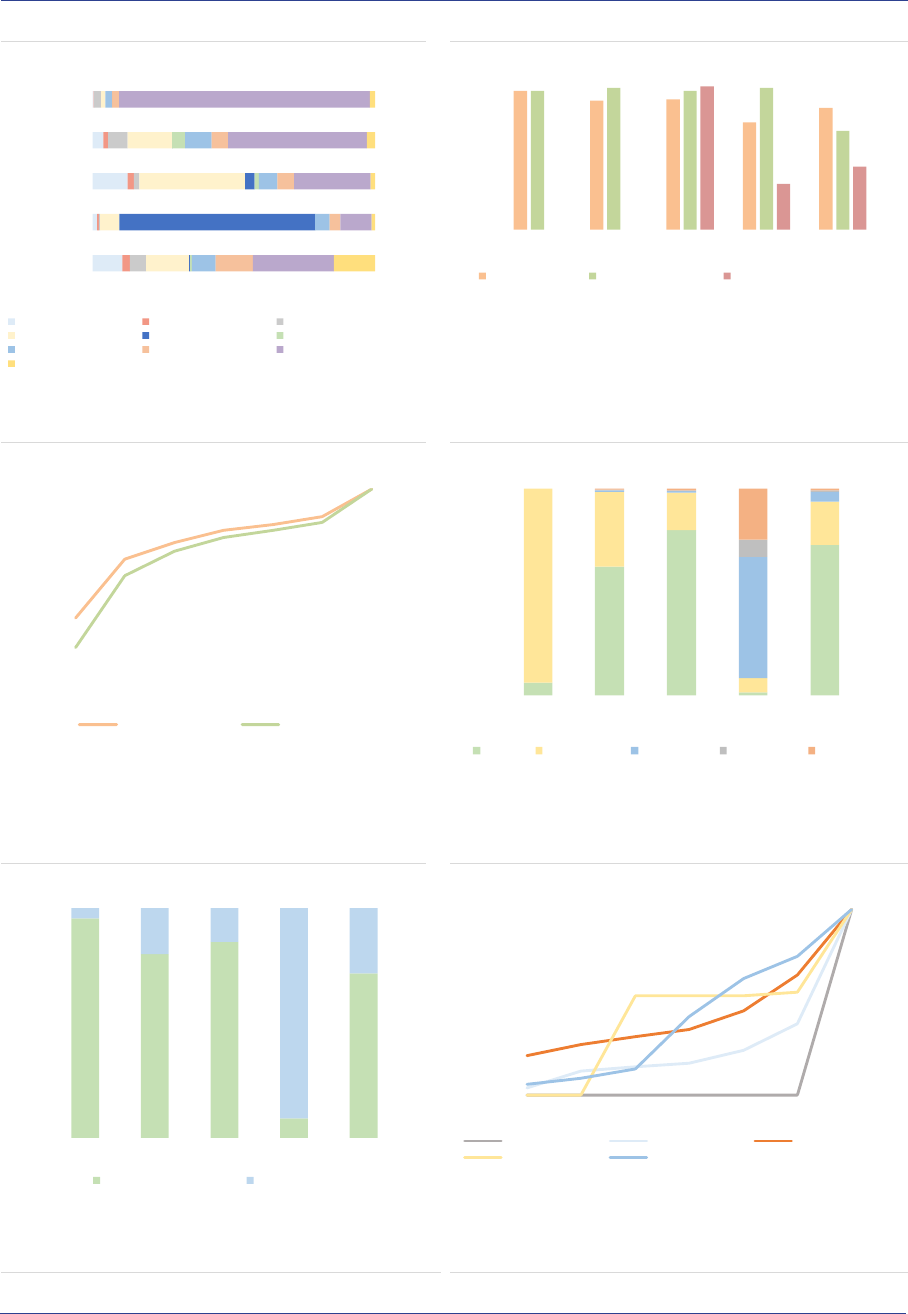
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 68
Liquidity and counterparty risk profile
ASR-AIF-S.121
ASR-AIF-S.122
Ownership of ‘other AIFs’
Top five beneficial owners
ASR-AIF-S.123
ASR-AIF-S.124
Other: liquidity profile
Redemption frequencies
ASR-AIF-S.125
ASR-AIF-S.126
Redemption rights to investors
Liquidity financing
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100%
Other
Infrastructure
Fixed income
Equity
Commodity
Banks General gov. Households
Insurances Non-profit None
Oth. CIUs Oth. fin. institutions Pension funds
Unknown
Note: Ownership of units in AIFs classified as Other AIFs managed and/or
marketed by authorised EU AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. CIUs=Collective
investment undertakings. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Commodity Equity Fixed
income
Infra-
structure
Other fund
EU passport EU w/o passport Non-EU w/o passport
Note: Investor concentration of AIFs classified as Other managed and/or marketed
by authorised EU AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Investor concentration
computed as share of AIF equity beneficially owned by the 5 largest investors. Data
for 28 EEA countries..
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
33%
63%
72%
78%
82%
100%
18%
55%
68%
75%
79%
83%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day or
less
2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180 d 181-365
d
> 365 d
Investor Portfolio
Note: Portfolio and investor liquidity profiles of AIFs classified as Other
managed and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020. Portfolio
liquidity defined as the percentage of the funds’ assets capable of being
liquidated within each specified period, investor liquidity defined as the
shortest period for which investors can redeem. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs
by authorised AIFMs marketed, respectively, w/ and w/o passport. d=Days.
Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Commodity Equity Fixed
income
Infra-
structure
Other
funds
Daily Weekly
to monthly
Quarterly Quarterly
to yearly
Other
Note: Investor redemption frequencies allowed byopen-end AIFs classified as
Othe rmanaged and/or marketed by authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of
NAV. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised EU AIFMs marketed,
respectively, w/ and w/o passport. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
Commodity Equity Fixed
income
Infra-
structure
Other
funds
Open-end Closed-end
Note: Redemption rights provided in the ordinary course to investors in AIFs
classified as Other managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs, end
of 2020, in % of NAV. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
100%
22%
100%
1%
54%
56%
100%
7%
100%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day 2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180 d 181-365
d
> 365 d
Commodity Equity Fixed income
Infrastructure Other
Note: Liquidity financing of AIFs classified as Other managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs, end of 2020. Aggregate amount of borrowing and cash financing
divided depending on longest period for which creditors are contractually committed
to provide such financing, Borrowing and cash financing include drawn and undrawn,
committed and uncommitted lines of credit as well as any term financing. Data for the
EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
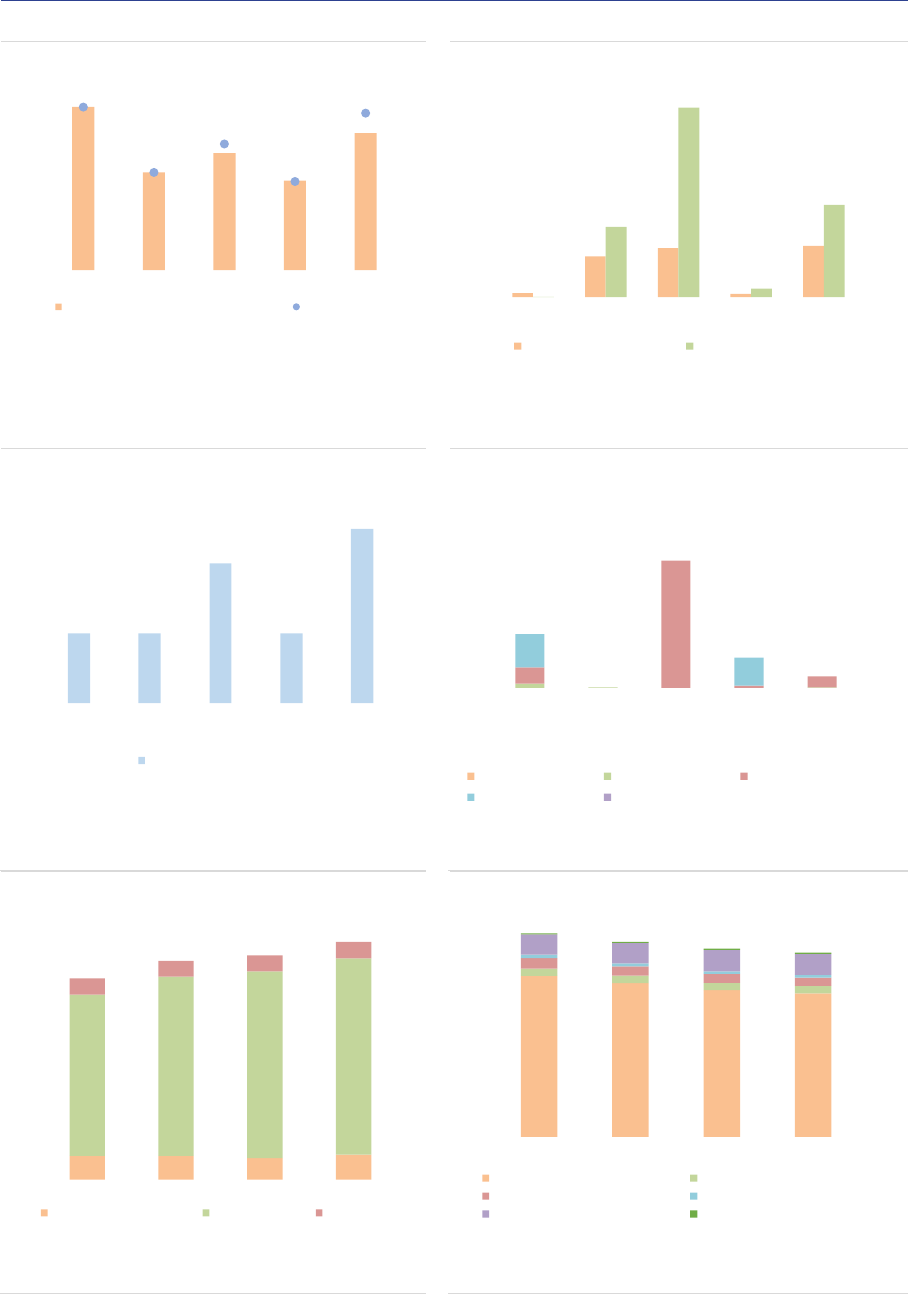
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 69
Leverage and exposure
ASR-AIF-S.127
ASR-AIF-S.128
Adjusted gross leverage
Leveraged and unleveraged AIFs
ASR-AIF-S.129
ASR-AIF-S.130
Unencumbered cash
Financial leverage
ASR-AIF-S.131
ASR-AIF-S.132
Equities
Sovereign bonds
0%
40%
80%
120%
160%
200%
Commodity Equity Fixed
income
Infra-
structure
Other funds
Median adjusted gross leverage AuM/NAV
Note: Adjusted gross leverage of funds of funds managed and/or marketed by
authorised AIFMs, end of 2020, in % of NAV. Adjusted gross leverage computed as
total exposure less IRDs with respect to NAV. FoF= Funds of funds, PE=Private
equity fund, HF=Hedge fund. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National competent authorities, ESMA.
0
350
700
1050
1400
Commodity Equity Fixed
income
Infra-
structure
Other
Leveraged AIFs Unleveraged AIFs
Note: Leveraged and unleveraged of AIFs classified as Other and managed
and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs and sub-threshold managers
registered only in national jurisdictions, end of 2019, Leveraged funds
identified using the AIF reporting code as specified in Annex 2 of ESMA
guidelines on AIFMD reporting obligations Data for 27 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Comptent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
2%
4%
6%
Commodity Equity Fixed
income
Infra-
structure
Other
funds
Unencumbered cash
Note: Unencumbered cash held by AIFs classified as Other, end of 2020, in %
of NAV. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed,
respectively, w/ and w/o passport. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
1%
2%
3%
Unsecured
borrowing
Secured
via PB
Reverse
repo
Secured
via other
Short
position
borrowing
sec.
Commodity Fund Equity fund Fixed income fund
Infrastructure fund
Note: Cash and securities borrowed by AIFs classified as Other, end of 2020,
in % of NAV. EEA30 and non-EEA30 AIFs by authorised AIFMs marketed,
respectively, w/ and w/o passport. Data for the EEA30.
Sources: AIFMD databse, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
5%
10%
15%
20%
25%
30%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Hundreds
Listed financial inst. Other listed Unlisted
Note: Exposure to equity of funds classified as Other, AIFs reported quarterly,
in % of NAV. AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised EU AIFMs. Data
for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
6%
12%
18%
24%
30%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
EU Sov >1Y TM EU Sov up 1Y TM
G10 Sov >1Y TM G10 Sov up 1Y TM
Non-G10 Sov >1Y TM Non-G10 Sov up 1Y TM
Note: Sovereign bonds exposure exposure of classified as Other, AIFs
reported quarterly, in % of NAV. AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised
EU AIFMs. Sov=Sovereign bonds, TM=Time to Maturity. Data for 28 EEA
countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
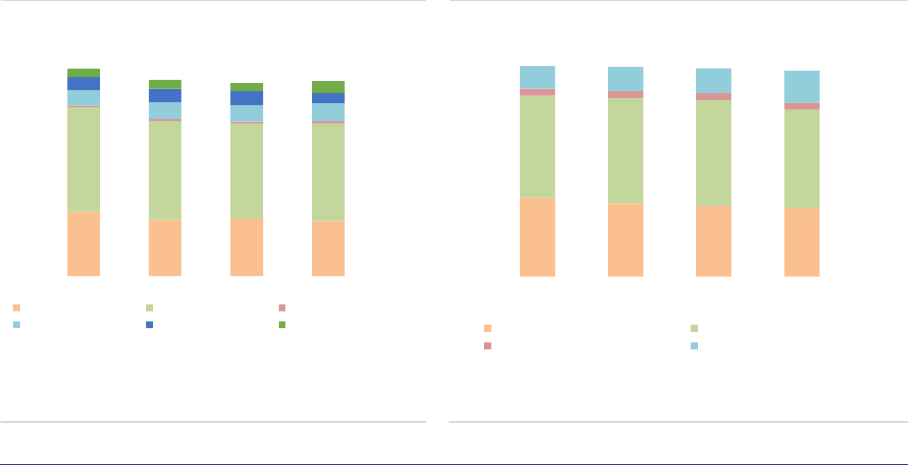
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 70
ASR-AIF-S.133
ASR-AIF-S.134
Collective investment undertakings
Corporate bond quality:
0%
5%
10%
15%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Hundreds
CIUs by the AIFM CIUs by others ETF by the AIFM
ETF by others MMFs by the AIFM MMFs by others
Note: Collective investment undertakings exposure of funds classified as
Other, AIFs reported quarterly, in % of NAV. AIFs managed and/or marketed
by authorised EU AIFMs. CIUs=Collective Investment Undertakings. Data for
28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
7%
14%
21%
28%
1Q20 2Q20 3Q20 4Q20
Hundreds
IG by fin. inst. IG by non-fin. inst.
Non-IG by fin. inst. Non-IG by non-fin. inst.
Note: Corporate bonds exposure of funds classified as Other, AIFs reported
quarterly, in % of NAV. AIFs managed and/or marketed by authorised EU
AIFMs. Data for 28 EEA countries.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
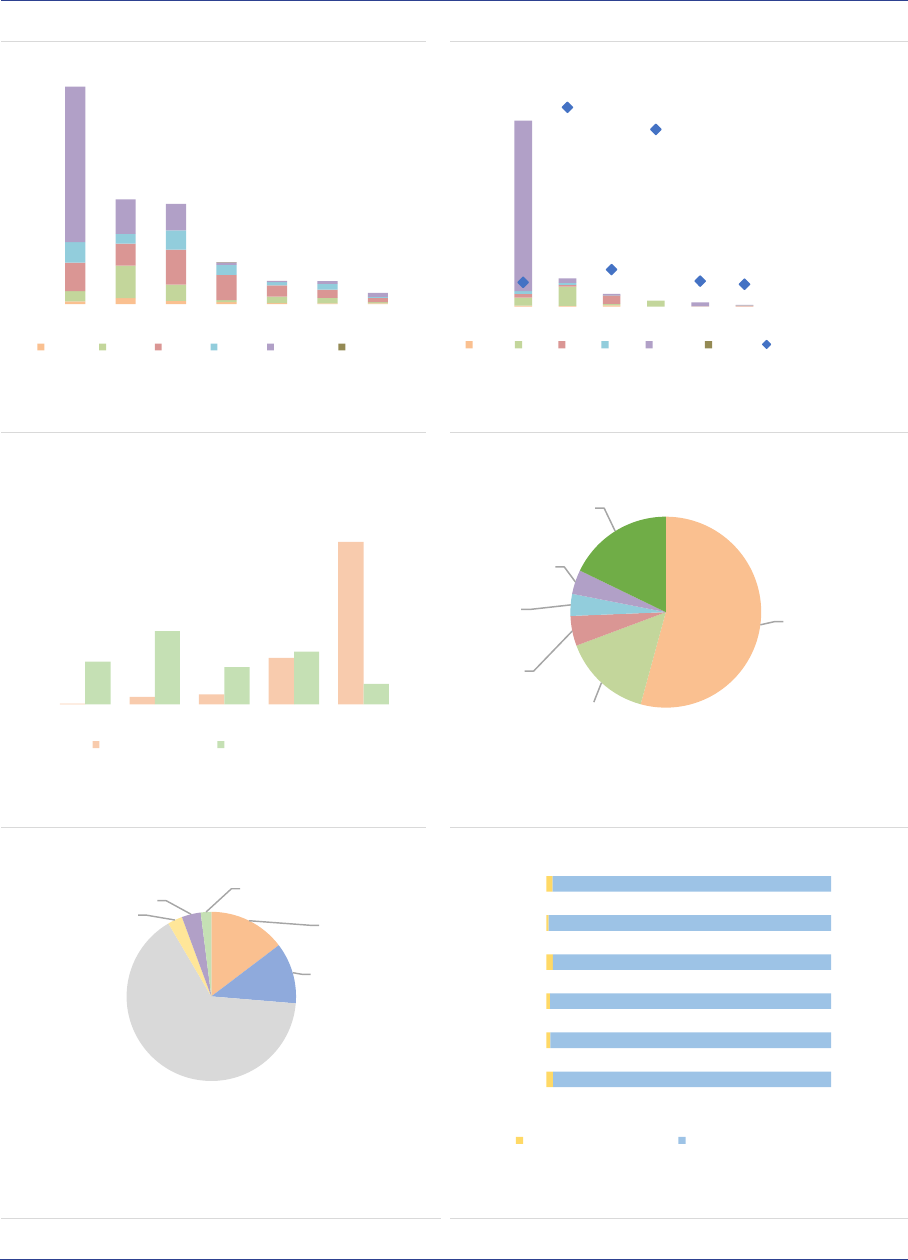
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 71
Non-EU AIFs (NPPR)
AIF characteristics
ASR-AIF-S.135
ASR-AIF-S.136
EU jurisdictions
Non-EU AIFs’ domicile
ASR-AIF-S.137
ASR-AIF-S.138
AIF distribution by size
Investment strategy by NAV
ASR-AIF-S.139
ASR-AIF-S.140
Investment regions by NAV
Investor type
0
400
800
1,200
FI IE LU DE BE NO Other
FoF HF PE RE Other None
Note: NAV by authorising EEA30 country of AIFs marketed by non-EEA30
AIFMs w/o passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2020, in EUR bn.
AIFs identified via international standard identifiers (LEIs, ISIN, Cusip).
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
200%
400%
600%
800%
1000%
0
200
400
600
800
1,000
1,200
US KY GG VI CH UK
FoF HF PE RE Other None Leverage (rhs)
Note: NAV by domicile of AIFs marketed by non-EEA30 AIFMs w/o
passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2020, in EUR bn. AIFs identified
via international standard identifiers (LEIs, ISIN, Cusip). in EUR bn.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
<100mn 100-
500mn
500mn-
1bn
1-5bn >5bn
NAV Number of AIFs
Note: Share of AIFs marketed by non-EEA30 AIFMs w/o passporting rights
(art. 42 of AIFMD) by size, end of 2020. In %. AIFs identified via international
standard identifiers (LEI, ISIN, Cusip).
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
Equity
54%
Fixed
income
15%
Other HF
5%
Other PE
4%
Other fund
4%
Remaining
strategies
18%
Note: Investment strategies of AIFs marketed by non-EEA30 AIFMs w/o
passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2020, in % of NAV. AIFs
identified via international standard identifiers (LEIs, ISIN, Cusip).
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
Asia
15%
EEA
12%
North
America
65%
Other
Europe
3%
Rest
3%
Supra National
2%
Note: Regional investment focus of AIFs marketed by non-EEA30 AIFMs w/o
passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2020, in EUR bn. AIFs identified
via international standard identifiers (LEIs, ISIN, Cusip). in EUR bn. Geo-focus
determined according to the domicile of investments, supra national category
including investments without predominant geo-focus.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0% 50% 100%
FoF
Hedge fund
Private equity
Real estate
Other AIF
Total NPPR
Retail investors Professional investors
Note: Clients of AIFs marketed by non-EEA30 AIFMs w/o passporting rights
(art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2209, in % of NAV. AIFs identified via international
standard identifiers (LEIs, ISIN, Cusip). FoF=Fund of Funds
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
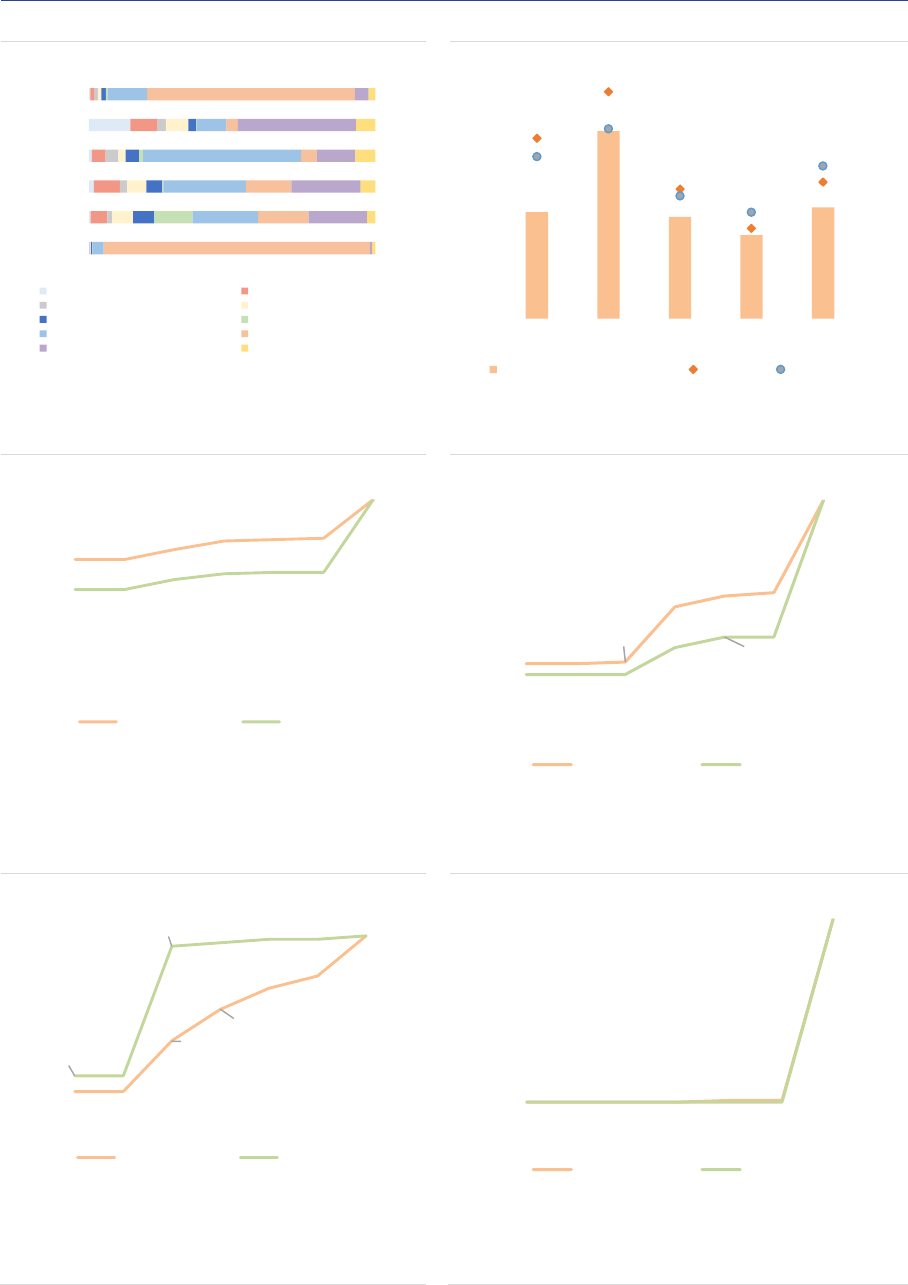
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 72
Liquidity and counterparty risk profile
ASR-AIF-S.141
ASR-AIF-S.142
Ownership of ‘other AIFs’
Top five beneficial owners
ASR-AIF-S.143
ASR-AIF-S.144
Non-EU AIFs: Liquidity profile
Non-EU FoFs: Liquidity profile
ASR-AIF-S.145
ASR-AIF-S.146
Non-EU HFs: Liquidity profile
Non-EU PE funds: Liquidity profiles
0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100%
Other AIFs
RE
PE
HF
FoF
Total 2020
Banks General gov.
Households Insurances
Non-profit None
Oth. CIU Oth. fin. institutions
Pension funds Unknown
Note: Ownership of units in AIFs marketed by non-EEA30 AIFMs w/o
passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2020, in % of NAV. AIFs
identified via international standard identifiers (LEIs, ISIN, Cusip). FoF=Fund
of Funds;
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
FoF Hedge
fund
Private
equity
Real estate Other AIF
Top 5 beneficial investors Median Average
Note: Investor concentration of AIFs marketed by non-EEA30 AIFMs w/o
passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2020, in % of NAV. Investor
concentration computed as share of AIF equity beneficially owned by the 5
largest investors. FoF=Fund of funds.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
58%
65%
71%
72%
73%
100%
37%
44%
48%
49%
49%
-25%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 d or
less
2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180 d 181-365
d
> 365 d
Investor Portfolio
Note: Portfolio and investors liquidity profiles of AIFs marketed by non-EEA30
AIFMs w/o passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2020. AIFs identified
via international standard identifiers (LEIs, ISIN, Cusip). Portfolio liquidity
defined as the percentage of the funds’ assets capable of being liquidated
within each specified period, investor liquidity defined as the shortest period
for which investors can redeem. d= Days.
8%
8%
9%
40%
46%
48%
100%
2% 2%
2%
17%
23%
23%
-25%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 d or
less
2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180
d
181-365
d
> 365 d
Investor Portfolio
Note: Portfolio and investors liquidity profiles of funds of funds marketed by
non-EEA30 AIFMs w/o passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2020.
AIFs iAIFs identified via international standard identifiers (LEIs, ISIN, Cusip).
Portfolio liquidity defined as the percentage of the funds’ assets capable of
being liquidated within each specified period, investor liquidity defined as the
shortest period for which investors can redeem. d= Days.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
11%
11%
40%
58%
70%
77%
100%
20%
20%
94%
96%
98%
98%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 day or
less
2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180
d
181-365
d
> 365 d
Investor Portfolio
Note: Portfolio and investors liquidity profiles of hedge funds marketed by
non-EEA30 AIFMs w/o passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2020.
AIFs identified via international standard identifiers (LEIs, ISIN, Cusip).
Portfolio liquidity defined as the percentage of the funds’ assets capable of
being liquidated within each specified period, investor liquidity defined as the
shortest period for which investors can redeem. d= Days.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
0% 0%
0%
1%
100%
0%
0%
-10%
15%
40%
65%
90%
1 d or
less
2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180
d
181-365
d
> 365 d
Investor Portfolio
Note: Portfolio and investors liquidity profiles of private equity funds marketed
by non-EEA30 AIFMs w/o passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2020.
AIFs identified via international standard identifiers (LEIs, ISIN, Cusip).
Portfolio liquidity defined as the percentage of the funds’ assets capable of
being liquidated within each specified period, investor liquidity defined as the
shortest period for which investors can redeem. d= Days.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.

ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 73
ASR-AIF-S.147d
ASR-AIF-S.148
Non-EU RE funds: Liquidity profiles
Non-EU AIFs classified as Other: Liquidity profile
ASR-AIF-S.149
ASR-AIF-S.150
Redemption frequencies
Redemption rights to investors
Leverage and exposure
ASR-AIF-S.151
ASR-AIF-S.152
Adjusted gross leverage
Financial leverage
0%
0% 0%
17%
21%
24%
100%
0%
16%
17%
17%
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
1 d or
less
2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180
d
181-365
d
> 365 d
Investor Portfolio
Note: Portfolio and investors liquidity profiles of real estate funds marketed by
non-EEA30 AIFMs w/o passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2020.
AIFs identified via international standard identifiers (LEIs, ISIN, Cusip).
Portfolio liquidity defined as the percentage of the funds’ assets capable of
being liquidated within each specified period, investor liquidity defined as the
shortest period for which investors can redeem. d= Days.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
95% 95%
97%
98%
98%
99%
100%
90%
91%
95% 96%
96%
96%
-10%
12%
34%
56%
78%
100%
1 d or
less
2-7 d 8-30 d 31-90 d 91-180 d 181-365
d
> 365 d
Investor Portfolio
Note: Portfolio and investors liquidity profiles of AIFs classified as Other
marketed by non-EEA30 AIFMs w/o passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD), end
of 2020. AIFs identified via international standard identifiers (LEIs, ISIN,
Cusip). Portfolio liquidity defined as the percentage of the funds’ assets
capable of being liquidated within each specified period, investor liquidity
defined as the shortest period for which investors can redeem. d= Days.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
FoF Hedge fund Private
equity
Real estate Other AIF
Daily Weekly
to monthly
Quarterly Quarterly
to yearly
Other
Note: Investor redemption frequencies allowed by open-end AIFs marketed by
non-EEA30 AIFMs w/o passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2020, in
% of NAV. AIFs identified via international standard identifiers (LEIs, ISIN,
Cusip).
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
FoF Hedge fund Private
equity
Real estate Other AIF
Closed-end Open-end
Note: Redemption rights provided in the ordinary course to investors in AIFs
marketed by non-EEA30 AIFMs w/o passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD),
end of 2020, in % of NAV. AIFs identified via international standard identifiers
(LEIs, ISIN, Cusip). FoF=Fund of funds, None=No predominant type.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
200%
400%
600%
800%
1000%
0%
200%
400%
600%
FoF Hedge
fund
Private
equity
Real
estate
Other AIF
Adjusted gross leverage AuM/NAV (rhs)
Note: Adjusted gross leverage of AIFs AIFs marketed by non-EEA30 AIFMs
w/o passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD), end of 2020, in % of NAV. Adjusted
gross leverage does not include IRDs. FoF= Fund of funds,
Sources: AIFMD database, National competent authorities, ESMA.
0%
40%
80%
120%
160%
FoF Hedge
fund
Private
equity
Real estate Other AIF
Short position borrowing sec. Secured via other
Reverse repo Secured via PB
Unsecured borrowing
Note: Cash and securities borrowed, end of 2020, in % of NAV. marketed by
non-EEA30 AIFMs w/o passporting rights (art. 42 of AIFMD) in EUR bn. AIFs
identified via international standard identifiers (LEIs, ISIN, Cusip
FoF=Funds of Funds,
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.

ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 74
ASR-AIF-S.153
ASR-AIF-S.154
Unencumbered cash
Decomposition of exposures
0%
8%
16%
24%
FoF Hedge fund Private
equity
Real estate Other AIF
Unencumbered cash
Note: Unencumbered cash, end of 2020, in % of NAV. EEA30 and non-
EEA30 AIFs by authorised EU AIFMs marketed, respectively, w/ and w/o
passport. FoF=Fund of funds, None=No predominant type.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
0%
25%
50%
75%
100%
FoF Hedge fund Private
equity
Real estate Other AIF
Securities CIUs Physical assets
IRDs FX CDS
Other derivatives
Note: Share of gross exposures by AIF type, end of 2020, in % of total. AIFs
managed and/or marketed by authorised EEA30 AIFMs. FoF=Fund of funds,
None=No predominant type.
Sources: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 75
Annex

ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 76
EU AIFMD data reporting
Scope of ESMA AIF reporting
This report is based on data submitted by
National Competent Authorities (NCAs) to
ESMA, covering authorised EU and sub-
threshold AIFMs on behalf of the AIFs they
manage. Data for products marketed by non-
EU AIFMs under the ART 42 AIFMD (NPPR)
are described in the specific section ‘Non-EU
AIFs’ (see page 36). The EU data does not
include the UK anymore since this jurisdiction
was not part of the EU in 2021, when data were
transmitted to ESMA. Historical data for the EU
before that date exclude the UK to maintain the
same sample of countries over time.
The data are based on reports transmitted to
ESMA by 28 NCAs. Around 34,010 reports of
EU AIFs were transmitted to ESMA. Of those
reports, we excluded around 2,250 nil reports
(empty reports sent by new AIFs) and 1,690
feeder funds to avoid double counting. The final
sample is composed of around 30,035 AIFs.
15
The report relies on a set of risk indicators, a
subset of the data provided under the AIFMD.
The risk indicators were chosen based on their
relevance for risk analysis and the quality of the
data.
16
Looking forward, ongoing cooperation
with NCAs should allow ESMA to improve the
set of risk indicators in future editions.
Data quality
AIFMD reporting obligations cover a wide range
of indicators with different degrees of
complexity in their calculation. Some very
important indicators, such as leverage reported
by AIFs, even if data quality improved, cannot
be used at this stage owing to data-quality
issues. A variety of reporting errors (formatting,
monetary values instead of percentages, etc.)
prevent us from using the reported leverage
indicators. Some other indicators are not
always mandatory and may not be requested at
national level (e.g., the redemption frequency
for open-ended AIFs), which makes the use of
aggregate data more difficult. In this report,
when the data used for the analysis are based
on a subset of our sample, this is specified. A
detailed inventory of analysed data and
15
A description of the defined reference sample of AIFs
used in the analysis is available in the Annex.
indicators is provided in the inventory section at
the end of the report.
Definition of terms
Under the AIFMD, some concepts have a
different meaning from that commonly used in
the industry. For clarification a glossary is
provided at the end of the report. The main
concepts used are the following:
— Regulatory AuM: Value of all assets in a
portfolio, including all assets acquired
through use of leverage (borrowing of cash
or securities and leverage embedded in
derivative positions). This meaning of AuM
is different from the typical meaning of
AuM in the industry, which relates to the
assets on the balance sheet of the AIF
based on a mark-to-market valuation.
— NAV: The net value of the assets of the
AIF (as opposed to the NAV per unit or
proportion of the AIF). The NAV is equal to
the unit shares of the AIF, i.e. the money
placed in the AIF by investors, which
corresponds to the concept of total net
assets sometimes used in the industry.
— Leverage: In this report, leverage is
measured by the ratio of regulatory AuM to
NAV.
— Adjusted leverage: This measure
excludes IRDs from the computation of
leverage, following the approach used in
the previous reports (ESMA, 2019 and
2020). Indeed, the use of IRDs tends to
inflate leverage measures, since IRDs are
measured using notional amount (rather
than adjusted by duration as done under
the commitment approach).
AIF reference sample
AIF-specific information should be reported at
the level of the compartments or sub-funds
when the AIF takes the form of an umbrella
fund.
16
The data inventory on page 76 summarises the
coverage of each indicator used in this report.

ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 77
ESMA Guidelines
17
specify that AIFMs and
AIFs that have commenced have to start
reporting from the first day of the calendar
quarter following authorisation or registration.
AIFMs and AIFs that have not started any
activity must still report a nil return to the home
competent authority. Relatedly, AIFMs have to
provide a report upon liquidation of the AIFs
they manage.
Each AIF managed within the scope of the
Directive must have only one AIFM, responsible
for compliance with the requirements of the
AIFMD. For this reason, the inclusion in the
analysis of products marketed by non-EU sub-
threshold managers does not introduce any
bias or create double counting of entities, as
their AIFs cannot be passported.
As of 12 November 2020, NCAs have gathered
and made available to ESMA 34,010 reports for
the end of 2020 of AIFs managed and/or
marketed by authorised EU and sub-threshold
AIFMs. Of the initial data intake, around 2,250
AIFs reported a nil return. The definition of the
AIFs’ reference sample for the analysis requires
further data cleaning operations and
consistency checks (ASR-AIF.111).
The final reference sample is constituted by
30,035 AIFs. Overall, 81% of them are
managed by full-scope AIFMs benefiting from
the EU passport. The final sample includes 510
AIFs without a predominant type (i.e. reported
as ‘None’).
Feeder funds are excluded from analysis to
avoid any double counting of assets (ASR-
AIF.112).
ASR-AIF.111
Data cleaning
Definition of the AIF reference sample
A series of preliminary operations are performed to define the
sample of analysed AIFs and their characteristics. These
include the following:
— Exclusion of reports that are not workable.
As for AIFMs, AIFs’ reports may indicate that there is no
information to be reported for the specified reporting
period (nil return). Firms also have the opportunity to
cancel previously submitted erroneous reports or amend
existing ones. For this reason, multiple amended reports
by the same fund for the same reporting period have to
be detected so that the data can be properly
consolidated.
— Identification of feeder and master AIFs
— Identification of each AIFM jurisdiction and managed
and/o marketed AIFs domicile
17
Link to the Guidelines on reporting obligations under
Articles 3(3)(d) and 24(1), (2) and (4) of the AIFMD:
https://www.esma.europa.eu/sites/default/files/library/2
015/11/2014-869.pdf
ASR-AIF.112
Feeder AIFs
Prevalence of EU master-feeder AIFs
Feeder AIFs
EU
Non-EU
Total
AIFs filing
with EU master
895
49
944
without EU master
722
25
747
Total
1,617
74
1,691
NAV (EUR bn)
with EU master
127.5
4.5
132
without EU master
89.3
2.2
91.5
Total
216.7
6.9
2223.6
Note: Number and NAV of feeder AIFs by domicile, end of 2020.
Source: AIFMD database, National Competent Authorities, ESMA.
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 78
Data inventory
Indicator
Description and reporting guidelines
Reporting
content
Reporting
items
Technical
guidance
Data availability
Investment
regions
Geographical breakdown of the
investments held by the AIF by
percentage of the total NAV of the AIF.
See: ESMA guidelines, point 83; Q&As
Section III, 4 and 73.
3(3)(d)- and
24(1)
78-85
Mandatory
(all AIFs)
Total
100%
FoF
100%
HF
100%
PE
100%
RE
100%
OTH
100%
Top five
beneficial
owners
NAV held by the five beneficial owners
that have the largest equity interests in
the AIF.
See: ESMA guidelines, point 100.
Note: 11% of AIFs (sold mostly to retail
investors), report 0.
3(3)(d) and
24(1)
118
Mandatory
(all AIFs)
Total
100%
FoF
100%
HF
100%
PE
100%
RE
100%
OTH
100%
Clients
Investor concentration for retail and
professional investors.
See: ESMA guidelines, point 101; Q&As
Section III, 80.
3(3)(d) and
24(1)
119-120
Mandatory
(all AIFs)
Total
99%
FoF
99%
HF
99%
PE
99%
RE
100%
OTH
98%
Ownership
Ownership of units in the AIF beneficially
owned by investor type.
See: ESMA guidelines, point 123 and
Annex II.
24(2)
208-209
Mandatory
(all AIFs)
Total
98%
FoF
99%
HF
99%
PE
94%
RE
97%
OTH
99%
Redemption
frequencies
Frequency of investor redemptions. In
case of multiple classes of shares or
units, the largest share class by NAV shall
be considered.
See: ESMA guidelines, point 121 and
Annex II.
24(2)
194
Optional
(AIFs must
report if
information is
available)
Total
98%
FoF
98%
HF
99%
PE
97%
RE
96%
OTH
99%
Liquidity profile –
Portfolio
Portfolio liquidity profile.
See: ESMA guidelines, points 118-120;
Q&As Section III, 10, 11, 42 and 78.
24(2)
178-184,
186-192
Mandatory
(all AIFs
reporting
under
Article 24(2))
Total
90%
FoF
93%
HF
95%
PE
88%
RE
87%
OTH
92%
Liquidity profile –
Investor
Investor liquidity profiles.
See: ESMA guidelines, points 118-120;
Q&As Section III, 10, 11, 42 and 78.
24(2)
178-184,
186-192
Mandatory
(all AIFs
reporting
under
Article 24(2))
Total
89%
FoF
92%
HF
93%
PE
66%
RE
82%
OTH
92%
Liquidity
financing
Total financing amount by the longest
period during which the creditor is
contractually committed to providing such
financing.
See: Q&As Section III, 2, 67
24(2)
211-217
Optional
(AIFs must
report if
information is
available)
Total
26%
FoF
18%
HF
23%
PE
32%
RE
38%
OTH
26%
Unencumbered
cash
Value of unencumbered cash.
24(2)
185
Optional
(AIFs must
report if
information is
available)
Total
90%
FoF
93%
HF
94%
PE
77%
RE
87%
OTH
92%
Financial
leverage
Leverage created by direct borrowing of
money or securities from counterparties.
See: ESMA guidelines, point 124; Q&As
Section III, 34, 44 and 69.
24(2) and
24(4)
283-286,
289
Optional
(AIFs must
report if
information is
available)
Total EU
43%
FoF
47%
HF
46%
PE
20%
RE
35%
OTH
47%
Note: Main indicators and reporting template items analysed in the report. Relative coverage defined as the ratio of the total number of AIFs reporting
it to the number of AIFs expected to report it. Optional items filled only when information is applicable.

ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 79
Glossary
Alternative Investment Fund (AIF): An AIF is a collective investment undertaking, including
investment compartments of such an undertaking, that raises capital to invest it in accordance with a
defined investment policy for the benefit of investors. An AIF does not include an undertaking that
requires authorisation under the UCITS directive.
Alternative Investment Fund Manager (AIFM): An AIFM is an entity that provides portfolio-
management and risk-management services to one or more AIFs as its regular business, irrespective
of where the AIFs are located or what legal form the AIFM takes.
AIFMD passport: The AIFMD passport allows AIFMs to manage or market AIFs across the EU, on the
basis of a single authorisation in one EU Member State. Currently, only EU-authorised AIFMs managing
or marketing EU-domiciled AIFs have access to the passport.
Assets under management (AuM): Under the AIFMD, AuM are defined as the value of all assets in a
portfolio, including all assets acquired through the use of leverage (borrowing of cash or securities and
leverage embedded in derivative positions). This concept of AuM is different from the industry approach
to AuM, which typically relates to the assets of the balance sheet of the AIF.
Authorised Alternative Investment Fund Manager (AIFM): Authorised AIFMs are subject to more
stringent requirements than registered AIFMs and can manage or market their AIFs across the EU.
Commitment leverage: Ratio of exposures to the NAV, where exposures are computed using the
commitment approach, which takes into account netting and hedging, and adjusts IRDs by duration.
Financial leverage: The ratio of total assets to equity (NAV for funds), also called balance-sheet
leverage. Financial leverage involves outright borrowing and is defined as the ratio of total assets to
equity (or NAV for funds), in percentage. It can be measured by aggregating unsecured cash borrowing,
the value of securities borrowed for short positions, collateralised/secured cash borrowing via prime
broker, reverse repo or by other means.
Gross exposure: The absolute sum of all portfolio’s positions, long and short. It includes gross notional
value for derivatives. This measure provides a complete appreciation of all the leverage that is
employed by a fund to gain market exposure.
Gross leverage: Leverage computed under the gross method, as indicated in Commission Delegated
Regulation (EU) No 231/2013. It is expressed as the proportion of total gross exposure to NAV, in
percentage. Under the gross method, exposures are calculated as the absolute value of all positions in
the portfolio by including all assets and liabilities, relevant borrowings, derivatives (converted into their
equivalent underlying positions) and all other positions, even those held purely for risk-reduction
purposes. Cash held in the base currency of the AIF is excluded.
Interest rate derivatives (IRDs): Under the AIFMD reporting requirements, IRDs exposures are
reported as the total gross notional value of the AIF’s outstanding IRD contracts, including the total
notional value of futures and the delta-adjusted notional value of options. For the purpose of computing
the commitment leverage, IRDs are adjusted for duration.
Leverage: Ratio of fund market exposures to NAV. Market exposures can be defined according to a
variety of approaches, including the gross approach and the commitment approach.
Liquidity management tools (LMTs): Provisions and techniques established by a fund manager as
part of the share redemption policy for its funds. LMTs are generally communicated upfront in fund
disclosure documents.
Net asset value (NAV): The net value of the assets of the AIF (as opposed to the NAV per unit or
proportion of the AIF).
Registered Alternative Investment Fund Manager: Registered AIFMs are subject to lighter
requirements than authorised AIFMs and do not have access to the AIFMD passport.
ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 80
List of abbreviations
AIF
Alternative Investment Fund
AIFM
Alternative Investment Fund Manager
AIFMD
Alternative Investment Fund Manager Directive
AuM
Assets under Management
CIU
Collective Investment Undertakings
CLO
Collateralised Loan Obligation
CRE
Commercial Real Estate
CTA
Commodity Trading Advisor
ECB
European Central Bank
EEA
European Economic Area
EFAMA
European Fund and Asset Management Association
ESCB
European System of Central Banks
ESMA
European Securities and Markets Authority
ESRB
European Systemic Risk Board
ETF
Exchange-traded fund
FoF
Fund of Funds
HF
Hedge Funds
IOSCO
International Organization of Securities Commissions
IRD
Interest Rate Derivative
ISIN
International Securities Identification Number
LEI
Legal Entity Identifier
LMT
Liquidity management tools
MMF
Money Market Fund
NAV
Net asset value
NCA
National Competent Authority
NPPR
National Private Placement Regime
PE
PA
Private Equity
Physical Assets
pp
percentage point
QIF
Qualifying investor fund
RE
Real Estate
S
Securities
UCITS
Undertakings for the Collective Investment in Transferable Securities

ESMA Annual Statistical Report on EU Alternative Investment Funds 2022 81
