1
Verbs and Verb Tenses
There are two main types of verbs used in the English language: Regular Verbs
and Irregular Verbs. These verbs are not a different tense, but they are very important
nonetheless. There are three basic forms of verb tenses: simple, perfect, and progressive.
These three forms also work together. In this handout we will explain all of the verb tense
combinations, as well as the Regular and Irregular verbs, and give examples.
Verb Tenses
Simple Tense:
These are verbs that can take the place of past, present, and future. These verb
tenses are the easy ones to remember. Simple Tenses have three uses, Simple
Past, Simple Present, and Simple Future.
For Example:
Simple Past Tense Verbs
We played football in the backyard.
The boy tripped on the step.
Simple Present Tense Verbs
We play football in the backyard.
The boy trips on the step.
Simple Future Tense Verbs
We will play football in the backyard.
The boy will trip on the step.

2
Perfect Tenses:
The next three tenses are Perfect Tenses. Perfect Tenses are formed using the helping
verbs has, have, will, and shall. These verb tenses also use the past participle of the verb.
These three verb tenses are Past Perfect Tense, Present Perfect Tense, and Future Perfect
Tense.
For Example:
Past Perfect Tense
We had played football.
The boy had tripped on the step.
Present Perfect Tense
We have played football.
The boy has tripped on the step.
Future Perfect Tense
By tomorrow, we will have played football.
By noon, the boy will have tripped on the step.
3
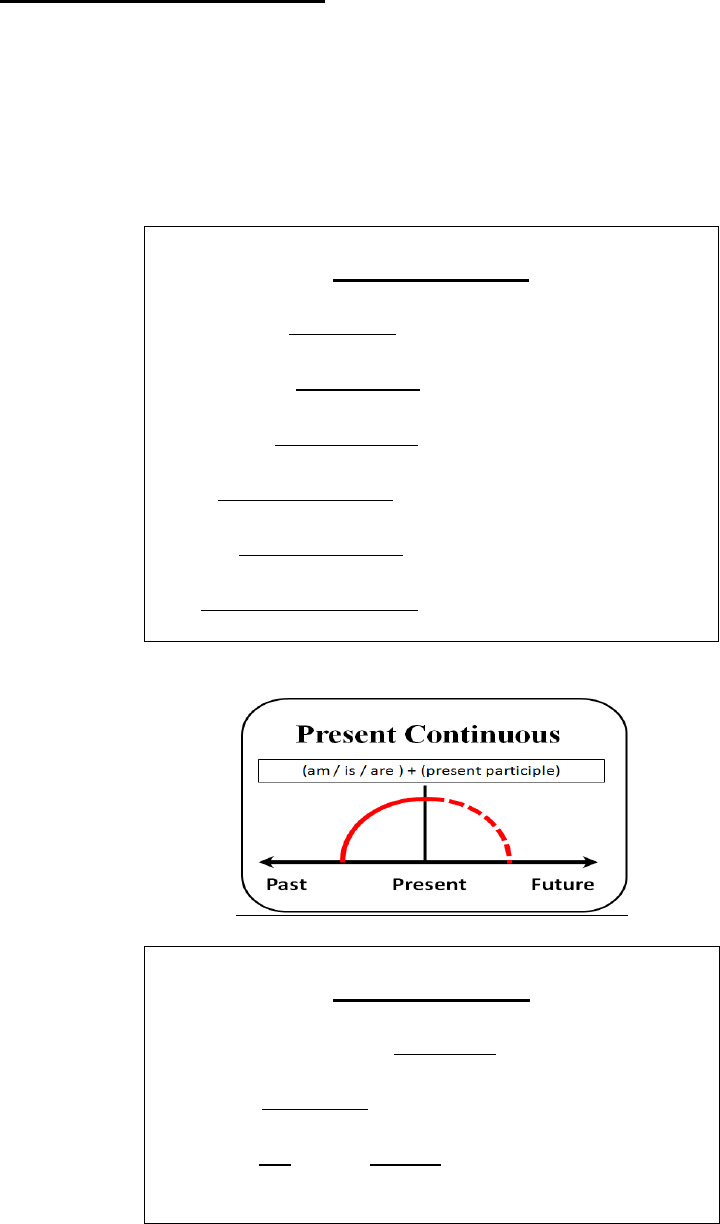
Progressive/Continuous Forms:
We have talked about the two categories of verb tenses, simple and perfect. Both
the simple and perfect tenses may be modified and made into progressive or continuous.
The reason for using progressive form is to show an action that is in progress or
continuing.
For Example:
Present Progressive
We are playing. (Present Progressive)
We were playing. (Past Progressive)
We will be playing. (Future Progressive)
We have been playing. (Present Perfect Progressive)
We had been playing. (Past Perfect Progressive)
We will have been playing. (Future Perfect Progressive)
Present Continuous
He is sleeping.
I am visiting grandpa in the afternoon.
You are always coming late for the meetings!
4
Regular Verbs:
Regular Verbs are verbs that add –d or –ed to their present form to change the
tense from present to past.
For example:
The dog jumped toward the squirrel.
We all noticed the stain on his shirt.
My grandmother knitted me a scarf.
(Notice that -ed is added to the verb to show that the action was performed in the past.
See also Verbs that end in –ed handout for more information.)
Irregular Verbs:
Irregular Verbs are not tense specific. What makes these verb types irregular is that the
past tense is unpredictable. These verbs do not use –d or –ed to signify past tense.
For Example:
I ate my vegetables.
We swam across the lake.
My mother read me a story.

5
Irregular verb chart
SIMPLE
FORM
SIMPLE
PAST
PAST
PARTICIPLE
SIMPLE
FORM
SIMPLE
PAST
PAST
PARTICIPLE
Be
Become
Begin
Bend
Bite
Blow
break
bring
broadcast
build
buy
catch
choose
come
cost
cut
dig
do
draw
drink
drive
eat
fall
feed
feel
fight
find
fit
fly
forget
forgive
freeze
get
give
go
grow
hang
have
hear
hide
hit
hold
hurt
keep
know
lay
lead
leave
lend
let
was, were
became
began
bent
bit
blew
broke
brought
broadcast
built
bought
caught
chose
came
cost
cut
dug
did
drew
drank
drove
ate
fell
fed
felt
fought
found
fit
flew
forgot
forgave
froze
got
gave
went
grew
hung
had
heard
hid
hit
held
hurt
kept
knew
laid
led
left
lent
let
been
become
begun
bent
bitten
blown
broken
brought
broadcast
built
bought
caught
chosen
come
cost
cut
dug
done
drawn
drunk
driven
eaten
fallen
fed
felt
fought
found
fit
flown
forgotten
forgiven
frozen
gotten (got)
given
gone
grown
hung
had
heard
hidden
hit
held
hurt
kept
known
laid
led
left
lent
let
lie
light
lose
make
mean
meet
pay
put
quit
read
ride
ring
rise
run
say
see
sell
send
set
shake
shot
shut
sing
sit
sleep
slide
speak
spend
spread
stand
steal
stick
strike
swear
sweep
swim
Take care, teach
tear
tell
think
throw
understand
upset
wake
wear
win
withdraw
write
lay
lit (lighted)
lost
made
meant
met
paid
put
quit
read
rode
rang
rose
ran
said
say
sold
sent
set
shook
shot
shut
sang
sat
slept
slid
spoke
spent
spread
stood
stole
stuck
struck
swore
swept
swam
took
taught
tore
told
thought
threw
understood
upset
woke
wore
won
withdrew
wrote
lain
lit (lighted)
lost
made
meant
met
paid
put
quit
read
ridden
rung
risen
run
said
seen
sold
sent
set
shaken
shot
shut
sung
sat
slept
slid
spoken
spent
spread
stood
stolen
stuck
struck
sworn
swept
swum
taken
taught
torn
told
thought
thrown
understood
upset
waked (woken)
worn
won
withdrawn
written
6
VERB TENSE CHART
Simple Present Tense
Simple Past Tense
Singular
Regular / irreg. / be
Plural
Regular / irreg. / be
I
you
he/she/it
talked, gave, was
talked, gave, were
talked, gave, was
we
you
they
talked, gave, were
talked, gave, were
talked, gave, were
Simple Future
Singular
Regular / irreg. / be
Plural
Regular / irreg. / be
I, you, he/she/it
will talk, will give, will
be
we, you, they
will talk, will give, will
be
Present Perfect
Regular / Irregular / be
I, you, we, they
he/she/it
have talked, have given, have been
has talked, has given, has been
Past Perfect
Regular / Irregular / be
I, you, he/she/it, we, they
had talked, had given, had been
Future Perfect
Regular / Irregular / be
I, you, he/she/it, we, they
will have talked, will have given, will have been
Present Progressive
Regular / Irregular / be
I
he/she/it
you, we, they
am talking, am giving, am being
is talking, is giving, is being
are talking, are giving, are being
Past Progressive
Regular / Irregular/ be
I, he/she/it
you, we, they
was talking, was giving, was being
were talking, were giving, were being
Future Progressive
Regular / Irregular/ be
I, you, he/she/it, we, they
will be talking, will be giving, will be being
Singular
Regular / irreg. / be
Plural
Regular / irreg. / be
I
you
he/she/it
talk, give, am
talk, give, are
talks, gives, is
we
you
they
talk, give, are
talk, give, are
talk, give, are

7
Exercises and Practice
Draw a circle around the action verb in each sentence. On the line, tell whether the verb
is past tense, present tense, or future tense.
1. Daniel will choose a baseball bat. _________________________________
2. He steps up to the plate. __________________________________
3. The pitcher tossed the ball. __________________________________
4. Daniel will swing hard. __________________________________
5. The ball struck the bat. ___________________________________
Fill in the spaces with the correct form of the verb in present progressive, past
progressive, and future progressive tenses.
1. I (play) _______ _______ the piano now.
2. You (play) _______ _______ the guitar now.
3. We (play) _______ _______ violins now.
4. It (play) ________ _______ the drums now.
5. When I was young, Grandma (usually, bake) _______ _______ _______ bread on
Monday morning.
6. Seagulls (frequently, steal) _______ _______ _______ from the fishermen's nets
as they pulled them in.
7. As he sat by the sunny window, the novelist (quickly, write) _______ _______
_______ the first chapter of his new book.
8. The class (listen) _______ _____ ________ closely during the review for the test.
9. The sergeant (train) _______ _____ ________ the new recruits for the next
month.
10. The scientists (launch) _______ _____ ________ a satellite in November.

8
More Practice:
Fill in the blanks with appropriate verb tenses.
I can't believe I (get) that apartment. I (submit) my application last
week, but I didn't think I had a chance of actually getting it. When I (show) up to
take a look around, there were at least twenty other people who (arrive) before
me. Most of them (fill, already) out their applications and were already leaving.
The landlord said I could still apply, so I did.
I (try) to fill out the form, but I couldn't answer half of the questions. They (want)
me to include references, but I didn't want to list my previous landlord because I
(have) some problems with him in the past and I knew he wouldn't recommend
me. I (end) up listing my father as a reference.
It was total luck that he (decide) to give me the apartment. It turns out that the
landlord and my father (go) to high school together. He decided that I could have
the apartment before he (look) at my credit report. I really lucked out!
This handout was based on the following texts:
Berry, Chris, Allen Brizee, and Elizabeth Angeli. "Verb Tenses." Purdue OWL. Purdue University, 14 Sept.
2013. Web. 09 Mar. 2015. <https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/601/01/>.
"Verb Tenses." Grammar Revolution. Elizabeth O'Brien, n.d. Web. 09 Mar. 2015. <http://www.english-
grammar-revolution.com/verb-tenses.html>.
All of the above texts are available in The Writing Center.
Please visit our website at www.lavc.edu/writingcenter/index.html for additional resources and services.
