Title stata.com
odbc — Load, write, or view data from ODBC sources
Syntax Menu Description Options
Remarks and examples Also see
Syntax
List ODBC sources to which Stata can connect
odbc list
Retrieve available names from specified data source
odbc query
"DataSourceName", verbose schema connect options
List column names and types associated with specified table
odbc describe
"TableName", connect options
Import data from an ODBC data source
odbc load
extvarlist
if
in
,
table("TableName") | exec("SqlStmt")
load options connect options
Export data to an ODBC data source
odbc insert
varlist
if
in
, table("TableName")
{dsn("DataSourceName") | connectionstring("ConnectionStr")}
insert options connect options
Allow SQL statements to be issued directly to ODBC data source
odbc exec("SqlStmt") ,
{dsn("DataSourceName") | connectionstring("ConnectionStr")}
connect options
Batch job alternative to odbc exec
odbc sqlfile("filename") ,
{dsn("DataSourceName") | connectionstring("ConnectionStr")}
loud connect options
Specify ODBC driver manager (Unix only)
set odbcmgr
iodbc | unixodbc
, permanently
1

2 odbc — Load, write, or view data from ODBC sources
where
DataSourceName is the name of the ODBC source (database, spreadsheet, etc.)
ConnectionStr is a valid ODBC connection string
TableName is the name of a table within the ODBC data source
SqlStmt is an SQL SELECT statement
filename is pure SQL commands separated by semicolons
and where extvarlist contains
sqlvarname
varname = sqlvarname
connect options Description
user(UserID) user ID of user establishing connection
password(Password) password of user establishing connection
dialog(noprompt) do not display ODBC connection-information dialog, and
do not prompt user for connection information
dialog(prompt) display ODBC connection-information dialog
dialog(complete) display ODBC connection-information dialog only if there
is not enough information
dialog(required) display ODBC connection-information dialog only if there
is not enough mandatory information provided
∗
dsn("DataSourceName") name of data source
∗
connectionstring("ConnectionStr") ODBC connection string
∗
dsn("DataSourceName") is not allowed with odbc query. You may not specify both DataSourceName and
connectionstring() with odbc query. Either dsn() or connectionstring() is required with odbc insert,
odbc exec, and odbc sqlfile.
load options Description
∗
table("TableName") name of table stored in data source
∗
exec("SqlStmt") SQL SELECT statement to generate a table to be read into
Stata
clear load dataset even if there is one in memory
noquote alter Stata’s internal use of SQL commands; seldom used
lowercase read variable names as lowercase
sqlshow show all SQL commands issued
allstring read all variables as strings
datestring read date-formatted variables as strings
∗
Either table("TableName") or exec("SqlStmt") must be specified with odbc load.
odbc — Load, write, or view data from ODBC sources 3
insert options Description
∗
table("TableName") name of table stored in data source
create create a simple ODBC table
overwrite clear data in ODBC table before data in memory is written to the table
insert default mode of operation for the odbc insert command
quoted quote all values with single quotes as they are inserted in ODBC table
sqlshow show all SQL commands issued
as("varlist") ODBC variables on the data source that correspond to the variables in
Stata’s memory
block use block inserts
∗
table("TableName") is required for odbc insert.
Menu
odbc load
File > Import > ODBC data source
odbc insert
File > Export > ODBC data source
Description
odbc allows you to load, write, and view data from Open DataBase Connectivity (ODBC) sources
into Stata. ODBC is a standardized set of function calls for accessing data stored in both relational and
nonrelational database-management systems. By default on Unix platforms, iODBC is the ODBC driver
manager Stata uses, but you can use unixODBC by using the command set odbcmgr unixodbc.
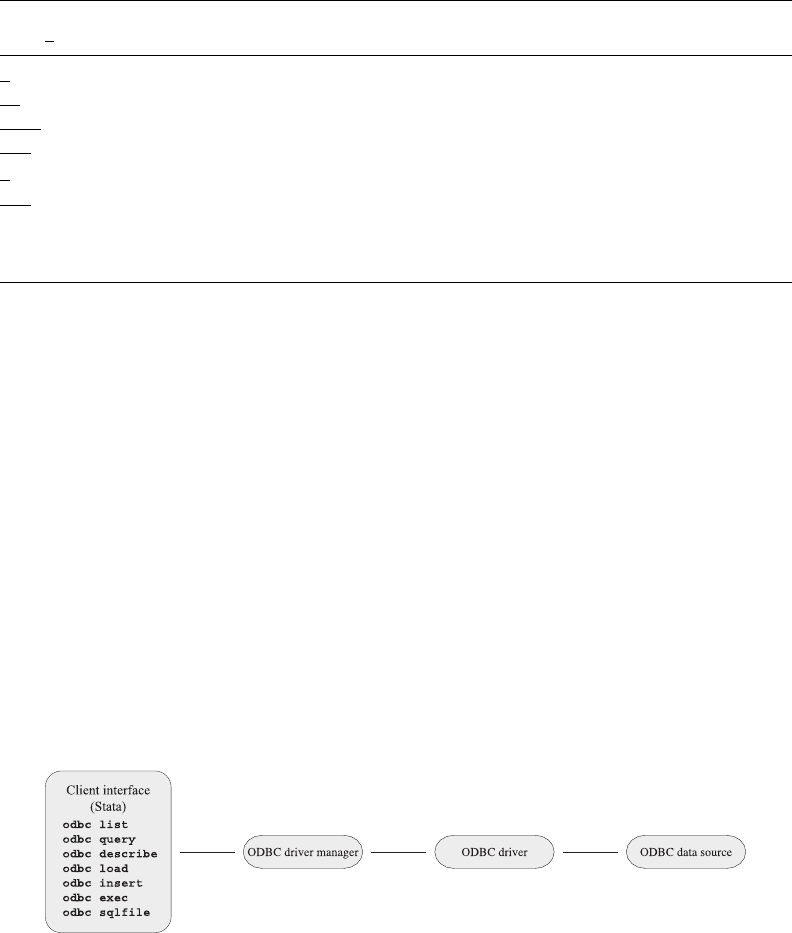
ODBC’s architecture consists of four major components (or layers): the client interface, the ODBC
driver manager, the ODBC drivers, and the data sources. Stata provides odbc as the client interface.
The system is illustrated as follows:
odbc list produces a list of ODBC data source names to which Stata can connect.
odbc query retrieves a list of table names available from a specified data source’s system catalog.
odbc describe lists column names and types associated with a specified table.
odbc load reads an ODBC table into memory. You can load an ODBC table specified in the table()
option or load an ODBC table generated by an SQL SELECT statement specified in the exec() option.
In both cases, you can choose which columns and rows of the ODBC table to read by specifying
extvarlist and if and in conditions. extvarlist specifies the columns to be read and allows you to
rename variables. For example,

4 odbc — Load, write, or view data from ODBC sources
. odbc load id=ID name="Last Name", table(Employees) dsn(Northwind)
reads two columns, ID and Last Name, from the Employees table of the Northwind data source.
It will also rename variable ID to id and variable Last Name to name.
odbc insert writes data from memory to an ODBC table. The data can be appended to an existing
table, replace an existing table, or be placed in a newly created ODBC table.
odbc exec allows for most SQL statements to be issued directly to any ODBC data source.
Statements that produce output, such as SELECT, have their output neatly displayed. By using Stata’s
ado language, you can also generate SQL commands on the fly to do positional updates or whatever
the situation requires.
odbc sqlfile provides a “batch job” alternative to the odbc exec command. A file is specified
that contains any number of any length SQL commands. Every SQL command in this file should be
delimited by a semicolon and must be constructed as pure SQL. Stata macros and ado-language syntax
are not permitted. The advantage in using this command, as opposed to odbc exec, is that only one
connection is established for multiple SQL statements. A similar sequence of SQL commands used
via odbc exec would require constructing an ado-file that issued a command and, thus, a connection
for every SQL command. Another slight difference is that any output that might be generated from
an SQL command is suppressed by default. A loud option is provided to toggle output back on.
set odbcmgr iodbc specifies that the ODBC driver manager is iODBC (the default). set odbcmgr
unixodbc specifies that the ODBC driver manager is unixODBC.
Options
user(UserID) specifies the user ID of the user attempting to establish the connection to the data
source. By default, Stata assumes that the user ID is the same as the one specified in the previous
odbc command or is empty if user() has never been specified in the current session of Stata.
password(Password) specifies the password of the user attempting to establish the connection to the
data source. By default, Stata assumes that the password is the same as the one previously specified
or is empty if the password has not been used during the current session of Stata. Typically, the
password() option will not be specified apart from the user() option.
dialog(noprompt | prompt | complete | required) specifies the mode the ODBC Driver Manager
uses to display the ODBC connection-information dialog to prompt for more connection information.
noprompt is the default value. The ODBC connection-information dialog is not displayed, and you
are not prompted for connection information. If there is not enough information to establish a
connection to the specified data source, an error is returned.
prompt causes the ODBC connection-information dialog to be displayed.
complete causes the ODBC connection-information dialog to be displayed only if there is not
enough information, even if the information is not mandatory.
required causes the ODBC connection-information dialog to be displayed only if there is not
enough mandatory information provided to establish a connection to the specified data source.
You are prompted only for mandatory information; controls for information that is not required to
connect to the specified data source are disabled.
dsn("DataSourceName") specifies the name of a data source, as listed by the odbc list command.
If a name contains spaces, it must be enclosed in double quotes. By default, Stata assumes that
the data source name is the same as the one specified in the previous odbc command. This option
is not allowed with odbc query. Either the dsn() option or the connectionstring() option

odbc — Load, write, or view data from ODBC sources 5
may be specified with odbc describe and odbc load, and one of these options must be specified
with odbc insert, odbc exec, and odbc sqlfile.
connectionstring("ConnectionStr") specifies a connection string rather than the name of a data
source. Stata does not assume that the connection string is the same as the one specified in the
previous odbc command. Either DataSourceName or the connectionstring() option may be
specified with odbc query; either the dsn() option or the connectionstring() option can be
specified with odbc describe and odbc load, and one of these options must be specified with
odbc insert , odbc exec, and odbc sqlfile.
table("TableName") specifies the name of an ODBC table stored in a specified data source’s system
catalog, as listed by the odbc query command. If a table name contains spaces, it must be
enclosed in double quotes. Either the table() option or the exec() option—but not both—is
required with the odbc load command.
exec("SqlStmt") allows you to issue an SQL SELECT statement to generate a table to be read into Stata.
An error message is returned if the SELECT statement is an invalid SQL statement. The statement
must be enclosed in double quotes. Either the table() option or the exec() option—but not
both—is required with the odbc load command.
clear permits the data to be loaded, even if there is a dataset already in memory, and even if that
dataset has changed since the data were last saved.
noquote alters Stata’s internal use of SQL commands, specifically those relating to quoted table
names, to better accommodate various drivers. This option has been particularly helpful for DB2
drivers.
lowercase causes all the variable names to be read as lowercase.
sqlshow is a useful option for showing all SQL commands issued to the ODBC data source from the
odbc insert or odbc load command. This can help you debug any issues related to inserting
or loading.
allstring causes all variables to be read as string data types.
datestring causes all date- and time-formatted variables to be read as string data types.
create specifies that a simple ODBC table be created on the specified data source and populated with
the data in memory. Column data types are approximated based on the existing format in Stata’s
memory.
overwrite allows data to be cleared from an ODBC table before the data in memory are written to
the table. All data from the ODBC table are erased, not just the data from the variable columns
that will be replaced.
insert appends data to an existing ODBC table and is the default mode of operation for the odbc
insert command.
quoted is useful for ODBC data sources that require all inserted values to be quoted. This option
specifies that all values be quoted with single quotes as they are inserted into an ODBC table.
as("varlist") allows you to specify the ODBC variables on the data source that correspond to the
variables in Stata’s memory. If this option is specified, the number of variables must equal the
number of variables being inserted, even if some names are identical.
loud specifies that output be displayed for SQL commands.
verbose specifies that odbc query list any data source alias, nickname, typed table, typed view, and
view along with tables so that you can load data from these table types.

6 odbc — Load, write, or view data from ODBC sources
schema specifies that odbc query return schema names with the table names from a data source.
Note: The schema names returned from odbc query will also be used with the odbc describe
and odbc load commands. When using odbc load with a schema name, you might also need to
specify the noquote option because some drivers do not accept quotes around table or schema
names.
block specifies that odbc insert use block inserts to speed up data-writing performance. Some
drivers do not support block inserts.
permanently (set odbcmgr only) specifies that, in addition to making the change right now, the
setting be remembered and become the default setting when you invoke Stata.
Remarks and examples stata.com
When possible, the examples in this manual entry are developed using the Northwind sample
database that is automatically installed with Microsoft Access. If you do not have Access, you can still
use odbc, but you will need to consult the documentation for your other ODBC sources to determine
how to set them up.
Remarks are presented under the following headings:
Setting up the data sources
Listing ODBC data source names
Listing available table names from a specified data source’s system catalog
Describing a specified table
Loading data from ODBC sources
Setting up the data sources
Before using Stata’s ODBC commands, you must register your ODBC database with the ODBC
Data Source Administrator. This process varies depending on platform, but the following example
shows the steps necessary for Windows.
Using Windows 7, XP, or Vista, follow these steps to create an ODBC User Data Source for the
Northwind sample database:
1. From the Start Menu, select the Control Panel .
2. In the Control Panel window, click on System and Security > Administrative Tools.
3. In the Data Sources (ODBC) dialog box,
a. click on the User DSN tab;
b. click on Add...;
c. choose Microsoft Access Driver (*.mdb,*.accdb) on the Create New Data Source dialog
box; and
d. click on Finish.
4. In the ODBC Microsoft Access Setup dialog box, type Northwind in the Data Source Name
field and click on Select.... Locate the Northwind.mdb database and click on OK to finish
creating the data source.

odbc — Load, write, or view data from ODBC sources 7
Technical note
In earlier versions of Windows, the exact location of the Data Source (ODBC) dialog varies, but
it is always somewhere within the Control Panel.
Listing ODBC data source names
odbc list is used to produce a list of data source names to which Stata can connect. For a
specific data source name to be shown in the list, the data source has to be registered with the ODBC
Data Source Administrator. See Setting up the data sources for information on how to do this.
Example 1
. odbc list
Data Source Name Driver
dBASE Files Microsoft Access dBASE Driver (*.dbf, *.ndx
Excel Files Microsoft Excel Driver (*.xls, *.xlsx, *.xl
MS Access Database Microsoft Access Driver (*.mdb, *.accdb)
Northwind Microsoft Access Driver (*.mdb, *.accdb)
In the above list, Northwind is one of the sample Microsoft Access databases that Access installs
by default.

8 odbc — Load, write, or view data from ODBC sources
Listing available table names from a specified data source’s system catalog
odbc query is used to list table names available from a specified data source.
Example 2
. odbc query "Northwind"
DataSource: Northwind
Path : C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office\Samples\Northwind.accdb
Customers
Employee Privileges
Employees
Inventory Transaction Types
Inventory Transactions
Invoices
Order Details
Order Details Status
Orders
Orders Status
Orders Tax Status
Privileges
Products
Purchase Order Details
Purchase Order Status
Purchase Orders
Sales Reports
Shippers
Strings
Suppliers

odbc — Load, write, or view data from ODBC sources 9
Describing a specified table
odbc describe is used to list column (variable) names and their SQL data types that are associated
with a specified table.
Example 3
Here we specify that we want to list all variables in the Employees table of the Northwind data
source.
. odbc describe "Employees", dsn("Northwind")
DataSource: Northwind (query)
Table: Employees (load)
Variable Name Variable Type
ID COUNTER
Company VARCHAR
Last Name VARCHAR
First Name VARCHAR
E-mail Address VARCHAR
Job Title VARCHAR
Business Phone VARCHAR
Home Phone VARCHAR
Mobile Phone VARCHAR
Fax Number VARCHAR
Address LONGCHAR
City VARCHAR
State/Province VARCHAR
ZIP/Postal Code VARCHAR
Country/Region VARCHAR
Web Page LONGCHAR
Notes LONGCHAR
Attachments LONGCHAR
Loading data from ODBC sources
odbc load is used to load an ODBC table into memory.
To load an ODBC table listed in the odbc query output, specify the table name in the table()
option and the data source name in the dsn() option.
Example 4
We want to load the Employees table from the Northwind data source.
. clear
. odbc load, table("Employees") dsn("Northwind")
E-mail_Address invalid name
- converted E-mail_Address to var5
State/Province invalid name
- converted State/Province to var13
ZIP/Postal_Code invalid name
- converted ZIP/Postal_Code to var14
Country/Region invalid name
- converted Country/Region to var15

10 odbc — Load, write, or view data from ODBC sources
. describe
Contains data
obs: 9
vars: 18
size: 4,407
storage display value
variable name type format label variable label
ID long %12.0g
Company str17 %17s
Last_Name str14 %14s Last Name
First_Name str7 %9s First Name
var5 str28 %28s E-mail Address
Job_Title str21 %21s Job Title
Business_Phone str13 %13s Business Phone
Home_Phone str13 %13s Home Phone
Mobile_Phone str1 %9s Mobile Phone
Fax_Number str13 %13s Fax Number
Address strL %9s
City str8 %9s
var13 str2 %9s State/Province
var14 str5 %9s ZIP/Postal Code
var15 str3 %9s Country/Region
Web_Page strL %9s Web Page
Notes strL %9s
Attachments strL %9s
Sorted by:
Note: dataset has changed since last saved
Technical note
When Stata loads the ODBC table, data are converted from SQL data types to Stata data types.
Stata does not support all SQL data types. If the column cannot be read because of incompatible data
types, Stata will issue a note and skip a column. The following table lists the supported SQL data
types and their corresponding Stata data types:

odbc — Load, write, or view data from ODBC sources 11
SQL data type Stata data type
SQL BIT byte
SQL TINYINT
SQL SMALLINT int
SQL INTEGER long
SQL DECIMAL double
SQL NUMERIC
SQL FLOAT double
SQL DOUBLE
SQL REAL double
SQL BIGINT string
SQL CHAR string
SQL VARCHAR
SQL LONGVARCHAR
SQL WCHAR
SQL WVARCHAR
SQL WLONGVARCHAR
SQL TIME
SQL DATE
SQL TIMESTAMP
SQL TYPE TIME double
SQL TYPE DATE
SQL TYPE TIMESTAMP
SQL BINARY
SQL VARBINARY
SQL LONGVARBINARY
You can also load an ODBC table generated by an SQL SELECT statement specified in the exec()
option.
Example 5
Suppose that, from the Northwind data source, we want a list of all the customers who have
placed orders. We might use the SQL SELECT statement
SELECT DISTINCT c.ID, c.Company
FROM Customers c
INNER JOIN Orders o
ON c.[Customer ID] = o.CustomerID
To load the table into Stata, we use odbc load with the exec() option.

12 odbc — Load, write, or view data from ODBC sources
. odbc load, exec(‘"SELECT DISTINCT c.ID, c.Company FROM Customers c INNER JOIN
> Orders o ON c.ID = o.[Customer ID]"’) dsn("Northwind") clear
. describe
Contains data
obs: 15
vars: 2
size: 210
storage display value
variable name type format label variable label
ID long %12.0g
Company str10 %10s
Sorted by:
Note: dataset has changed since last saved
The extvarlist is optional. It allows you to choose which columns (variables) are to be read and
to rename variables when they are read.
Example 6
Suppose that we want to load the ID column and the Last Name column from the Employees
table of the Northwind data source. Moreover, we want to rename ID as id and Last Name as name.
. odbc load id=ID name="Last Name", table("Employees") dsn("Northwind") clear
. describe
Contains data
obs: 9
vars: 2
size: 162
storage display value
variable name type format label variable label
id long %12.0g ID
name str14 %14s Last Name
Sorted by:
Note: dataset has changed since last saved
The if and in qualifiers allow you to choose which rows are to be read. You can also use a
WHERE clause in the SQL SELECT statement to select the rows to be read.

odbc — Load, write, or view data from ODBC sources 13
Example 7
Suppose that we want the information from the Order Details table, where Quantity is greater
than 50. We can specify the if and in qualifiers,
. odbc load if Quantity>50, table("Order Details") dsn("Northwind") clear
. sum Quantity
Variable Obs Mean Std. Dev. Min Max
Quantity 10 177.7 94.21966 87 300
or we can issue the SQL SELECT statement directly:
. odbc load, exec("SELECT * FROM [Order Details] WHERE Quantity>50")
> dsn("Northwind") clear
. sum Quantity
Variable Obs Mean Std. Dev. Min Max
Quantity 10 177.7 94.21966 87 300
Also see
[D] export — Overview of exporting data from Stata
[D] import — Overview of importing data into Stata
