
Utah State University Utah State University
DigitalCommons@USU DigitalCommons@USU
All Graduate Theses and Dissertations, Spring
1920 to Summer 2023
Graduate Studies
5-2012
A Demographic Evaluation of Increasing Rates of Suicide A Demographic Evaluation of Increasing Rates of Suicide
Mortality in Japan and South Korea Mortality in Japan and South Korea
Sun Young Jeon
Utah State University
Follow this and additional works at: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/etd
Part of the Sociology Commons
Recommended Citation Recommended Citation
Jeon, Sun Young, "A Demographic Evaluation of Increasing Rates of Suicide Mortality in Japan and South
Korea" (2012).
All Graduate Theses and Dissertations, Spring 1920 to Summer 2023
. 1299.
https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/etd/1299
This Thesis is brought to you for free and open access by
the Graduate Studies at DigitalCommons@USU. It has
been accepted for inclusion in All Graduate Theses and
Dissertations, Spring 1920 to Summer 2023 by an
authorized administrator of DigitalCommons@USU. For
more information, please contact
A DEMOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF INCREASING RATES
OF SUICIDE MORTALITY IN JAPAN AND SOUTH KOREA
by
Sun Young Jeon
A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment
of the requirements for the degree
of
MASTER OF SCIENCE
in
Sociology
Approved:
_________________________ __________________________
Eric N. Reither H. Reed Geertsen
Major Professor Committee Member
_________________________ __________________________
Michael B. Toney Mark R. McLellan
Committee Member Vice President for Research and
Dean of the School of Graduate Studies
UTAH STATE UNIVERSITY
Logan, Utah
2012
ii
Copyright © Sun Young Jeon 2012
All Rights Reserved
iii
ABSTRACT
A Demographic Evaluation of Increasing Rates
of Suicide Mortality in Japan and South Korea
by
Sun Young Jeon, Master of Science
Utah State University 2012
Major Professor: Dr. Eric N. Reither
Department: Sociology
Suicide is one of the major health issues and causes of mortality in modern
societies. A global morality rate of suicide is 16 persons per 100,000 according to the
World Health Organization report. Fortunately, the rates in most OECD countries
have shown a dramatic decrease over the last 20 years. There are, however, two
important exceptions, Japan and South Korea. The suicide rates in these two countries
have been on an increasing trend. Because the two neighboring countries share similar
socio-demographic contexts, I investigated the effects of the three time-related
demographic variables (age, period, and cohort) on suicide rates in Japan and South
Korea. The Age-Period-Cohort Intrinsic Estimator model was operated using data of
vital statistics and population census from the Statistics Bureau and the Ministry of
Internal Affairs and Communications in Japan, and cause of death data and population
census from Statistics Korea in South Korea. Even though the two countries are
neighboring countries that have had some similar socio-demographic contexts, the
factors contributing to increasing suicide rates vary in each country. The result
iv
showed age effects in Japan greatly contributed to suicide compared to period and
cohort effects, and the age effects were highest during the fifties age bracket. On the
other hand, South Korea turned out to have more compound reasons, showing
pronounced age effects in the elderly population, increasing period effects, and the
strong cohort effects of the current elderly and middle-aged populations. From this
result, although Japan and South Korea are neighboring countries with shared
histories, industrial structures, social systems, and some similar demographic
characteristics, the cause of increasing suicide rates in the two countries clearly varies
and the efforts for preventing suicide must also vary depending on the social contexts
of each country.
(67 pages)

v
PUBLIC ABSTRACT
A Demographic Evaluation of Increasing Rates
of Suicide Mortality in Japan and South Korea
by
Sun Young Jeon, Master of Science
Utah State University 2012
According to a World Health Organization report, about one million people
die by suicide each year. Fortunately, rates of suicide mortality have been decreasing
among most of the OECD countries, but Japan and South Korea are the only two
exceptions to this trend, which has shown increasing suicide rates over the last 25
years. A number of studies have focused on psychological motives and individual-
level causes of suicide, such as depression, mental disorder, and disability. However,
as Durkheim pointed out, suicide in a society does not have any obvious relationship
to the prevalence of mental disorder. With his theory indicating that suicide is a social
phenomenon that needs to be explained in a social context with social determinants,
this study aimed to understand the effects of three types of time-related socio-
demographic variables (age, period, and cohort) on suicide in Japan and South Korea.
This study focuses on (1) the relative contribution of age, period, and cohort
effects on suicide in each country and (2) the comparison between the impact of the
three effects on changes in suicide rates. I thought that it would be potentially
significant concerning the increasing suicide rates in the two countries that Japan and
South Korea are neighboring countries and share similar social contexts as well as
demographic transitions. I operated the Age-Period-Cohort Intrinsic Estimator model
to answer the questions using vital statistics and population census from the Statistics
Bureau and the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications for Japan, and cause
of death data and population census from Statistics Korea.
The results show that even though the two countries are neighbors that have
had some similar socio-demographic contexts, the factors contributing to the
increasing suicide rates vary in each country. Age effects are highest during the
elderly period in South Korea, whereas age effects in Japan are highest during the
fifties age bracket. Period effects in Japan increased sharply between 1995 and 2000,
while period effects in South Korea mounted rapidly between 2000 and 2005. Cohort
effects in Japan were highest among the 1905-1909 birth cohort and sustained a lower
level since the 1925-1929 birth cohort, whereas the birth cohort born between 1915-
1970 in South Korea showed high cohort effects.
vi
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
I would like to thank my committee professors, Drs. Eric N. Reither, H. Reed
Geertsen, and Michael B. Toney, for their insightful comments, feedback, and
recommendations. What I have learned from them in class as well as in personal
meetings have made this work possible. I especially thank my major professor Dr.
Eric N. Reither for his patience and encouragement that has helped me not to give up
even though I was frustrated by the language barrier. Besides my committee
professors, I am grateful to the sociology faculty, staff, and graduate students.
Without their companionship and thoughtfulness I could not have finished this thesis.
I also would like to thank Professor Atsuko Neely for helping me with data
collecting and allowing me to keep studying Japanese in a U.S. graduate school. I also
want to thank Dr. Yun Kim and President Syng-il Hyun for their persistent
encouragement that kept me focused on my studies in Utah State University.
Lastly, I would like to thank my family: dad, mom, elder sister, brother-in-
law, and my 2-year-old nephew. They have trusted me even when I could not trust
myself. With their help, I was able to overcome all of the loneliness, frustration, and
loss of confidence during my studying. They are also the reason why I live and want
to be a better person in this world.
Sun Y. Jeon
vii
CONTENTS
Page
ABSTRACT. ................................................................................................................ iii
PUBLIC ABSTRACT ...................................................................................................v
ACKOWLEDGMENTS .............................................................................................. vi
LIST OF TABLES ..................................................................................................... ix
LIST OF FIGURES .....................................................................................................x
CHAPTER
I. INTRODUCTION .......................................................................................1
Demographic Factors in Suicide Rates in Japan and South Korea ......4
Age-Period-Cohort (APC) Analysis ......................................................6
II. LITERATURE REVIEW .............................................................................8
Durkheim’s Social Determinants of Suicide..........................................8
A Demographic Approach to Understanding Suicide:
Age, Period, Cohort Effects .............................................................10
III. METHOD .................................................................................................19
Study Population ..................................................................................19
Statistical Analysis ...............................................................................20
IV. RESULTS ...............................................................................................23
Descriptive Analysis: Absolute Suicide Rate ......................................23
Descriptive Analysis: Proportional Suicide Rate .................................27
APC Analysis: Overall Mortality.........................................................32
APC Analysis: Suicide Mortality.........................................................33
V. DISCUSSION ............................................................................................41
Main Findings ......................................................................................41
Will the Suicide Rates in Japan and South Korea Keep Increasing? ...43
VI. CONCLUSION.........................................................................................45
viii
REFERENCES ............................................................................................................47
APPENDIXES .............................................................................................................51
A. The Identification Problem of Conventional APC Model .........................52
B. The Unstableness of CGLIM Model ..........................................................56
ix
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
1.1 Absolute Suicide Rate, 1985-2010, Japan ................................................24
1.2 Absolute Suicide Rate, 1985-2010, South Korea .....................................25
2.1 Proportional Suicide Rate, 1985-2010, Japan ...........................................29
2.2 Proportional Suicide Rate, 1985-2010, South Korea ................................30
3.1 APC-IE Result: Overall Mortality, Japan .................................................35
3.2 APC-IE Result: Overall Mortality, South Korea ......................................36
4.1 APC-IE Result: Suicide Mortality, Japan .................................................38
4.2 APC-IE Result: Suicide Mortality, South Korea ......................................39
x
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure Page
1.1 Deaths by Suicide per 100,000 PYL in Hungary, Finland,
Japan and South Korea, 1995-2009 ............................................................2
2.1 Absolute Suicide Rate, 1985-2010, Japan ................................................26
2.2 Absolute Suicide Rate, 1985-2010, South Korea .....................................26
2.3 Gender Stratified Absolute Suicide Rates, 2010,
Japan and South Korea ............................................................................27
3.1 Proportional Suicide Rate, 1985-2010, Japan ...........................................31
3.2 Proportional Suicide Rate, 1985-2010, South Korea ................................31
3.3 Gender Stratified Proportional Suicide Rates,
2010, Japan and South Korea ....................................................................32
4.1 APC-IE Result: Overall Mortality, Age Effects .......................................37
4.2 APC-IE Result: Overall Mortality, Period Effects ....................................37
4.3 APC-IE Result: Overall Mortality, Cohort Effects ...................................37
5.1 APC-IE Result: Suicide Mortality, Age Effects .......................................40
5.2 APC-IE Result: Suicide Mortality, Period Effects....................................40
5.3 APC-IE Result: Suicide Mortality, Cohort Effects ...................................40
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
Suicide is a significant health issue that has attracted the attention of social
scientists for generations, beginning with Emile Durkheim’s (1897/1951) comparison of
suicide rates among Protestants and Catholics. Despite this attention, suicide remains an
important social problem and cause of morbidity and mortality in modern societies. To
illustrate, according to a recent WHO report (2002), about one million people die by
suicide each year—and almost 10 to 20 times as many people attempt suicide. This
means that, somewhere in the world, a person dies by suicide every 40 seconds and a
suicide attempt occurs every 3 seconds.
Fortunately, rates of suicide mortality (hereafter simply referred to as suicide
rates) have been decreasing among most OECD countries. Some countries such as
Hungary, Finland, Denmark and Austria have shown dramatically decreasing suicide
rates during the last 20 years. The suicide rate in Hungary was the highest among OECD
countries in 1990 (35.3 persons per 100,000 person-years lived (PYL)), but since then it
has steadily declined to 19.8 persons in 2009. The suicide rate in Finland, which was the
second highest in 1990 (27.8 persons per 100,000 PYL), has also declined to 17.3 persons
in 2009. Trends toward lower suicide rates have characterized most OECD countries,
even though rates of suicide were once high in several of these nations (OECD Health
Data 2011). Overall, the average suicide rate among OECD countries has decreased from
15.3 persons in 1985 to 11.3 in 2009.
2
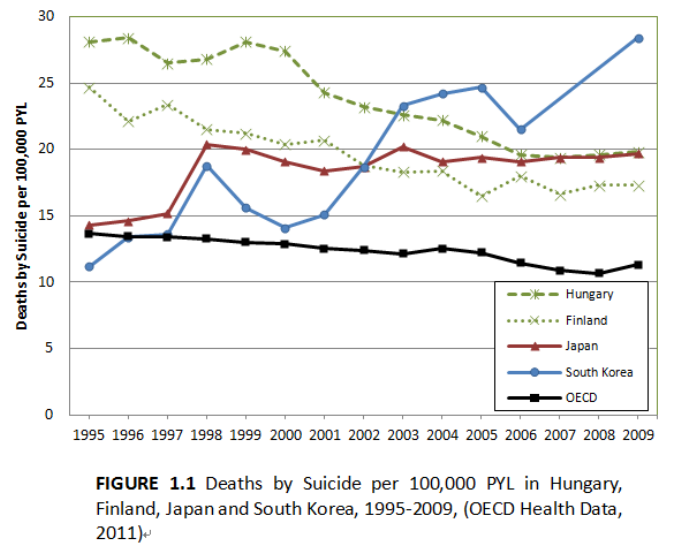
However, South Korea and Japan are two important exceptions to the broader
trend toward lower suicide rates in OECD countries (Figure 1.1). Contrary to most
OECD nations, the suicide rate in Japan increased from 14.5 per 100,000 PYL in 1990 to
19.4 per 100,000 in 2009. Even though Japanese suicide rates slightly decreased
immediately after the two peaks of suicide mortality in 1998 and 2003, they resumed
increasing shortly thereafter. The suicide rate in Japan was fourteenth highest among
OECD countries in 1990 but, as a result of this unfortunate trend, Japan now exhibits the
second highest rate of suicide among OECD nations.
The increase in suicide mortality in South Korea has been even more dramatic in
recent decades (Kwon, Chun, and Cho 2009). In 1990, the rate of suicide mortality in
South Korea was just 7.9 per 100,000 PYL. By 2009, it had climbed to 28.4 per 100,000
PYL, an increase of about 360 percent. As Japan experienced, there were two large peaks
of suicide mortality—one in 1998, and the other in 2003-2005. The suicide rate decreased
immediately following these peaks, only to resume its upward march within a couple of
years. The suicide rate in South Korea ranked as the twenty-fifth highest in 1990 among
OECD countries, but by 2009 its rate of suicide mortality was higher than any other
nations in the OECD.
There have been several studies to determine the causes of this dramatic increase
in suicide rates in Japan and South Korea and most of these studies have focused on
individual-level variables such as depression, mental disorder and disability (Chiu,
Takahashi, and Suh 2004; Kawakami et al. 2005). These approaches are obviously
persuasive in that suicide is, at least to some extent, driven by an individual’s state of
mind and psychological motives. However, if the suicide rates in one society are
3
persistently higher than in another, it becomes difficult to explain such disparities with
individual-level approaches (Lee and Kim 2010).
For example, if suicide is understood just as a result of depression, then scholars
cannot explain higher suicide rates among males in South Korea. According to a report of
the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service in South Korea (2010), despite the
fact that the prevalence of depression was higher among females than males from 2005 to
2009, suicide rates were nevertheless substantially higher among males. In addition, Lee
and Kim (2010) pointed out researchers cannot explain the unusually high increase in
suicide rates among older adults since the 1990s only as a result of depression. While the
suicide rate among older adults has been increasing, the prevalence of depression in the
4
same group has decreased from 3.4% to 2.5%.
These examples support Durkheim’s claim (1897/1951) that suicide in a society
does not have any obvious relationship to the prevalence of mental disorders. Rather than
being the result of mental disorders or depression, suicide is a social phenomenon that
needs to be explained with social determinants in a social context (Leo 2002). For
instance, Figure 1 shows that suicide rates in Japan and South Korea peaked in 1998.
Several socio-demographic studies have surmised that the sharp increase in suicides in
1998 in the two countries was triggered by an economic crisis that affected most Asian
countries from 1997 to 1998 (Chang et al. 2009; Kim et al. 2011).
Likewise, various socio-demographic variables have been analyzed to gain a
deeper understanding of suicide rates. Economic factors (Yang 1992), divorce rates (Kim
et al. 2011), and marriage rates (Park and Lester 2006) have been important variables,
and these studies have shed more light on the etiology of suicide by investigating
correlations between those factors and suicide rates or by comparing trajectories of those
factors to variations in suicide rates. The question then becomes, which demographic
factors contributed to the unprecedented rise in suicide rates in Japan and South Korea?
Demographic Factors in Suicide Rates
in Japan and South Korea
Japan and South Korea are two glaring exceptions to the world’s broad trend
toward lower suicide rates. It is potentially significant that Japan and Korea are
neighboring countries and share similar social contexts, as well as demographic
transitions which caused rapid population aging (Goodman and Peng 1996; Kim and
Maeda 2001). Japan colonized Korea for 36 years in the early 20th century, and Japan has
5
heavily influenced Korea in contemporary history (Kim et al. 2011). The two countries
have similar industrial structures, education systems, and judicial and political institutions
(Goodman and Peng 1996).
Both have experienced rapid socioeconomic development, industrialization, and
urbanization (Kim and Maeda 2001), and the dramatic social changes have caused drastic
demographic transitions in both countries, such as decreases in fertility and mortality in a
short period. Both countries have also experienced the aging of their populations at a
faster rate than in any Western countries (Kim and Maeda 2001). In addition, fertility
rates have plummeted in a short time in both countries and have stayed significantly
below the replacement rate. Furthermore, before the demographic transition started, the
two countries experienced a baby boom with the end of World War 2 and the Korean War.
There have been fluctuations in fertility rates in the two countries over the last century
and these rapid variations in fertility rates, in turn, have caused rapid variations in birth
cohort size.
Despite the fact that several studies have previously attempted to understand the
effects of socio-demographic factors on suicide rates in Japan and South Korea, the
majority of them have focused on each country in isolation (Kwon et al. 2009; Odagiri,
Uchida, and Nakano 2011; Ooe, Ohno, and Nakamura 2009), and a comparative study
between the two countries has not yet been carried out. This study aims to understand the
effects of demographic factors on suicide rates in both Japan and South Korea and to
compare the extent of the differences between the two countries with regards to the
contribution that the demographic factors make to these suicide rates.
6
Age-Period-Cohort (APC) Analysis
Durkheim (1897/1951) was the first to demonstrate that suicide has a social
component, and as a result, socio-demographic contextual variables can help us
understand variations in suicide rates. A number of previous suicide studies in Japan and
South Korea have focused on factors such as marriage rates, divorce rates, and economic
factors and their relationship to suicide (Kim et al. 2011; Park and Lester 2006). However,
relatively few studies have concentrated on the relative contributions of factors associated
with demographic changes through different dimensions of time – namely age, period,
and cohort effects.
By measuring these three effects and comparing them, one can determine not
only whether an aging population (age), an economic crisis (period), or rapid variation in
cohort size (cohort) has contributed to increasing suicide rates, but also the relative
impact of each of these factors to increasing suicide rates in both countries. In addition,
by comparing results in Japan and South Korea, one can better understand how age,
period and cohort factors may have differed or worked in unison in each country’s
increasing vulnerability to suicide mortality.
My study investigates how age, period, and cohort factors affect suicide mortality
in Japan and South Korea by (a) disentangling the three effects and (b) reviewing each
effect’s contribution to increasing suicide rates in Japan and South Korea. The research
questions are:
1. What are the relative contributions of age, period, and cohort effects to
changes in suicide rates in Japan and South Korea?
7
2. To what extent do Japan and South Korea differ with respect to the impact of
age, period, and cohort on changes in suicide rates?

8
CHAPTER II
LITERATURE REVIEW
Durkheim’s Social Determinants of Suicide
With the limitations of individual-level approaches in mind, Durkheim
(1897/1951) insisted that suicide rates in a society should be considered as a new fact
with its own social nature. He particularly emphasized social integration and regulation in
predicting suicide rates in a society. Social integration refers to how much the members
of a society are bound to social networks. Social regulation means how much the
members of the society are controlled by social rules and norms (Park and Lester 2006).
According to Durkheim, if the social integration and regulation in a society are unusually
weak, individuals are likely to experience anomie, which fails to dissuade them from
encourages destructive acts, including self-destructive acts such as suicide.
To examine associations between social integration, regulation and suicide,
studies have attempted to measure social integration and regulation in various ways (Kim
et al. 2011; Park and Lester 2006). The most widely used measures of social integration
are divorce and marriage rates, since creating a family and being a member of a family
tend to facilitate the integration of an individual into society. Those studies suppose that if
the divorce rate is higher or the marriage rate is lower in one society than in others, it
could cause a weakening of social integration and therefore, trigger higher suicide rates.
In this context, Kim et al. (2011) examined correlation coefficients between
divorce rates and suicide rates in Japan and South Korea. According to the results, the
coefficients varied significantly depending on gender and country. The correlations
9
between suicide rates and high divorce rates for Korean men and women turned out to be
very strong, while the correlation for Japanese men was relatively weak. Japanese women,
on the other hand, showed a negative correlation between the suicide rates and high
divorce rates. Park and Lester (2006) also focused on the correlation between suicide
rates and marriage/divorce rates in South Korea. In spite of their efforts to develop useful
statistical models, Park and Lester (2006) finally concluded that the marriage rate in
predicting Korean suicide rates was ambiguous since the result of regression analysis
between marriage rates and suicide rates were opposite to those found for simple
correlations. They pointed out that the association between the traditional measures of
social integration/regulation was only applied for elderly, not for younger people. With
socio-cultural changes, the authors suggest that the risk factors for younger people could
be different from those for elderly people.
Other than marriage and divorce rates, some studies measure social integration
and regulation via economic indicators. Durkheim claimed that economic forces affect
suicide rates indirectly by decreasing social integration and regulation (Yang 1992). With
this perspective, many studies include factors such as the unemployment rate and
economic growth rate to reflect economic conditions and compare the trajectories of
those factors to trends in suicide rates. Chang et al. (2009) compared variations in
unemployment rates, gross domestic product (GDP) per capita, and suicide rates in
several East/Southeast Asian countries. The results showed that suicide rates in Japan and
South Korea increased during economic crises, but a similar increase in suicide was not
found during economic crises in Taiwan and Singapore. Thus, Chang et al. (2009)
concluded that unemployment rates and economic crises are closely associated with
10
suicide rates in certain East/Southeast Asian countries. However, given mixed evidence
on this issue, it is premature to say that economic factors are causally related to suicide
rates.
A Demographic Approach to Understanding Suicide:
Age, Period, and Cohort Effects
Due to the limitations of the aforementioned studies, investigators have attempted
to identify other determinants of suicide rates. For example, age, period, and birth cohorts
are three time-related factors have been useful in research on the determinants of other
types of premature mortality in demography and epidemiology (Yang 2008). Studies of
suicide have also examined the three effects.
Age Effects on Suicide
There is no doubt that age is a significant factor in mortality risk. Biological aging
increases mortality risk, as described by Benjamin Gompertz and other prominent
demographers and epidemiologists. This universal phenomenon makes similar
trajectories of mortality with age across countries and time (Yang 2008). As the
proportion of elderly people increases, both in developing and developed countries with
prolonged life expectancy and lowered fertility rates, age effects have become a greater
concern within the field of epidemiology (Shah 2007).
In reference to the correlation between age and suicide, Pampel (1996) stated that
people’s psychological and physiological experiences at different stages in the life cycle
affect their decision to commit suicide. According to Durkheim (1897/1951), variations
in age effects reflect the degree of social integration at different stages of the life cycle.
11
He wrote that suicide rarely occurs during childhood, increases steadily with age, and
occurs most frequently during old age. In other words, elderly people have more
determinants negatively affecting social integration (Girard 1993), such as retirement
from a job and the loss of spouse and friends. Elias (1985) also pointed out that loneliness
tends to increase with age. In summary, age effects are greatest among the elderly
population.
Cattell (2000) pointed out that suicide rates in industrialized countries usually
increase with age and are highest among elderly men. Since the elderly appear most
vulnerable to suicide, “population aging” (which refers to increases in the elderly
population, relative to the population as a whole) could be an important determinant of
suicide rates in nations affected by this demographic phenomenon.
It is notable that Japan and South Korea have experienced particularly fast
population aging compared to any other Western developed countries (Kim and Maeda
2001). Lee and Shinkai (2003) point out that Japan and South Korea have had the most
rapidly aging populations among East and Southeast Asian countries. The portion of
people aged over 65 comprised 10.3% of the total population of Japan in 1985, 14.5% in
1995, 19.6% in 2005 and 22.0% in 2010. By 2050, this proportion is expected to increase
to 36.5%. The proportion was much lower in South Korea, only 4.3% in 1985, 5.9% in
1995, 8.6% in 2005 and 9.8% in 2010, but Chan (2006) expects that, by 2050, it will
increase sharply by 30.5% with particularly tremendous momentum.
Is the rapid aging of the population responsible for the increase in suicide rates in
Japan and South Korea? Using APC analysis, Lee and Kim (2010) showed that the age
effects on suicide in South Korea from 1983 to 2003 were strongest among elderly people
12
aged 80 and over. Age effects for both males and females were relatively weak among
people in their forties, but they increased sharply thereafter. In South Korea where the
elderly have unusually high rates of suicide, an increase in the elderly population could
be largely responsible for the increase in the overall suicide rate.
Conversely, an APC analysis in Japan showed that age effects peak in the fifties,
at least in the period the study examined, between 1985 and 2006 (Odagiri et al. 2011).
Among Japanese males, the peak was prominent during their fifties, while among females,
age effects kept increasing after their fifties. In Japan, therefore, it is hard to say that the
increase in the elderly population is directly responsible for the increasing suicide rate.
There could be various explanations for differences in age effects between the two
countries. As Lee and Kim (2010) pointed out, age effects in suicide could be interpreted
as an index representing how well individuals adjust to social roles in a society. They
assert that strong age effects on suicide mortality among South Korean elderly from 1983
to 2003 could be evidence of poor social conditions for elderly people in terms of role
adjustments and socio-economic security. In that the speed of population aging has been
faster in South Korea than in Japan (Kim and Maeda 2001), South Korean society has
had comparatively less time to make the proper adjustments for their increase in the
elderly population than Japan.
Japan, on the other hand, has had more time to make adjustments for the
increasing number of elderly people. The particularly strong age effects on suicide among
middle-aged Japanese could be explained as a reflection of work-related pressures,
declining family incomes, and challenging, unstable work environments (Odagiri et al.
2011) for people in this age range. Also, contrary to the young adult population, older
13
adults may have consumption and health care needs that exceed their income from labor
(Bloom, Canning, and Fink 2008). This deficiency has to be supported by social
institutions, including families and entitlement programs. Considering Japan is the only
country in Asia that has experienced a decline in the working-age population (Mason, Lee,
and Lee 2008), an increasing elderly population and the pressure of supporting them
could be a burden to the working-age segment of the population and therefore, could
contribute to high suicide rates among Japanese in their fifties.
Based on previous research, I hypothesized that: (1) age effects would remain
highest among the elderly in South Korea. This is derived from the fact that South Korea
has gone through a more rapid population aging process, as noted above, and has not had
as much time, relatively speaking, as Japan to make proper adjustments for an increase in
the number of its elderly citizens; (2) the age effects in Japan would be highest among
people in their fifties. This hypothesis was based on the fact that there is a relatively small
proportion of working-age people compared to the elderly population in Japan, and that
this burden and other work-related pressures most acutely affects people during midlife.
Period Effects on Suicide
Period effects are distinct from age and cohort effects in that they influence the
whole population simultaneously (Reither, Hauser, and Yang 2009). War, economic crisis,
pandemics of infectious disease, as well as sweeping interventions in public health or
medicine that affect the entire population are all examples of period effects (Yang 2008).
In terms of suicide studies, during rapid social change or disruption, individuals are more
likely to be isolated, and this condition makes people become more vulnerable to self-
14
destruction (Turner 2004).
Recent suicide studies that have examined period effects have primarily focused
on economic crisis and growth, and their effects on suicide. Durkheim (1897/1951) wrote
that suicide rates tend to increase during both economic booms and busts, with weakened
social integration and regulation than usual. During such periods, a society experiences
unstable norms, and these anomic conditions are reflected in higher suicide rates.
Since Durkheim, suicide studies have tried to verify the relationship between
economic factors and suicide. In spite a number of previous studies that have tried to
provide empirical verification of this relationship, there is no consensus incorporating all
the results (Lee and Kim 2010). Ruhm (1996) insisted that 9 out of the 10 major causes of
death in the United States (malignant neoplasm; major cardiovascular diseases;
pneumonia and influenza; chronic liver diseases and cirrhosis of the liver; motor vehicle
accidents; other accident and adverse effects; suicide, homicide, and legal intervention;
infant mortality; neonatal mortality) showed negative associations with unemployment
rate that were statistically significant. Suicide, on the other hand, was the only exception,
showing a positive association. Yang (1992) pointed out that the overall suicide rate in the
United States decreased with economic improvements from 1940 to 1984 but the female
suicide rate showed an opposite result. Brenner (1979) pointed out economic crises have
negative effects on mortality including suicide mortality by the loss of material resources,
psychological distress from such loss, and actions to alleviate distress with alcohol or
drugs. He verified his point by using data from the United States, England, and
Wales. Suicide rates in Helsinki, Finland were, on the other hand, stable during economic
15
crises and even decreased among males (Ostamo and Lönnqvist 2001).
Since a severe economic crisis struck East and Southeast Asian countries in the
late 1990s, a considerable amount of research has been devoted to the impact of the
economic crisis on mortality rates, including suicide rates (Chang et al. 2009; Khang,
Lynch, and Kaplan 2005; Kondo et al. 2008). Khang et al. (2005) insisted that suicide
rates in South Korea increased during the economic crisis, whereas deaths by other
causes such as cerebrovascular disease, cancer, and liver disease, decreased. The suicide
rates among males aged 35–64 showed a particularly sharp increase during this period.
Kondo et al. (2008) pointed out that the age-adjusted suicide rate in Japan also
dramatically increased during the economic recession and has sustained a high level
afterward. The greatest increase in Japan was also observed among males of working age.
This might be because they are more likely to be exposed to high unemployment rates
and reduced family income, which could promote psychological distress and increase the
risk of suicide (Kondo et al. 2008; Odagiri et al. 2011).
According to previous research, suicide rates increased in both Japan and South
Korea during the economic crisis of the late 1990. This study will, therefore, focus on a
complete separation of period effects from two other effects (age and cohort) and
compare their respective contributions to increasing suicide rates in Japan and South
Korea. This study hypothesizes that: (1) period effects on suicide would be high in the
late 1990s in both Japan and South Korea because of the effects of the economic
recession of 1997–1998, and (2) South Korea would exhibit stronger period effects than
Japan, due to the severity of the economic crisis in South Korea during this period of time.
This hypothesis is based on the fact that South Korea was more affected than Japan by
16
the economic recession, based on their respective GDP growth and unemployment rates
(GDP growth in 1998 was -2.0% in Japan and -6.9% in South Korea. The unemployment
rate in 1998 was 4.1% in Japan and 7.0% in South Korea [Chang et al. 2009]).
Cohort Effects on Suicide
A cohort is a group of individuals who experience the same event within the same
time frame (Ryder 1965). The event is supposed as birth in most cohort studies and those
studies hypothesize each birth cohort has unique characteristics that reflect historical
experiences associated with age, which make the cohort distinctive from others. The
cohort, therefore, reveals its own uniqueness that cannot be shown by an individual level
of analysis.
One of the most salient characteristics of a birth cohort is its size in relation to
other birth cohorts. The relative size of a birth cohort fundamentally affects members of
that cohort across their lifetimes. That is, when cohorts of different sizes reach each
major juncture in the life cycle, society has the problem of assimilating them. For
example, when members of a large cohort jump into the job market upon the completion
of their schooling, they experience a more crowded job market than the members of a
relatively smaller birth cohort. Ryder (1965) insisted that these circumstances could cause
persistent changes in the attitudes and behaviors of cohort members during their entire
lifetimes.
Suicide studies regarding cohort size posit that the fluctuation of cohort size could
be a significant factor in variations in suicide rates. Easterlin (1978) pointed out that a
large cohort is likely to have a high suicide rate because of reduced standards of living
17
and other factors. The members of a large cohort experience a shortage of schools and
teachers during their school days, a competitive job market with rising unemployment
rates, and relatively low income after graduation as well as limited public pensions during
their retirement years. In other words, lower standards of living and associated stressors
that accompany life in a highly competitive society with limited resources could account
for increases in suicide.
Contrary to this view, Preston (1994) insisted that members of large birth cohorts
tend to have lower suicide rates because the cohort holds relatively more political and
social power, which translates into better life circumstances and enhanced psychological
well-being. To examine these arguments, Pampel (1996) analyzed the relationship
between cohort size and suicide in 18 high-income nations from 1953 to 1986. The result
shows that individuals belonging to large cohorts tend to have higher suicide rates if they
are either young or middle-aged, but they have lower suicide rates if they are elderly. He
concluded the relationship of cohort size to suicide varies depending on four factors: age,
gender, national context, and time period.
Among the three effects, cohort effects in Japan and South Korea have been
studied least. In spite of the limited number of studies, cohort effects were most
responsible for rising suicide in South Korea among the three effects in the period 1983
to 2003 (Lee and Kim 2010). The cohort effects in South Korea started to decrease after
the 1948–1952 birth cohort but were still a significant factor for suicide rates. Lee and
Kim (2010) pointed out that suicide rates in South Korea were forecasted to remain high
until 2011, when the 1938–1947 birth cohort, which has the highest cohort effects on
suicide, becomes the next elderly population. Considering the baby boom in South Korea
18
that occurred from 1955 to 1964, variations in birth cohort size were not a significant
factor for the cohort effects on suicide in South Korea.
Cohort effects on suicide in Japan turned out to have dramatic variations (Odagiri
et al. 2011). The patterns were largely dependent on gender. While birth cohort effects
decreased in South Korea, they increased in Japan. The cohort effects among males have
been increasing since the 1920–1924 birth cohort, but the effects among females started
to increase since the 1951–1955 birth cohort. Considering the baby boom in Japan that
occurred from 1947 to 1949, variations in birth cohort size were not a significant factor
for the cohort effects on suicide in Japan, as well.
In regard to birth cohort effects on suicide, this study hypothesized that: (1) birth
cohort membership would have strong effects on suicide in both countries, but cohort
effects would exhibit a decreasing trend in South Korea since the 1940-1949 birth cohorts,
while in Japan birth cohorts effects would show an increasing trend since the 1920-24
birth cohort among males and the 1951-1955 birth cohort among females, and (2)
variations in birth cohort size would not be a significant factor for the birth cohort effect
on suicide in either country. In other words, the baby boomers (1947–1949 birth cohorts
in Japan, 1955–1964 birth cohorts in South Korea) would not have any distinctive cohort
effects on suicide compared to other cohort groups.
19
CHAPTER III
METHOD
Study Population
For an age-period cohort (APC) analysis of mortality, a researcher needs two
types of data: (a) the number of people exposed to the risk and (b) the number of deaths
from the risk. The population exposed to the risk in my research is the population for
each country (divided by sex and age), which came from the population census in each
country. Japan and South Korea both conduct a population census every five years and
offer the data set through their respective organizations—the Ministry of Internal Affairs
and Communications in Japan and Statistics Korea.
In this study, deaths are attributable only to suicide. Deaths by suicide in South
Korea are offered by Statistics Korea. The numbers are based on death reports, which is
an obligation of one of the deceased’s family members. Once the death report is
submitted to local organizations, the death is enrolled in the Web system. Statistics Korea,
a central government organization for statistics, sums up the whole number of deaths
annually, from January 1 to December 31.
Deaths by suicide in Japan are included in the Vital Statistics Survey, conducted
by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare. Based on Family Registry, municipal heads
fill in “vital statistics survey forms”, including information about births, deaths, stillborn
infants, marriages, and divorces of family members, and then send these statistics to the
prefectural government. The prefectural government inspects the forms submitted by the
health centers and sends them to the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare. The results
20
cover information from January 1 to December 31 of the survey year and are offered by
the Statistics Bureau.
My investigation divided the period between 1985 and 2010 into five-year
intervals to analyze the data by five-year age groups and five-year cohort groups. I
excluded the age groups of 0–4 and 5–9 because suicide rates for these cohorts are mostly
zero. To unify the classification of age categories of the data for the two countries across
the entire period, I summed up the categories over the age of 80 into one category of 80
years and over.
Statistical Analysis
The APC model has been used to analyze cohort effects when a researcher is also
interested in age and period effects (Yang, Fu, and Land 2004). The model is particularly
useful in research concerning risk factors for mortality in demography and epidemiology
(Hobcraft, Menken, and Preston 1982; Robertson, Gandini, and Boyle 1999) because it
distinguishes three types of time-related effects.
Distinguishing the three effects is important (Ooe et al. 2009). If a researcher does
not distinguish the cohort effects from the other two effects, the analysis will yield biased
interpretations regarding age and period effects by assuming equal declines across birth
cohorts (Reither et al. 2009). As a result, the variation in cohort effects could be regarded
as the variation of age or period effects. Therefore, I separated the three effects and
evaluated them independently by the APC model.
The APC model set by Mason et al. (1973) is written in log-linear regression form
as follows:

21
r
ijk
denotes the rate of deaths for the i-th age group, at the j-th time period and the
k-th period group. d
ijk
denotes the number of deaths in the ijk-th group. n
ij
denotes the
number of people exposed to the risk, which means the whole population in the ij-th
group. μ denotes the intercept, meaning an adjusted mean of death rate.
denotes the
age effect in the i-th row.
denotes the period effect in the j-th column.
denotes the
cohort effect in the k-th diagonal with k = a‒i+j. (Yang et al. 2004).
In that this model measures the three effects, respectively, it is a useful method for
researchers. However, this method has one chronic difficulty, despite its strong theoretical
background and statistical relevance: This weakness is an “identification problem” (See
details in Appendix A). Because age, period, and cohort variables are linearly dependent
on each other (period = age + cohort), a matrix of one less than full rank yields multiple
estimators of those three effects. It is difficult, therefore, to define the uniquely separated
set of three effects among them (Yang and Land 2008; Yang et al. 2008).
Conventional APC models such as Conventional Generalized Linear Models
(CGLIM) have tried to resolve this problem by finding a relevant constraint.
Unfortunately, that technique has significant limitations; to establish the constraint a
researcher needs to depend on additional, a priori information, but this information is
generally difficult to acquire or verify. Otherwise, the researcher can test a wide range of
models with different coefficient equality constraints for age, period, and cohort groups.
22
This method helps to establish the degree of sensitivity to various changes in coefficient
constraints, but Hobcraft et al. (1982) point out that the method may still not be
statistically dependable. The results from the method, consequently, are not stable and are
difficult to interpret (Yang 2008; See details in Appendix B).
With this limitation, recent researchers of APC methodology have studied the
estimable function, which is not dependent on the variation of constraints. The alternative
method suggested by Fu (2000), called the Intrinsic Estimator (IE) model, has been
adopted in recent studies. This model yields trustworthy estimates of mortality and
morbidity by age, period, and cohort, which determine the unique coefficient. Through
empirical analysis utilizing the IE model, Yang et al. (2004) concluded that it can be a
useful alternative to conventional methods for APC. For any fixed number p of time
period, the IE model is not only unbiased but has a smaller variance than that of any other
conventional model. For any finite number p of time periods, the intrinsic estimator B has
a reduced variance than that of any conventional general linear model estimator.
In this study, I estimated the APC-IE model of suicide rates in Japan and South
Korea using the STATA module.

23
CHAPTER IV
RESULTS
Descriptive Analysis
Absolute Suicide Rate
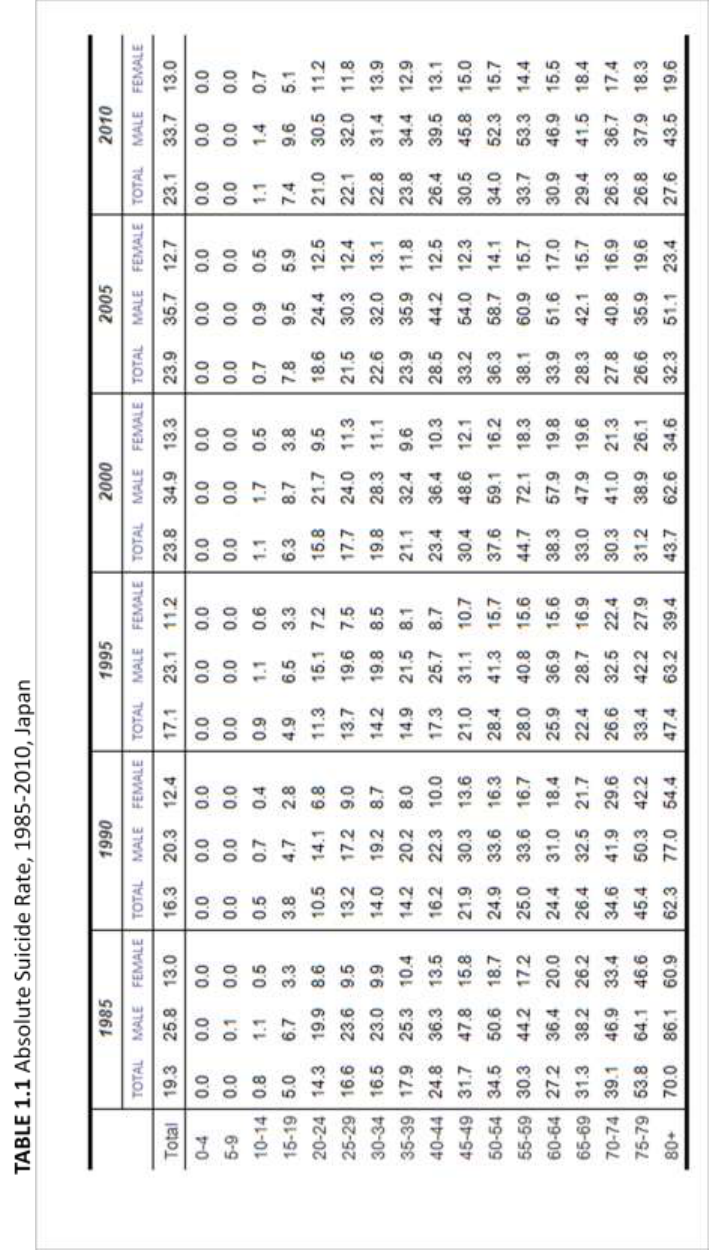
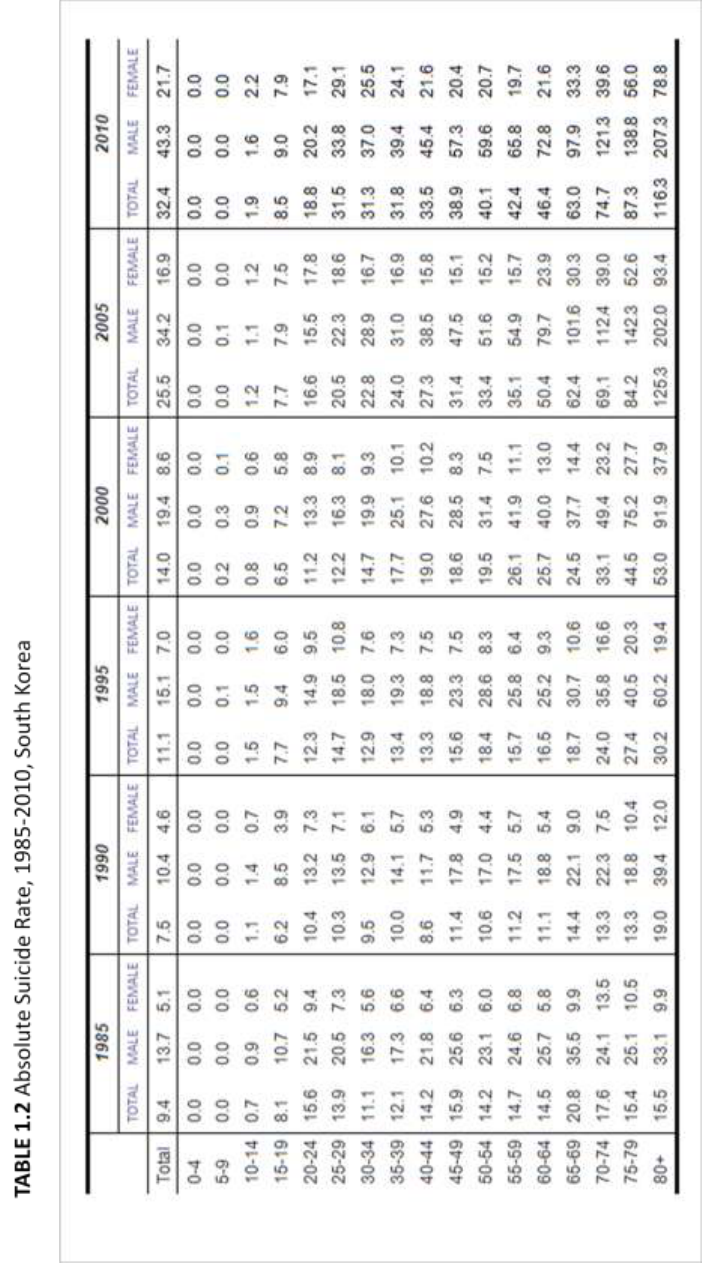
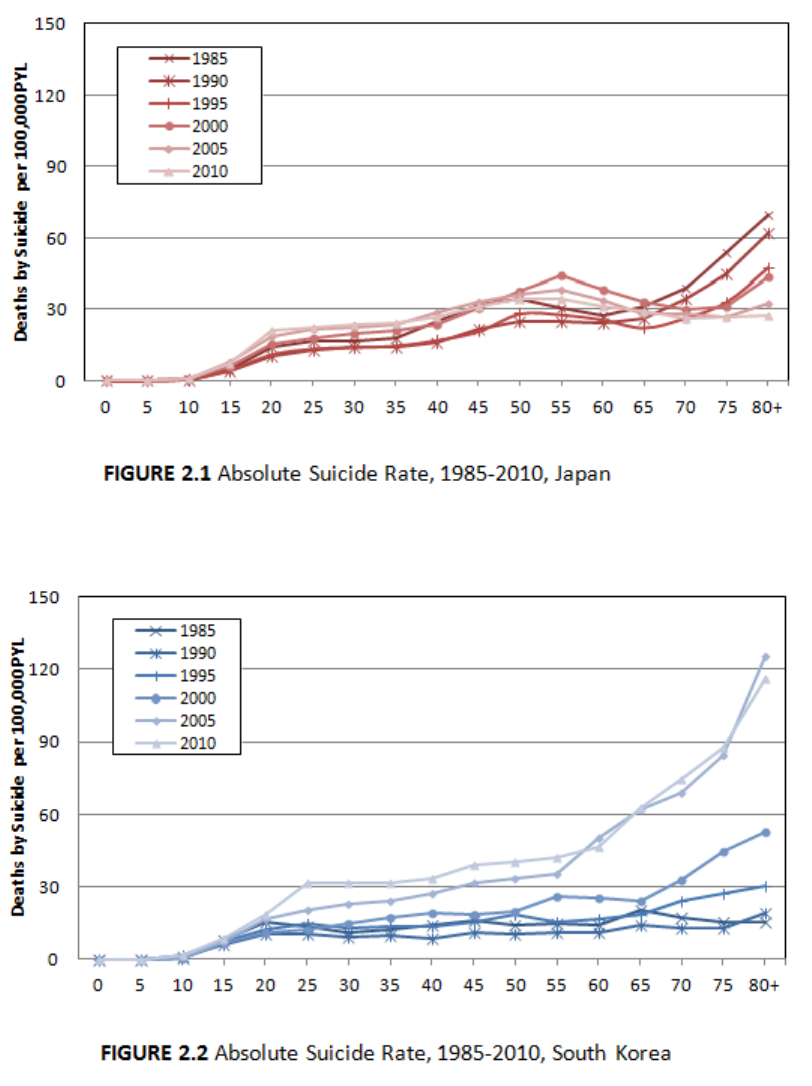
Descriptive statistics are shown in Table 1.1, 1.2 and Figure 2.1, 2.2. They show
absolute suicide rates in Japan and South Korea, i.e. the number of deaths by suicide per
100,000 PYL. The absolute suicide rate in Japan (Table 1.1) increased from 19.3 in 1985
to 23.1 in 2010. The rate has been flattening across all ages since 2000, meaning that
differences between age groups have been narrowing (Figure 2.1). The suicide rate
among the elderly decreased while the rates among younger people in their twenties,
thirties and forties have increased. In 2010, the rate was highest among people in their
fifties with 34.0 deaths per 100,000 PYL among age groups 50-54 and 55-59.
The absolute suicide rate in South Korea (Table 1.2) increased from 9.4 in 1985
to 32.4 in 2010. Compared to Japan, which has the highest suicide rate among middle
aged people, absolute suicide rates in South Korea have had a tendency to increase with
age (Figure 2.2). The absolute suicide rates in South Korea have been increasing across
all ages since 1985, and have increased particularly drastically among the elderly. The
eldest groups’ (80 years old and over) suicide rate, which was 15.5 per 100,000 PYL in
1985, skyrocketed to 116.3 in 2010. This represents an increase of more than 700%. The
rise turned out to be particularly drastic between 2000 and 2005 (53.0 in 2000, 125.31 in
2005).
24
25
26
27
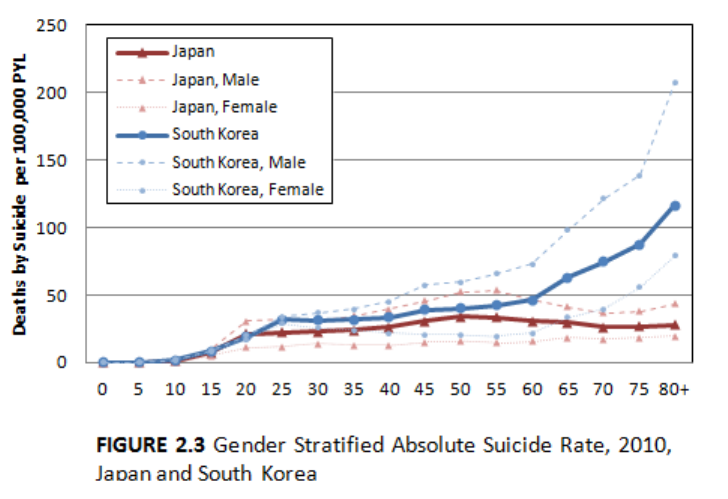
Absolute suicide rates were generally higher among males than females in both
countries. In 2010 (Figure 2.3), the gender difference in Japan was largest among people
in their fifties. The rate among males in this age group was more than three times higher
than that among females of the same age (52.7 among males, 15.0 among females per
100,000 PYL). On the other hand, the gender differences in South Korea increased with
age. The oldest group (80 years and older) in 2010 showed the largest difference between
the sexes, with the suicide rate for males about three times greater than that of females
(207.3 in males and 78.8 in females per 100,000 PYL). The only exception is among
Korean females aged 10-14. In this group, the rate for females was slightly higher than
that for males (1.6 in males and 2.24 in females per 100,000PYL).
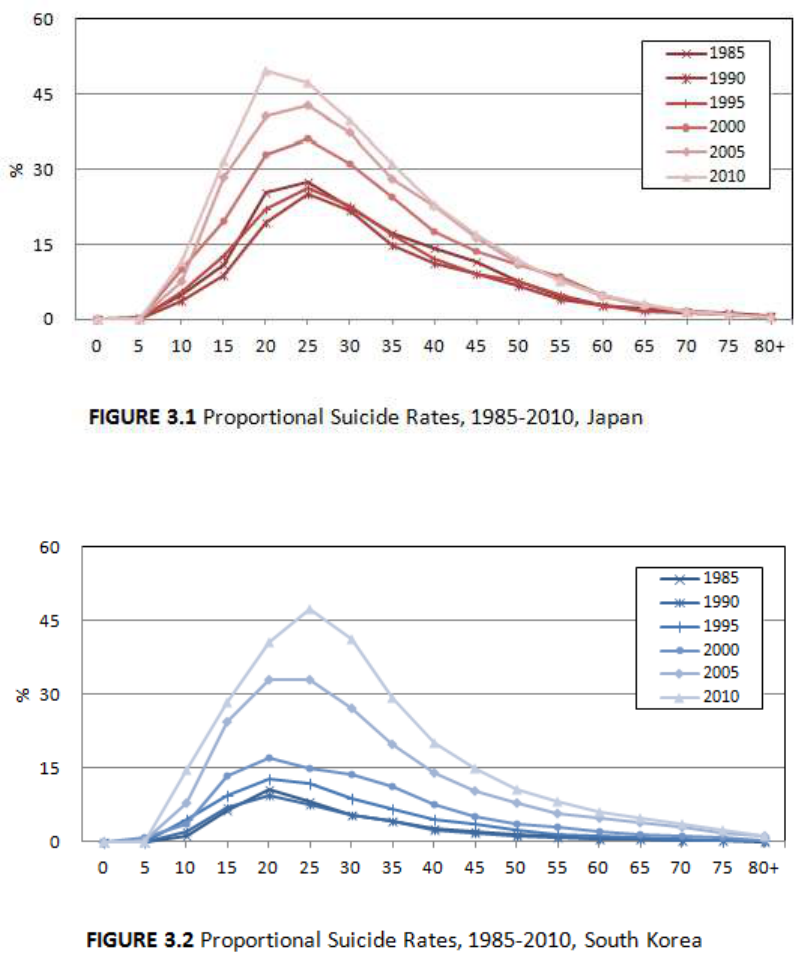
Proportional Suicide Rate
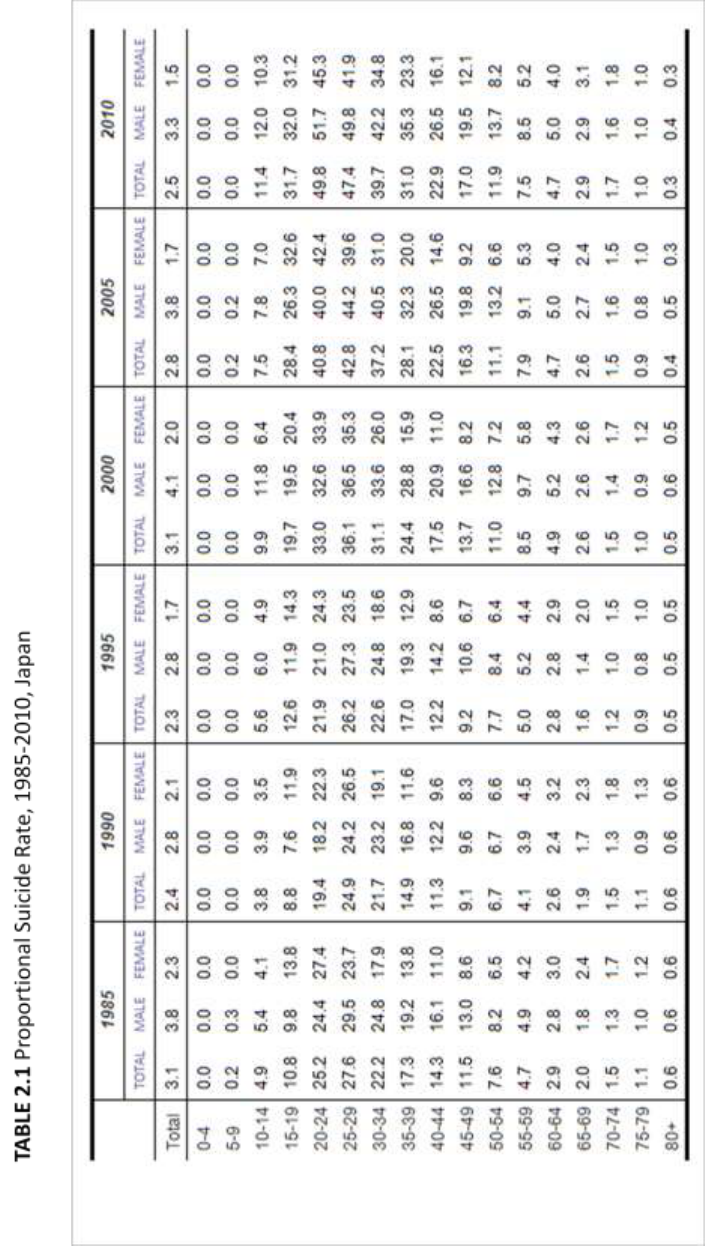
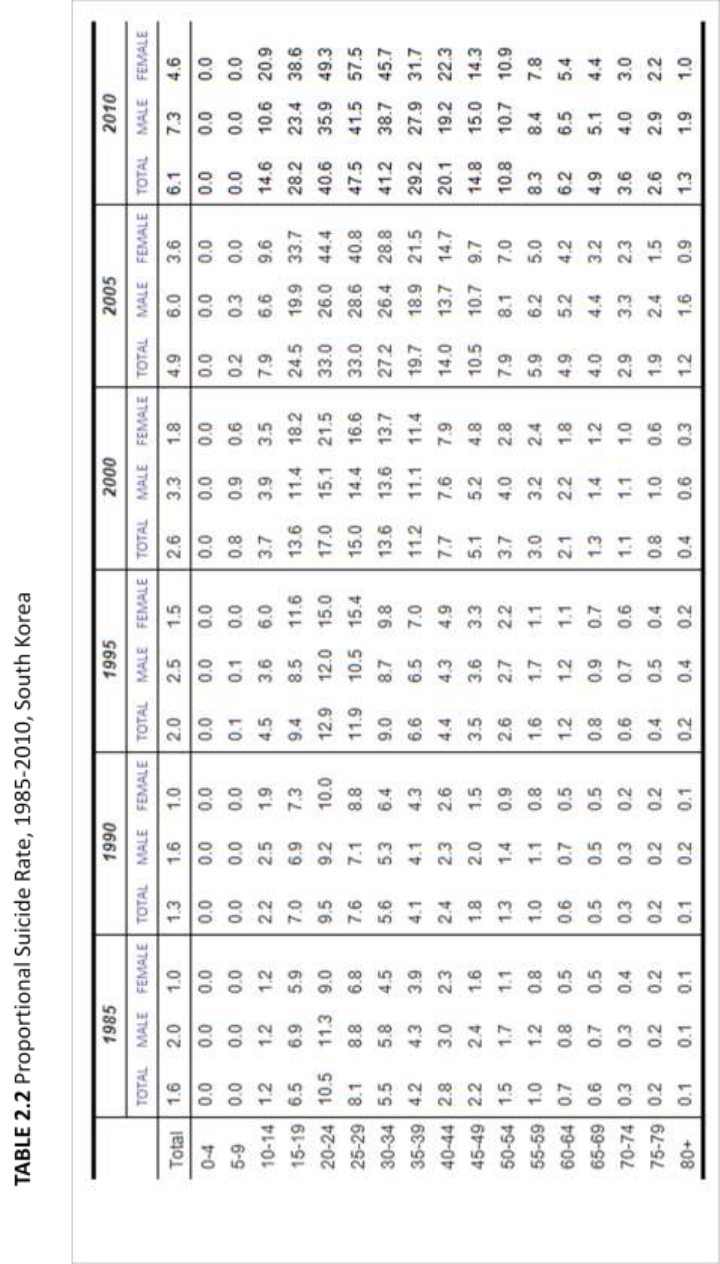
Table 2.1 and Table 2.2 show proportional suicide rates in Japan and South Korea,
28
i.e. the percentage of all deaths that are attributable to suicide. While the overall
proportional suicide rate in South Korea increased from 1.6% in 1985 to 6.1% in 2010,
the rate in Japan decreased from 3.1% from 1985 to 2.5% in 2010. In sum, in South
Korea, both absolute and proportional suicide rates have increased over the last 25 years,
whereas in Japan, the proportional suicide rate has decreased despite the rise in absolute
suicide rates.
In both countries, the proportional rate was highest among younger people,
particularly in their twenties. In 2010, 49.8% of all deaths among people aged 20-24 were
by suicide in Japan (Table 2.1). That proportion has increased from 21.9% in 1995, to
33.0% in 2000 and 40.8% in 2005. In South Korea, 47.5% of total deaths among people
aged 25-29 in 2010 were due to suicide (Table 2.2). That proportion has increased from
11.9% in 1995, to 15.0% in 2000 and 33.0% in 2005. Contrary to absolute suicide rates,
the proportional rates among elderly in both countries were lower than those among the
younger population.
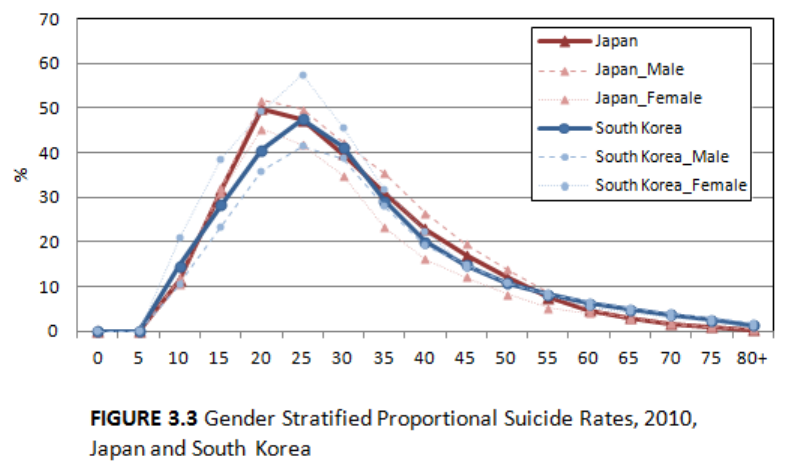
In terms of gender differences (Figure 3.3), the proportional suicide rate in Japan
was mostly higher among males than females. The only exception was the age group of
70-74, but the difference is negligible (1.6% in males and 1.8% in females). Conversely,
the proportional suicide rate in South Korea is, higher among females for teenagers,
people in their twenties, thirties and early forties. In summation, in South Korea, the total
number of deaths by suicide is higher for males when compared with that of females but
the proportion of suicides is lower for males when compared to females.
29
30
31
32
APC Analysis
Overall Mortality
Prior to investigating suicide through APC-IE analysis, I used the APC-IE method
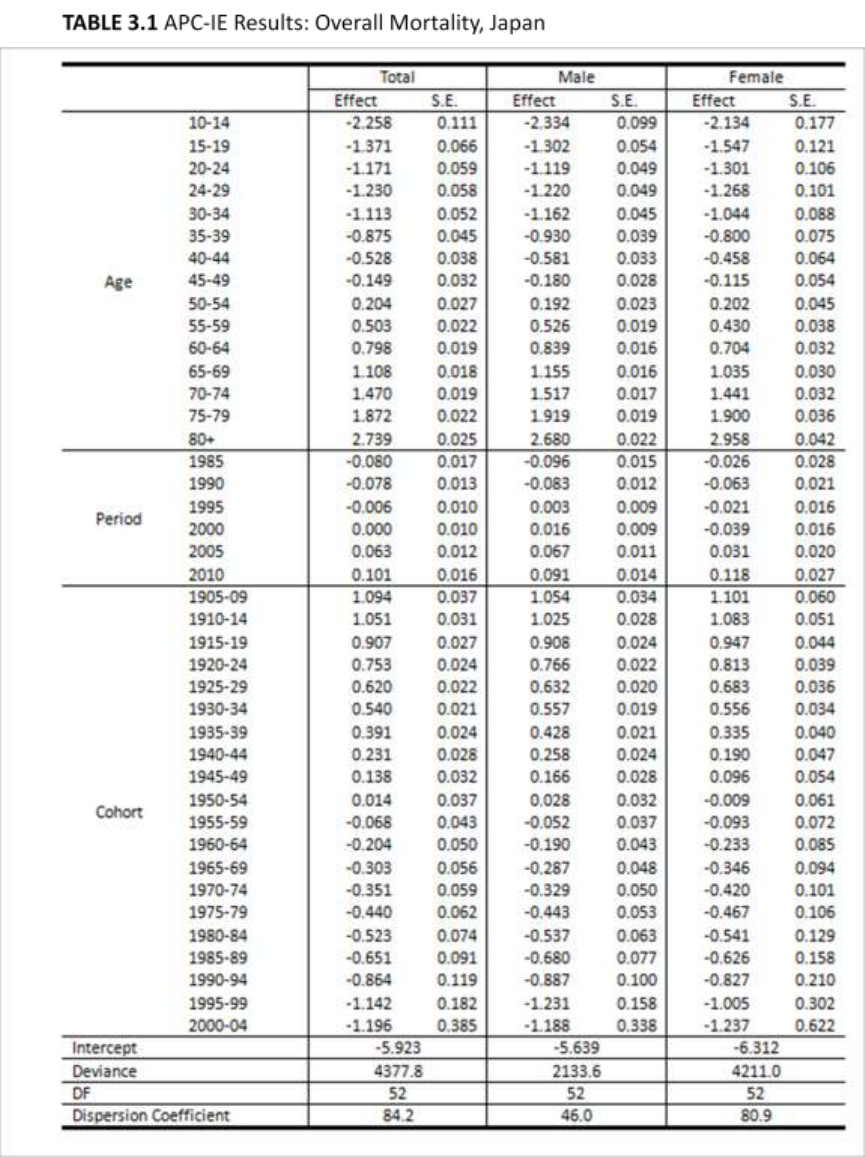
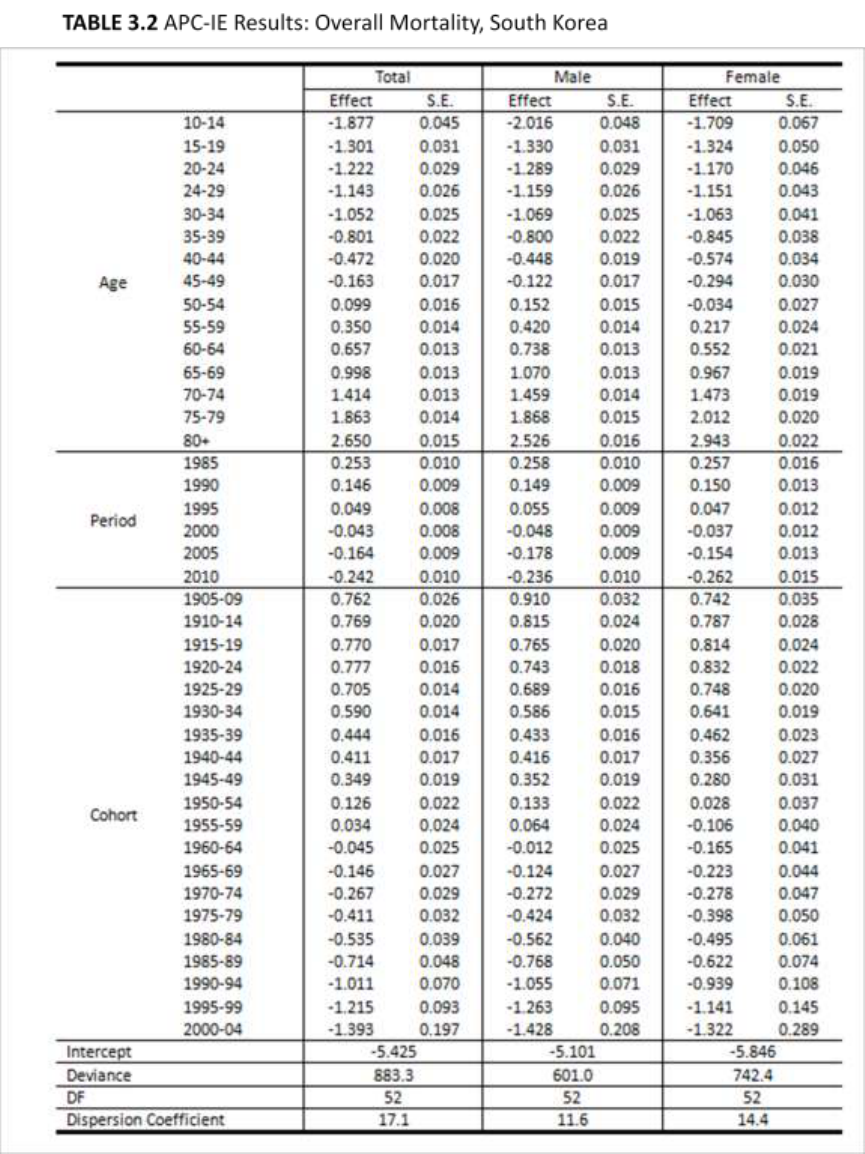
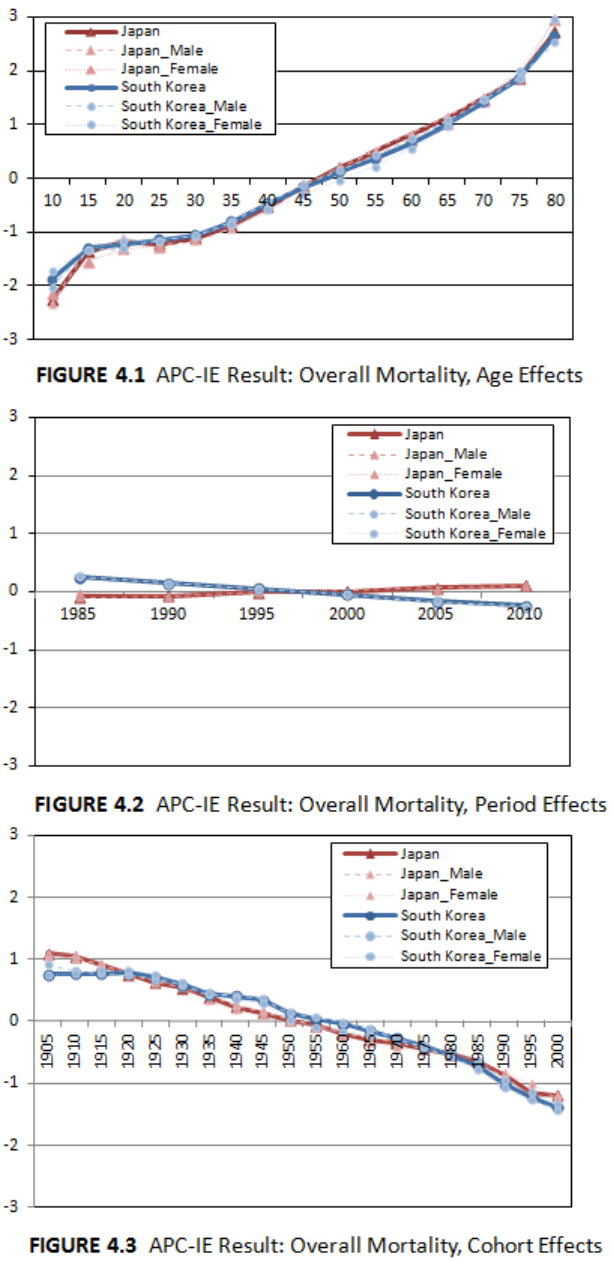
to analyze overall mortality rates in Japan and South Korea. Figure 4.1, 4.2 and 4.3 show
the results: age and cohort effects show similar trends in the two countries. Period effects
show a difference between the two countries having an increasing trend in Japan and a
decreasing tend in South Korea.
In comparing the results of the two countries, the most similar trend was age
effects on overall mortality rates, reflecting the increasing risk of death with age due to
the general biological process of aging. Cohort effects also showed similar trends in the
two countries. The cohort effects in Japan appear to decrease almost linearly; the more
recent the birth cohort, the lower the cohort effect. This trend was similar in South Korea.
Compared to Japan, South Korea showed slightly lower cohort effects among the oldest
33
three birth cohorts (1905–1909, 1910–1914, and 1915–1919) and somewhat higher
effects among people born between 1940 and 1974. Nevertheless, differences between
the two countries were negligible.
In addition, when I compared the gender-stratified results, there were no
noteworthy differences for the age and cohort effects. Period effects, however, showed
somewhat differentiated trends in the two countries. Whereas period effects in South
Korea have continually decreased since 1985, the effects in Japan have continually
increased. The contribution of period effects to mortality rates was smaller than those of
age and cohort effects. Gender-stratified results did not yield any significant findings in
the period effects.
Suicide Mortality
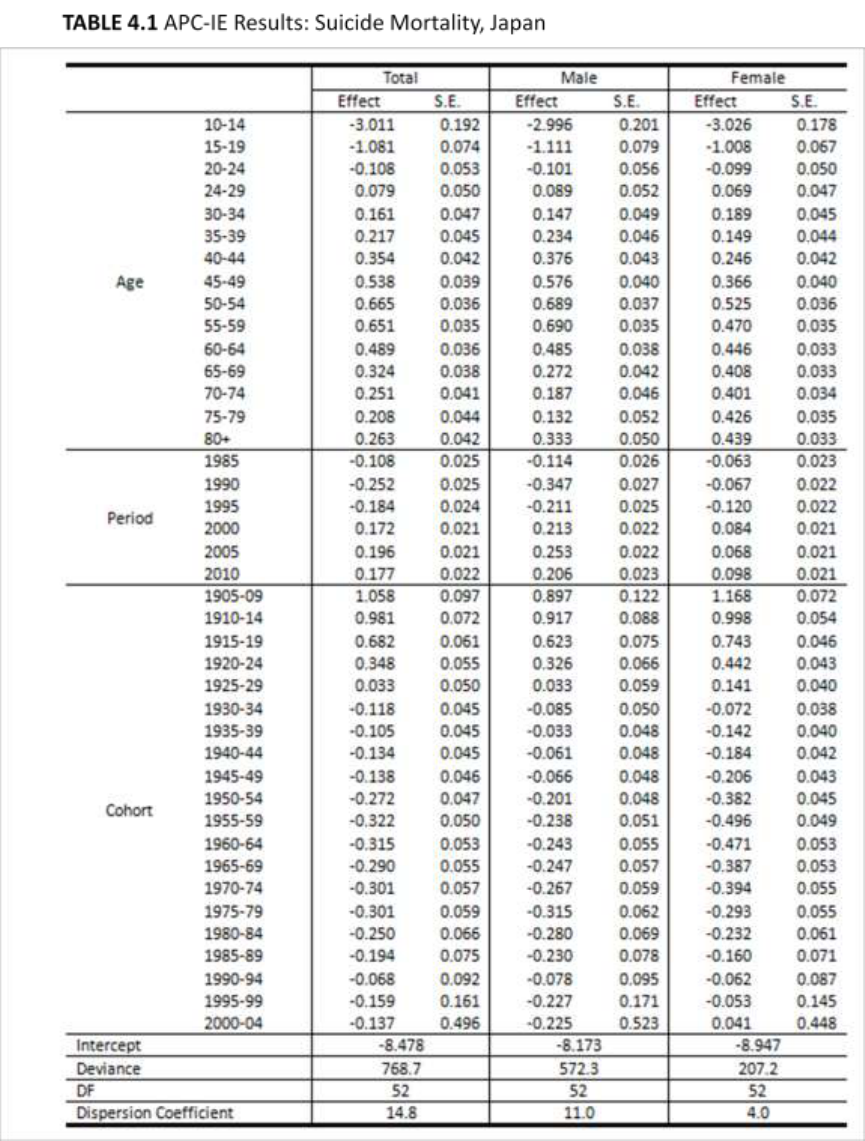
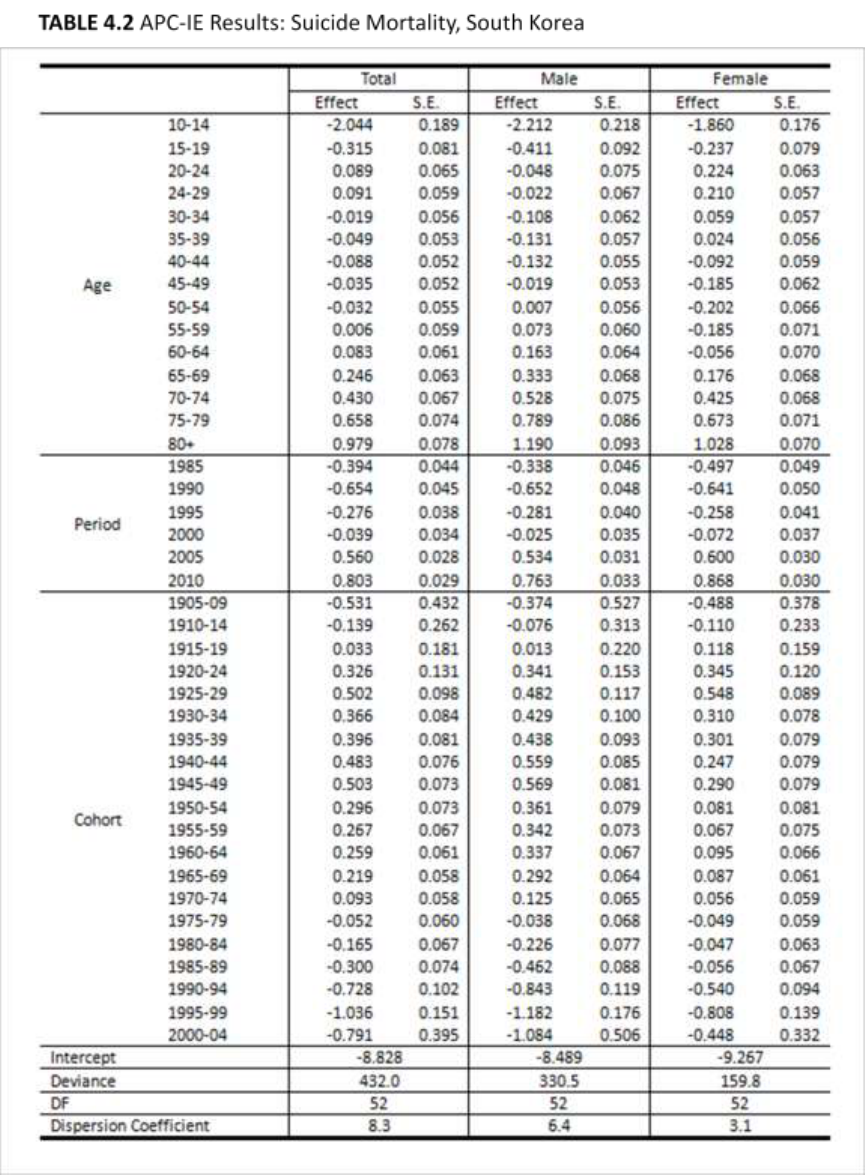
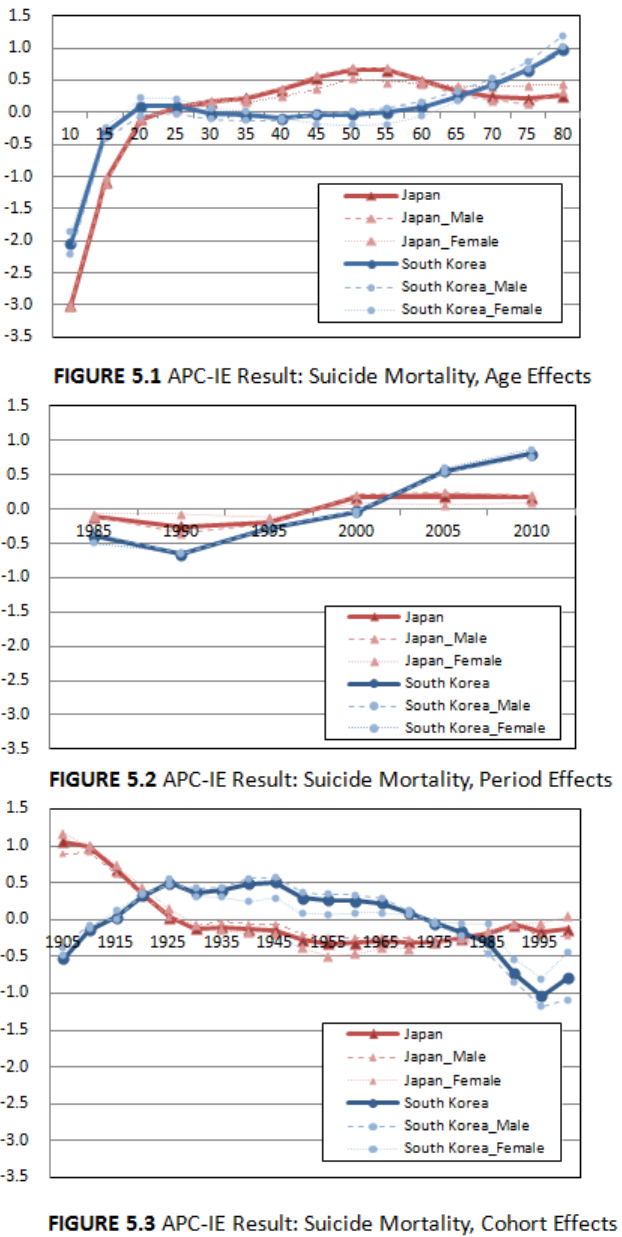
Figure 5.1, 5.2, and 5.3 show the APC-IE results of suicide rates in both countries.
Contrary to the overall mortality results, the suicide rate results showed distinctive
differences between nations in the three effects. In Japan, age effects increased with age
until the fifties age bracket and then decreased after the peak, following my hypothesis.
Thus, age effects among elderly people above 60 years of age turned out to be lower than
those among people in their fifties. This trend was similar among males and females, but
cohort effects among males showed a wider variation.
Conversely, in South Korea, age effects were relatively lower among middle-aged
people and were highest in elderly persons of age 80 and over. Age effects increased with
age until the twenties age bracket, slightly dropped in the thirties, kept the lower level in
middle age, and sharply increased with age after the sixties. This trend appeared among
34
both males and females, but the age effects among elderly people were higher in females
than in males.
Period effects increased in both countries since 1990. Period effects in Japan
greatly increased between 1995 and 2000, which was a period of economic crisis.
Conversely, in South Korea, period effects showed rapid growth between 2000 and 2005,
several years after the economic crisis. The period effects in South Korea sharply
increased until recently, whereas those in Japan have been moderate since 2000. The
range of variation was wider in South Korea than in Japan. Japanese females are
particularly less vulnerable to period effects and show the narrowest range in variation.
The cohort effects showed the most dramatic variations. The two countries show
inverse trends in cohort effects. The birth cohorts born between 1915 and 1970 in South
Korea have high cohort effects, but their counterparts in Japan have the lowest cohort
effects. The birth cohort effects in South Korea began to decrease after the 1945–1949
birth cohort, slightly increasing after the 1995 birth cohort. The birth cohort effects in
Japan were highest among the 1905–1909 birth cohort, the eldest population of my
analysis, and sustained relatively lower levels since the 1925–1929 birth cohort.
35
36
37
38
39
40

41
CHAPTER V
DISCUSSION
Main Findings
Japan and South Korea are neighboring countries that have experienced similar
demographic circumstances (i.e., rapid demographic transitions and fast population aging)
and historical events (i.e., economic crisis in the late 1990s). However, the details of how
those factors affected suicide are complex. Even though Japan and South Korea share
several characteristics, these characteristics do not affect each society in the same way.
For example, although both nations underwent an economic crisis in the late 1990s, the
impacts of the crisis are not identical. Unemployment rates were higher in South Korea
than Japan and GDP growth slowed down more in South Korea than Japan (Chang et al.
2009). Similarly, both have experienced rapid population aging, but the decline in the
working-age population has occurred only in Japan. Those issues may have caused some
differentiation of age, period, and cohort effects in the suicide rates of the two nations.
Compared to the similar trajectories of age effects on overall mortality in Japan
and South Korea, age effects on suicide are dissimilar in the two countries. In South
Korea, the age effects are highest during the elderly period, whereas age effects in Japan
are highest during the fifties age bracket. According to Pampel (1996), variation in
suicide rates could reflect an age group’s relative social well-being and economic status.
Following this argument, the highest age effects on suicide rates among Korean elderly
people could be explained by the lack of social well-being and poor economic status.
Conversely, although Japan has gone through a fast population aging period, the age

42
effects among the Japanese elderly population are relatively low; however, the effects are
high among middle-aged Japanese people, particularly those in their fifties. This could be
explained by Japan’s relatively well-established social system for elderly persons but low
well-being for middle-aged people. Considering the age effects in middle-aged Japanese
females, the figure is much higher for their male counterparts. In turn, middle-aged
Japanese males appear to be the most vulnerable to suicide in Japan. As the working-age
population decreased and the elderly population that the working-age population had to
support increased, social well-being and economic status of middle-aged Japanese males
declined, contributing to high suicide rates.
In regard to period effects, one notable detail is that before the economic crisis in
1997–1998, period effects on suicide in both countries had already seen an increasing
trend since 1990. Therefore, the economic crisis does not appear to be the factor that
initiated the increase in suicide rates in the two countries. However, it could have been
one critical factor that accelerated the rise in suicide in Japan; period effects in Japan
significantly increased from 1995 to 2000. Period effects in South Korea, on the other
hand, increased more sharply during 2000–2005 than during the economic crisis in the
late 1990s.
It is unclear that the increase in suicide mortality during 2000-2005 reflects the
delayed impacts of the economic crisis, but it is obvious that the period effects on suicide
in South Korea have continued to increase until recently, while the period effects in Japan
have been moderate since 2000. Considering relatively weak and decreasing period
effects on overall mortality in South Korea, the increasing trend in period effects for
suicide mortality is notable. Furthermore, although period effects make a small

43
contribution to overall mortality, its effects on suicide are noticeably higher in South
Korea than age and cohort effects. No one has determined a specific reason for why the
period effects in South Korea have been increasing. Future studies on suicide in South
Korea need to have a strong focus on specific factors attributed to period effects.
Cohort effects show opposite trends in the two countries. Baby boomers in Japan
(people born in 1947–1949) do not show high cohort effects compared to the other birth
cohorts. Rather, the 1945–1949 birth cohorts have relatively modest cohort effects on
suicide. Baby boomers in South Korea (born in 1955–1963) also do not show notable
cohort effects on suicide. The cohort effects in South Korea started to decrease after the
1945–1949 birth cohorts. In summation, cohort size is not a decisive factor for
determining cohort effects in the two countries.
Even after the cohort effects started to decrease in South Korea after 1945-1949,
the birth cohort groups that had the strongest cohort effects were still alive and had just
begun to comprise part of the elderly population. The overall contribution of cohort
effects, therefore, should remain high for at least a couple of decades in South Korea.
Conversely, the contribution of cohort effects in Japan should remain low in the near
future because the cohort effects have been low since the 1925–1929 birth cohort (people
80–84 years of age in 2010).
Will the Suicide Rates in Japan and South Korea
Keep Increasing?
The suicide rate in South Korea is expected to continue to increase for several
decades. The period effects have been increasing since 1990 and show the highest levels
in 2010, the most recent time period of my analysis. Furthermore, as the birth cohorts

44
with the strongest cohort effects become elderly (this group has the strongest age effects
as well), it is unlikely that the suicide rate in South Korea will decrease in the near future.
Conversely, the suicide rates in Japan are expected to become somewhat more
moderate in the coming years. Period effects in Japan are decreasing, and the cohort
effects have remained at a low level since the 1925–1929 birth cohort. The only decisive
factor appears to be age effects among Japanese persons in middle age, particularly
people in their fifties. Studies to determine the specific factors behind strong age effects
for Japanese individuals in their fifties should aid in the prevention of suicide in Japan.

45
CHAPTER VI
CONCLUSION
Suicide rates in Japan and South Korea have gradually increased in recent years
and this appears to be contrary to patterns that are been observed elsewhere in the world,
where there is a broad decreasing trend. This study aimed to (a) identify the age, period,
and cohort effects on suicide in Japan and South Korea and (b) compare the extent to
which each effect contributed to the increasing suicide rates that are being observed in
both countries. Using previous research into this area, which did not separate the three
effects (Kwon et al. 2009), this study examined the three effects on suicide respectively
using the APC-IE method. Furthermore compared to previous APC works which focused
on each individual country (Lee and Kim, 2010; Odagiri et al. 2011; Ooe et al. 2009), this
study attempted to compare differences in the suicide events in Japan and South Korea in
terms of the three effects.
In answer to my primary research questions, age effects in Japan greatly
contributed to suicide. Period effects have been moderate since 2000 and cohort effects
sustained relatively lower levels since the 1945-1949 birth cohort that correspond with
current middle-aged people. Reasons for suicide in South Korea were more complex
than in Japan. Pronounced age effects among the elderly population, increasing period
effects, and strong cohort effects of the elderly and middle-aged populations all
contributed to high suicide rates in South Korea. Based on the results, I anticipate the
suicide rate in Japan to be level off in the near future, whereas the suicide rate in South
Korea will more likely remain at a high level for at least a couple of decades.

46
In creating intervention plans to prevent suicide, Japan and South Korea need
different approaches. To be effective in Japan, (a) suicide studies need to determine the
specific factors making suicide so prevalent among people in their fifties, and (b)
interventions need to focus primarily on this highly vulnerable age group. Conversely, in
South Korea, (a) suicide studies must determine why age effects are disproportionately
strong among the elderly population, (b) suicide studies must determine the major factors
that have recently caused period effects to increase and (c) interventions need to focus
primarily on the elderly population and on birth cohort groups born between 1925 and
1969.
Although Japan and South Korea are neighboring countries with shared histories,
industrial structures, social systems, and some demographic characteristics, the causes of
increasing suicide rates in the two countries clearly varies. This means the efforts for pre
venting suicide must also vary, depending on social contexts of each country.
47
REFERENCES
Bloom, D. E., D. Canning, and G. Fink. 2010. “Implication of Population Ageing for
Economic Growth.” Oxford Review of Economic Policy 26 (4):583-612.
Brenner, M. H. 1979. “Mortality and the National Economy.” The Lancet 314(8142):568-
573.
Cattell, H. 2000. “Suicide in the Elderly.” Advances in Psychiatric Treatment 6:102-108.
Chan, A. 2006. “Aging in Southeast and East Asia: Issues and Policy Directions.”
Journal of Cross-cultural Gerontology 20:269-284.
Chang, S., D. Gunnell, J. A. C. Sterne, T. Lu, and T. A. Cheng. 2009. “Was the
Economic Crisis 1997-1998 Responsible for Rising Suicide Rates in
East/Southeast Asia? A Time-trend Analysis for Japan, Hong Kong, South Korea,
Taiwan, Singapore and Thailand.” Social Science & Medicine 68:1322-1331.
Chiu, H. F. K., Y. Takahashi, and G. H. Suh. 2004. “Elderly Suicide Prevention in East
Asia.” International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 18:973-976.
Durkheim, E. 1951. Suicide: A Study in Sociology. Trans. J. A. Spaulding and G.
Simpson. Glencoe, IL.: Free Press. (Orig. pub. 1897)
Easterlin, R. A. 1978. “What Will 1984 Be Like? Socioeconomic Implications of Recent
Twists in Age Structure.” Demography 15 (4):397-432.
Elias, N. 1985. The Loneliness of the Dying. Trans. E. Jephcott. Oxford UK: Basil
Blackwell.
Fu, W. J. 2000. “Ridge Estimator in Singulah Oesiun with Application to Age-Period-
Cohort Analysis of Disease Rates.” Communications in Statistics- Theory and
Method 29(2):263-278.
Girard, C. 1993. “Age, Gender, and Suicide: A Cross-National Analysis” American
Sociological Review 58(4):553-574.
Goodman, R. and Peng, I. 1996. “The East Asian Welfare States: Peripatetic Learning,
Adaptive Change, and Nation-building.” Pp. 192-224 in Welfare States in
Transition, edited by G. Esping-Andersen. London: Sage.
Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service in South Korea . 2010. “The
Depression Prevalence is higher among females than males (in Korean).”
Retreived, April 6, 2010
(http://www.hira.or.kr/dummy.do?pgmid=HIRAA020041000000&cmsurl=/cms/n
otice/2/1199281_13390.html).
48
Hobcraft, J., J. Menken, and S. Preston. 1982. “Age, Period and Cohort Effects in
Demography: A Review.” Population Index 48(1):4-43.
Kawakami, N., T. Takeshima, Y. Ono, H. Uda, Y. Hata, Y. Nakane, H. Nakane, N. Iwata,
T. Furukawa, and T. Kikkawa. 2005. “Twelve-Month Prevalence, Severity, and
Treatment of Common Mental Disorders in Communities in Japan: Preliminary
Finding From the World Mental Health Japan Survey 2002-2003.” Psychiatry and
Clinical Neurosicences 59(4):441-452.
Khang, Y. H., J. W. Lynch, and G. A. Kaplan. 2005. “Impact of Economic Crisis on
Cause-Specific Mortality in South Korea.” International Journal of Epidemiology
34:1291-1301.
Kim, I. K., and D. Maeda. 2001. “A Comparative Study on Sociodemographic Changes
and Long-term Health Care Needs of the Elderly in Japan and South Korea.”
Journal of Cross-Cultural Gerontology 16:237-255.
Kim, S. Y., M. H. Kim, I. Kawachi, and Y. T. Cho. 2011. “Comparative Epidemiology of
Suicide in South Korea and Japan: Effects of Age, Gender and Suicide Methods.”
Crisis: The Journal of Crisis Intervention and Suicide Prevention 32(1):5-14.
Kondo, N., S. V. Subramanian, I. Kawachi, and Z. Yamagata. 2008. “Economic
Recession and Health Inequalities in Japan: Analysis with a National Sample
1986-2001.” Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health 62(10): 869-875.
Kupper, L. L., M. J. Joseph, A. Karamous, and B. G. Greenberg. 1985. “Statistical Age-
Period-Cohort Analysis: A Review and Critique.” Journal of Chronic Diseases
38(10):811-830.
Kwon , J., H. Chun, and S. Cho. 2009. “A Closer Look at the Increase in Suicide Rates in
South Korea from 1986-2005” BMC Public Health 9(72).
Lee, J. Y., S. H. Kim. 2010. “Suicide in Korea (in Korean).” Korean Sociological
Association 44:63-94.
Lee, Y., and S. Shinkai. 2003. “A Comparison of Correlates of Self-Rates Health and
Functional Disability of Older Persons in the Far East: Japan and Korea.”
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics 37:63-76.
Leo, D. D. 2002. “Struggling Against Suicide: The Need for an Integrative Approach.”
Crisis: The Journal of Crisis Intervention and Suicide Prevention 23 (1):23-31.
Mason, K. O., W. M. Mason, H. H. Winsborough, and W. K. Poole. 1973. “Some
Methodological Issues in Cohort Analysis of Archival Data.” American
Sociological Review 38(2): 242-258.
49
Mason, A., R. Lee, S. H. Lee. 2008. “The Demographic Transition and Economic Growth
in the Pacific Rim.” East Asian Seminar on Economics. Retrieved August 16,
2008. (http://hdl.handle.net/10125/3002 )
Odagiri, Y., H. Uchida, and M. Nakano. 2011. “Gender Differences in Age, Period, and
Birth-Cohort Effects on the Suicide Mortality Rate in Japan, 1985-2006.” Asia-
Pacific Journal of Public Health 23(4):581-587.
Ooe, Y., Y. Ohno, and T. Nakamura. 2009. “Age-Period-Cohort Analysis of Suicides
among Japanese 1950-2003: A Bayesian Cohort Model Analysis.” The Journal of
the Japan Hospital Association 28: 71-8.
Organisastion for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). 2011. “OECD
Health Data 2011.” Retrieved June 30, 2011
(http://www.oecd.org/document/30/0,3746,en_2649_37407_12968734_1_1_1_37
407,00Html) .
Ostamo, A., J. Lönnqvist. 2001. “Attempted Suicide Rates and Trends during a Period of
Severe Economic Recession in Helsinki, 1989-1997.” Social Psychiatry and
Psychiatric Epidemiology 36(7):354-360.
Pampel, F. C., 1996. “Cohort Size and Age-Specific Suicide Rates: A Contingent
Relationship.” Demography, 33(3):341-355.
Park, B. C. B., and D. Lester. 2006. “Social Integration and Suicide in South Korea.”
Crisis: The Journal of Crisis Intervention and Suicide Prevention 27(1):48-50.
Preston, S. H. 1984. “Children and the Elderly: Divergent Paths for America’s
Dependents.” Demography 21(4):435-457.
Reither, E. N., R. M. Hauser, and Y. Yang. 2009. “Do Birth Cohorts Matter? Age-Period-
Cohort Analyses of the Obesity Epidemic in the United States.” Social Science &
Medicine 69:10:1439-1448.
Robertson, G., S. Gandini, and P. Boyle. 1999. “Age-Period-Cohort Models: A
Comparative Study of Available Methodologies.” Journal of Clinical
Epidemiology 52(6):569-583.
Ruhm, C. J. 1996. “Are Recessions Good for Your Health?” The Quarterly Journal of
Economics 115(2):617-650.
Ryder, N. B. 1965. “The Cohort as a Concept in the Study of Social Change.” American
Sociological Review 30(6):843-861.
Shah, A. 2007. “The Relationship Between Suicide Rates and Age: An Analysis of
Multinational Data From the World Health Organization.” International
Psychogeriatrics 19(6):1141-1152.
50
Turner, B. 2004. The New Medical Sociology: Social Forms of Health and Illness. Trans.
J. C. Alexander. W. W. Norton & Company, New York London.
World Health Organization. 2002. “Mental Health: Introduction.” Retrieved March, 2002
(http://www.who.int/mental_health/media/en/382.pdf).
Yang, B. 1992. “The Economy and Suicide: A Time-Series Study of the U.S.A.”
American Journal of Economics and Sociology 51(1):87-99.
Yang, Y. 2004. “APC Anlysis of Table of Rates: 1.1. Stata module.”
(http://www.unc.edu/~yangy819/apc/sectionE.html).
Yang, Y. 2008. “Trends in U.S. Adults Chronic Disease Mortality, 1960-1999: Age,
Period, and Cohort Variations.” Demography 45(2):387-416.
Yang, Y., and K. C. Land. 2008. “Age-Period-Cohort Analysis of Repeated Cross-
Section Surveys: Fixed or Random Effects?” Sociological Methods & Research
36(3):297-326.
Yang, Y., S. Schulhofer-Wohl, W. J. Fu, and K. C. Land. 2008. “The Intrinsic Estimator
for Age-Period-Cohort Analysis: What It Is and How to Use It.” American
Journal of Sociology 113(6):1697-1736.
Yang, Y., W. J. Fu, and K. C. Land. 2004. “A Methodological Comparison of Age-
Period-Cohort Models: The Intrinsic Estimator and Conventional Generalized
Linear Models.” Sociological Methodology 34(1):75-110.
51
APPENDIXES
52
APPENDIX A
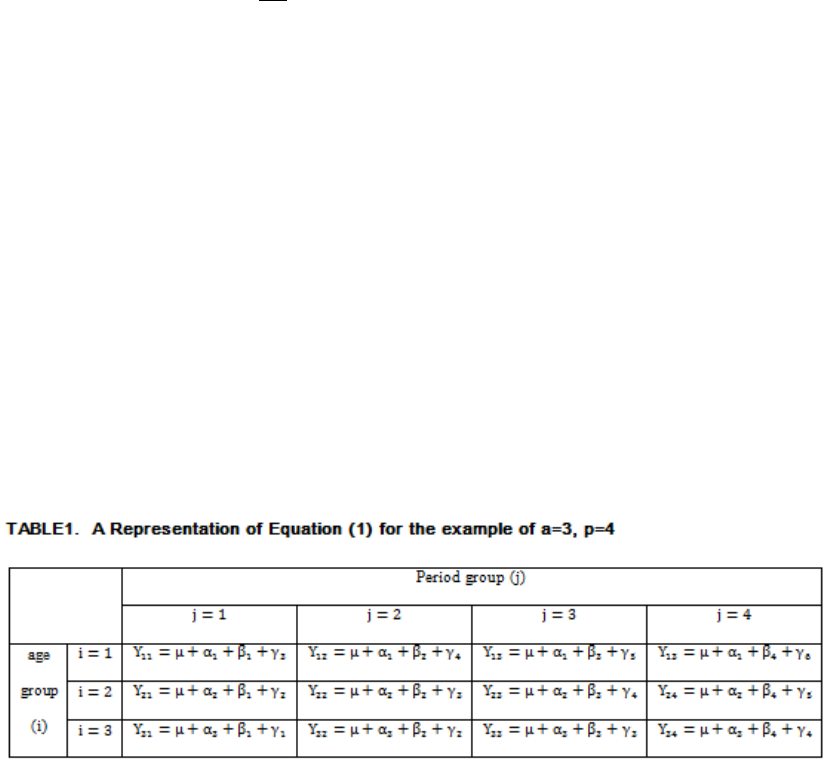
The Identification Problem of Conventional APC Model
The APC model for demography was set by Mason et al. (1973). The model
for mortality rates can be written in linear regression as follows:
M
ij
denotes the rate of deaths for the i-th age group at the j-th time period. D
ij
denotes the number of deaths in the ij-th group. P
ij
denotes the whole population in ij-
th group, which means the number of people exposed to the risk. μ denotes the
intercept, meaning the adjusted mean of death rate. α
i
denotes the age effect in the i-
th row. β
j
denotes the period effect in the j-th column. γ
a-i+j
denotes the cohort effect in
the k-th diagonal. means the random errors expected to E (ε
ij
)=0 (Yang et al. 2004).
For example, let us suppose that a=3, p=4 (Kupper et al. 1985).
In Table 1, cells in the same row share the same age effect: α
i
Cells in the
same column share the same period effect: β
j.
Cells in the same diagonal share the
same cohort effect: γ
a-i+j
After re-parameterization for ANOVA-type models, the equation (1) can be
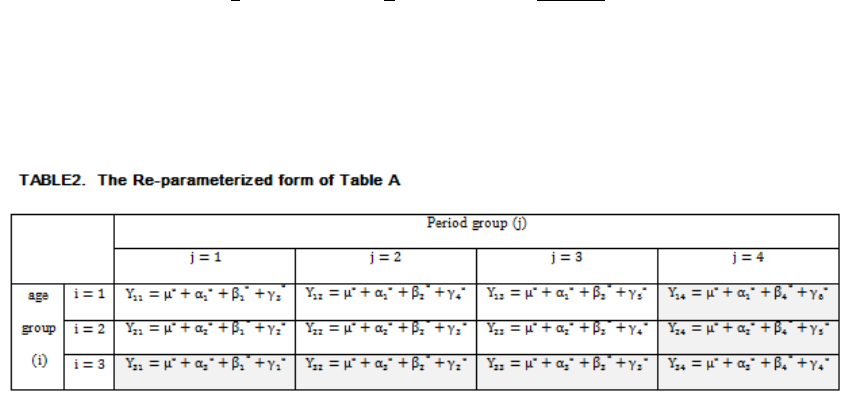
53
written in the following form;
The re-parameterization here means to define
,
,
and
, where
are defined as
parametric means such as;
(2)
Then, we can write Table A into the re-parameterized form;
Everything in Table 2 is equivalent to Table 1 except with an asterisk.
However, we can write Y
14
, Y
24
, Y
31
, Y
32
, Y
33
and Y
34
in other forms without the final
clauses of each effect,
and
using (2) and the followings;
(Applied for β and γ as well)
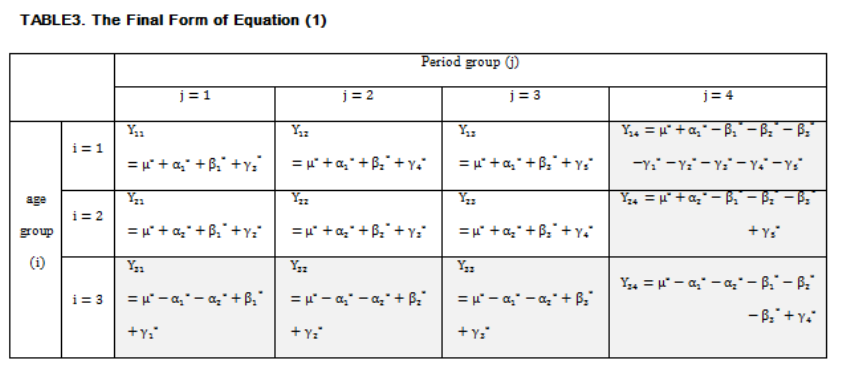
54
Then, the final expression of Y can be written as Table 3.
Then, we can put it in a matrix form as follows;
ε(Y)
=
X* ξ (3)
Where,
Y
T
= │Y
11
, Y
12
, Y
13
, Y
14
, Y
21
, Y
22
, Y
23
, Y
24
, Y
31
, Y
32
, Y
33
, Y
34
│
ξ*
T
=│ μ*,α
1
*, α
2
*,β
1
*,β
2
*,β
3
*,γ
1
*,γ
2
*,γ
3
*,γ
4
*,γ
5
*│

55
(※A
T
means the transposition of a matrix A)
Hypothesizing ξ* is the ordinary least square, the solution of (3) follows;
X*
T
Y
=
X*
T
X* ξ*
However, an inverse matrix of (X*
T
X*)-1 does not exist because X*is a
singular matrix having one less than a full rank. This is ultimately derived from a
linear relationship between age, period and cohort (Period=Age + Cohort). A unique
ξ*, therefore, cannot be defined without an additional constraint.
56
APPENDIX B
The Unstableness of CGLIM Model
In Yang et al. (2004), their CGLIM results show largely different trajectories
of each effect following the different constraints. Among the various constraints, they
picked up the one appropriate constraint and compared the result to the result by IE.
CGLIM is a great method if a researcher can find out the appropriate
constraint. However, as mentioned above, picking up the appropriate constraint is not
a straightforward work. Following are the age effects calculated by the CGLIM model
with different age constraints using suicide data of South Korea.
As shown in Figure 1, the age effects largely changes following the constraint.
The constraint simultaneously affects the period effects and cohort effects as well. To

57
get an appropriate constraint, the researcher needs to compare all of the variation of
three effects following every possible constraint. In my case, I have 15 age variables,
6 period variables and 20 cohort variables. Thus, I need to examine 820 possible
combinations to find an appropriate constraint. Even after examining 820 possibilities,
an appropriate constraint cannot be guaranteed due to the unstableness of the results.
