Objectives
After completion of this chapter you will be able to:
1. Describe the location of the main cardiovascular and lymphatic structures in the
body.
2. De ne terms related to the heart, the vascular system, and the lymphatic system.
3. De ne combining forms, pre xes, and suf xes related to the cardiovascular and
lymphatic systems.
4. De ne common medical terminology related to the cardiovascular and
lymphatic systems, including adjectives and related terms, symptoms and
conditions, tests and procedures, surgical interventions and therapeutic
procedures, medications and drug therapies, and specialties.
5. Explain abbreviations for terms related to the cardiovascular and lymphatic
systems.
6. Successfully complete all chapter exercises.
7. Explain terms used in medical records and case studies involving the
cardiovascular and lymphatic systems.
8. Successfully complete all pronunciation and spelling exercises, and complete all
interactive exercises included with the companion Student Resources.
Chapter Outline
Anatomy and Physiology, 196
Functions of the Cardiovascular
System, 196
Structures of the Cardiovascular
System, 196
Functions of the Lymphatic
System, 196
Structures of the Lymphatic
System, 197
Terms Related to the Cardiovascular
and Lymphatic Systems, 197
Word Parts, 204
Combining Forms, 204
Pre xes, 205
Suf xes, 205
Medical Terms, 209
Adjectives and Other Related
Terms, 209
Symptoms and Medical Conditions, 211
Tests and Procedures, 221
Surgical Interventions and
Therapeutic Procedures, 226
Medications and Drug Therapies, 231
Specialties and Specialists, 232
Abbreviations, 233
Chapter Review, 236
7
Cardiovascular and
Lymphatic Systems
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 195LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 195 10/19/10 9:43:06 PM10/19/10 9:43:06 PM
196 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
Functions of the Cardiovascular System
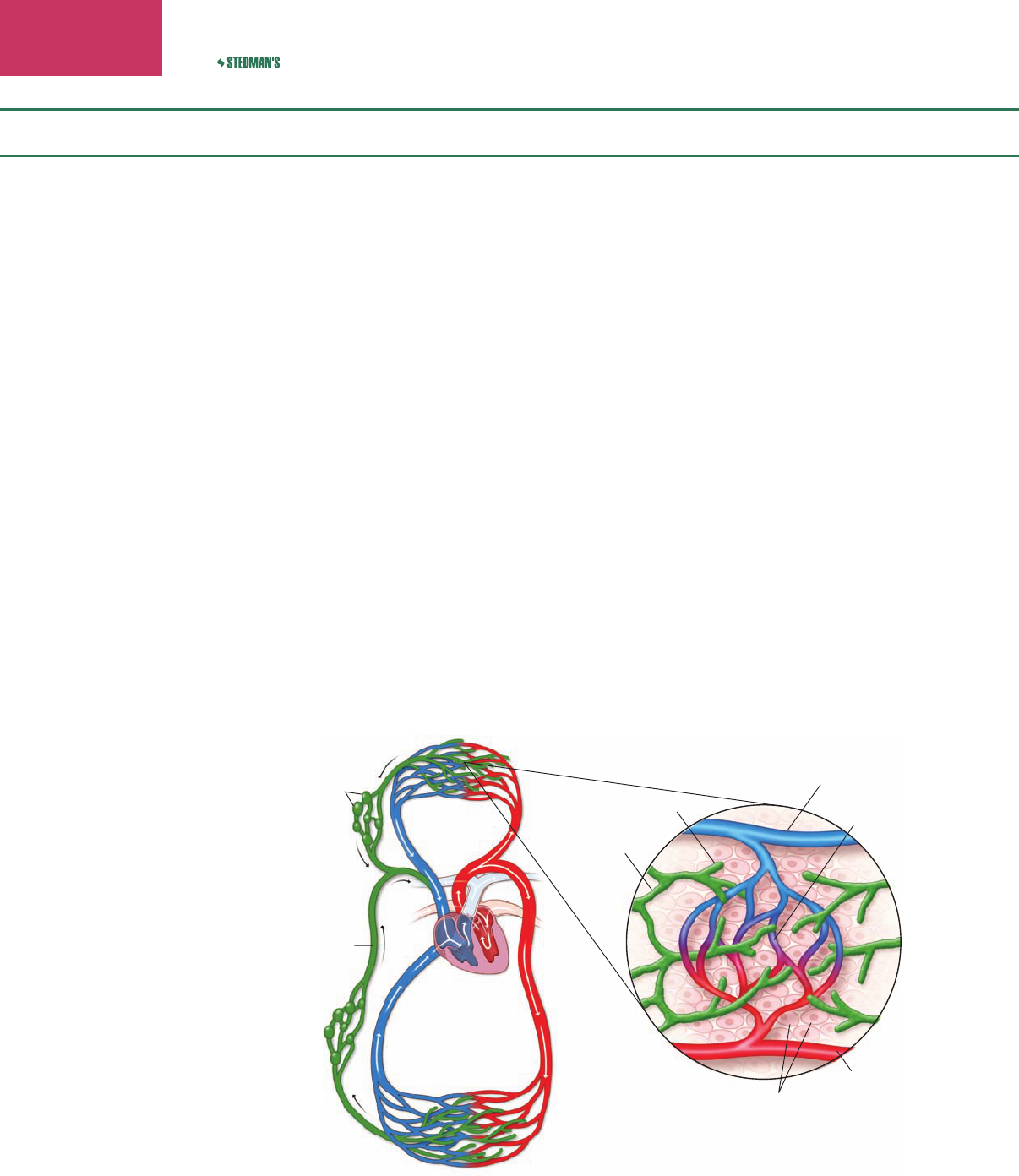
To transport blood throughout the body (Fig. 7-1)
To deliver oxygen and nutrients to body cells through arteries and capillaries
To remove waste products from body cells through capillaries and veins
To pump blood through the heart with the aid of electrical conduction
Structures of the Cardiovascular System
The heart wall consists of three tissue layers.
The heart has four chambers aided by four valves to keep blood moving in one
direction.
The heart has specialized tissue that transmits electrical impulses.
The heart muscle contracts in a rhythmic sequence, pushing blood through
the chambers and vessels.
The arteries carry blood away from the heart.
The capillaries allow exchange of gasses, nutrients, and wastes between the
blood and body cells.
The veins return blood back to the heart.
Functions of the Lymphatic System
To return lymph from body tissues to the blood (Fig. 7-1)
To protect the body by ltering microorganisms and foreign particles from the lymph
To maintain the body’s internal uid level
To absorb fats from the small intestines
Tissue cells
Venule
Arteriole
Blood
capillary
Lymph capillary
Lymph vessel
Circulation to lower body
Circulation to upper body
Lymph
nodes
Lymph
vessel
Figure 7-1 Blood and lymph ow in the cervical region.
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 196LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 196 10/19/10 9:43:08 PM10/19/10 9:43:08 PM
Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 197
Structures of the Lymphatic System
The lymph is clear tissue uid consisting of white blood cells and a few red blood
cells.
The lymph nodes lter the lymph.
The lymph nodes are primarily concentrated in the neck, chest, armpits, and groin.
The lymph vessels transport the lymph from the body tissues to the venous system.
The lymph vessels have valves that facilitate one-way transport of lymph.
Terms Related to the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
Term Pronunciation Meaning
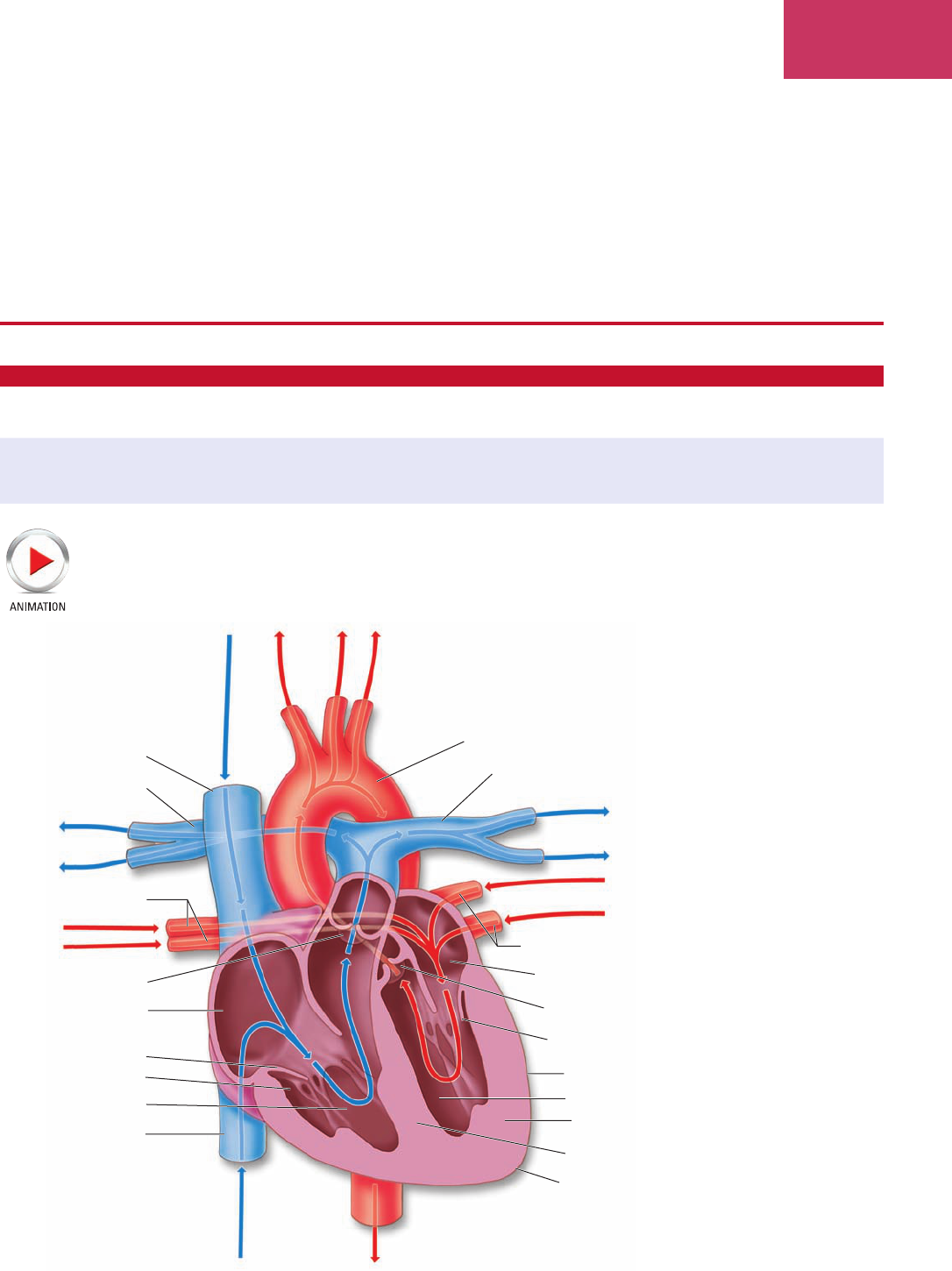
The Heart (Fig. 7-2)
cardiovascular system
kahr’d
ē-ō-vas’kyū-lăr
sis’t
ĕm
heart and blood vessels carrying oxygen and nutrients to the
body cells and carrying away waste (Fig. 7-3)
heart hahrt muscular organ taking deoxygenated blood from the veins,
pumping it to the lungs for oxygen, and returning it to the
body through the arteries (Fig. 7-4)
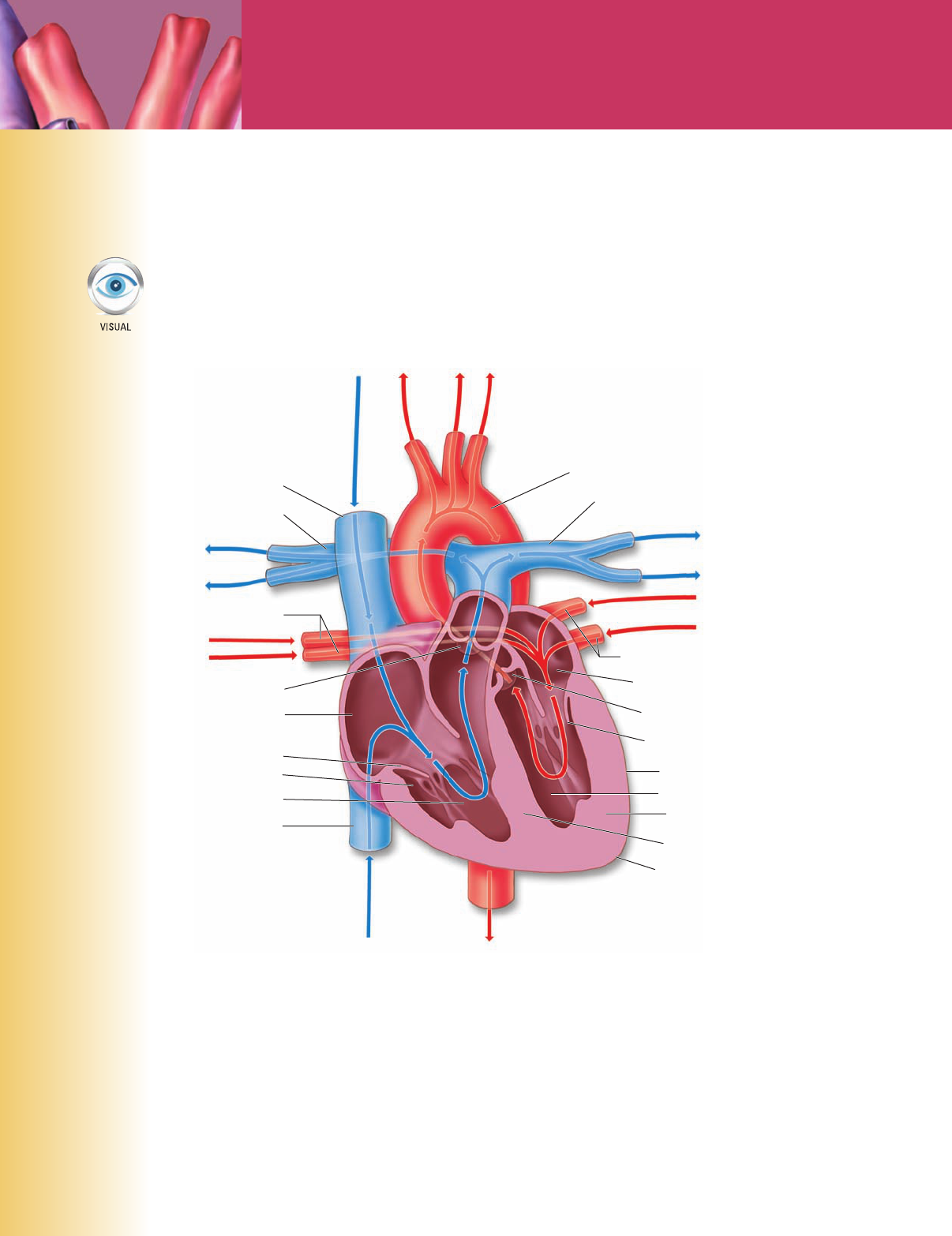
Aorta
Left pulmonary artery
Left pulmonary veins
Left atrium
Aortic valve
Mitral valve
Epicardium
Myocardium
Apex
Inferior vena cava
Right ventricle
Endocardium
Tricuspid valve
Right atrium
Pulmonary valve
Right pulmonary veins
Right pulmonary artery
Superior vena cava
Left ventricle
Septum
Figure 7-2 Heart and great
vessels.
View the animation Cardiac Cycle on the Student Resources to learn
how blood ows through the heart.
(continued)
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 197LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 197 10/19/10 9:43:12 PM10/19/10 9:43:12 PM
198 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
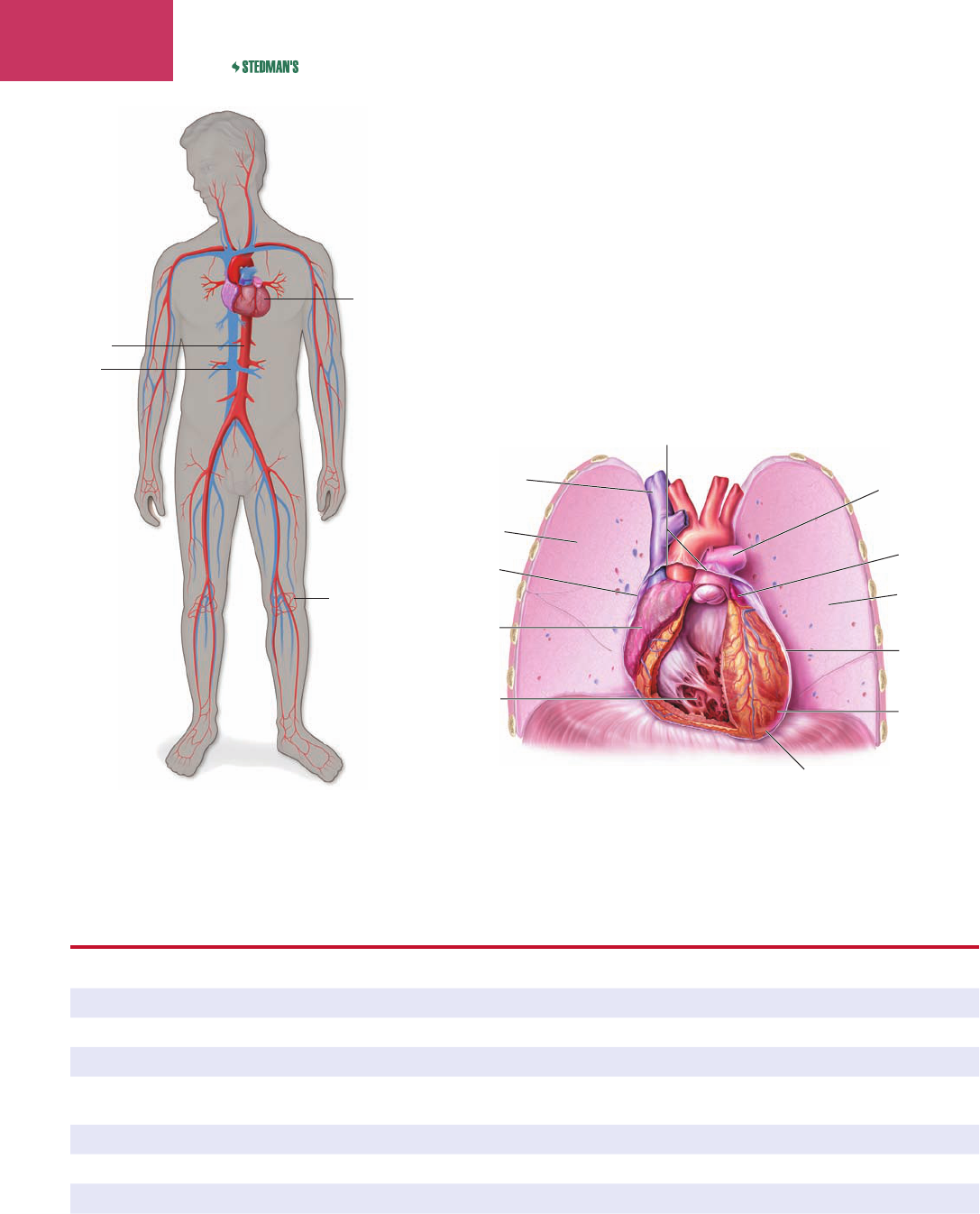
Heart
Artery
Vein
Capillaries
Figure 7-3 The cardiovascular system.
Left pulmonary
artery
Left lung
Pericardium
(cut edge)
Pericardial sac
(cut edge)
Superior
vena cava
Right lung
Pericardial sac
(cut edge)
Right atrium
Right ventricle
Left atrium
Left ventricle
Apex of heart
Figure 7-4 Cross-section of the heart and lungs showing the heart’s
relative position in the body.
Terms Related to the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic
Systems (continued)
Term Pronunciation Meaning
apex
ā’peks
the lower pointed end of the heart
septum
sep’t
ŭm
wall of heart tissue separating the right and left sides
atrium
ā’terē-ŭm
upper receiving chamber of the heart; right and left
ventricle
ven’tri-k
ĕl
lower pumping chamber of the heart; right and left
structures
endocardium
en’d
ō-kahr’dē-ŭm
inner lining of the heart
myocardium
m
ī’ō-kahr’dē-ŭm
middle muscular layer of heart tissue
epicardium
ep’i-kahr’d
ē-ŭm
outer lining of the heart
pericardium
per’i-kahr’d
ē-ŭm
sac around the heart that facilitates movement of the heart as
it beats
(continued)
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 198LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 198 10/19/10 9:43:13 PM10/19/10 9:43:13 PM
Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 199
Terms Related to the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic
Systems (continued)
Term Pronunciation Meaning
aortic valve
ā-ōr’tik valv
heart valve between the left ventricle and aorta
mitral valve
m
ī’trăl valv
heart valve between the left atrium and left ventricle; also
called a bicuspid valve
pulmonary valve
pul’m
ŏ-nār-ē valv
heart valve between the right ventricle and the pulmonary
artery; also called a semilunar valve due to the half-moon
shape of its three cusps
tricuspid valve
tr
ī-kŭs’pid valv
heart valve between the right atrium and right ventricle; also
called a semilunar valve due to the half-moon shape of its
three cusps
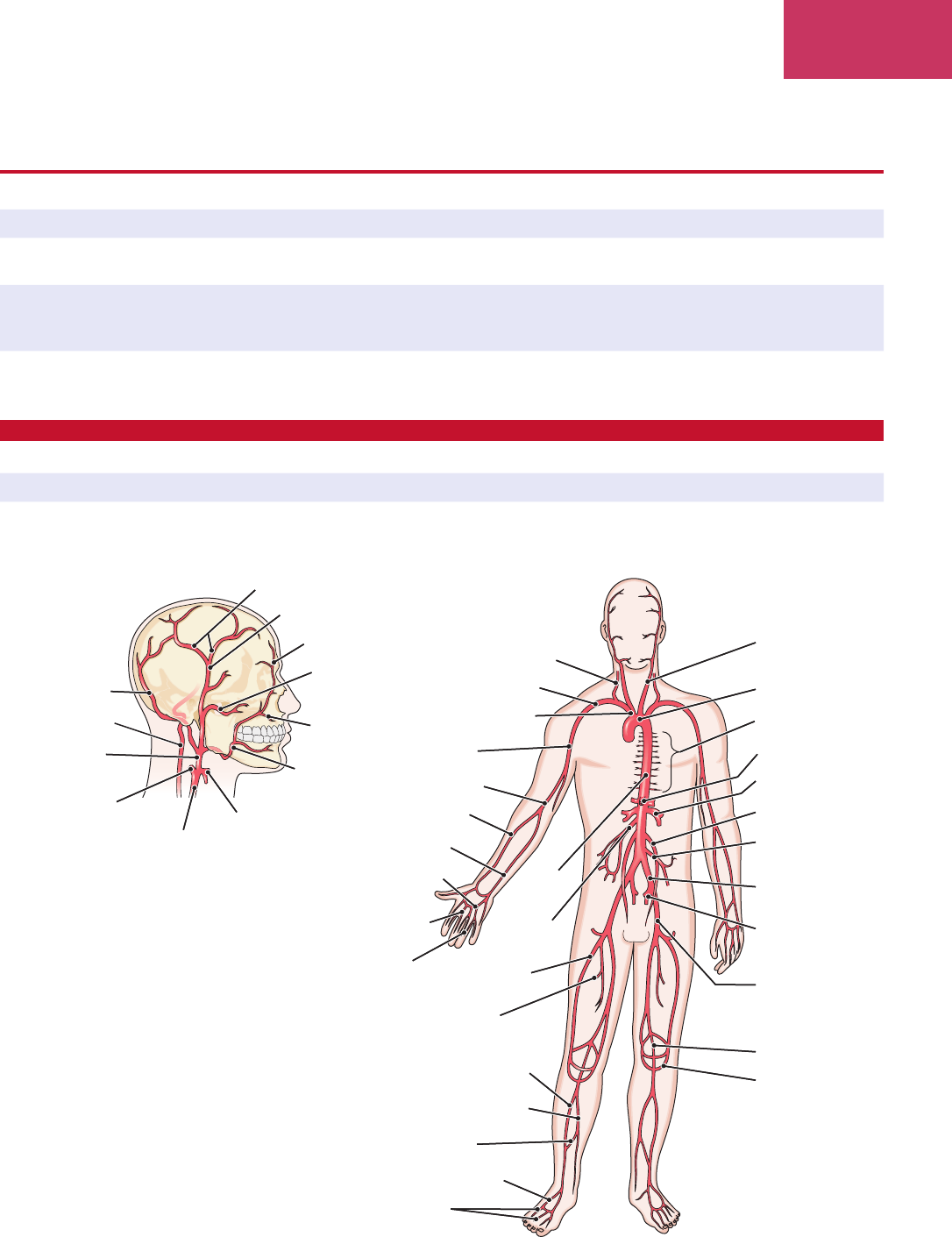
The Vascular System
blood vessels
bl
ŭd ves’ĕlz
structures that carry or transport blood
artery
ar’t
ĕr-ē
vessel carrying blood away from the heart (Fig. 7-5)
arteriole
ahr-t
ēr’ē-ōl
small artery
Superficial temporal
Superior temporal
Frontal
Transverse
facial
Labial
Maxillary
Superior
thyroid
Common
carotid
Internal
carotid
External
carotid
Vertebral
Occipital
Common
carotid
Celiac
Renal
Aortic arch
Testicular
Inferior
mesenteric
Common
iliac
External
iliac
Popliteal
Genicular
Internal
iliac
Intercostals
Subclavian
Vertebral
Dorsal
metatarsals
Dorsalis pedis
Peroneal
Posterior tibial
Anterior tibial
Deep
femoral
Femoral
Digitals
Volar
metacarpals
Volar arch
Ulnar
Radial
Brachial
Axillary
Brachiocephalic
Superior
mesenteric
Thoracic
aorta
Figure 7-5 The principal arteries.
(continued)
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 199LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 199 10/19/10 9:43:16 PM10/19/10 9:43:16 PM

200 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
Terms Related to the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic
Systems (continued)
Term Pronunciation Meaning
capillary
kap’i-l
ār-ē
microscopic thin-walled vessel connecting arterioles and
venules where gas, nutrient, and waste exchange take place
between the blood and cells of the body
lumen
l
ū’mĕn
interior space of a vessel
venule
ven’y
ūl
small vein
vein
v
ān
vessel carrying blood to the heart
aorta
ā-ōr’tă
largest artery that begins as an arch from the left ventricle then
branches and descends through the thoracic and abdominal
cavities; carries oxygenated blood away from the heart
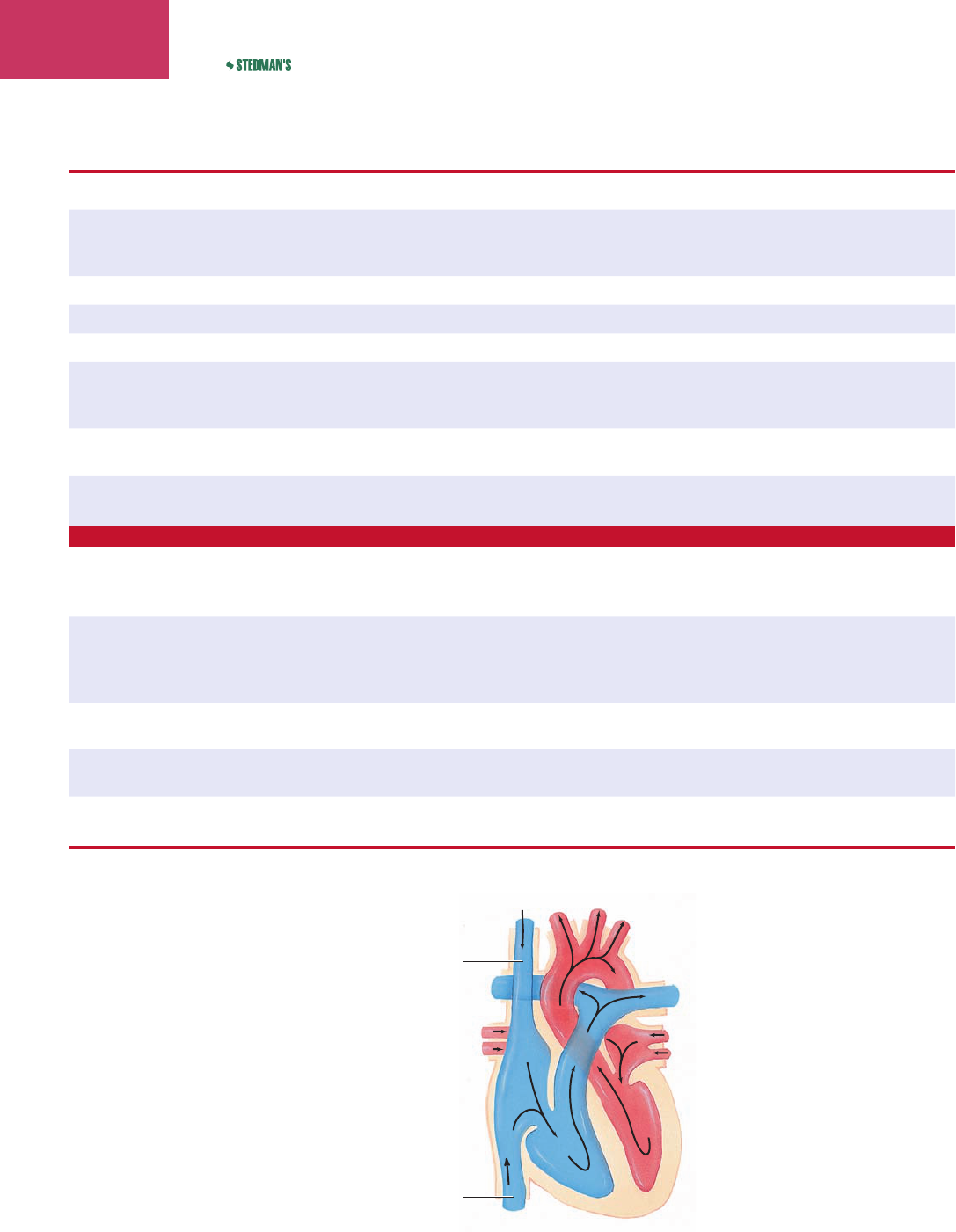
inferior vena cava
in-f
ēr’ē-ŏr vē’nă kā’vă
large vein carrying blood to the heart from the lower part of
the body (Fig. 7-6)
superior vena cava
sŭ-pēr’ē-ŏr vē’nă kā’vă
large vein carrying blood to the heart from the upper part of
the body (Fig. 7-6)
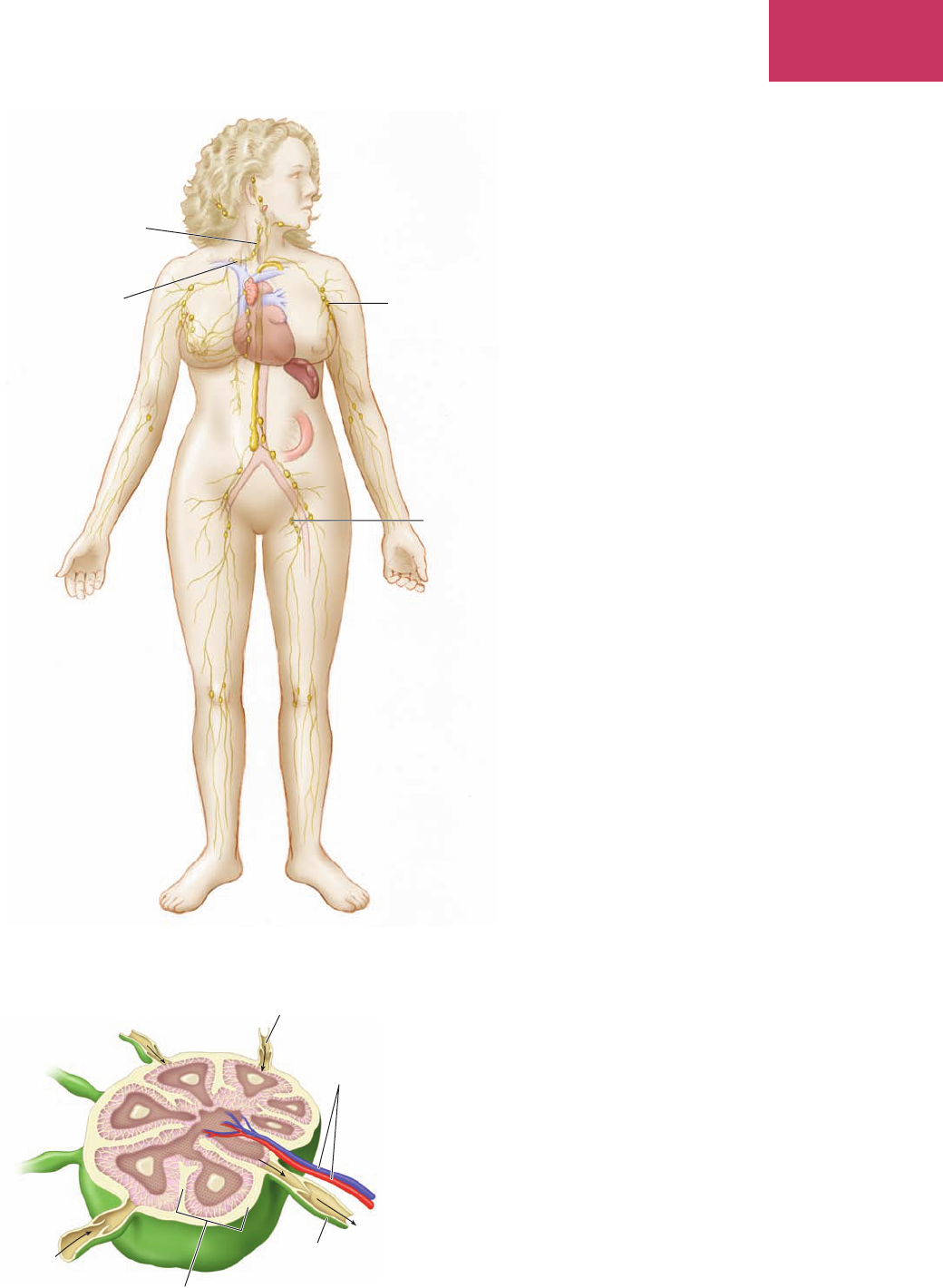
The Lymphatic System (Fig. 7-7)
lymph limf clear uid consisting of uctuating amounts of white blood
cells and a few red blood cells that accumulates in tissue and
is removed by the lymphatic capillaries
lymph nodes, syn.
lymph glands
limf n
ōdz, limf glandz
small bean-shaped masses of lymphatic tissue that lter
bacteria and foreign material from the lymph; located on
larger lymph vessels in the axillary, cervical, inguinal, and
mediastinal areas (Fig. 7-8)
lymph vessels
limf ves’
ĕlz
vessels transporting lymph from body tissues to the venous
system
lymph capillaries
limf kap’i-lar-
ēz
microscopic thin-walled lymph vessels that pick up lymph,
proteins, and waste from body tissues
lymph ducts
limf d
ŭkts
the largest lymph vessels that transport lymph to the venous
system
Superior vena cava
Inferior vena cava
Figure 7-6 The venae cavae carry blood to the
heart.
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 200LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 200 10/19/10 9:43:16 PM10/19/10 9:43:16 PM
Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 201
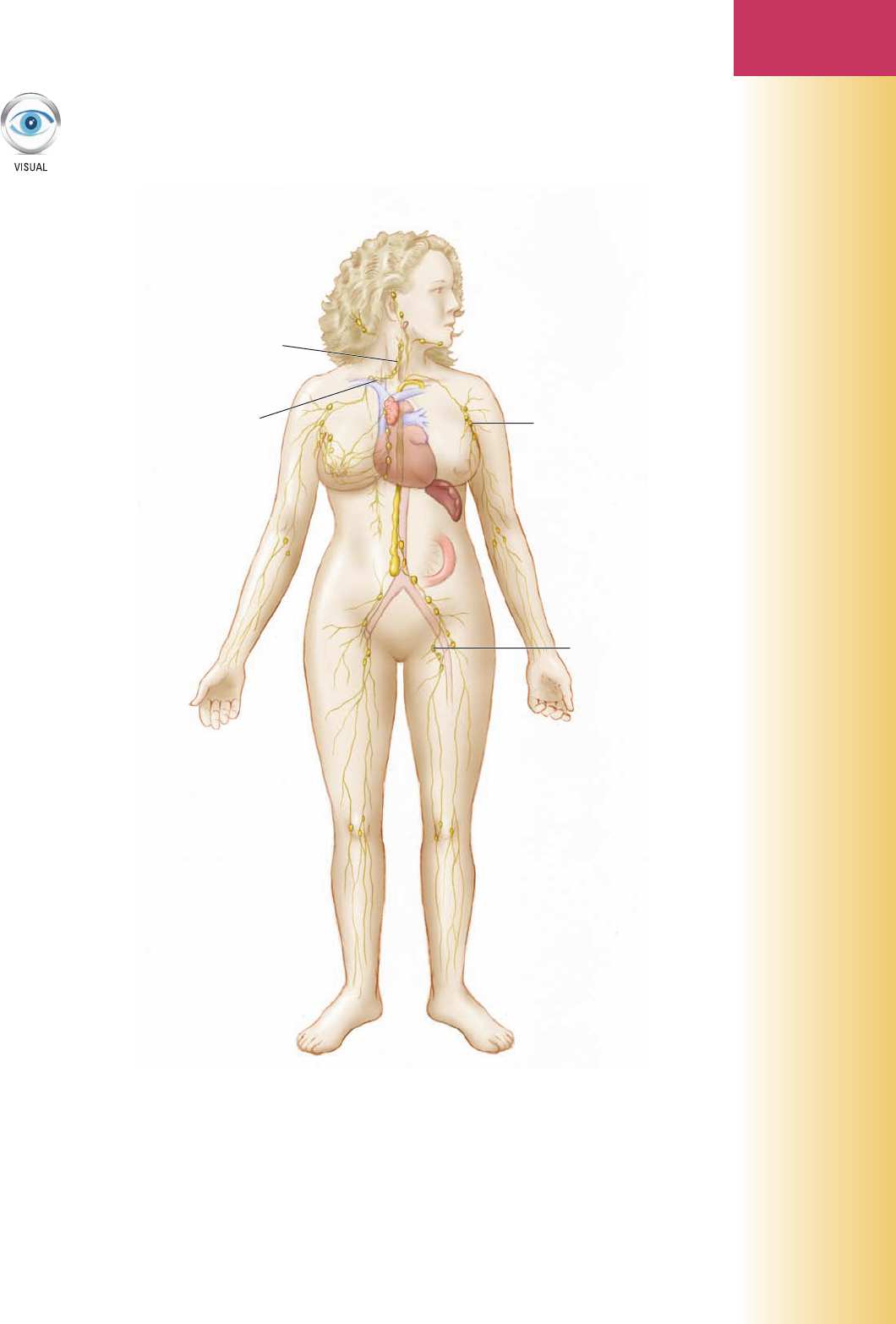
Cervical lymph node
Mediastinal lymph node
Axillary lymph node
Inguinal lymph node
Figure 7-7 Major lymph node locations.
Afferent
lymphatic
vessel
Efferent
lymphatic
vessel
Lymph node
artery (red)
and vein (blue)
Lymph nodule
Lymph from
body tissues
Lymph continuing
toward venous system
Figure 7-8 The interior of a lymph
node.
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 201LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 201 10/19/10 9:43:17 PM10/19/10 9:43:17 PM
202 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
Exercises: Anatomy and Physiology
Exercise 1
Write the correct anatomic structure for the meaning given.
1. upper chamber of the heart
2. small vein
3. middle muscular layer of heart
4. valve between the left ventricle and aorta
5. wall of heart tissue
6. small artery
7. large veins carrying blood to the heart
8. muscular pumping organ
9. inner lining of the heart
10. sac around the heart
Exercise 2
Write the meaning or function of the term given.
1. lymph
2. artery
3. vein
4. lymph capillaries
5. aorta
6. blood vessels
7. lymph vessels
8. lymph ducts
9. lymph nodes
10. tricuspid valve
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 202LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 202 10/19/10 9:43:20 PM10/19/10 9:43:20 PM

Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 203
Exercise 3
Circle the term that is most appropriate for the meaning of the sentence.
1. The two upper receiving chambers of the heart are called the right and left (aortas, atria,
ventricles).
2. The epicardium is the (inner, middle, outer) lining of the heart.
3. The (endocardium, myocardium, pericardium) is the inner lining of the heart.
4. Another name for the mitral valve is the (semilunar, bicuspid, tricuspid) valve.
5. The largest artery in the body is the (inferior vena cava, superior vena cava, aorta).
6. The pulmonary valve is located between the right ventricle and the pulmonary (vein, artery,
vena cava).
7. The lymph (nodes, ducts, capillaries) pick up lymph, proteins, and waste from the body cells.
8. The inferior vena cava is a large (artery, vein, capillary).
9. The smallest blood vessel where gas and nutrients are exchanged is a(n) (arteriole, capillary,
venule).
10. The (aortic, mitral, tricuspid) valve is also referred to as a semilunar valve.
11. The mitral valve has (one, two, three) cusps or lea ets that open and close.
12. The (endocardium, myocardium, pericardium) is the sac around the heart.
13. A small artery is called a(n) (arteriolo, arteriole, capillary).
14. The muscular organ pumping blood through the body is the (circulatory system, pulmonary
system, heart).
Exercise 4
Match each medical term with its meaning.
myocardium septum lymph
pulmonary valve lumen apex
Meaning Term
1. structure between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery
2. middle muscular layer of heart tissue
3. interior space of a vessel
4. clear uid that accumulates in tissues
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 203LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 203 10/19/10 9:43:21 PM10/19/10 9:43:21 PM

204 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
5. wall inside the heart
6. the lower pointed end of the heart
Exercise 5
Complete each sentence by writing in the correct medical term.
1. Bacteria and foreign material are ltered out of circulation by the
.
2. The bottom chambers of the heart responsible for forcing the blood through the body are the
.
3. The vessels that carry blood away from the heart are
.
4. The
regulates the ow of blood between the left ventricle and the aorta.
5. The
is a sac found around the heart that facilitates movement as it beats.
6. The interior space of a vessel is called a(n)
.
7. A microscopic vessel that picks up uid and proteins from the cells is a lymph
.
8. The lymph
are the largest lymph vessels.
9. The clear uid that accumulates in tissue is called
.
10. The ______________ vena cava carries blood to the heart from the lower part of the body.
WORD PARTS
Note that some word parts that have been introduced earlier in the book may not
be repeated here.
Combining Forms
Combining Form Meaning
Related to the Cardiovascular System
angi/o, vas/o, vascul/o vessel, duct
aort/o aorta
arteri/o artery
ather/o fatty paste
atri/o atrium
(continued)
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 204LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 204 10/19/10 9:43:21 PM10/19/10 9:43:21 PM

Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 205
Combining Forms (continued)
Combining Form Meaning
cardi/o heart
coron/o circle or crown
electr/o electric, electricity
my/o muscle
phleb/o, ven/i, ven/o vein
pulmon/o lung
scler/o hard
son/o sound, sound waves
sphygm/o pulse
steth/o, thorac/o thorax, chest
thromb/o blood clot
valv/o, valvul/o valve
varic/o swollen or twisted vein
ventricul/o ventricle
Related to the Lymphatic System
aden/o gland
lymph/o lymph
Pre xes
Pre x Meaning
Related to the Cardiovascular System
brady- slow
de- away from, cessation, without
endo- in, within
epi- on, following
inter- between
intra- within
peri- around, surrounding
tachy- rapid, fast
tel- end
trans- across, through
tri- three
Suf xes
Suf x Meaning
Related to the Cardiovascular System
-al, -ar, -ary, -ic pertaining to
-ectasia dilation, stretching
(continued)
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 205LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 205 10/19/10 9:43:21 PM10/19/10 9:43:21 PM

206 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
Suf xes (continued)
Suf x Meaning
-gram record, recording
-graph instrument for recording
-graphy process of recording
-icle, -ole, -ule small
-lytic pertaining to destruction, breakdown,
separation
-ium tissue, structure
-stenosis stricture, narrowing
Related to the Lymphatic System
-oid resembling
Exercises: Word Parts
Exercise 6
Write the meaning of the combining form given.
1. atri/o
2. my/o
3. vas/o
4. angi/o
5. ven/o
6. electr/o
7. arteri/o
8. cardi/o
9. ventricul/o
10. pulmon/o
11. coron/o
12. phleb/o
13. vascul/o
14. thorac/o
15. valvul/o
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 206LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 206 10/19/10 9:43:21 PM10/19/10 9:43:21 PM

Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 207
Exercise 7
Write the correct combining form(s) for the meaning given.
1. hard
2. pulse
3. swollen or twisted vein
4. lymph
5. valve
6. aorta
7. artery
8. atrium
9. heart
10. thorax, chest
Exercise 8
Write the meaning of the pre x or suf x given.
1. -stenosis
2. -ule, -icle, -ole
3. tachy-
4. trans-
5. intra-
6. inter-
7. endo-
8. -graph
9. brady-
10. epi-
11. peri-
12. -ium
13. -al, -ar, -ary, -ic
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 207LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 207 10/19/10 9:43:21 PM10/19/10 9:43:21 PM

208 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
14. tri-
15. de-
16. -lytic
Exercise 9
Considering the meaning of the combining form from which the medical term
is made, write the meaning of the medical term. (You have not yet learned
many of these terms but can build their meaning from the word parts.)
Combining Form Meaning Medical Term Meaning of Term
phleb/o vein phlebitis 1.
cardi/o heart cardiology 2.
my/o, cardi/o muscle, heart myocardium 3.
thromb/o blood clot thrombosis 4.
ven/o vein venogram 5.
ather/o fatty paste atherectomy 6.
lymph/o lymph lymphoid 7.
aort/o aorta aortography 8.
Exercise 10
Using the given combining form, build a medical term for the meaning given.
Combining Form Meaning of Medical Term Medical Term
angi/o surgical repair or reconstruction 1.
of a vessel
thorac/o pertaining to the chest 2.
arteri/o small artery 3.
ven/o small vein 4.
vascul/o pertaining to vessels, ducts 5.
aden/o resembling a gland 6.
lymph/o disease of the lymph vessels or nodes 7.
son/o process of recording using sound 8.
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 208LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 208 10/19/10 9:43:22 PM10/19/10 9:43:22 PM

Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 209
MEDICAL TERMS
Adjectives and Other Related Terms
Term Pronunciation Meaning
arteriovenous (AV)
ahr-t
ēr’ē-ō-vē’nŭs
pertaining to both arteries and veins
atrioventricular (AV)
ā’trē-ō-ven-trik’yū-lăr
pertaining to the atria and ventricles
cardiovascular
kahr’d
ē-ō-vas’kyū-lăr
pertaining to the heart and blood vessels
constriction
k
ŏn-strik’shŭn
process of narrowing or tightening of a structure
cyanotic
s
ī’ă-not’ik
pertaining to a blue or purple discoloration due to
deoxygenated blood
deoxygenation
d
ē-ok’si-jĕ-nā’shŭn
process of removing or having a lack of oxygen
diastole
d
ī-as’tŏ-lē
the relaxation phase of the ventricles in the heartbeat
cycle
ischemic
is-k
ē’mik
pertaining to a lack of blood ow
oxygenation
ok’si-j
ĕ-nā’shŭn
process of adding oxygen
paroxysmal
par-ok-siz’m
ăl
sudden
patent
p
ā’tĕnt
open or exposed
precordial
pr
ē-kōr’dē-ăl
pertaining to the anterior left chest
sphygmic s g’mik pertaining to the pulse
stenotic sten-ot’ik pertaining to the condition of narrowing
supraventricular
s
ū’pră-ven-trik’yū-lăr
pertaining to above the ventricles
systole
sis’t
ŏ-lē
the contraction phase of the ventricles in the heartbeat
cycle
thoracic
th
ōr-as’ik
pertaining to the chest
thrombotic throm-bot’ik pertaining to a thrombus or blood clot
varicose
var’i-k
ōs
pertaining to swollen or twisted veins
Exercises: Adjectives and Other Related Terms
Exercise 11
Circle the term that is most appropriate for the meaning of the sentence.
1. The term supraventricular refers to (above, below, beside) the ventricles.
2. A sudden arrhythmia, such as an atrial tachycardia, is described as (stenotic, precordial,
paroxysmal).
3. An open coronary artery is referred to as (patent, stenotic, varicose).
4. A stenotic vessel is one that is (widened, narrowed, stretched).
5. The medical term used to describe a blue or purple discoloration is (pathologic, varicose, cyanotic).
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 209LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 209 10/19/10 9:43:22 PM10/19/10 9:43:22 PM

210 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
6. (Diastole, Systole, Stenosis) refers to the contraction phase of the ventricles in the heartbeat
cycle.
7. The relaxation phase of the ventricles in the heartbeat cycle is (diastole, stenosis, systole).
Exercise 12
Match each medical term with its meaning.
precordial constriction cardiovascular cyanotic deoxygenation
varicose oxygenation atrioventricular ischemic thoracic
Meaning Term
1. process of narrowing or tightening
2. pertaining to the heart and blood vessels
3. pertaining to a blue or purple discoloration
4. pertaining to the anterior left chest
5. pertaining to twisted, swollen veins
6. process of adding oxygen
7. pertaining to the chest
8. pertaining to lack of blood ow
9. pertaining to atria and ventricles
10. process of removing oxygen
Exercise 13
Write the combining form(s) used in the medical term, followed by the
meaning of the combining form.
Term Combining Form(s) Combining Form Meaning(s)
1. sphygmic
2. cardiovascular
3. varicose
4. arteriovenous
5. thrombosis
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 210LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 210 10/19/10 9:43:22 PM10/19/10 9:43:22 PM

Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 211
Figure 7-9 Aortic arteriogram in a 68-year-old man
demonstrates an infrarenal abdominal aortic
aneurysm (arrows).
Symptoms and Medical Conditions
Term Pronunciation Meaning
Related to the Cardiovascular System
Disorders of the Heart and Arteries
acute coronary syndrome
(ACS)
ă-kyūt’ kōr’ŏ-nār-ē
sin’dr
ōm
chest pain and other signs and symptoms associated
with cardiac ischemia
aneurysm
an’y
ūr-izm
dilation of an artery; usually due to a weakness in the wall
of the artery (Fig. 7-9)
angina pectoris
an’ji-n
ă pek’tō’ris
chest pain or pressure resulting from lack of blood
ow to the myocardium
angiostenosis
an’j
ē-ō-stĕ-nō’sis
narrowing of a blood vessel
aortic stenosis
ā-ōr’tik stĕ-nō’sis
narrowing of the aortic valve opening (Fig. 7-10)
arteriosclerosis, syn.
arteriosclerotic heart disease
(ASHD)
ahr-t
ēr’ē-ō-skler-ō’sis,
ahr-t
ēr’ē-ō-skler-ot’ik
hahrt diz’
ēz
hardening or loss of elasticity of the arteries
(continued)
Figure 7-10 Stenosis of a semilunar valve. The aortic and pulmonary valves are semilunar valves.
Normal semilunar valve
Stenotic semilunar valve
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 211LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 211 10/19/10 9:43:22 PM10/19/10 9:43:22 PM

212 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
Symptoms and Medical Conditions (continued)
Term Pronunciation Meaning
atherosclerosis
ath’
ĕr-ō-skler-ō’sis
buildup of plaque or fatty paste inside arterial
walls (Fig. 7-11)
cardiac arrest
kahr’d
ē-ak ă-rest’
complete, sudden cessation of cardiac activity
cardiac tamponade
kahr’d
ē-ak tam’pŏ-nahd’
compression of the heart due to an increase of
uid in the pericardium
cardiomegaly
kahr’d
ē-ō-meg’ă-lē
enlargement of the heart
cardiomyopathy
kahr’d
ē-ō-mī-op’ă-thē
disease of the heart muscles
cardiopathy
kahr’d
ē-op’ă-thē
any disease of the heart
RISK FACTORS FOR CARDIOPATHY Risk factors for heart disease can be placed
in two categories: those that are changeable and those that cannot be changed.
Risk factors that are changeable include obesity, hypertension, smoking, lack of
exercise, and poor diet. Diabetes and stress are also considered changeable risk
factors because they can be controlled. Unchangeable risk factors include age,
gender, race, and family history.
cardiovalvulitis
kahr’d
ē-ō-val-vyū-lī’tis
in ammation of the valves of the heart
coarctation of the aorta
k
ō’ahrk-tā’shŭn ā-ōr’tă
narrowing of the aorta causing hypertension,
ventricular strain, and ischemia
congestive heart failure
(CHF)
k
ŏn-jes’tiv hahrt fāl’yŭr
inef ciency of cardiac circulation causing
edema and pulmonary congestion
coronary artery disease
(CAD)
k
ōr’ŏ-nār-ē ahr’tĕr-ē di-zēz’
narrowing of coronary arteries causing a
decrease of blood ow or ischemia to the
myocardium
coronary occlusion
k
ōr’ŏ-nār-ē ŏ-klū’zhŭn
blockage of a coronary vessel often leading to
a myocardial infarction
embolus
em’b
ō-lŭs
vascular blockage made up of a thrombus,
bacteria, air, plaque, and/or other foreign
material
(continued)
Figure 7-11 The progression of atherosclerosis.
Normal artery
with open lumen
Lumen
Small area of
atherosclerosis
Moderate atherosclerosis
causing narrowing of lumen
Complete/almost
complete occlusion
due to atherosclerosis
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 212LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 212 10/19/10 9:43:24 PM10/19/10 9:43:24 PM
Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 213
Symptoms and Medical Conditions (continued)
Term Pronunciation Meaning
endocarditis
en’d
ō-kahr-dī’tis
in ammation of the endocardium
hypertension
h
ī’pĕr-ten’shŭn
persistently elevated blood pressure
hypotension
h
ī’pō-ten’shŭn
blood pressure that is below normal
intermittent claudication
in’t
ĕr-mit’ĕnt klaw’di-kā’shŭn
cramping of the lower leg muscles usually
caused by lack of blood ow
ischemia
is-k
ē’mē-ă
lack of blood ow
mitral valve prolapse
m
ī’trăl valv prō’laps
backward movement of the mitral valve cusps
allowing regurgitation
mitral valve stenosis
m
ī’trăl valv stĕ-nō’sis
narrowing of the mitral valve opening usually
caused by scarring from rheumatic fever
murmur
m
ŭr’mŭr
abnormal heart sound
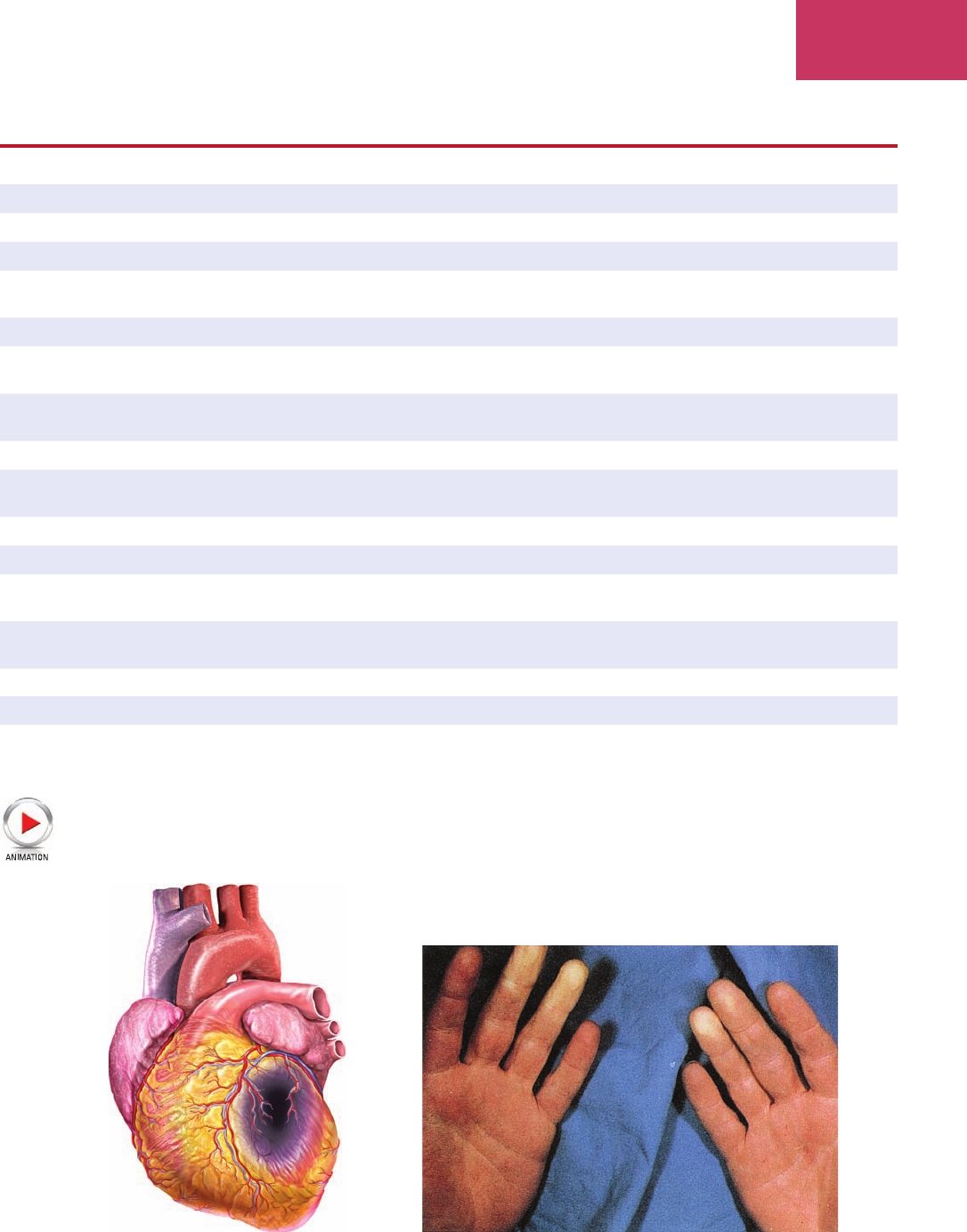
myocardial infarction (MI)
m
ī’ō-kahr’dē-ăl in-fahrk’shŭn
death of heart tissue usually due to coronary
artery occlusion (Fig. 7-12)
myocarditis
m
ī’ō-kahr-dī’tis
in ammation of the heart muscle
occlusion
ŏ-klū’zhŭn
blockage or closure
pericarditis
per’i-kahr-d
ī’tis
in ammation of the pericardial sac around the
heart
peripheral arterial disease
(PAD)
p
ĕr-if’ĕr-ăl ahr-tēr’ē-ăl di-zēz’
any disorder of the arteries outside of, or
peripheral to, the heart
plaque plak fat or lipid deposit on an arterial wall
polyarteritis
pol’
ē-ahr-tĕr-ī’tis
in ammation of many arteries
Raynaud disease, syn.
Raynaud syndrome
r
ā-nō’ diz’ēz, rā-nō’ sin’drōm
cyanosis of the ngers or toes due to vascular
constriction, usually caused by cold tem
peratures or emotional stress (Fig. 7-13)
Figure 7-13 Raynaud disease as indicated by
cyanosis (white areas) on the ends of the ngers.
Figure 7-12 Myocardial infarction (MI)
(darkened area).
(continued)
Learn how elevated blood pressure affects the heart and other organs of the
body by viewing the animation Hypertension in the electronic Student Resources.
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 213LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 213 10/19/10 9:43:28 PM10/19/10 9:43:28 PM

214 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
Symptoms and Medical Conditions (continued)
Term Pronunciation Meaning
rheumatic heart disease
(RHD)
r
ū-mat’ik hahrt di-zēz’
valvular disease resulting from rheumatic fever
stenosis
st
ĕ-nō’sis
narrowing or stricture of a vessel
thrombus
throm’b
ŭs
blood clot
Heart Rhythm and Conduction Disorders
arrhythmia
ā-ridh’mē-ă
abnormality or disturbance of heart rhythm
(Fig. 7-14)
bradycardia
brad’
ē-kahr’dē-ă
slow heart rate
dysrhythmia
dis-ridh’m
ē-ă
defective heart rhythm
brillation
b’ri-l
ā’shŭn
rapid irregular muscular contractions of the
atria or ventricles
utter
ŭt’ĕr
rapid regular muscular contractions of the atria
or ventricles
palpitation
pal-pi-t
ā’shŭn
forceful or irregular heart beat felt by the
patient
premature ventricular
contraction (PVC)
pr
ē’mă-chŭr’ ven-trik’yū-lăr
k
ŏn-trak’shŭn
early contraction of the ventricles
tachycardia
tak’i-kahr’d
ē-ă
fast heart rate
Disorders of the Veins
deep venous thrombosis
(DVT)
d
ēp vē’nŭs throm-bō’sis
blood clot formation in a deep vein, usually of
the legs or pelvic region
phlebitis
e-b
ī’tis
in ammation of a vein
telangiectasia
tel-an’j
ē-ek-tā’zē-ă
dilation of small or terminal vessels
thrombophlebitis
throm’b
ō- ĕ-bī’tis
in ammation of a vein with formation of
a clot
varicose vein
var’i-k
ōs vān
swollen and/or twisted veins, usually of the
legs (Fig. 7-15)
Related to the Lymphatic System
edema
ĕ-dē’mă
accumulation of excess uid in intercellular
spaces; can be caused by blockage of lymph
vessels
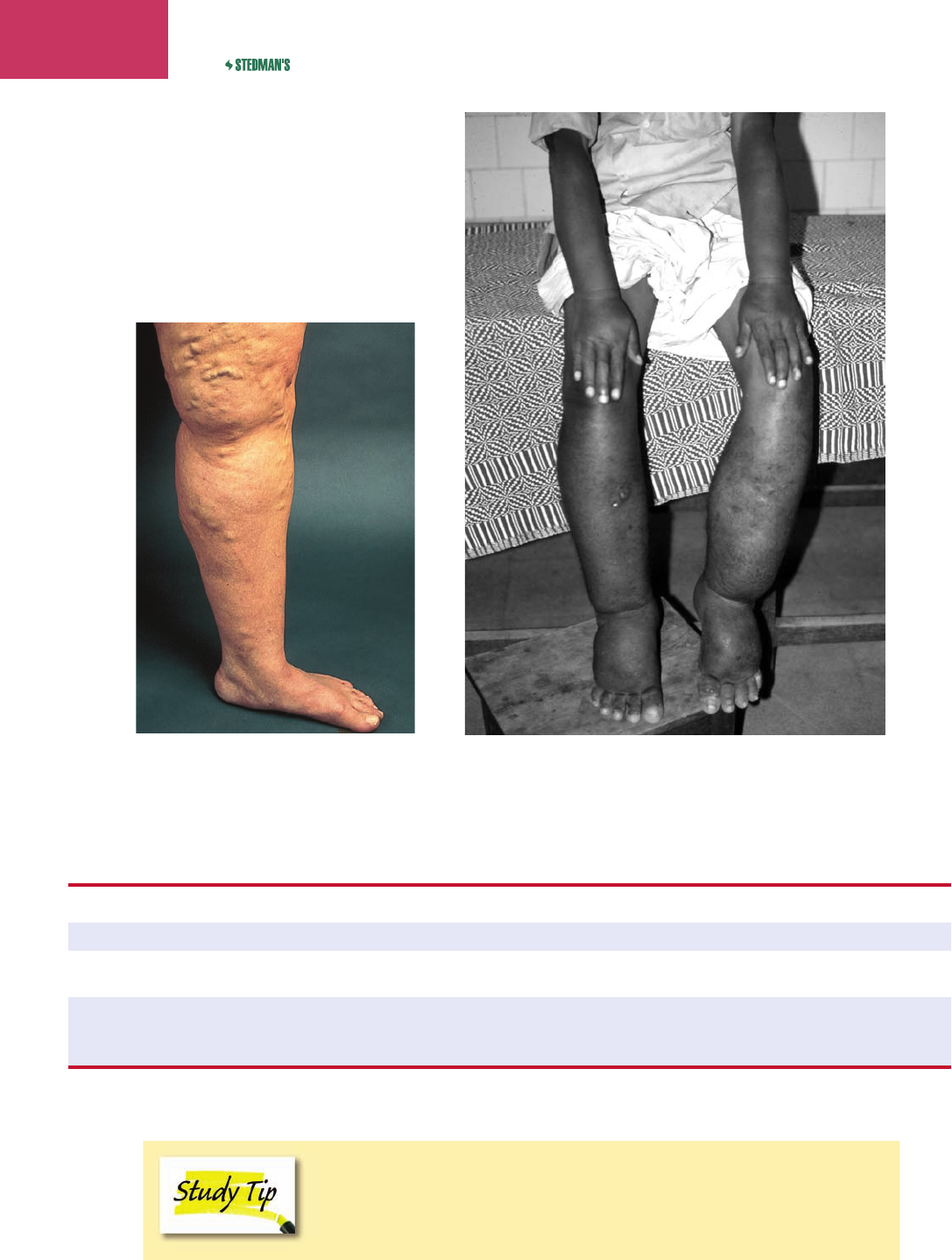
elephantiasis
el’
ĕ-fan-tī’ă-sis
enlargement of the lower extremities due to
blockage of lymph vessels commonly caused
by larial worms ( lariae) (Fig. 7-16)
lariae
-lar’
ē-ē
small parasitic worms that are transmitted
by mosquitoes; the worms invade tissues
as embryos and block lymph vessels as they
grow
lymphadenitis
lim-fad’
ĕ-nī’tis
in ammation of the lymph nodes
lymphadenitis
lim-fad’
ĕ-nī’tis
in ammation of the lymph nodes
lymphadenopathy
lim-fad’
ĕ-nop’ă-thē
disease of the lymph nodes; usually causes
enlargement of the nodes
(continued)
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 214LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 214 10/19/10 9:43:30 PM10/19/10 9:43:30 PM
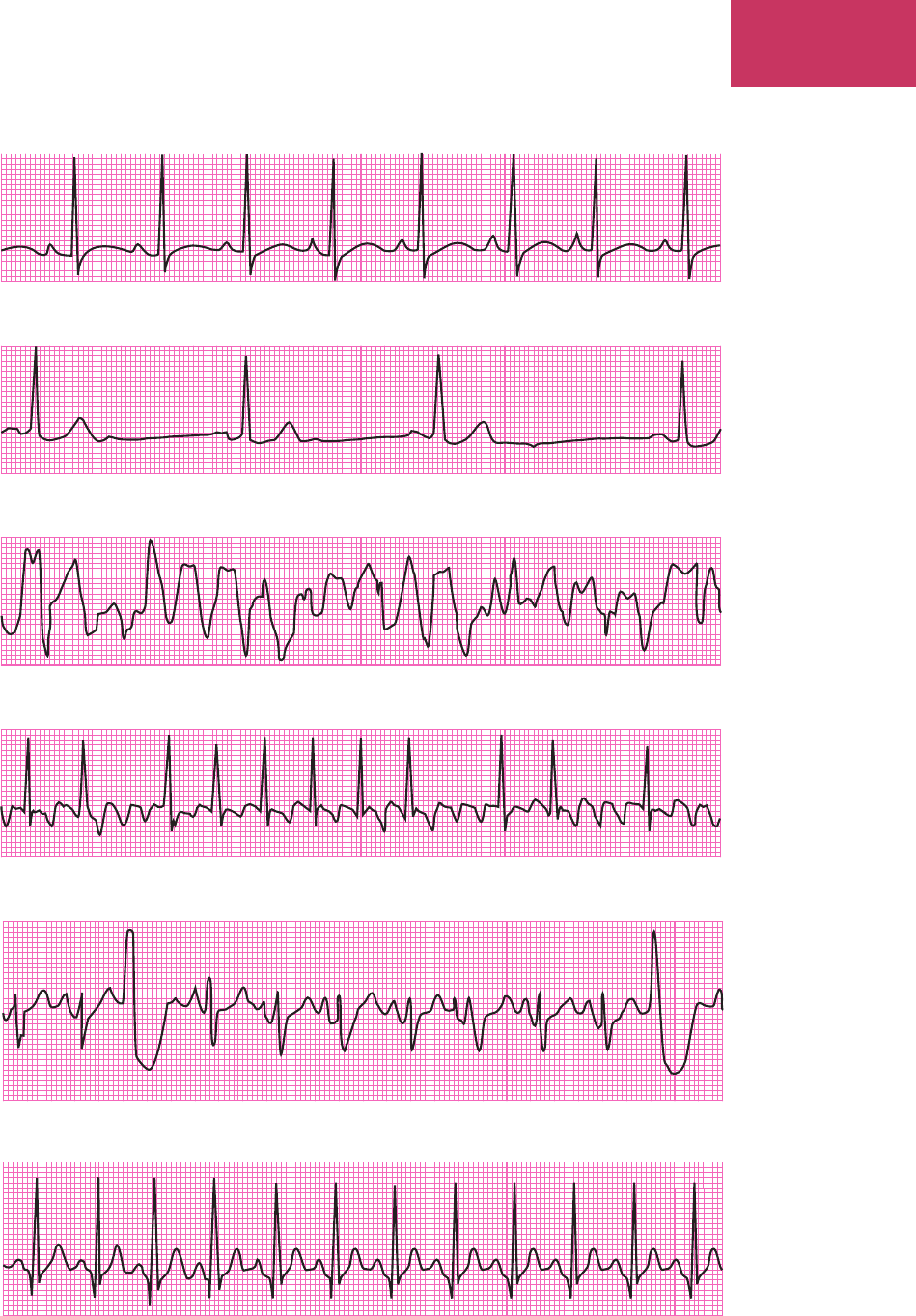
Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 215
Bradycardia
Fibrillation (ventricular)
Tachycardia (sinus)
Flutter (atrial)
Normal sinus rhythm (NSR)
Premature ventricular contraction (PVC)
Figure 7-14 Common types of arrhythmias shown through electrocardiogram tracings.
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 215LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 215 10/19/10 9:43:31 PM10/19/10 9:43:31 PM
216 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
Symptoms and Medical Conditions (continued)
Term Pronunciation Meaning
lymphangiitis
lim-fan’j
ē-ī’tis
in ammation of a lymph vessel
lymphedema
lim’f
ĕ-dē’mă
edema due to a blocked lymph node or lymph
vessel
pitting edema
pit’ing
ĕ-dē’mă
edema that retains an indentation of a nger
that had been pressed rmly on the skin
(Fig. 7-17)
Figure 7-15 Varicose veins.
Figure 7-16 Patient with advanced elephantiasis.
Arteriosclerosis vs. Atherosclerosis: To avoid confusing the meanings of the terms
arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis, focus on the combining forms. Arteri/o means
artery, so arteriosclerosis refers to hardening of the arteries. Ather/o means fatty
paste, so atherosclerosis refers to buildup of plaque or fatty paste, which hardens
the artery walls. Atherosclerosis is actually a type of arteriosclerosis.
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 216LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 216 10/19/10 9:43:31 PM10/19/10 9:43:31 PM
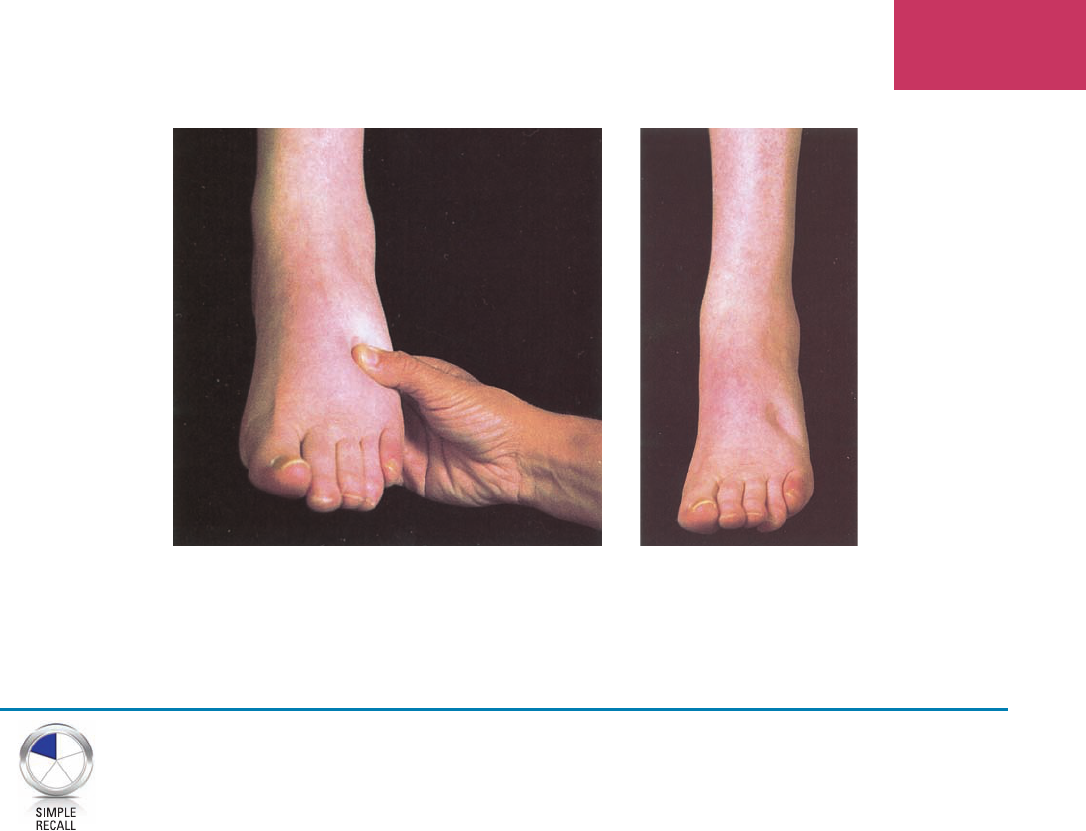
Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 217
A
B
Figure 7-17 A. Palpation of the foot. B. Pitting edema.
Exercises: Symptoms and Medical Conditions
Exercise 14
Circle the word that best completes the meaning given.
1. aneurysm = (weakening, rupture) of an arterial wall
2. atherosclerosis = condition of fatty build-up and (enlarging, hardening) of blood vessels
3. hypertension = (low, high) blood pressure
4. hypotension = (low, high) blood pressure
5. aortic stenosis = (hardening, narrowing) of the aortic valve opening
6. myocardial infarction = (death, pain) of the myocardium due to lack of blood supply
7. rheumatic heart disease = damage to the heart (ventricle, valve) due to rheumatic fever
8. ischemia = (lack of, increase in) blood ow
9. brillation = rapid (irregular, regular) heart contractions
10. utter = rapid (irregular, regular) heart contractions
11. premature ventricular contraction = (early, late) contraction of the ventricles
12. murmur = (normal, abnormal) heart sounds
13. elephantiasis = (anemia, edema) of the lower extremities due to lymph vessel blockage
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 217LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 217 10/19/10 9:43:33 PM10/19/10 9:43:33 PM

218 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
14. acute coronary syndrome = (Raynaud disease, chest pain) and other signs and symptoms
associated with cardiac ischemia
15. intermittent claudication = (cramping, edema) of the lower legs
16. peripheral artery disease = any disorder of the arteries (inside, outside) of, or peripheral to, the heart
Exercise 15
Circle the term that is most appropriate for the meaning of the sentence.
1. Mitral valve prolapse is when the blood ow moves (backward, forward, circuitously) through
the valve.
2. Edema is the excess accumulation of intercellular (blood, uid, lymph).
3. In coarctation of the aorta, the aorta is (widened, dilated, narrowed).
4. Small parasitic worms that invade tissues and cause elephantiasis are called (telangiectasia,
lariae, ringworm).
5. The death of heart tissue usually due to coronary artery occlusion is called a(n) (cardiac
arrest, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris).
6. Chest pain or pressure resulting from lack of blood ow to the myocardium is called (cardiac
arrest, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris).
7. The medical term for when the heart stops beating is (cardiac arrest, myocardial infarction,
angina pectoris).
8. With Raynaud disease, the ngers and toes become (cyanotic, diaphoretic, syncopal) due to
vascular constriction.
9. Congestive heart failure is inef ciency of cardiac (circulation, valves, pressure) causing edema
and pulmonary congestion.
10. A sudden onset of a fast heart rate is called (tachycardia, palpitation, utter).
11. An in ammation of a vein is called (phlebitis, telangiectasia, varicose vein).
12. Coronary artery disease is a narrowing of the coronary arteries causing a(n) (increase,
decrease, leakage) of blood ow to the myocardium.
13. A vascular blockage that is a combination of clotted blood and other foreign materials is a(n)
(regurgitation, embolus, thrombus).
14. Deep vein thrombosis is (plaque, fat, blood clot) formation in a deep vein.
15. Swollen and/or twisted veins are called (deep, varicose, phlebitis) veins.
16. Blockage of a coronary vessel often leading to a myocardial infarction is called (coronary
stenosis, coronary occlusion, congestive heart failure).
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 218LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 218 10/19/10 9:43:40 PM10/19/10 9:43:40 PM

Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 219
Exercise 16
Match each medical term with its meaning.
palpitation lymphedema angiostenosis dysrhythmia cardiomegaly
lymphadenitis occlusion plaque mitral valve stenosis arrhythmia
Meaning Term
1. narrowing of a blood vessel
2. forceful irregular heart beat felt by the patient
3. abnormality or disturbance of heart rhythm
4. edema due to blocked lymph node
5. blockage or closure
6. fat deposit on an arterial wall
7. narrowing of the mitral valve opening
8. in ammation of the lymph nodes
9. defective heart rhythm
10. enlargement of the heart
Exercise 17
Build a medical term from an appropriate pre x, combining form, and suf x,
given their meanings.
Pre x Combining Form Suf x Term
1. slow heart condition of
2. around or heart in ammation
surrounding
3. in, within heart tissue, structure
4. between ventricles pertaining to
5. around, heart tissue, structure
surrounding
6. rapid, fast heart condition of
7. many, much artery in ammation
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 219LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 219 10/19/10 9:43:40 PM10/19/10 9:43:40 PM

220 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
Exercise 18
Break the given medical term into its word parts and de ne each part. Then de ne
the medical term. (Note: This exercise uses some suf xes learned previously.)
For example:
pericarditis word parts: peri- / cardi/o / -itis
meanings: around, surrounding / heart / in ammation
term meaning: in ammation of the pericardial sac around the heart
1. lymphangiitis word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
2. lymphadenopathy word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
3. thrombophlebitis word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
4. cardiomyopathy word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
5. endocarditis word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
6. cardiovalvulitis word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
7. myocarditis word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
8. telangiectasia word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 220LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 220 10/19/10 9:43:40 PM10/19/10 9:43:40 PM

Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 221
Tests and Procedures
Term Pronunciation Meaning
Laboratory Tests Related to the Cardiovascular System
cardiac enzyme tests
kahr’d
ē-ak en’zīm tests
blood tests used to measure the level of
creatine kinase (CK), creatine phosphokinase
(CPK), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) that,
when such levels are increased, may indicate a
myocardial infarction
cardiac troponin
kahr’d
ē-ak trō’pō-nin
blood test used to measure the level of a
protein that is released in the blood when
myocardial cells die
C-reactive protein (CRP)
s
ē-rē-ak’tiv prō’tēn
blood test used to measure the level of
in ammation in the body; may indicate
conditions that lead to cardiovascular disease
electrolyte panel
ĕ-lek’trō-līt pan’ĕl
blood test used to measure the level of sodium
(Na), potassium (K), chloride (Cl), and carbon
dioxide (CO
2
); used to diagnose an acid-base
or pH imbalance that may cause arrhythmias,
muscle damage, or death
lipid panel, syn. lipid
pro le
lip’id pan’
ĕl, lip’id
pr
ō’fīl
blood test to measure the level of total
cholestrol, high density lipoprotein (HDL), low
density lipoprotein (LDL), and triglycerides,
all of which may signal an increased risk of
cardiovascular disease
Diagnostic Procedures Related to the Cardiovascular System
Imaging Studies
angioscopy
an’j
ē-os’kŏ-pē
insertion of a catheter with an attached camera
to visualize a structure or vessel
aortography
ā-ōr-tog’ră-fē
process of recording the aorta after injection of
a dye
arteriography
ahr-ter’
ē-og’ră-fē
process of recording an artery after injection of
a dye
coronary angiography, syn.
cardiac catheterization
k
ōr’ŏ-nār-ē an’jē-og’ră-fē,
kahr’d
ē-ak kath’ĕ-tĕr-ī-zā’shŭn
process of recording the heart and major
vessels after injection of a dye (Fig. 7-18)
magnetic resonance imaging
(MRI)
mag-net’ik rez’
ŏ-năns
im’
ăj-ing
imaging technique that uses magnetic elds
and radiofrequency waves to visualize
anatomic structures
magnetic resonance
angiography (MRA)
mag-net’ik rez’
ŏ-năns
an’j
ē-og’ră-fē
MRI of the heart and blood vessels with an
injection of dye
multiple uptake gated
acquisition (MUGA) scan
m
ŭl’ti-pĕl-gāt’ĕd ak-wi-zi’shŭn
skan
nuclear medicine technique used to assess
ventricular function by producing an image of
a beating heart
sonography, syn.
ultrasonography
s
ŏ-nog’ră-fē, ŭl’tră-sŏ-nog’ră-fē
use of ultrasonic sound waves to visualize
internal organs
Doppler sonography (DS)
dop’l
ĕr sŏ-nog’ră-fē
technique used to record velocity of blood ow
echocardiography
ek’
ō-kahr-dē-og’ră-fē
process of recording the structure and
function of the heart at rest and with exercise
(Fig. 7-19)
(continued)
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 221LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 221 10/19/10 9:43:41 PM10/19/10 9:43:41 PM
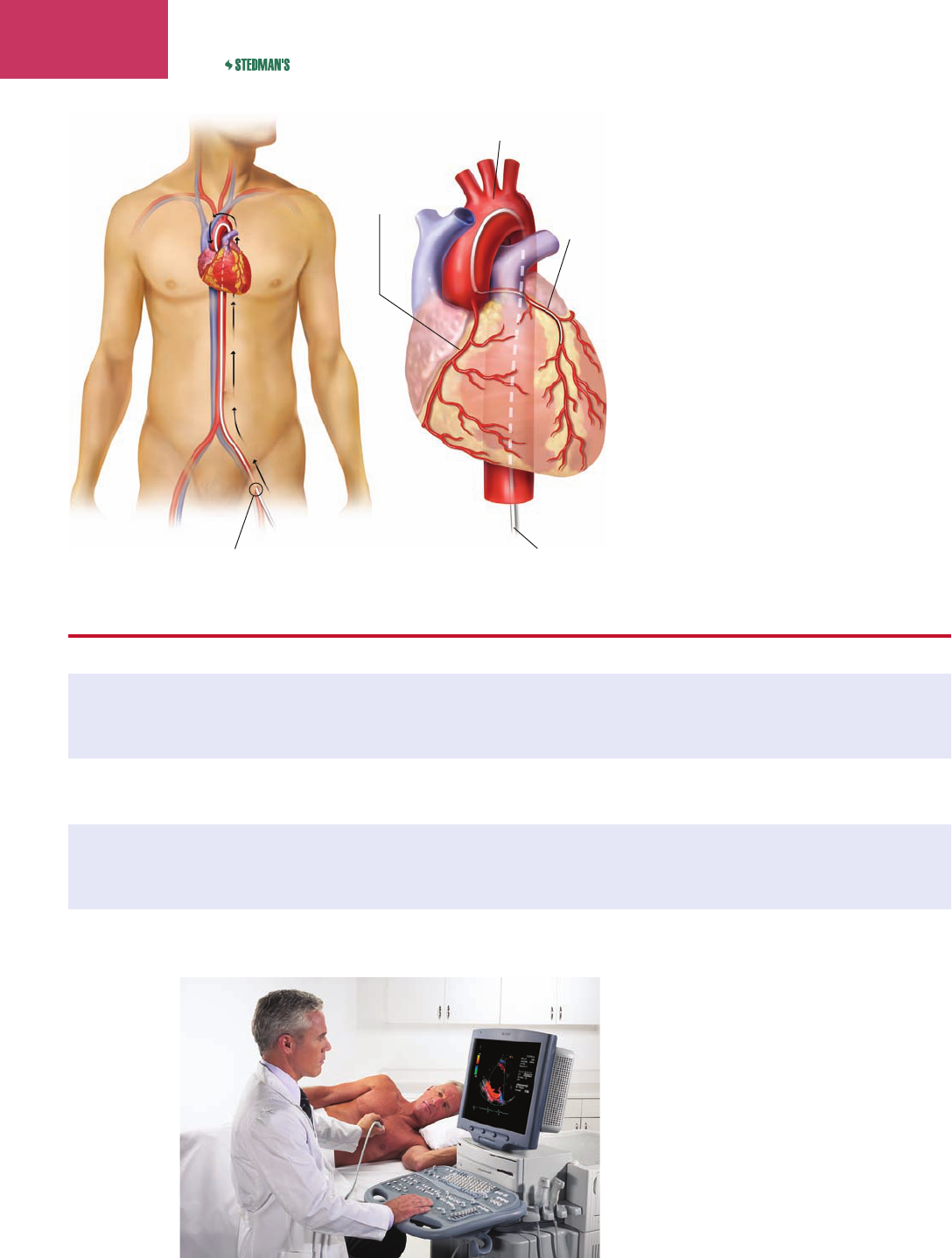
222 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
Catheter entrance Catheter
Aorta
Right coronary
artery
Anterior
interventricular
artery
Figure 7-18 Coronary angiography.
(continued)
Figure 7-19 Echocardiography.
Tests and Procedures (continued)
Term Pronunciation Meaning
transesophageal
echocardiography
(TEE)
tranz-
ē-sō-fā’jē-ăl
ek’
ō-kahr-dē-og’ră-fē
placement of the ultrasonic transducer
inside the patient’s esophagus to assess
cardiac function and examine cardiac
structure
vascular sonography
vas’ky
ū-lăr sŏ-nog’ră-fē
placement of the ultrasound transducer at the
tip of a catheter within a blood vessel to assess
blood ow
single photon emission
computed tomography
(SPECT) scan
sing’g
ĕl fō’ton ē-mi’shŭn
k
ŏm-pyūt’ĕd tŏ-mog’ră-fē
skan
nuclear medicine technique used to
assess ventricular function by producing
a three-dimensional image of a beating
heart
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 222LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 222 10/19/10 9:43:41 PM10/19/10 9:43:41 PM

Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 223
Tests and Procedures (continued)
Term Pronunciation Meaning
venography
v
ē-nog’ră-fē
process of recording a vein after injection of a
dye
ventriculography
ven-trik’y
ū-log’ră-fē
process of recording the heart ventricles after
injection of a dye or radioactive substance
(radionuclide)
Other Procedures
auscultation
aws’k
ŭl-tā’shŭn
listening to body sounds with a stethoscope
blood pressure monitoring
(BP)
bl
ŭd presh’ŭr mon’i-tŏr’ing
auscultation of the systolic and diastolic
arterial pressure using a stethoscope and a
sphygmomanometer
electrocardiography (ECG or
EKG)
ĕ-lek’trō-kahr-dē-og’ră-fē
process of recording (in a graphic format) the
heart’s electrical activity; the waves are labeled
with the letters P, Q, R, S, and T (see Fig. 7-14)
graded exercise test (GXT),
syn. stress electrocardiogram,
exercise stress test
gr
ād’ĕd eks’ĕr-sīz test, stres
ĕ-lek’trō-kahr’dē-ō-gram,
eks’
ĕr-sīz stres test
electrocardiogram performed with controlled
stress, usually with a treadmill or bicycle
(Fig. 7-20)
Holter monitor (HM)
h
ōl’tĕr mon’i-tŏr
portable electrocardiographic device usually
worn for 24 hours
(continued)
Figure 7-20 Exercise stress test.
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 223LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 223 10/19/10 9:43:43 PM10/19/10 9:43:43 PM
224 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
Tests and Procedures (continued)
Term Pronunciation Meaning
percussion
p
ĕr-kŭsh’ŭn
physical examination method of tapping over
the body to elicit vibrations and sounds to
estimate the size, border, or uid content of a
cavity
pulse
p
ŭls
rhythmic dilation of an artery with each heart
contraction, usually felt at the wrist or neck
sphygmomanometer
s g’m
ō-mă-nom’ĕ-tĕr
device used for measuring blood pressure
stethoscope
steth’
ŏ-skōp
instrument used for auscultation of vascular or
other sounds in the body
Diagnostic Procedures Related to the Lymphatic System
lymphangiography
lim-fan’j
ē-og’ră-fē
process of recording a lymph node or lymph
vessel after injection of a dye
STETHOSCOPE Did you know that the rst stethoscope was invented by a
French physician who rolled paper into the shape of a cylinder to listen to heart
sounds? Prior to this, physicians would listen to a patient’s chest by placing
their ear directly on the chest wall.
Exercises: Tests and Procedures
Exercise 19
Circle the term that is most appropriate for the meaning of the sentence.
1. A portable ECG monitoring device that can be worn for 24 hours is a (graded exercise test,
Holter monitor, MUGA scan).
2. The process of recording an artery after injecting a dye or radionuclide is called
(arteriography, angiography, aortography).
3. The process of recording a lymph vessel after injecting a dye is called (angiography, vascular
sonography, lymphangiography).
4. Insertion of a catheter with a camera to visually assess a vessel is called (angioscopy,
ne-needle aspiration, cardiac catheterization).
5. The process of listening to body sounds with a stethoscope is called (echocardiography,
ultrasound, auscultation).
6. The process of recording the heart’s electrical activity is called (echocardiography,
electrocardiography, sonography).
7. A(n) (MUGA, MRI, SPECT) scan produces a three-dimensional image of a beating heart.
8. Doppler (electrocardiography, venography, sonography) is used to record the velocity of blood
ow.
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 224LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 224 10/19/10 9:43:45 PM10/19/10 9:43:45 PM

Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 225
9. The examination method of tapping over the body to elicit vibrations and sounds is called
(percussion, auscultation, blood pressure).
10. An MRI of the heart and blood vessels with an injection of dye is called (magnetic resonance
imaging, MUGA, magnetic resonance angiography).
Exercise 20
Complete each sentence by writing in the correct medical term.
1. An ECG performed with controlled stress is a(n)
.
2. The process of recording the structure and function of the heart using sonography is called
.
3. To perform
, an ultrasound transducer is placed inside the
patient’s esophagus.
4. Two examples of nuclear medicine studies that assess ventricular function are
and .
5. The process of recording the heart and major vessels after injection of a dye is called
or .
6. An echocardiogram assesses structure and function of the heart at rest and with
.
7. A ventriculography records the
after injection with dye.
8. Magnetic resonance imaging uses magnetic elds and
to visual anatomic structures.
9. Measurement of blood pressure requires a(n)
.
10. A stethoscope is used to
to body sounds.
Exercise 21
Match each type of lab test with the description of the test.
cardiac troponin electrolyte panel C-reactive protein
lipid panel cardiac enzyme tests
Description Term
1. evaluation of Na, K, Cl, and CO
2
2. evaluation of CK, CPK, and LDH
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 225LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 225 10/19/10 9:43:45 PM10/19/10 9:43:45 PM

226 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
3. evaluation of protein released when myocardial cells die
4. evaluation of cholesterol, HDL, LDL, and triglycerides
5. measurement of in ammation in the body
Exercise 22
Using the given suf x, build a medical term for the meaning given.
Suf x Meaning of Medical Term Medical Term
-graphy process of recording using sound waves 1.
-graphy process of recording a vein 2.
-graphy process of recording the ventricles 3.
-graphy process of recording the aorta 4.
-graphy process of recording a blood vessel 5.
Surgical Interventions and Therapeutic Procedures
Term Pronunciation Meaning
Related to the Cardiovascular System
angioplasty
an’j
ē-ō-plas-tē
surgical repair of a vessel
aortocoronary bypass
(ACB)
ā-ōr’tō-kōr’ō-nar-ē
b
ī’pas
attachment of a grafted vessel to the aorta to go
around a damaged coronary artery
aneurysmectomy
an’y
ūr-iz-mek’tŏ-mē
excision of an aneurysm
atherectomy
ath’er-ek’t
ŏ-mē
surgical removal of fatty plaque from a vessel
surgically or using catheterization
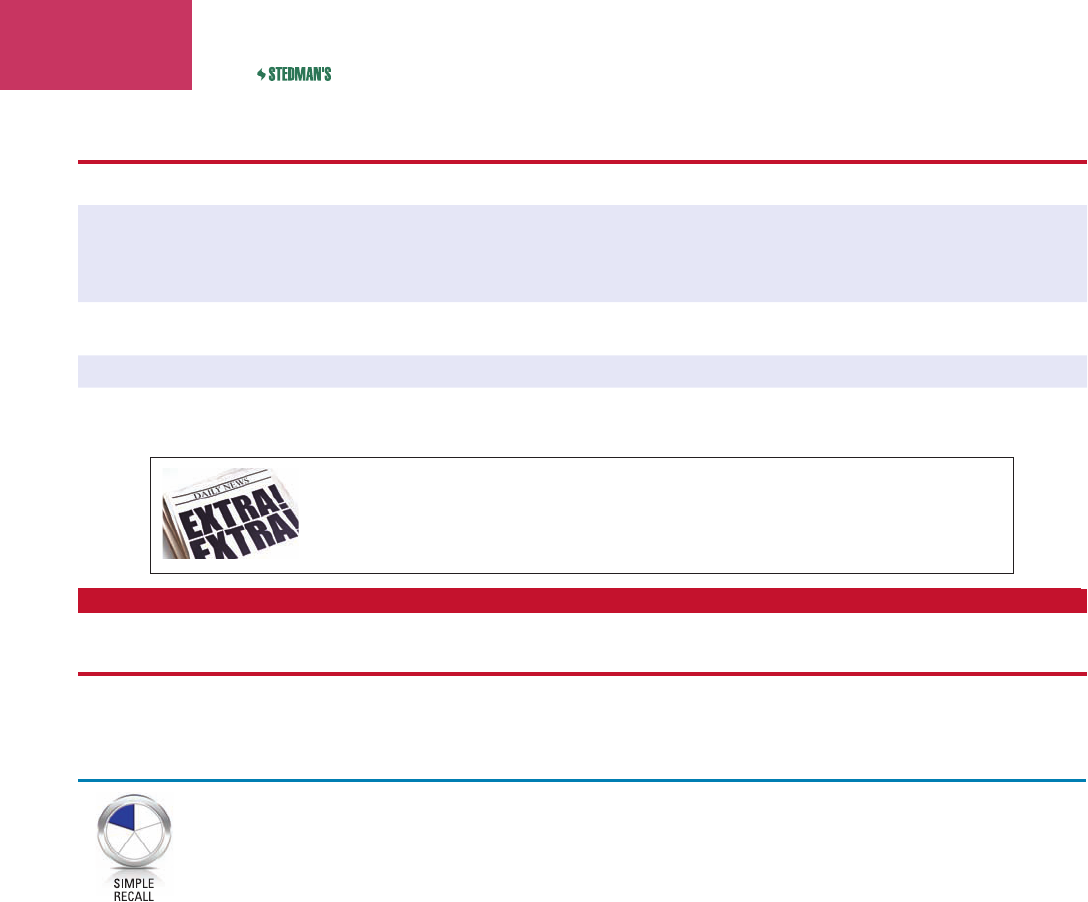
cardiac pacemaker
kahr’d
ē-ak pās’mā-kĕr
surgically placed mechanical device connected to
stimulating leads (electrodes) on or within the heart,
programmed to help maintain normal heart rate and
rhythm (Fig. 7-21)
cardioversion
kahr’d
ē-ō-vĕr’zhŭn
use of de brillation or drugs to restore the heart’s
normal rhythm
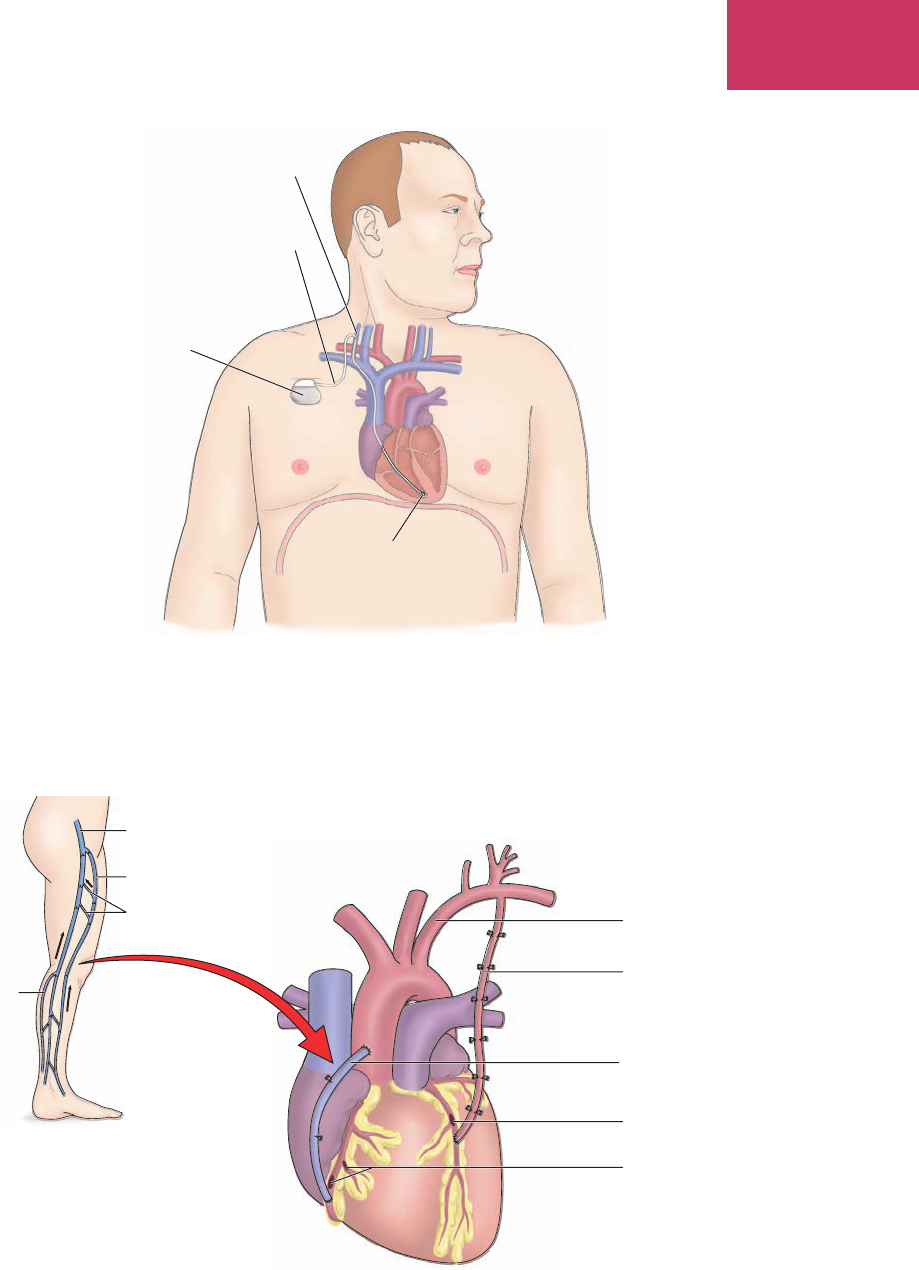
coronary artery bypass
graft (CABG)
k
ōr’ŏ-nār-ē ahr’tĕr-ē
b
ī’pās graft
surgical procedure in which a damaged section of a
coronary artery is replaced or bypassed with a graft
vessel (Fig. 7-22)
(continued)
THE EVOLUTION OF CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS SURGERY Advances in
technology have led to the development of several types of coronary artery
bypass surgery. Traditionally, this procedure involved opening the chest via a large
incision through the middle of the sternum; a heart-lung machine circulated the
blood while the heart was stopped. A newer type of bypass surgery, called
“off-pump,” uses special agents to stabilize the heart while the surgery takes place.
In addition, surgeons now perform minimally invasive bypass surgery, which uses
small incisions in the side of the chest and special instruments for the operation.
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 226LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 226 10/19/10 9:43:45 PM10/19/10 9:43:45 PM
Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 227
Figure 7-22 Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG).
Iliofemoral vein
Great saphenous
vein
Small
saphenous
vein
Intact communicating
veins
Left subclavian
artery
Internal
mammary
artery graft
Saphenous
vein graft
Blockage
Blockages
Figure 7-21 Insertion of a pacemaker.
Tip of lead (electrode)
lodged in apex of
right ventricle
Pacemaker lead enters
external jugular vein
Pacemaker
generator
placed
beneath
skin in
pectoral
region
Pacemaker lead tunneled
subcutaneously between
pacemaker and external
jugular vein
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 227LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 227 10/19/10 9:43:46 PM10/19/10 9:43:46 PM

228 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
AB
Artery wall Plaque
Figure 7-23 Coronary angioplasty (PTCA). A. Plaque buildup in an artery. B. Balloon inserted and in ated, thus
enlarging the lumen.
Artery wall
Atherosclerotic
material (plaque)
Balloon catheter with
expandable stent
Expanded stent
presses plaque
against artery wall
Inflated balloon
Figure 7-24 Arterial stent.
Surgical Interventions and Therapeutic Procedures (continued)
Term Pronunciation Meaning
de brillation
d
ē- b’ri-lā’shŭn
use of an electric shock to stop brillation or cardiac arrest
embolectomy
em’b
ō-lek’tŏ-mē
surgical removal of an embolus or blood clot,
usually with a catheter
endarterectomy
end’ahr-t
ĕr-ek’tŏ-mē
surgical removal of atheromatous deposits, usually in
a coronary or carotid artery
pericardiocentesis
per’i-kahr’d
ē-ō-sen-tē’sis
surgical puncture to aspirate uid from the pericardium
percutaneous transluminal
coronary angioplasty (PTCA)
p
ĕr’kyū-tā’nē-ŭs trans-
l
ū’mĕn-ăl kōr’ŏ-nār-ē
an’j
ē-ō-plas-tē
advancement of a cardiac catheter with a balloon
attachment that can be in ated at the site of stenosis,
thereby enlarging the lumen (Fig. 7-23)
phlebectomy
e-bek’t
ō-mē
excision of a vein
stent stent intravascular insertion of a hollow mesh tube
designed to keep a vessel open or patent (Fig. 7-24)
(continued)
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 228LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 228 10/19/10 9:43:47 PM10/19/10 9:43:47 PM

Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 229
Mechanical heart valve
Tricuspid valve
A
ortic valve
Pulmonary valve
Mitral valve
Figure 7-25 Mitral valve prosthesis.
Exercises: Surgical Interventions and Therapeutic Procedures
Exercise 23
Write the correct medical term for the meaning given.
1. excision of a gland
2. in ation of a balloon catheter in a coronary artery
3. surgical removal of an embolus or blood clot
4. surgical repair of a valve
5. surgical removal of fatty plaque
Surgical Interventions and Therapeutic Procedures (continued)
Term Pronunciation Meaning
valve replacement
valv r
ē-plās’mĕnt
surgical replacement of a valve with a biologic or
mechanical device (Fig. 7-25)
valvotomy
val-vot’
ŏ-mē
incision into a valve
valvuloplasty
val’vy
ū-lō-plas-tē
surgical repair of a valve
Related to the Lymphatic System
adenectomy
ad’
ĕ-nek’tŏ-mē
excision of a gland
lymphadenectomy
lim-fad’
ĕ-nek’tŏ-mē
excision of a lymph node
lymphadenotomy
lim-fad’
ĕ-not’ŏ-mē
incision into a lymph node
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 229LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 229 10/19/10 9:43:49 PM10/19/10 9:43:49 PM

230 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
6. excision of a lymph node
7. incision into a lymph node
Exercise 24
Circle the correct term that is appropriate for the meaning of the sentence.
1. Dr. Johansson explained to Mr. Curren that his (valvuloplasty, valve replacement, atherectomy)
would be with a biologic or mechanical device.
2. A(n) (angioplasty, cardioversion, valve replacement) was performed on Mrs. Campbell to correct
her irregular and fast heart rate.
3. Mr. Torres had a(n) (endarterectomy, embolectomy, stent) to surgically remove the fatty buildup
in his carotid artery.
4. After having several syncopal episodes due to bradycardia, Mr. DeHaan was scheduled
for implantation of a (cardiac pacemaker, valve replacement, stent) to help maintain normal
heart rate and rhythm.
5. Dr. LaPenna decided to do a(n) (ACB, PTCA, CABG) to open Mr. Thompson’s narrowed
coronary artery using a catheter with a balloon attachment.
6. A (pacemaker, PTCA, stent) was inserted in Ms. Andretti’s coronary artery to help keep it
open.
7. After documenting the restenosis of his coronary arteries by angiography, Dr. Ayerdi advised
Mr. Johnson to have a(n) (CABG, cardioversion, adenectomy).
8. Dr. Nowak grafted the saphenous vein to the aorta in a procedure called a(n) (aortocoronary
bypass, endarterectomy, PTCA).
Exercise 25
Using the given suf x, build a medical term for the meaning given.
Suf x Meaning of Medical Term Medical Term
-plasty surgical repair of a blood vessel 1.
-ectomy excision of an aneurysm 2.
-centesis puncture to aspirate uid from 3.
the pericardium
-ectomy excision of a gland 4.
-tomy incision into a valve 5.
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 230LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 230 10/19/10 9:43:50 PM10/19/10 9:43:50 PM

Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 231
Exercise 26
Break the given medical term into its word parts and de ne each part. Then
de ne the medical term.
For example:
carditis word parts: cardi/o / -itis
meanings: heart / in ammation
term meaning: in ammation of the heart
1. valvuloplasty word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
2. angioplasty word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
3. atherectomy word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
4. phlebectomy word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
5. valvotomy word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
Medications and Drug Therapies
Term Pronunciation Meaning
anticoagulant
an’t
ē-kō-ag’yŭ-lănt
drug used to prolong clotting time
antiarrhythmic agent
an’t
ē-ā-ridh’mik ā’jĕnt
drug used to suppress fast or irregular heart rhythms
hemostatic agent
h
ē’mō-stat’ik ā’jĕnt
drug that stops the ow of blood within vessels
hypolipidemic agent
h
ī’pō-lip’id-ē-mĭc a’jĕnt
drug used to lower cholesterol levels
nitroglycerin
n
ī’trŏ-glĭs-er-in
vasodilator used for angina pectoris
thrombolytic therapy
throm’b
ō-lit’ik thār’ă-pē
administration of an intravenous drug to dissolve a
blood clot
vasoconstrictor
v
ā’sō-kŏn-strik’tŏr
drug that decreases the size of blood vessels
vasodilator
v
ā’sō-dī’lā-tŏr
drug that increases the size of blood vessels
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 231LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 231 10/19/10 9:43:51 PM10/19/10 9:43:51 PM

232 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
Exercise: Medications and Drug Therapies
Exercise 27
Write the correct medication or drug therapy term for the meaning given.
1. drug that decreases the size of blood vessels
2. drug that prolongs clotting time
3. administration of an IV drug to dissolve a clot
4. drug that increases the size of blood vessels
5. drug that stops the ow of blood
6. drug that suppresses fast or irregular heart rhythms
7. drug used for angina pectoris
8. drug used to lower cholesterol
Exercise: Specialties and Specialists
Exercise 28
Match each medical specialist or specialty with its description.
cardiac electrophysiology cardiologist cardiology
lymphedema therapy lymphedema therapist cardiac electrophysiologist
1. study of heart disease
2. specialty related to the treatment of lymphedema
3. physician who specializes in heart disease
Specialties and Specialists
Term Pronunciation Meaning
cardiology
kahr’d
ē-ol’ŏ-jē
medical specialty concerned with diagnosis
and treatment of heart disease
cardiologist
kahr’d
ē-ol’ŏ-jist
physician who specializes in cardiology
cardiac electrophysiology
kahr’d
ē-ak ĕ-lek’trō- z’ē-ol’ŏ-jē
medical speciality concerned with the
electrical activities of the heart
cardiac electrophysiologist
kahr’d
ē-ak ĕ-lek’trō- z’ē-ol’ŏ-jist
physician who specializes in cardiac
electrophysiology
lymphedema therapy
lim’f
ĕ-dē’mă thār’ă-pē
medical specialty concerned with the
treatment of lymphedema
lymphedema therapist
lim’f
ĕ-dē’mă thār’ă-pist
one who specializes in lymphedema therapy
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 232LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 232 10/19/10 9:43:51 PM10/19/10 9:43:51 PM

Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 233
Abbreviations
Abbreviation Meaning
Related to the Cardiovascular System
ACB aortocoronary bypass
ACS acute coronary syndrome
ASHD arteriosclerotic heart disease
AV arteriovenous, atrioventricular
BP blood pressure
CABG coronary artery bypass graft
CAD coronary artery disease
CHF congestive heart failure
DS Doppler sonography
DVT deep venous thrombosis
ECG or EKG electrocardiography
GXT graded exercise test
HM Holter monitor
HTN hypertension
MI myocardial infarction
MRA magnetic resonance angiography
MRI magnetic resonance imaging
MUGA multiple uptake gated acquisition
PAD peripheral arterial disease
PTCA percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty
PVC premature ventricular contraction
RHD rheumatic heart disease
SPECT single photon emission computed tomography
TEE transesophageal echocardiography
4. specialty related to the heart’s electrical activities
5. one who specializes in lymphedema therapy
6. physician specialized in the heart’s electrical activities
Exercises: Abbreviations
Exercise 29
Write the meaning for the following abbreviations.
1. CHF
2. ACB
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 233LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 233 10/19/10 9:43:51 PM10/19/10 9:43:51 PM

234 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
3. SPECT
4. ASHD
5. DVT
6. PVC
7. BP
8. ACS
9. HTN
10. CABG
Exercise 30
Write the meaning of each abbreviation used in these sentences.
1. Dr. Erickson ordered a HM for Mr. Hadley to investigate his complaints of irregular
heartbeats.
2. Mrs. Cuthbert underwent a PTCA to enlarge the lumen of her stenotic artery.
3. The cardiologist ordered an MRA of the brain to locate the blocked vessel.
4. Dr. Anderson’s specialty is repair of AV defects.
5. Dr. Macken had dif culty visualizing the heart structures on the echocardiogram, so he
ordered a TEE, a procedure in which the patient swallows the transducer, to obtain a different
perspective.
6. Angie Smith was diagnosed with CAD because of her ischemia.
7. Mr. Javovich’s heart valve was damaged after having RHD as a child.
8. Mr. John’s GXT was performed using a treadmill.
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 234LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 234 10/19/10 9:43:51 PM10/19/10 9:43:51 PM

Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 235
9. Dr. Francis diagnosed Ms. Snyder with an MI caused by coronary artery occlusion.
10. Mrs. Adkins was diagnosed with PAD through the use of Doppler sonography.
Exercise 31
Match each abbreviation with the appropriate description.
DS MUGA MRA
MRI ECG
1. recording of the heart’s electrical activity
2. imaging technique using magnetic elds and radiofrequency waves
3. MRI of the heart and blood vessels with an injection of dye
4. technique used to record velocity of blood ow
5. nuclear medicine technique used to assess ventricular function
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 235LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 235 10/19/10 9:43:52 PM10/19/10 9:43:52 PM
236
Chapter Review
Review of Terms for Anatomy
and Physiology
Exercise 32
Write the correct terms on the blanks for the anatomic structures indicated.
Aorta
Left pulmonary artery
Left pulmonary veins
(6)________________
Aortic valve
Mitral valve
(7)________________
(9)________________
(10)________________
(5)________________
(4)________________
(3)________________
Tricuspid valve
(2)________________
Pulmonary valve
Right pulmonary veins
Right pulmonary artery
(1)________________
(8)________________
Septum
Chapter Review
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 236LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 236 10/19/10 9:43:52 PM10/19/10 9:43:52 PM
Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 237
Exercise 33
Write the correct terms on the blanks for the anatomic structures illustrated.
(1) __________________
(2) __________________
(3) __________________
(4) __________________
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 237LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 237 10/19/10 9:43:53 PM10/19/10 9:43:53 PM

238 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
Understanding Term Structure
Exercise 34
Break the given medical term into its word parts and de ne each part. Then
de ne the medical term. (Note: you may need to use word parts from other
chapters.)
For example:
carditis word parts: cardi/o / -itis
meanings: heart / in ammation
term meaning: in ammation of the heart
1. angiostenosis word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
2. phlebitis word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
3. electrocardiography word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
4. atrioventricular word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
5. tachycardia word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
6. interventricular word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
7. thrombosis word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 238LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 238 10/19/10 9:43:55 PM10/19/10 9:43:55 PM

Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 239
8. polyarteritis word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
9. thrombophlebitis word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
10. cardiomyopathy word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
11. arteriosclerosis word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
12. sphygmic word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
13. venography word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
14. bradycardia word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
15. atherosclerosis word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
16. myocardium word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 239LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 239 10/19/10 9:43:55 PM10/19/10 9:43:55 PM

240 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
17. valvulotomy word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
18. lymphadenopathy word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
19. lymphangiitis word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
20. thrombolytic word parts:
meanings:
term meaning:
Comprehension Exercises
Exercise 35
Fill in the blank with the correct term.
1. The
is located between the endocardium and epicardium.
2. The wall that separates the right and left parts of the heart is called the
.
3. A(n)
is one who specializes in the study of the heart.
4. The heart valve between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery is called the
valve.
5. The
carries oxygenated blood away from the heart.
6. When the ventricles are in the relaxation phase of the heartbeat cycle, it is referred to as
.
7. Dilation of small terminal vessels is a condition called
.
8. Swollen or twisted veins are referred to as
.
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 240LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 240 10/19/10 9:43:56 PM10/19/10 9:43:56 PM

Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 241
9. A rhythm of rapid regular contractions of the atria is called atrial .
10. A rhythm of rapid irregular contractions of the ventricles is called ventricular
.
11.
is the enlargement of the lower extremities due to worms blocking
the lymph vessels.
12. Cramping of the legs due to lack of blood ow is called
.
13. Lack of blood ow is a condition called
.
14. When the heart muscle is deprived of oxygen or blood ow for a signi cant amount of time,
tissue death may occur. Death of heart muscle is called a(n)
.
15. Cardiac arrest is complete, sudden cessation of
activity.
16. Prolonged immobility during air travel can increase the risk of blood clot formation in the
large veins, also called
.
17. An early contraction of the ventricles is referred to as a(n)
.
18. Abnormal heart sounds are also referred to as
.
19. Patent means
, such as in a patent ductus arteriosus where the fetal
circulatory vessels fail to close.
20. C-reactive protein is a blood test used to measure the level of
in the
body.
Exercise 36
Write a short answer for each question.
1. Which type of drug stops the ow of blood within vessel?
2. The pulse is usually felt at which two points on the body?
3. During vascular sonography, where is the catheter placed?
4. What four substances are measured in a lipid panel?
5. What is the difference between hypotension and hypertension?
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 241LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 241 10/19/10 9:43:56 PM10/19/10 9:43:56 PM

242 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
6. Blood pressure monitoring involves the use of what two instruments?
7. The drug nitroglycerin is used to treat what condition?
8. What procedure might be used to treat uid around the pericardium?
9. What physical activity does a physician perform during percussion?
10. Why might a SPECT scan be performed to diagnose arrhythmias?
11. What two types of treatment might be done in cardioversion?
12. What is the opposite of tachycardia?
13. In what two situations might a de brillation be performed?
14. Which two procedures are done to bypass damaged coronary arteries?
15. How does the balloon attachment function in a PTCA?
Exercise 37
Circle the letter of the best answer in the following questions.
1. Which of the following would not be used
to describe an abnormal heart beat?
A. aneurysm
B. dysrhythmia
C. tachycardia
D. palpitation
2. Using the plural form of the term, the two
upper receiving chambers of the heart are
called the:
A. aorta
B. atria
C. arterioles
D. atrium
3. In ammation of the lymph vessels is
referred to as:
A. lymphangiitis
B. lymphadenitis
C. lymphedema
D. lymphadenopathy
4. Edema that retains an indentation of a
pressed nger is called:
A. dissecting
B. pitting
C. ischemic
D. stenotic
5. Cardiac tamponade is compression of the
heart. Which procedure might be used to
treat this condition?
A. angioplasty
B. cardioversion
C. myocentesis
D. pericardiocentesis
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 242LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 242 10/19/10 9:43:56 PM10/19/10 9:43:56 PM

Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 243
6. A patient with mitral valve stenosis might
have previously had which condition?
A. rheumatic fever
B. Raynaud syndrome
C. murmur
D. peripheral arterial disease
7. Which of the following is not a diagnostic
test designed to record arrhythmias?
A. lipid pro le
B. graded exercise test
C. electrocardiogram
D. Holter monitor
8. ECG electrodes are usually placed at the
precordial region or the:
A. abdomen
B. anterior left chest
C. anterior right chest
D. shoulders
9. CABG stands for:
A. coronary artery bypass graft
B. cardiac artery bypass graft
C. cerebrovascular accident bypass graft
D. aortocoronary bypass
10. During a PTCA, a catheter is advanced
through a vessel. Which term pertains to
the italicized phrase?
A. percutaneous
B. transluminal
C. coronary
D. angiogram
11. Which of the following is a hollow mesh
tube used to keep a vessel patent?
A. pacemaker
B. valvotomy
C. de brillation
D. stent
12. What substance is injected during a cardiac
catheterization?
A. uid
B. dye
C. blood
D. lymph
13. Which blood test diagnoses an acid-base or
pH imbalance?
A. cardiac enzyme test
B. C-reactive protein
C. cardiac troponin
D. electrolyte panel
14. Filariae cause elephantiasis by blocking
which type of vessels?
A. arteries
B. veins
C. lymph
D. capillaries
15. A patient who states that she can “feel her
heartbeat” is experiencing:
A. palpitations
B. tachycardia
C. bradycardia
D. percussion
16. Vessels carrying blood to the heart might
be tested using which diagnostic
procedure?
A. arteriography
B. aortography
C. transesophageal echocardiography
D. venography
17. Which condition is not a heart rhythm or
conduction disorder?
A bradycardia
B. tachycardia
C. phlebitis
D. dysrhythmia
18. Lack of blood ow to the lower limbs causes:
A. phlebitis
B. lymphangitis
C. intermittent claudication
D. thrombus
19. Which procedure treats the buildup of
plaque or fatty paste inside arterial walls?
A. pericardiocentesis
B. atherectomy
C. valve replacement
D. aneurysmectomy
20. An ECG produces a recording of the heart’s
electrical activity in what type of format?
A. x-ray
B. three-dimensional image
C. sonogram
D. graph
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 243LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 243 10/19/10 9:43:56 PM10/19/10 9:43:56 PM

244 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
Application and Analysis
CASE REPORTS
Exercise 38
Read the case reports and circle the letter of your answer choice for the
questions that follow.
CASE 7-1
1. What of the following best describes a
CABG?
A. noninvasive procedure to open a
clogged artery
B. surgical replacement or bypass of a
damaged coronary artery
C. removal of a clot using catheterization
D. intravascular insertion of a hollow mesh
tube
2. Atrial brillation is best described as:
A. rapid irregular rhythm of the lower
heart chambers
B. rapid regular rhythm of the upper heart
chambers
C. rapid irregular rhythm of the upper
heart chambers
D. rapid regular rhythm of the lower heart
chambers
3. Mr. Terrigo’s symptoms could best be
described as:
A. acute coronary syndrome
B. cardiac arrest
C. intermittent claudication
D. Raynaud disease
4. Which of the following are waves found on
an ECG?
A. QRS waves
B. TUV waves
C. ultrasound waves
D. Doppler waves
5. Which of the following would typically not
be true of stenotic coronary arteries?
A. caused by CAD
B. caused by a thrombus
C. caused by atherosclerosis
D. caused by lymphedema
6. All of the following are true for a PTCA
except:
A. attempts to enlarge the vessel lumen
B. involves a cardiac catheter
C. involves the use of electric shock
D. uses a balloon catheter attachment
Mr. Terrigo reported to the emergency room with complaints of chest pressure and
palpitations. He has a history of a triple CABG done in March 2008 with a history of
atrial brillation prior to surgery. He was doing well until this morning when he
started feeling chest pressure and palpitations. Dr. Francis ordered an ECG that
showed evidence of premature ventricular contractions and ST-segment depression.
A cardiac catheterization and subsequent PTCA was performed on the stenotic right
coronary artery.
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 244LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 244 10/19/10 9:43:57 PM10/19/10 9:43:57 PM
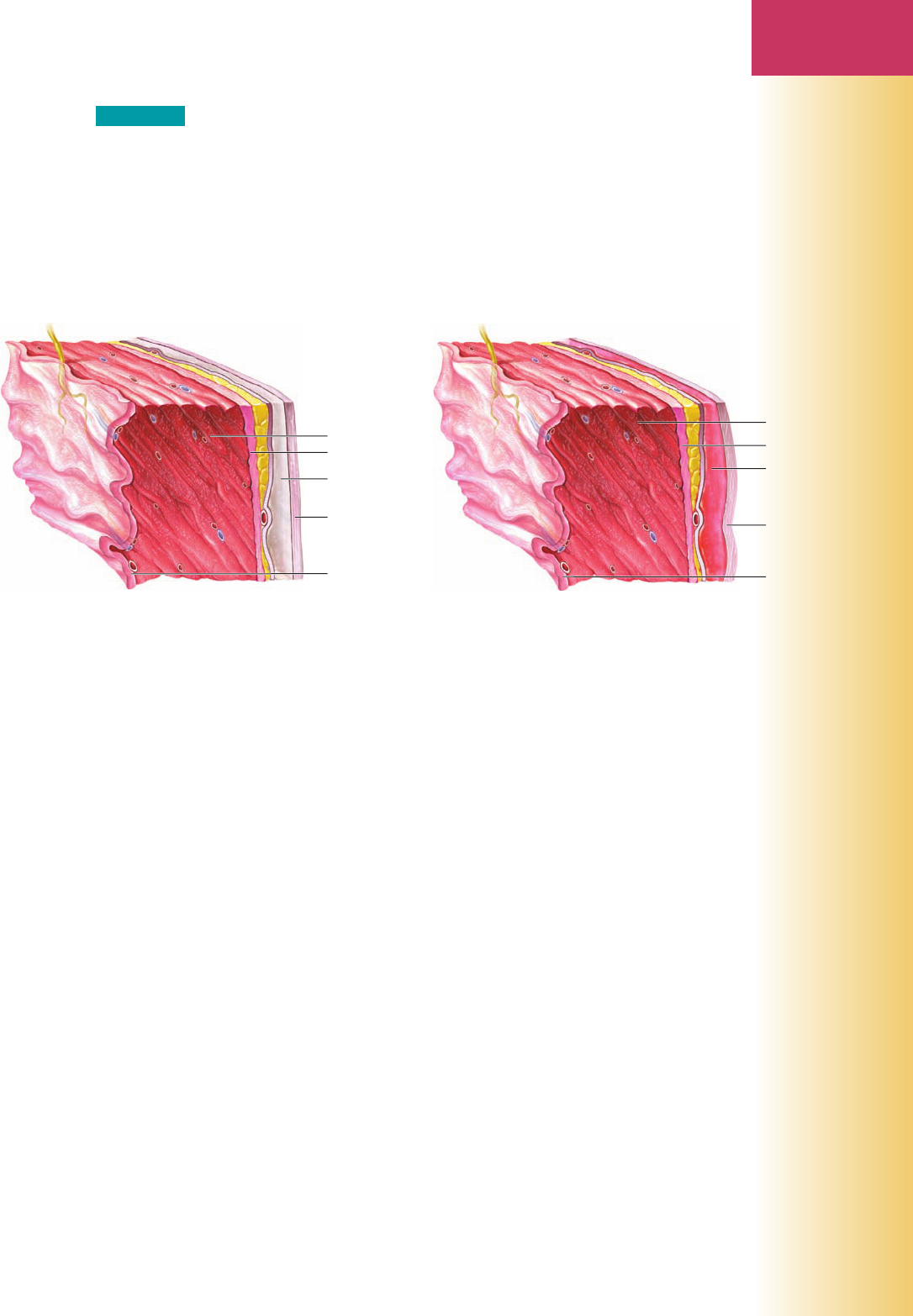
Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 245
7. The pericardium is:
A. a membrane that protects the heart
valves
B. the heart muscle
C. inside the heart
D. the sac surrounding the heart
8. Cardiac tamponade can occur if which
condition progresses?
A. occlusion
B. chest pain
C. fatigue
D. pericarditis
9. Auscultation is an examination by:
A. microscope
B. viewing through a scope or tube
C. palpation
D. listening
10. The term precordial refers to the:
A. anterior right chest
B. anterior left chest
C. heart
D. lungs
11. An echocardiogram uses _______ to assess
heart structure and function:
A. radiographic rays
B. electrical waves
C. ultrasound waves
D. nuclear imaging
CASE 7-2
Normal heart wall
Myocardium
Epicardium
Parietal
pericardium
Fibrous
pericardium
Endocardium
Pericarditis
Myocardium
Epicardium
Inflamed
parietal
pericardium
Fibrous
pericardium
Endocardium
Figure 7-26 Tissue changes in pericarditis.
Mr. Peterson had symptoms of fatigue, cough, and a fever over the past few days.
Last night he began experiencing chest pain radiating to his back, which was worse
lying down and relieved by sitting up. During the precordial exam, Dr. Macken
detected by auscultation a “squeaky leather” sound characteristic of a pericardial rub.
An ECG and echocardiogram were performed. Mr. Peterson was diagnosed with
pericarditis (Fig. 7-26) and placed on antiin ammatory drugs.
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 245LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 245 10/19/10 9:43:57 PM10/19/10 9:43:57 PM

246 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
MEDICAL RECORD ANALYSIS
MEDICAL RECORD 7-1
As a clinical medical assistant working in a cardiac clinic, you work directly with
patients, measuring vital signs, assisting with examinations, and performing other
procedures as directed by the physician. Last week one of the clinic’s patients,
Mr. Johnson, was admitted to the hospital for chest pain. He has now been discharged
and is returning to the clinic. You are reviewing the history and physical from his
hospital admission.
HISTORY
CHIEF COMPLAINT: Chest pain.
HISTORY OF PRESENT ILLNESS: Mr. Johnson presents here today with complaints of chest
pressure with pain radiating to left arm and jaw. Onset 4 days ago. These symptoms usually begin
when he has been jogging for 1 to 2 miles and get worse when he runs uphill. The pain subsides
if he slows down or rests. He has admitted to diaphoresis and shortness of breath during these
episodes. He exercises ve to seven times per week, usually running or jogging 3–5 miles per day.
He is not on any medications at this time other than an over-the-counter daily vitamin.
PAST MEDICAL HISTORY: His family history is positive for heart disease because his father died at
the age of 61 from a myocardial infarction.
SOCIAL HISTORY: Nondrinker, nonsmoker.
OCCUPATIONAL HISTORY: Has been working at the executive level for a land development
company for 27 years.
REVIEW OF SYSTEMS: On review of systems, his medical history is unremarkable. He denies any
cognitive, visual, auditory, musculoskeletal, digestive, or urinary problems.
PHYSICAL EXAM
GENERAL APPEARANCE: On examination this patient is a well-developed, well-nourished 57-year-
old man in no acute distress.
VITAL SIGNS: BP 122/78, P 59 reg, R 12, T 98.8 Wt 190# Ht 6’1’’
HEENT: Pupils are equal, round, and reactive to light and accommodation.
HISTORY AND PHYSICAL
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 246LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 246 10/19/10 9:44:00 PM10/19/10 9:44:00 PM

Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 247
NECK: The neck is supple. Carotid pulses are strong. No masses or tenderness.
LUNGS: Clear to percussion and auscultation. Breath sounds are easily heard and normal.
HEART: The heart rate and rhythm are regular. Pulse is 59. No murmurs, gallops, or rubs.
EXTREMITIES: No clubbing, cyanosis, or edema.
DIAGNOSTICS: Chest x-ray: suggestive of slight left ventricular enlargement, ECG: positive for
ST-segment depression, occasional PVC.
ASSESSMENT
IMPRESSION: Rule out ischemia, rule out cardiovascular disease
PLAN: CBC, chemistry pro le, echocardiogram, and GXT today. If positive, schedule cardiac
catheterization within a week. Instructions were given to patient to discontinue jogging until further
notice. Patient was given a sample of sublingual nitroglycerin and instructed on its use.
Exercise 39
Write the appropriate medical terms used in this medical record on the blanks
after their meanings. Note that not all the terms appear in the chapter, but you
should be able to identify these terms based on word parts that are included in
this chapter.
1. pertaining to the heart and vessels
2. ultrasound recording of heart structure
3. GXT is an abbreviation for
4. death of heart tissue
5. pertaining to a ventricle
6. abnormal condition characterized by purple or blue discoloration
Bonus Questions
Atherosclerosis is a form of arteriosclerosis. These two medical terms sound similar
but have two different meanings. Write in the correct term after each meaning:
7. hardening of the arteries
8. hardening of vessels due to plaque buildup
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 247LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 247 10/19/10 9:44:04 PM10/19/10 9:44:04 PM

248 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
SUBJECTIVE: Patient returns for follow-up after starting chemotherapy for his condition.
He complains of continued edema in both of his lower extremities. This is probably due to
lymphangiitis and the interrupted ow of lymph and uid buildup. He has symptoms of chills,
fever, and general malaise, which are all to be expected for this stage of his illness.
OBJECTIVE: Lab results con rm the presence of a bacterial infection from adult larial worms. His
temperature is 100.5°F today. His weight has stayed around 210 lb, which is up 2 lb from last visit.
On palpation of lower extremities, there is pitting edema and the right lower leg is erythematic.
ASSESSMENT:
1. Filarial elephantiasis
2. Lymphedema
3. Lymphangiitis
4. Fever
5. General malaise
PLAN:
1. Review appropriate hygiene plan
2. Continue with chemotherapy as prescribed
3. Begin massage therapy as tolerated for lymphedema
4. Follow up in 1 month to monitor signs of lymphadenitis or lymphadenopathy.
FOLLOW-UP FOR FILARIAL ELEPHANTIASIS
MEDICAL RECORD 7-2
You are a massage therapist seeing Mr. Vanden Berg for the rst time
for treatment of his lymphedema. He and his wife were missionaries
for the past 10 years in Ethiopia, Africa, where he contracted larial
elephantiasis. He has brought his medical record from his last
physician visit.
A massage therapist uses
touch to assist patients
with various conditions.
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 248LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 248 10/19/10 9:44:05 PM10/19/10 9:44:05 PM

Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 249
Exercise 40
Read the medical report and circle the letter of your answer choice for the
following questions. Note: Although some of the medical terms in these questions
do not appear in this chapter, you should understand them from their word parts.
1. What is causing Mr. Vanden Berg’s
elephantiasis?
A. red clay soil
B. lariae
C. food poisoning
D. heat
2. What is lymphedema?
A. infection of a lymph node
B. in ammation of a lymph node
C. swelling due to blocked blood vessels
D. swelling due to blocked lymph vessels
and uid buildup
3. What are lariae?
A. worms
B. bacteria
C. germs
D. eas
4. What is lymphangiitis?
A. infection of a lymph vessel
B. in ammation of a lymph node
C. in ammation of a lymph vessel
D. malignant tumor of lymph tissue
5. Which of the following statements about
elephantiasis is not true?
A. it occurs most commonly in South
America
B. lariae get into a body via mosquito
bites
C. lariae block lymph vessels
D. lymphedema and lymphangiitis are
common symptoms
Bonus Question
6. Although this chapter does not describe this term, what does the word erythema mean?
Pronunciation and Spelling
Exercise 41
Review the Chapter 7 terms in the Dictionary/Audio Glossary in the Student
Resources and practice pronouncing each term, referring to the pronunciation
guide as needed.
Exercise 42
Circle the correct spelling of each term.
1. aneurism anyerism aneurysm
2. lymphangeitis lymphangiitis lymphanitis
3. valvoplasty valvuplasty valvloplasty
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 249LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 249 10/19/10 9:44:07 PM10/19/10 9:44:07 PM

250 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY
4. telangietasia telengiectasia telangiectasia
5. Dopplier Dopler Doppler
6. sphygmomanometer sphymonometer sphymomenometer
7. vasoconstricter vasoconstrictor vasoconstitor
8. diastoli diestole diastole
9. ascultation ausultation auscultation
10. elephantiasis elephanitis elephantiosis
11. paroxysmal paroxismal paroximal
12. ischimic iskemic ischemic
13. dysrhythmia dysrrythmia dysrythmia
14. arrhythmia arrythmia arythmia
15. claudication claudacation claudocation
Media Connection
Exercise 43
Complete each of the following activities available with the Student Resources.
Check off each activity as you complete it, and record your score for the
Chapter Quiz in the space provided.
Chapter Exercises
____
Flash Cards
____
Concentration
____
Abbreviation Match-Up
____
Roboterms
____
Word Builder
____
Fill the Gap
____
Break It Down
____
True/False Body Building
____
Quiz Show
____
Complete the Case
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 250LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 250 10/19/10 9:44:07 PM10/19/10 9:44:07 PM

Chapter 7 Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 251
____
Medical Record Review
____
Look and Label
____
Image Matching
____
Spelling Bee
____ Chapter Quiz Score: _______%
Additional Resources
____
Animation: Cardiac Cycle
____
Animation: Hypertension
____
Dictionary/Audio Glossary
____ Health Professions Careers: Clinical Medical Assistant
____ Health Professions Careers: Massage Therapist
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 251LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 251 10/19/10 9:44:08 PM10/19/10 9:44:08 PM
LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 252LWBK568-C07_195-252.indd 252 10/19/10 9:44:09 PM10/19/10 9:44:09 PM
