
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use
ADDERALL XR safely and effectively. See full prescribing information
for ADDERALL XR.
ADDERALL XR
®
(mixed salts of a single-entity amphetamine product)
extended release capsules, for oral use, CII
Initial U.S. Approval: 2001
WARNING: ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning
• CNS stimulants, including ADDERALL XR, other amphetamine-
containing products, and methylphenidate, have a high potential
for abuse and dependence (5.1, 9.3)
•
Assess the risk of abuse prior to prescribing and monitor for signs
of abuse and dependence while on therapy (9.2, 9.3).
-------------------------INDICATIONS AND USAGE------------------------------
ADDERALL XR, a CNS stimulant, is indicated for the treatment of attention
deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). (1)
• Children (ages 6-12): Efficacy was established in one 3-week outpatient,
controlled trial and one analogue classroom, controlled trial in children
with ADHD. (14)
• Adolescents (ages 13-17): Efficacy was established in one 4-week
controlled trial in adolescents with ADHD. (14)
• Adults: Efficacy was established in one 4-week controlled trial in adults
with ADHD. (14)
---------------------------DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION-------------------
• Pediatric patients (ages 6-17): 10 mg once daily in the morning.
Maximum dose for children 6-12 years of age is 30 mg once daily. (2.2,
2.3, 2.4)
• Adults: 20 mg once daily in the morning. (2.5)
• Pediatric patients (ages 6-17) with severe renal impairment: 5 mg once
daily in the morning. Maximum dose for children 6- 12 years of age with
severe renal impairment is 20 mg once daily. (2.6, 8.6)
• Adults with severe renal impairment: 15 mg once daily in the morning.
(2.6, 8.6)
• Patients with ESRD: not recommended. (2.6, 8.6)
-----------------------DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS--------------------
• Extended release capsules: 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 25 mg, 30 mg (3)
------------------------------CONTRAINDICATIONS----------------------------
• Advanced arteriosclerosis (4)
• Symptomatic cardiovascular disease (4)
• Moderate to severe hypertension (4)
• Hyperthyroidism (4)
• Known hypersensitivity or idiosyncrasy to amphetamine (4)
• Glaucoma (4)
• Agitated states (4)
• History of drug abuse (4)
• During or within 14 days following the administration of monoamine
oxidase inhibitors (MAOI) (4, 7.1)
--------------------------WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS---------------------
• Serious Cardiovascular Reactions: Sudden death has been reported with
usual doses of CNS stimulants in children and adolescents with structural
cardiac abnormalities or other serious heart problems; sudden death,
stroke, and myocardial infarction have been reported in adults taking CNS
stimulants at usual doses. Stimulant drugs should not be used in patients
with known structural cardiac abnormalities, cardiomyopathy, serious
heart rhythm abnormalities, coronary artery disease, or other serious heart
problems. (5.2)
• Increase in Blood Pressure: Monitor blood pressure and pulse at
appropriate intervals. Use with caution in patients for whom blood
pressure increases may be problematic. (5.2)
• Psychiatric Adverse Events: Stimulants may cause treatment-emergent
psychotic or manic symptoms in patients with no prior history, or
exacerbation of symptoms in patients with pre-existing psychosis.
Evaluate for bipolar disorder prior to stimulant use. Monitor for
aggressive behavior. (5.3)
• Long-Term Suppression of Growth: Monitor height and weight at
appropriate intervals. (5.4)
• Seizures: May lower the convulsive threshold. Discontinue in the
presence of seizures. (5.5)
• Peripheral Vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s phenomenon: Stimulants
used to treat ADHD are associated with peripheral vasculopathy,
including Raynaud’s phenomenon. Careful observation for digital
changes is necessary during treatment with ADHD stimulants. (5.6)
• Serotonin Syndrome: Increased risk when co-administered with
serotonergic agents (e.g., SSRIs, SNRIs, triptans), but also during
overdosage situations. If it occurs, discontinue ADDERALL XR and
initiate supportive treatment (4, 5.7, 10).
• Visual Disturbance: Difficulties with accommodation and blurring of
vision have been reported with stimulant treatment. (5.8)
• Tics: May exacerbate tics. Evaluate for tics and Tourette’s syndrome
prior to stimulant administration. (5.9)
--------------------------------ADVERSE REACTIONS-----------------------------
• Children (ages 6 to 12): Most common adverse reactions (≥5% and with a
higher incidence than on placebo) were loss of appetite, insomnia,
abdominal pain, emotional lability, vomiting, nervousness, nausea, and
fever. (6.1)
• Adolescents (ages 13 to 17): Most common adverse reactions (≥5% and
with a higher incidence than on placebo) were loss of appetite, insomnia,
abdominal pain, weight loss, and nervousness. (6.1)
• Adults: Most common adverse reactions ≥5% and with a higher incidence
than on placebo were dry mouth, loss of appetite, insomnia, headache,
weight loss, nausea, anxiety, agitation, dizziness, tachycardia, diarrhea,
asthenia, and urinary tract infections. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Takeda
Pharmaceuticals at 1-800-828-2088 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or
www.fda.gov/medwatch
--------------------------------DRUG INTERACTIONS-----------------------------
• MAOI antidepressants are contraindicated; MAOIs potentiate the effects
of amphetamine. Do not administer ADDERALL XR during or within 14
days after use of MAOI. (4, 7.1)
• Alkalinizing agents (GI antacids and urinary): These agents increase blood
levels of amphetamine. (7.1)
• Acidifying agents (GI and urinary): These agents reduce blood levels of
amphetamine. (7.1)
• Adrenergic blockers, antihistamines, antihypertensives, phenobarbital,
phenytoin, veratrum alkaloids, and ethosuximide: Effects may be reduced
by amphetamines. (7.1)
• Tricyclic antidepressants, norepinephrine, and meperidine: Effects may be
potentiated by amphetamines. (7.1)
--------------------------USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS---------------------
• Pregnancy: May cause fetal harm. (8.1)
• Lactation: Breastfeeding not recommended. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication
Guide.
Revised: 2/2022
Reference ID: 4943991
1

FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Information Prior to Initiating Treatment
2.2 Dosing Considerations for All Patients
2.3 Children
2.4 Adolescents
2.5 Adults
2.6 Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Potential for Abuse and Dependence
5.2 Serious Cardiovascular Reactions
5.3 Psychiatric Adverse Events
5.4 Long-Term Suppression of Growth
5.5 Seizures
5.6 Peripheral Vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s
Phenomenon
5.7 Serotonin Syndrome
5.8 Visual Disturbance
5.9 Tics
5.10 Prescribing and Dispensing
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Adverse Reactions Associated with the Use of
Amphetamine, ADDERALL XR, or ADDERALL
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Clinically Important Interactions with Amphetamines
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
9.2 Abuse
9.3 Dependence
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
*Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing
information are not listed
Reference ID: 4943991
2
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
CNS stimulants, including ADDERALL XR, other amphetamine-containing products, and
methylphenidate, have a high potential for abuse and dependence. Assess the risk of abuse prior to
prescribing and monitor for signs of abuse and dependence while on therapy [see Warnings and
Precautions (5.1) and Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2, 9.3)].
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
ADDERALL XR
®
is indicated for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
The efficacy of ADDERALL XR in the treatment of ADHD was established on the basis of two
controlled trials in children aged 6 to 12, one controlled trial in adolescents aged 13 to 17, and one
controlled trial in adults who met DSM-IV
®
criteria for ADHD [see Clinical Studies (14)].
A diagnosis of ADHD (DSM-IV
) implies the presence of hyperactive-impulsive or inattentive
symptoms that caused impairment and were present before age 7 years. The symptoms must cause
clinically significant impairment, e.g., in social, academic, or occupational functioning, and be present in
two or more settings, e.g., school (or work) and at home. The symptoms must not be better accounted for
by another mental disorder. For the Inattentive Type, at least six of the following symptoms must have
persisted for at least 6 months: lack of attention to details/careless mistakes; lack of sustained attention;
poor listener; failure to follow through on tasks; poor organization; avoids tasks requiring sustained
mental effort; loses things; easily distracted; forgetful. For the Hyperactive-Impulsive Type, at least six of
the following symptoms must have persisted for at least 6 months: fidgeting/squirming; leaving seat;
inappropriate running/climbing; difficulty with quiet activities; "on the go;" excessive talking; blurting
answers; can't wait turn; intrusive. The Combined Type requires both inattentive and hyperactive-
impulsive criteria to be met.
Special Diagnostic Considerations
Specific etiology of this syndrome is unknown, and there is no single diagnostic test. Adequate diagnosis
requires the use not only of medical but of special psychological, educational, and social resources.
Learning may or may not be impaired. The diagnosis must be based upon a complete history and
evaluation of the patient and not solely on the presence of the required number of DSM-IV
characteristics.
Need for Comprehensive Treatment Program
ADDERALL XR is indicated as an integral part of a total treatment program for ADHD that may include
other measures (psychological, educational, social) for patients with this syndrome. Drug treatment may
not be indicated for all patients with this syndrome. Stimulants are not intended for use in the patient who
exhibits symptoms secondary to environmental factors and/or other primary psychiatric disorders,
including psychosis. Appropriate educational placement is essential and psychosocial intervention is often
helpful. When remedial measures alone are insufficient, the decision to prescribe stimulant medication
will depend upon the physician's assessment of the chronicity and severity of the child's symptoms.
Long-Term Use
The effectiveness of ADDERALL XR for long-term use, i.e., for more than 3 weeks in children and 4 weeks
in adolescents and adults, has not been systematically evaluated in controlled trials. Therefore, the physician
who elects to use ADDERALL XR for extended periods should periodically re-evaluate the long-term
usefulness of the drug for the individual patient.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Reference ID: 4943991
3
2.1 Important Information Prior to Initiating Treatment
Prior to initiating treatment with ADDERALL XR, assess for the presence of cardiac disease (e.g.,
perform a careful history, family history of sudden death or ventricular arrhythmia, and physical exam)
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Assess the risk of abuse prior to prescribing and monitor for signs of abuse and dependence while on
therapy. Maintain careful prescription records, educate patients about abuse, monitor for signs for abuse
and overdose, and periodically re-evaluate the need for ADDERALL XR use [see Warnings and
Precautions (5.1), Drug Abuse and Dependence (9)].
2.2 Dosing Considerations for All Patients
Individualize the dosage according to the therapeutic needs and response of the patient. Administer
ADDERALL XR at the lowest effective dosage.
Based on bioequivalence data, patients taking divided doses of immediate-release ADDERALL, (for
example, twice daily), may be switched to ADDERALL XR at the same total daily dose taken once daily.
Titrate at weekly intervals to appropriate efficacy and tolerability as indicated.
ADDERALL XR extended release capsules may be taken whole, or the capsule may be opened and the
entire contents sprinkled on applesauce. If the patient is using the sprinkle administration method, the
sprinkled applesauce should be consumed immediately; it should not be stored. Patients should take the
applesauce with sprinkled beads in its entirety without chewing. The dose of a single capsule should not
be divided. The contents of the entire capsule should be taken, and patients should not take anything less
than one capsule per day.
ADDERALL XR may be taken with or without food.
ADDERALL XR should be given upon awakening. Afternoon doses should be avoided because of the
potential for insomnia.
Where possible, ADDERALL XR therapy should be interrupted occasionally to determine if there is a
recurrence of behavioral symptoms sufficient to require continued therapy.
2.3 Children
In children with ADHD who are 6-12 years of age and are either starting treatment for the first time or
switching from another medication, start with 10 mg once daily in the morning; daily dosage may be
adjusted in increments of 5 mg or 10 mg at weekly intervals. When in the judgment of the clinician a
lower initial dose is appropriate, patients may begin treatment with 5 mg once daily in the morning. The
maximum recommended dose for children 6-12 years of age is 30 mg/day; doses greater than 30 mg/day
have not been studied in children. ADDERALL XR has not been studied in children under 6 years of age.
2.4 Adolescents
The recommended starting dose for adolescents with ADHD who are 13-17 years of age and are either
starting treatment for the first time or switching from another medication is 10 mg/day. The dose may be
increased to 20 mg/day after one week if ADHD symptoms are not adequately controlled.
2.5 Adults
In adults with ADHD who are either starting treatment for the first time or switching from another
medication, the recommended dose is 20 mg/day.
Reference ID: 4943991
4

2.6 Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment
In adult patients with severe renal impairment (GFR 15 to < 30 mL/min/1.73m
2
), the recommended dose
is 15 mg once daily in the morning. In pediatric patients (6 to 17 years of age) with severe renal
impairment, the recommended dose is 5 mg once daily. The maximum dose for children 6 to 12 years of
age with severe renal impairment is 20 mg once daily. ADDERALL XR is not recommended in patients
with end stage renal disease (ESRD) (GFR < 15 mL/min/1.73m
2
) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6),
Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
ADDERALL XR 5 mg extended release capsules: Clear/blue (imprinted ADDERALL XR 5 mg)
ADDERALL XR 10 mg extended release capsules: Blue/blue (imprinted ADDERALL XR 10 mg)
ADDERALL XR 15 mg extended release capsules: Blue/white (imprinted ADDERALL XR 15 mg)
ADDERALL XR 20 mg extended release capsules: Orange/orange (imprinted ADDERALL XR 20 mg)
ADDERALL XR 25 mg extended release capsules: Orange/white (imprinted ADDERALL XR 25 mg)
ADDERALL XR 30 mg extended release capsules: Natural/orange (imprinted ADDERALL XR 30 mg)
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
ADDERALL XR administration is contraindicated in patients with the following conditions:
• Advanced arteriosclerosis
• Symptomatic cardiovascular disease
• Moderate to severe hypertension
• Hyperthyroidism
• In patients known to be hypersensitive to amphetamine, or other components of ADDERALL
XR. Hypersensitivity reactions such as angioedema and anaphylactic reactions have been
reported in patients treated with other amphetamine products [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]
• Glaucoma
• Agitated states
• History of drug abuse
• Patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), or within 14 days of stopping MAOIs
(including MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue), because of an increased risk
of hypertensive crisis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) and Drug Interactions (7.1)]
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Potential for Abuse and Dependence
CNS stimulants, including ADDERALL XR, other amphetamine-containing products, and
methylphenidate, have a high potential for abuse and dependence. Assess the risk of abuse prior to
prescribing, and monitor for signs of abuse and dependence while on therapy [see Boxed Warning, Drug
Abuse and Dependence (9.2, 9.3)].
5.2 Serious Cardiovascular Reactions
Sudden Death and Pre-existing Structural Cardiac Abnormalities or Other Serious Heart Problems
Reference ID: 4943991
5

Children and Adolescents
Sudden death has been reported in association with CNS stimulant treatment at usual doses in children
and adolescents with structural cardiac abnormalities or other serious heart problems. Although some
serious heart problems alone carry an increased risk of sudden death, stimulant products generally should
not be used in children or adolescents with known serious structural cardiac abnormalities,
cardiomyopathy, serious heart rhythm abnormalities, or other serious cardiac problems that may place
them at increased vulnerability to the sympathomimetic effects of a stimulant drug [see Contraindications
(4)].
Adults
Sudden deaths, stroke, and myocardial infarction have been reported in adults taking stimulant drugs at
usual doses for ADHD. Although the role of stimulants in these adult cases is also unknown, adults have
a greater likelihood than children of having serious structural cardiac abnormalities, cardiomyopathy,
serious heart rhythm abnormalities, coronary artery disease, or other serious cardiac problems. Adults
with such abnormalities should also generally not be treated with stimulant drugs [see Contraindications
(4)].
Hypertension and Other Cardiovascular Conditions
Stimulant medications cause a modest increase in average blood pressure (about 2-4 mmHg) and average
heart rate (about 3-6 bpm), and individuals may have larger increases. While the mean changes alone
would not be expected to have short-term consequences, all patients should be monitored for larger
changes in heart rate and blood pressure. Caution is indicated in treating patients whose underlying
medical conditions might be compromised by increases in blood pressure or heart rate, e.g., those with
pre-existing hypertension, heart failure, recent myocardial infarction, or ventricular arrhythmia [see
Contraindications (4) and Adverse Reactions (6)].
Assessing Cardiovascular Status in Patients being Treated with Stimulant Medications
Children, adolescents, or adults who are being considered for treatment with stimulant medications should
have a careful history (including assessment for a family history of sudden death or ventricular
arrhythmia) and physical exam to assess for the presence of cardiac disease, and should receive further
cardiac evaluation if findings suggest such disease (e.g. electrocardiogram and echocardiogram). Patients
who develop symptoms such as exertional chest pain, unexplained syncope, or other symptoms
suggestive of cardiac disease during stimulant treatment should undergo a prompt cardiac evaluation.
5.3 Psychiatric Adverse Events
Pre-Existing Psychosis
Administration of stimulants may exacerbate symptoms of behavior disturbance and thought disorder in
patients with pre-existing psychotic disorder.
Bipolar Illness
Particular care should be taken in using stimulants to treat ADHD patients with comorbid bipolar disorder
because of concern for possible induction of mixed/manic episode in such patients. Prior to initiating
treatment with a stimulant, patients with comorbid depressive symptoms should be adequately screened to
determine if they are at risk for bipolar disorder; such screening should include a detailed psychiatric
history, including a family history of suicide, bipolar disorder, and depression.
Emergence of New Psychotic or Manic Symptoms
Treatment-emergent psychotic or manic symptoms, e.g., hallucinations, delusional thinking, or mania in
children and adolescents without prior history of psychotic illness or mania can be caused by stimulants at
usual doses. If such symptoms occur, consideration should be given to a possible causal role of the
stimulant, and discontinuation of treatment may be appropriate. In a pooled analysis of multiple short-
term, placebo-controlled studies, such symptoms occurred in about 0.1% (4 patients with events out of
3482 exposed to methylphenidate or amphetamine for several weeks at usual doses) of stimulant-treated
patients compared to 0 in placebo-treated patients.
Reference ID: 4943991
6

Aggression
Aggressive behavior or hostility is often observed in children and adolescents with ADHD, and has been
reported in clinical trials and the postmarketing experience of some medications indicated for the
treatment of ADHD. Although there is no systematic evidence that stimulants cause aggressive behavior
or hostility, patients beginning treatment for ADHD should be monitored for the appearance of or
worsening of aggressive behavior or hostility.
5.4 Long-Term Suppression of Growth
Monitor growth in children during treatment with stimulants. Patients who are not growing or gaining
weight as expected may need to have their treatment interrupted.
Careful follow-up of weight and height in children ages 7 to 10 years who were randomized to either
methylphenidate or non-medication treatment groups over 14 months, as well as in naturalistic subgroups
of newly methylphenidate-treated and non-medication treated children over 36 months (to the ages of 10
to 13 years), suggests that consistently medicated children (i.e., treatment for 7 days per week throughout
the year) have a temporary slowing in growth rate (on average, a total of about 2 cm less growth in height
and 2.7 kg less growth in weight over 3 years), without evidence of growth rebound during this period of
development.
In a controlled trial of ADDERALL XR in adolescents, mean weight change from baseline within the
initial 4 weeks of therapy was −1.1 lbs. and −2.8 lbs., respectively, for patients receiving 10 mg and 20
mg ADDERALL XR. Higher doses were associated with greater weight loss within the initial 4 weeks of
treatment. Chronic use of amphetamines can be expected to cause a similar suppression of growth.
5.5 Seizures
There is some clinical evidence that stimulants may lower the convulsive threshold in patients with prior
history of seizures, in patients with prior EEG abnormalities in the absence of seizures, and very rarely, in
patients without a history of seizures and no prior EEG evidence of seizures. In the presence of seizures,
ADDERALL XR should be discontinued.
5.6 Peripheral Vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s Phenomenon
Stimulants, including ADDERALL XR, used to treat ADHD are associated with peripheral vasculopathy,
including Raynaud’s phenomenon. Signs and symptoms are usually intermittent and mild; however, very
rare sequelae include digital ulceration and/or soft tissue breakdown. Effects of peripheral vasculopathy,
including Raynaud’s phenomenon, were observed in post-marketing reports at different times and at
therapeutic doses in all age groups throughout the course of treatment. Signs and symptoms generally
improve after reduction in dose or discontinuation of drug. Careful observation for digital changes is
necessary during treatment with ADHD stimulants. Further clinical evaluation (e.g., rheumatology
referral) may be appropriate for certain patients.
5.7 Serotonin Syndrome
Serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening reaction, may occur when amphetamines are used in
combination with other drugs that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter systems such as MAOIs,
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs),
triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, and St. John’s Wort
[see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Amphetamines and amphetamine derivatives are known to be metabolized,
to some degree, by cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) and display minor inhibition of CYP2D6
metabolism [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The potential for a pharmacokinetic interaction exists
with the co-administration of CYP2D6 inhibitors which may increase the risk with increased exposure to
ADDERALL XR. In these situations, consider an alternative non-serotonergic drug or an alternative drug
that does not inhibit CYP2D6 [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include
mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g.,
Reference ID: 4943991
7

tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular
symptoms (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, and/or
gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea).
Concomitant use of ADDERALL XR with MAOI drugs is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4)].
Discontinue treatment with ADDERALL XR and any concomitant serotonergic agents immediately if
symptoms of serotonin syndrome occur, and initiate supportive symptomatic treatment. Concomitant use
of ADDERALL XR with other serotonergic drugs or CYP2D6 inhibitors should be used only if the
potential benefit justifies the potential risk. If clinically warranted, consider initiating ADDERALL XR
with lower doses, monitoring patients for the emergence of serotonin syndrome during drug initiation or
titration, and informing patients of the increased risk for serotonin syndrome.
5.8 Visual Disturbance
Difficulties with accommodation and blurring of vision have been reported with stimulant treatment.
5.9 Tics
Amphetamines have been reported to exacerbate motor and phonic tics and Tourette’s syndrome.
Therefore, clinical evaluation for tics and Tourette’s syndrome in patients and their families should
precede use of stimulant medications.
5.10 Prescribing and Dispensing
The least amount of amphetamine feasible should be prescribed or dispensed at one time in order to
minimize the possibility of overdosage. ADDERALL XR should be used with caution in patients who use
other sympathomimetic drugs.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in
the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and
may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
The premarketing development program for ADDERALL XR included exposures in a total of 1315
participants in clinical trials (635 pediatric patients, 350 adolescent patients, 248 adult patients, and 82
healthy adult subjects). Of these, 635 patients (ages 6 to 12) were evaluated in two controlled clinical
studies, one open-label clinical study, and two single-dose clinical pharmacology studies (N= 40). Safety
data on all patients are included in the discussion that follows. Adverse reactions were assessed by
collecting adverse reactions, results of physical examinations, vital signs, weights, laboratory analyses,
and ECGs.
Adverse reactions during exposure were obtained primarily by general inquiry and recorded by clinical
investigators using terminology of their own choosing. Consequently, it is not possible to provide a
meaningful estimate of the proportion of individuals experiencing adverse reactions without first grouping
similar types of reactions into a smaller number of standardized event categories. In the tables and listings
that follow, COSTART terminology has been used to classify reported adverse reactions.
The stated frequencies of adverse reactions represent the proportion of individuals who experienced, at
least once, a treatment-emergent adverse event of the type listed.
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation of Treatment
Reference ID: 4943991
8
In two placebo-controlled studies of up to 5 weeks duration among children with ADHD, 2.4% (10/425)
of ADDERALL XR-treated patients discontinued due to adverse reactions (including 3 patients with loss
of appetite, one of whom also reported insomnia) compared to 2.7% (7/259) receiving placebo.
The most frequent adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of ADDERALL XR in controlled and
uncontrolled, multiple-dose clinical trials of children (N=595) were anorexia (loss of appetite) (2.9%),
insomnia (1.5%), weight loss (1.2%), emotional lability (1%), and depression (0.7%). Over half of these
patients were exposed to ADDERALL XR for 12 months or more.
In a separate placebo-controlled 4-week study in adolescents with ADHD, five patients (2.1%)
discontinued treatment due to adverse events among ADDERALL XR-treated patients (N=233) compared
to none
who received placebo (N=54). The most frequent adverse event leading to discontinuation and
considered to be drug-related (i.e. leading to discontinuation in at least 1% of ADDERALL XR-treated
patients and at a rate at least twice that of placebo) was insomnia (1.3%, n=3).
In one placebo-controlled 4-week study among adults with ADHD with doses 20 mg to 60 mg, 23
patients (12.0%) discontinued treatment due to adverse events among ADDERALL XR-treated patients
(N=191) compared to one patient (1.6%) who received placebo (N=64). The most frequent adverse
events leading to discontinuation and considered to be drug-related (i.e. leading to discontinuation in at
least 1% of ADDERALL XR-treated patients and at a rate at least twice that of placebo) were insomnia
(5.2%, n=10), anxiety (2.1%, n=4), nervousness (1.6%, n=3), dry mouth (1.6%, n=3), anorexia (1.6%,
n=3), tachycardia (1.6%, n=3), headache (1.6%, n=3), and asthenia (1.0%, n=2).
Adverse Reactions Occurring in Controlled Trials
Adverse reactions reported in a 3-week clinical trial of children and a 4-week clinical trial in adolescents
and adults, respectively, treated with ADDERALL XR or placebo are presented in the tables below.
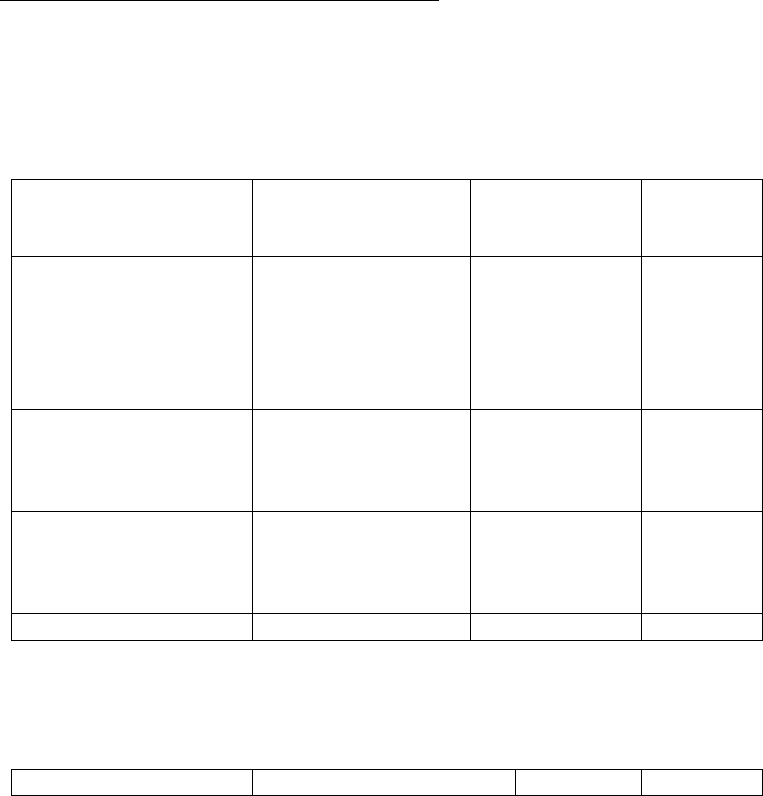
Table 1 Adverse Reactions Reported by 2% or More of Children (6-12 Years Old) Receiving
ADDERALL XR with Higher Incidence Than on Placebo in a 584-Patient Clinical
Study
Body System
Preferred Term
ADDERALL
XR
(n=374)
Placebo
(n=210)
General
Abdominal Pain
(stomachache)
Fever
Infection
Accidental Injury
Asthenia (fatigue)
14%
5%
4%
3%
2%
10%
2%
2%
2%
0%
Digestive System
Loss of Appetite
Vomiting
Nausea
Dyspepsia
22%
7%
5%
2%
2%
4%
3%
1%
Nervous System
Insomnia
Emotional Lability
Nervousness
Dizziness
17%
9%
6%
2%
2%
2%
2%
0%
Metabolic/Nutritional
Weight Loss
4%
0%
Table 2 Adverse Reactions Reported by 5% or More of Adolescents (13-17 Years Old) Weighing
≤ 75 kg/165 lbs Receiving ADDERALL XR with Higher Incidence Than Placebo in a
287 Patient Clinical Forced Weekly-Dose Titration Study*
Body System
Preferred Term
ADDERA
Placebo
Reference ID: 4943991
9
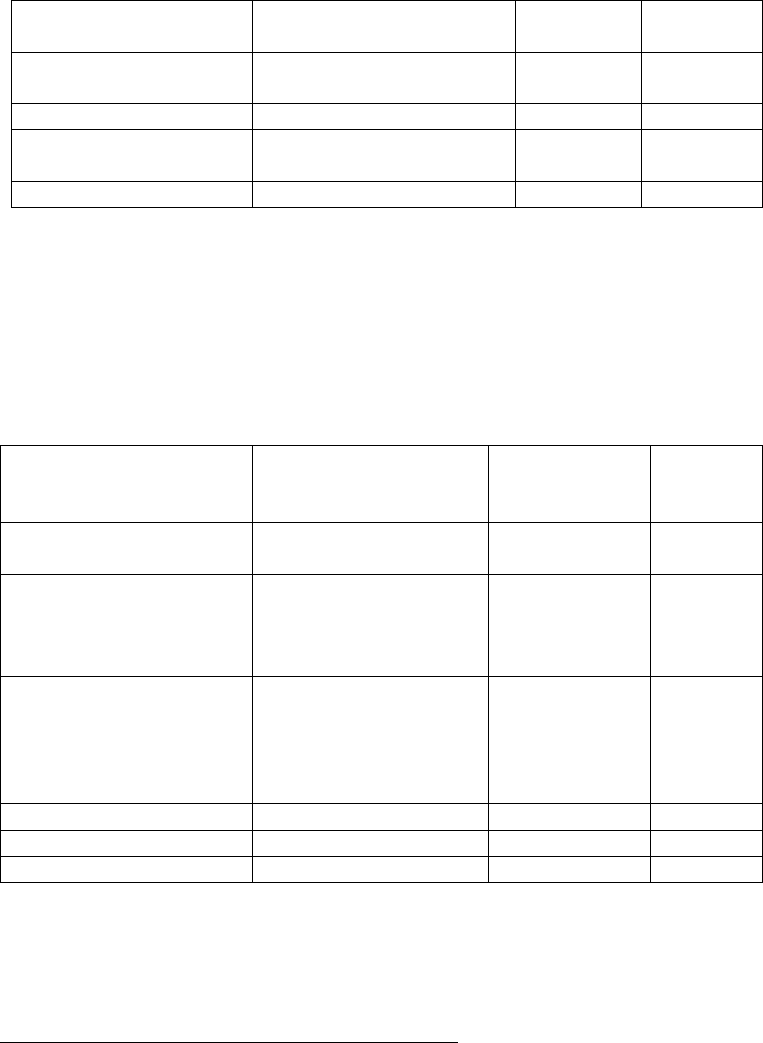
LL XR
(n=233)
(n=54)
General
Abdominal Pain
(stomachache)
11%
2%
Digestive System
Loss of Appetite
b
36%
2%
Nervous System
Insomnia
b
Nervousness
12%
6%
4%
6%
a
Metabolic/Nutritional
Weight Loss
b
9%
0%
*Included doses up to 40 mg
a
Appears the same due to rounding
b
Dose-related adverse reactions
Note: The following reactions did not meet the criterion for inclusion in Table 2 but were reported by 2% to 4% of adolescent patients receiving
ADDERALL XR with a higher incidence than patients receiving placebo in this study: accidental injury, asthenia (fatigue), dry mouth,
dyspepsia, emotional lability, nausea, somnolence, and vomiting.
Table 3 Adverse Reactions Reported by 5% or More of Adults Receiving ADDERALL XR with
Higher Incidence Than on Placebo in a 255 Patient Clinical Forced Weekly-Dose
Titration Study*
Body System
Preferred Term
ADDERALL
XR
(n=191)
Placebo
(n=64)
General
Headache
Asthenia
26%
6%
13%
5%
Digestive System
Dry Mouth
Loss of Appetite
Nausea
Diarrhea
35%
33%
8%
6%
5%
3%
3%
0%
Nervous System
Insomnia
Agitation
Anxiety
Dizziness
Nervousness
27%
8%
8%
7%
13%
13%
5%
5%
0%
13%
a
Cardiovascular System
Tachycardia
6%
3%
Metabolic/Nutritional
Weight Loss
10%
0%
Urogenital System
Urinary Tract Infection
5%
0%
*Included doses up to 60 mg.
a
Appears the same due to rounding
Note: The following reactions did not meet the criterion for inclusion in Table 3 but were reported by 2% to 4% of adult patients receiving
ADDERALL XR with a higher incidence than patients receiving placebo in this study: infection, photosensitivity reaction, constipation, tooth
disorder (e.g., teeth clenching, tooth infection), emotional lability, libido decreased, somnolence, speech disorder (e.g., stuttering, excessive
speech), palpitation, twitching, dyspnea, sweating, dysmenorrhea, and impotence.
Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
In a controlled 4-week outpatient clinical study of adolescents with ADHD, isolated systolic blood
pressure elevations ≥15 mmHg were observed in 7/64 (11%) placebo-treated patients and 7/100 (7%)
patients receiving ADDERALL XR 10 or 20 mg. Isolated elevations in diastolic blood pressure ≥ 8
mmHg were observed in 16/64 (25%) placebo-treated patients and 22/100 (22%) ADDERALL XR-
treated patients. Similar results were observed at higher doses.
In a single-dose pharmacokinetic study in 23 adolescents with ADHD, isolated increases in systolic blood
pressure (above the upper 95% CI for age, gender, and stature) were observed in 2/17 (12%) and 8/23
(35%), subjects administered 10 mg and 20 mg ADDERALL XR, respectively. Higher single doses were
associated with a greater increase in systolic blood pressure. All increases were transient, appeared
maximal at 2 to 4 hours post dose and not associated with symptoms.
6.2 Adverse Reactions Associated with the Use of Amphetamine, ADDERALL XR, or ADDERALL
Reference ID: 4943991
10

The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of amphetamine,
ADDERALL XR, or ADDERALL. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of
uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal
relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiovascular
Palpitations. There have been isolated reports of cardiomyopathy associated with chronic amphetamine
use.
Central Nervous System
Psychotic episodes at recommended doses, overstimulation, restlessness, irritability, euphoria, dyskinesia,
dysphoria, depression, tremor, tics, aggression, anger, logorrhea, dermatillomania, paresthesia (including
formication), and bruxism.
Eye Disorders
Vision blurred, mydriasis.
Gastrointestinal
Unpleasant taste, constipation, intestinal ischemia, and other gastrointestinal disturbances.
Allergic
Urticaria, rash, hypersensitivity reactions including angioedema and anaphylaxis. Serious skin rashes,
including Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis have been reported.
Endocrine
Impotence, changes in libido, frequent or prolonged erections.
Skin
Alopecia.
Vascular Disorders
Raynaud’s phenomenon.
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders
Rhabdomyolysis
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Clinically Important Interactions with Amphetamines
Table 4: Drugs Having Clinically Important Interactions with Amphetamines
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
Clinical
Impact
Concomitant use of MAOIs and CNS stimulants can cause hypertensive crisis.
Potential outcomes include death, stroke, myocardial infarction, aortic dissection,
ophthalmological complications, eclampsia, pulmonary edema, and renal failure.
Intervention
Do not administer ADDERALL XR concomitantly or within 14 days after
discontinuing MAOI [see Contraindications (4)].
Examples
selegiline, tranylcypromine, isocarboxazid, phenelzine, linezolid, methylene blue
Serotonergic Drugs
Clinical
Impact
The concomitant use of ADDERALL XR and serotonergic drugs increases the risk
of serotonin syndrome.
Reference ID: 4943991
11
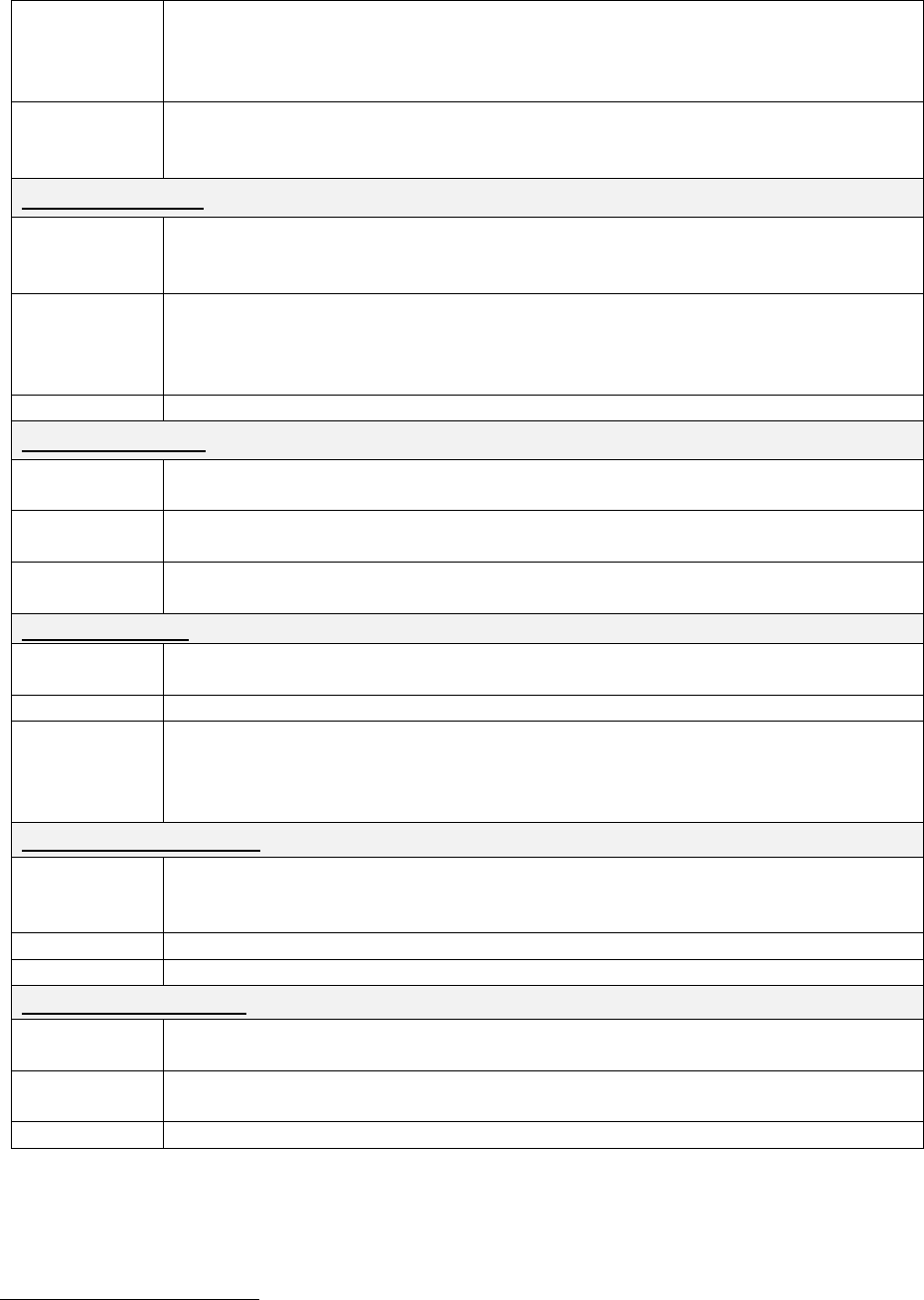
Intervention
Initiate with lower doses and monitor patients for signs and symptoms of serotonin
syndrome, particularly during ADDERALL XR initiation or dosage increase. If
serotonin syndrome occurs, discontinue ADDERALL XR and the concomitant
serotonergic drug(s) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Examples
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI), serotonin norepinephrine reuptake
inhibitors (SNRI), triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol,
tryptophan, buspirone, St. John’s Wort
CYP2D6 Inhibitors
Clinical
Impact
The concomitant use of ADDERALL XR and CYP2D6 inhibitors may increase the
exposure of ADDERALL XR compared to the use of the drug alone and increase
the risk of serotonin syndrome.
Intervention
Initiate with lower doses and monitor patients for signs and symptoms of serotonin
syndrome particularly during ADDERALL XR initiation and after a dosage
increase. If serotonin syndrome occurs, discontinue ADDERALL XR and the
CYP2D6 inhibitor [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) and Overdosage (10)].
Examples
paroxetine and fluoxetine (also serotonergic drugs), quinidine, ritonavir
Alkalinizing Agents
Clinical
Impact
Increase blood levels and potentiate the action of amphetamine.
Intervention
Co-administration of ADDERALL XR and gastrointestinal or urinary alkalinizing
agents should be avoided.
Examples
Gastrointestinal alkalinizing agents (e.g., sodium bicarbonate). Urinary alkalinizing
agents (e.g. acetazolamide, some thiazides).
Acidifying Agents
Clinical
Impact
Lower blood levels and efficacy of amphetamines.
Intervention
Increase dose based on clinical response.
Examples
Gastrointestinal acidifying agents (e.g., guanethidine, reserpine, glutamic acid HCl,
ascorbic acid).
Urinary acidifying agents (e.g., ammonium chloride, sodium acid phosphate,
methenamine salts).
Tricyclic Antidepressants
Clinical
Impact
May enhance the activity of tricyclic or sympathomimetic agents causing striking
and sustained increases in the concentration of d-amphetamine in the brain;
cardiovascular effects can be potentiated.
Intervention
Monitor frequently and adjust or use alternative therapy based on clinical response.
Examples
desipramine, protriptyline
Proton Pump Inhibitors
Clinical
Impact
Time to maximum concentration (T
max
) of amphetamine is decreased compared to
when administered alone.
Intervention
Monitor patients for changes in clinical effect and adjust therapy based on clinical
response.
Examples
Omeprazole
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to
ADDERALL XR during pregnancy. Healthcare providers are encouraged to register patients by calling
the National Pregnancy Registry for Psychostimulants at 1-866-961-2388 or visiting online at
https://womensmentalhealth.org/clinical-and-research-programs/pregnancyregistry/othermedications/.
Reference ID: 4943991
12

Risk Summary
Available data from published epidemiologic studies and postmarketing reports on use of prescription
amphetamine in pregnant women have not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects and
miscarriage (see Data). Adverse pregnancy outcomes, including premature delivery and low birth weight,
have been seen in infants born to mothers taking amphetamines during pregnancy (see Clinical
Considerations).
No apparent effects on morphological development were observed in embryo-fetal development studies,
with oral administration of amphetamine to rats and rabbits during organogenesis at doses 2 and 12 times,
respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 20 mg/day given to adolescents, on a
mg/m
2
basis. However, in a pre- and post-natal development study, amphetamine (d- to l- ratio of 3:1)
administered orally to pregnant rats during gestation and lactation caused a decrease in pup survival and a
decrease in pup body weight that correlated with a delay in developmental landmarks at clinically
relevant doses of amphetamine. In addition, adverse effects on reproductive performance were observed
in pups whose mothers were treated with amphetamine. Long-term neurochemical and behavioral effects
have also been reported in animal developmental studies using clinically relevant doses of amphetamine
(see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is
unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the
U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically
recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Amphetamines, such as ADDERALL XR, cause vasoconstriction and thereby may decrease placental
perfusion. In addition, amphetamines can stimulate uterine contractions, increasing the risk of premature
delivery. Infants born to mothers taking amphetamines during pregnancy have an increased risk of
premature delivery and low birth weight.
Monitor infants born to mothers taking amphetamines for symptoms of withdrawal such as feeding
difficulties, irritability, agitation, and excessive drowsiness.
Data
Animal Data
Amphetamine (d- to l- enantiomer ratio of 3:1) had no apparent effects on embryofetal morphological
development or survival when administered orally to pregnant rats and rabbits throughout the period of
organogenesis at doses of up to 6 and 16 mg/kg/day, respectively. These doses are approximately 2 and
12 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 20 mg/day given to
adolescents, on a mg/m
2
basis. Fetal malformations and death have been reported in mice following
parenteral administration of d-amphetamine doses of 50 mg/kg/day (approximately 10 times the MRHD
given to adolescents on a mg/m
2
basis) or greater to pregnant animals. Administration of these doses was
also associated with severe maternal toxicity.
A study was conducted in which pregnant rats received daily oral doses of amphetamine (d- to l-
enantiomer ratio of 3:1) of 2, 6, and 10 mg/kg from gestation day 6 to lactation day 20. These doses are
approximately 0.8, 2, and 4 times the MRHD of 20 mg/day given to adolescents, on a mg/m
2
basis. All
doses caused hyperactivity and decreased weight gain in the dams. A decrease in pup survival was seen at
all doses. A decrease in pup body weight was seen at 6 and 10 mg/kg which correlated with delays in
developmental landmarks, such as preputial separation and vaginal opening. Increased pup locomotor
activity was seen at 10 mg/kg on day 22 postpartum but not at 5 weeks postweaning. When pups were
Reference ID: 4943991
13

tested for reproductive performance at maturation, gestational weight gain, number of implantations, and
number of delivered pups were decreased in the group whose mothers had been given 10 mg/kg.
A number of studies from the literature in rodents indicate that prenatal or early postnatal exposure
to
amphetamine (d- or d, l-) at doses similar to those used clinically can result in long-term neurochemical
and behavioral alterations. Reported behavioral effects include learning and memory deficits, altered
locomotor activity, and changes in sexual function.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Based on limited case reports in published literature, amphetamine (d- or d, l-) is present in human milk,
at relative infant doses of 2% to 13.8% of the maternal weight-adjusted dosage and a milk/plasma ratio
ranging between 1.9 and 7.5. There are no reports of adverse effects on the breastfed infant. Long-term
neurodevelopmental effects on infants from amphetamine exposure are unknown. It is possible that large
dosages of amphetamine might interfere with milk production, especially in women whose lactation is not
well established. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, advise patients
that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with ADDERALL XR.
8.4 Pediatric Use
ADDERALL XR is indicated for use in children 6 years of age and older.
The safety and efficacy of ADDERALL XR in children under 6 years of age have not been studied. Long-
term effects of amphetamines in children have not been well established.
Long-Term Growth Suppression
Growth should be monitored during treatment with stimulants, including ADDERALL XR, and pediatric
patients aged 6 to 17 years who are not growing or gaining weight as expected may need to have their
treatment interrupted [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Juvenile Animal Toxicity Data
Juvenile rats treated with mixed amphetamine salts early in the postnatal period through sexual
maturation demonstrated transient changes in motor activity. Learning and memory was impaired at
approximately 6 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) given to children on a mg/m
2
basis. No recovery was seen following a drug free period. A delay in sexual maturation was observed at a
dose approximately 6 times the MRHD given to children on a mg/m
2
basis, although there was no effect
on fertility.
In a juvenile developmental study, rats received daily oral doses of amphetamine (d to l enantiomer ratio
of 3:1) of 2, 6, or 20 mg/kg on days 7-13 of age; from day 14 to approximately day 60 of age these doses
were given b.i.d. for total daily doses of 4, 12, or 40 mg/kg. The latter doses are approximately 0.6, 2, and
6 times the MRHD of 30 mg/day, given to children on a mg/m
2
basis. Post dosing hyperactivity was seen
at all doses; motor activity measured prior to the daily dose was decreased during the dosing period but
the decreased motor activity was largely absent after an 18 day drug-free recovery period. Performance in
the Morris water maze test for learning and memory was impaired at the 40 mg/kg dose, and sporadically
at the lower doses, when measured prior to the daily dose during the treatment period; no recovery was
seen after a 19 day drug-free period. A delay in the developmental milestones of vaginal opening and
preputial separation was seen at 40 mg/kg but there was no effect on fertility.
8.5 Geriatric Use
ADDERALL XR has not been studied in the geriatric population.
Reference ID: 4943991
14

8.6 Renal Impairment
Due to reduced clearance of amphetamines in patients with severe renal impairment (GFR 15 to <30
mL/min/1.73m
2
), the recommended dose should be reduced. ADDERALL XR is not recommended in
patients with ESRD (GFR < 15 ml/min/1.73m
2
) [see Dosage and Administration (2.6), Clinical
Pharmacology (12.3)].
d-Amphetamine is not dialyzable.
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
ADDERALL XR contains amphetamine, a Schedule II controlled substance.
9.2 Abuse
ADDERALL XR is a CNS stimulant that contains amphetamine, which has a high potential for abuse.
Abuse is characterized by impaired control of drug use, compulsive use despite harm, and craving.
Signs and symptoms of amphetamine abuse may include increased heart rate, respiratory rate, blood
pressure, and/or sweating, dilated pupils, hyperactivity, restlessness, insomnia, decreased appetite, loss of
coordination, tremors, flushed skin, vomiting, and/or abdominal pain. Anxiety, psychosis, hostility,
aggression, suicidal or homicidal ideation have also been observed. Abusers of amphetamines may use
other unapproved routes of administration which can result in overdose and death [see Overdosage (10)].
To reduce the abuse of CNS stimulants, including ADDERALL XR, assess the risk of abuse prior to
prescribing. After prescribing, keep careful prescription records, educate patients and their families about
abuse and proper storage and disposal of CNS stimulants. Monitor for signs of abuse while on therapy and
re-evaluate the need for ADDERALL XR use.
9.3 Dependence
Tolerance (a state of adaptation in which exposure to a specific dose of a drug results in a reduction of the
drug’s desired and/or undesired effects over time, in such a way that a higher dose of the drug is required
to produce the same effect that was once obtained at a lower dose) may occur during chronic therapy of
CNS stimulants including ADDERALL XR.
Physical Dependence (which is manifested by a withdrawal syndrome produced by abrupt cessation, rapid
dose reduction, or administration of an antagonist) may occur in patients treated with CNS stimulants
including ADDERALL XR. Withdrawal symptoms after abrupt cessation of CNS stimulants include
dysphoric mood; fatigue; vivid, unpleasant dreams; insomnia or hypersomnia; increased appetite; and
psychomotor retardation or agitation.
10 OVERDOSAGE
Manifestations of amphetamine overdose include restlessness, tremor, hyperreflexia, rapid respiration,
confusion, assaultiveness, hallucinations, panic states, hyperpyrexia and rhabdomyolysis. Fatigue and
depression usually follow the central nervous system stimulation. Serotonin syndrome has been reported
with amphetamine use, including ADDERALL XR. Cardiovascular effects include arrhythmias,
hypertension or hypotension and circulatory collapse. Gastrointestinal symptoms include nausea,
vomiting, diarrhea and abdominal cramps. Fatal poisoning is usually preceded by convulsions and coma.
Treatment
Consult with a Certified Poison Control Center for up to date guidance and advice.
Reference ID: 4943991
15

The prolonged release of mixed amphetamine salts from ADDERALL XR should be considered when
treating patients with overdose.
d-Amphetamine is not dialyzable.
11 DESCRIPTION
ADDERALL XR extended-release capsules contain mixed salts of a single-entity amphetamine, a CNS
stimulant. ADDERALL XR contains equal amounts (by weight) of four salts: dextroamphetamine sulfate,
amphetamine sulfate, dextroamphetamine saccharate and amphetamine (D,L)-aspartate monohydrate.
This results in a 3.1:1 mixture of dextro- to levo- amphetamine base equivalent.
The 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 25 mg and 30 mg strength extended release capsules are for oral
administration. Adderall XR contains two types of drug-containing beads (immediate-release and delayed
release) which prolong the release of amphetamine compared to the ADDERALL (immediate-release)
tablet formulation.
Each capsule contains:
Capsule Strength
Dextroamphetamine Saccharate
Amphetamine (D,L)-Aspartate Monohydrate 1.25 mg 2.5 mg
Dextroamphetamine Sulfate
Amphetamine Sulfate
5 mg 10 mg
1.25 mg 2.5 mg
1.25 mg 2.5 mg
1.25 mg 2.5 mg
15 mg
3.75 mg
3.75 mg
3.75 mg
3.75 mg
20 mg
5.0 mg
5.0 mg
5.0 mg
5.0 mg
25 mg
6.25 mg
6.25 mg
6.25 mg
6.25 mg
30 mg
7.5 mg
7.5 mg
7.5 mg
7.5 mg
Total amphetamine base equivalence
mg
d-amphetamine base equivalence
mg
l-amphetamine base equivalence
3.1 mg 6.3 mg
2.4 mg 4.7 mg
0.75 mg 1.5 mg
9.4 mg
7.1 mg
2.3 mg
12.5 mg
9.5 mg
3.0 mg
15.6 mg
11.9 mg
3.8 mg
18.8
14.2
4.5 mg
Inactive Ingredients and Colors
The inactive ingredients in ADDERALL XR extended release capsules include: gelatin capsules,
hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, methacrylic acid copolymer, opadry beige, sugar spheres, talc, and
triethyl citrate. Gelatin capsules contain edible inks, kosher gelatin, and titanium dioxide. The 5 mg, 10
mg, and 15 mg capsules also contain FD&C Blue #2. The 20 mg, 25 mg, and 30 mg capsules also
contain red iron oxide and yellow iron oxide.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Amphetamines are non-catecholamine sympathomimetic amines with CNS stimulant activity. The mode
of therapeutic action in ADHD is not known.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Amphetamines block the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine into the presynaptic neuron and
increase the release of these monoamines into the extraneuronal space.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetic studies of ADDERALL XR have been conducted in healthy adult and pediatric (children
aged 6-12 yrs) subjects, and adolescent (13-17 yrs) and children with ADHD. Both ADDERALL
(immediate-release) tablets and ADDERALL XR extended release capsules contain d-amphetamine and
Reference ID: 4943991
16
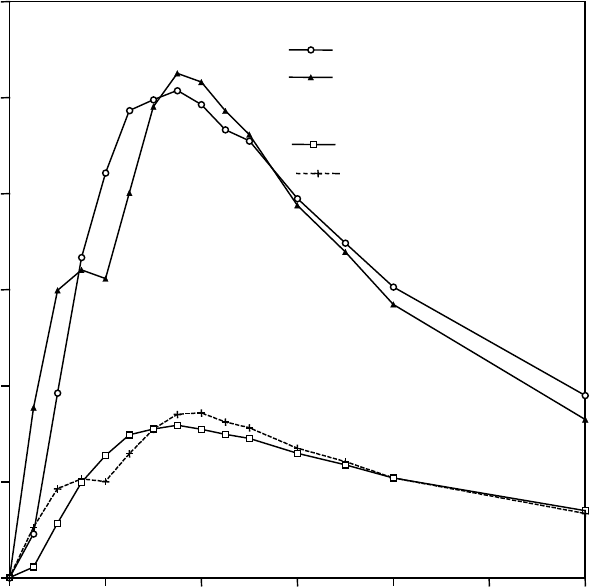
l-amphetamine salts in the ratio of 3:1. Following administration of ADDERALL (immediate-release), the
peak plasma concentrations occurred in about 3 hours for both d-amphetamine and l-amphetamine.
The time to reach maximum plasma concentration (T
max
) for ADDERALL XR is about 7 hours, which is
about 4 hours longer compared to ADDERALL (immediate-release). This is consistent with the
extended-release nature of the product.
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
TIME (HOURS)
Figure 1 Mean d-amphetamine and l-amphetamine Plasma Concentrations Following
Administration of ADDERALL XR 20 mg (8 am) and ADDERALL (immediate-release) 10 mg Twice
Daily (8 am and 12 noon) in the Fed State.
A single dose of ADDERALL XR 20 mg extended release capsules provided comparable plasma
concentration profiles of both d-amphetamine and l-amphetamine to ADDERALL (immediate-release) 10
mg twice daily administered 4 hours apart.
The mean elimination half-life for d-amphetamine is 10 hours in adults; 11 hours in adolescents aged 13-
17 years and weighing less than or equal to 75 kg/165 lbs; and 9 hours in children aged 6 to 12 years. For
the l-amphetamine, the mean elimination half-life in adults is 13 hours; 13 to 14 hours in adolescents; and
11 hours in children aged 6 to 12 years. On a mg/kg body weight basis, children have a higher clearance
than adolescents or adults (see Special Populations below).
ADDERALL XR demonstrates linear pharmacokinetics over the dose range of 20 to 60 mg in adults and
adolescents weighing greater than 75 kg/165 lbs, over the dose range of 10 to 40 mg in adolescents
weighing less than or equal to 75 kg/165 lbs, and 5 to 30 mg in children aged 6 to 12 years. There is no
unexpected accumulation at steady state in children.
Food does not affect the extent of absorption of d-amphetamine and l-amphetamine, but prolongs T
max
by
2.5 hours (from 5.2 hrs at fasted state to 7.7 hrs after a high-fat meal) for d-amphetamine and 2.7 hours
(from 5.6 hrs at fasted state to 8.3 hrs after a high fat meal) for l-amphetamine after administration of
MEAN PLASMA CONCENTRATIONS OF DEXTRO AND LEVOAMPHETAMINE (ng/mL)
ADDERALL XR
®
20 mg qd
ADDERALL
®
10 mg bid
ADDERALL XR
®
20 mg qd
ADDERALL
®
10 mg bid
DEXTROAMPHETAMINE
LEVOAMPHETAMINE
0
4
8
12
16
20
24
Reference ID: 4943991
17

ADDERALL XR 30 mg. Opening the capsule and sprinkling the contents on applesauce results in
comparable absorption to the intact capsule taken in the fasted state. Equal doses of ADDERALL XR
strengths are bioequivalent.
Metabolism and Excretion
Amphetamine is reported to be oxidized at the 4 position of the benzene ring to form 4-
hydroxyamphetamine, or on the side chain α or β carbons to form alpha-hydroxy-amphetamine or
norephedrine, respectively. Norephedrine and 4-hydroxy-amphetamine are both active and each is
subsequently oxidized to form 4-hydroxy-norephedrine. Alpha-hydroxy-amphetamine undergoes
deamination to form phenylacetone, which ultimately forms benzoic acid and its glucuronide and the
glycine conjugate hippuric acid. Although the enzymes involved in amphetamine metabolism have not
been clearly defined, CYP2D6 is known to be involved with formation of 4-hydroxy-amphetamine. Since
CYP2D6 is genetically polymorphic, population variations in amphetamine metabolism are a possibility.
Amphetamine is known to inhibit monoamine oxidase, whereas the ability of amphetamine and its
metabolites to inhibit various P450 isozymes and other enzymes has not been adequately elucidated. In
vitro experiments with human microsomes indicate minor inhibition of CYP2D6 by amphetamine and
minor inhibition of CYP1A2, 2D6, and 3A4 by one or more metabolites. However, due to the probability
of auto-inhibition and the lack of information on the concentration of these metabolites relative to in vivo
concentrations, no predications regarding the potential for amphetamine or its metabolites to inhibit the
metabolism of other drugs by CYP isozymes in vivo can be made.
With normal urine pHs, approximately half of an administered dose of amphetamine is recoverable in
urine as derivatives of alpha-hydroxy-amphetamine and approximately another 30-40% of the dose is
recoverable in urine as amphetamine itself. Since amphetamine has a pKa of 9.9, urinary recovery of
amphetamine is highly dependent on pH and urine flow rates. Alkaline urine pHs result in less ionization
and reduced renal elimination, and acidic pHs and high flow rates result in increased renal elimination
with clearances greater than glomerular filtration rates, indicating the involvement of active secretion.
Urinary recovery of amphetamine has been reported to range from 1% to 75%, depending on urinary pH,
with the remaining fraction of the dose hepatically metabolized. Consequently, both hepatic and renal
dysfunction have the potential to inhibit the elimination of amphetamine and result in prolonged
exposures. In addition, drugs that effect urinary pH are known to alter the elimination of amphetamine,
and any decrease in amphetamine’s metabolism that might occur due to drug interactions or genetic
polymorphisms is more likely to be clinically significant when renal elimination is decreased [see Drug
Interactions (7)].
Special Populations
Comparison of the pharmacokinetics of d- and l-amphetamine after oral administration of ADDERALL
XR in children (6-12 years) and adolescent (13-17 years) ADHD patients and healthy adult volunteers
indicates that body weight is the primary determinant of apparent differences in the pharmacokinetics of
d- and l-amphetamine across the age range. Systemic exposure measured by area under the curve to
infinity (AUC
∞
) and maximum plasma concentration (C
max
) decreased with increases in body weight,
while oral volume of distribution (V
Z
/F), oral clearance (CL/F), and elimination half-life (t
1/2
) increased
with increases in body weight.
Pediatric Patients
On a mg/kg weight basis, children eliminated amphetamine faster than adults. The elimination half-life
(t
1/2
) is approximately 1 hour shorter for d-amphetamine and 2 hours shorter for l-amphetamine in
children than in adults. However, children had higher systemic exposure to amphetamine (C
max
and AUC)
than adults for a given dose of ADDERALL XR, which was attributed to the higher dose administered to
children on a mg/kg body weight basis compared to adults. Upon dose normalization on a mg/kg basis,
children showed 30% less systemic exposure compared to adults.
Gender
Reference ID: 4943991
18

Systemic exposure to amphetamine was 20-30% higher in women (N=20) than in men (N=20) due to the
higher dose administered to women on a mg/kg body weight basis. When the exposure parameters (C
max
and AUC) were normalized by dose (mg/kg), these differences diminished. Age and gender had no direct
effect on the pharmacokinetics of d- and l-amphetamine.
Race
Formal pharmacokinetic studies for race have not been conducted. However, amphetamine
pharmacokinetics appeared to be comparable among Caucasians (N=33), Blacks (N=8) and Hispanics
(N=10).
Patients with Renal Impairment
The effect of renal impairment on d- and l-amphetamine after administration of ADDERALL XR has not
been studied. The impact of renal impairment on the disposition of amphetamine is expected to be similar
between oral administration of lisdexamfetamine and Adderall XR.
In a pharmacokinetic study of lisdexamfetamine in adult subjects with normal and impaired renal
function, mean d-amphetamine clearance was reduced from 0.7 L/hr/kg in normal subjects to 0.4 L/hr/kg
in subjects with severe renal impairment (GFR 15 to <30mL/min/1.73m
2
). Dialysis did not significantly
affect the clearance of d-amphetamine [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
No evidence of carcinogenicity was found in studies in which d,l-amphetamine (enantiomer ratio of 1:1)
was administered to mice and rats in the diet for 2 years at doses of up to 30 mg/kg/day in male mice, 19
mg/kg/day in female mice, and 5 mg/kg/day in male and female rats. These doses are approximately 2.4,
1.5, and 0.8 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose of 30 mg/day given to children,
on a mg/m
2
basis.
Mutagenesis
Amphetamine, in the enantiomer ratio d- to l- ratio of 3:1, was not clastogenic in the mouse bone marrow
micronucleus test in vivo and was negative when tested in the E. coli component of the Ames test in vitro.
d,l-Amphetamine (1:1 enantiomer ratio) has been reported to produce a positive response in the mouse
bone marrow micronucleus test, an equivocal response in the Ames test, and negative responses in the in
vitro sister chromatid exchange and chromosomal aberration assays.
Impairment of Fertility
Amphetamine, in the enantiomer ratio d- to l- ratio of 3:1, did not adversely affect fertility or early
embryonic development in the rat at doses of up to 20 mg/kg/day (approximately 8 times the maximum
recommended human dose of 20 mg/day given to adolescents, on a mg/m
2
basis).
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Acute administration of high doses of amphetamine (d- or d,l-) has been shown to produce long-lasting
neurotoxic effects, including irreversible nerve fiber damage, in rodents. The significance of these
findings to humans is unknown.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Pediatric Patients
A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study was conducted in children aged 6-
12 (N=584) who met DSM-IV
®
criteria for ADHD (either the combined type or the hyperactive-
Reference ID: 4943991
19

impulsive type). Patients were randomized to fixed-dose treatment groups receiving final doses of 10, 20,
or 30 mg of ADDERALL XR or placebo once daily in the morning for three weeks. Significant
improvements in patient behavior, based upon teacher ratings of attention and hyperactivity, were
observed for all ADDERALL XR doses compared to patients who received placebo, for all three weeks,
including the first week of treatment, when all ADDERALL XR subjects were receiving a dose of 10
mg/day. Patients who received ADDERALL XR showed behavioral improvements in both morning and
afternoon assessments compared to patients on placebo.
In a classroom analogue study, patients (N=51) receiving fixed doses of 10 mg, 20 mg or 30 mg
ADDERALL XR demonstrated statistically significant improvements in teacher-rated behavior and
performance measures, compared to patients treated with placebo.
A double-blind, randomized, multi-center, parallel-group, placebo-controlled study was conducted in
adolescents aged 13-17 (N=327) who met DSM-IV
®
criteria for ADHD. The primary cohort of patients
(n=287, weighing ≤ 75kg/165lbs) was randomized to fixed-dose treatment groups and received four
weeks of treatment. Patients were randomized to receive final doses of 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg, and 40 mg
ADDERALL XR or placebo once daily in the morning. Patients randomized to doses greater than 10 mg
were titrated to their final doses by 10 mg each week. The secondary cohort consisted of 40 subjects
weighing >75kg/165lbs who were randomized to fixed-dose treatment groups receiving final doses of 50
mg and 60 mg ADDERALL XR or placebo once daily in the morning for 4 weeks. The primary efficacy
variable was the Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder-Rating Scale IV
(ADHD-RS-IV) total score for
the primary cohort. The ADHD-RS-IV is an 18-item scale that measures the core symptoms of ADHD.
Improvements in the primary cohort were statistically significantly greater in all four primary cohort
active treatment groups (ADDERALL XR 10 mg, 20 mg, 30 mg, and 40 mg) compared with the placebo
group. There was not adequate evidence that doses greater than 20 mg/day conferred additional benefit.
Adult Patients
A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study was conducted in adults (N=255)
who met DSM-IV
®
criteria for ADHD. Patients were randomized to fixed-dose treatment groups
receiving final doses of 20, 40, or 60 mg of ADDERALL XR or placebo once daily in the morning for
four weeks. Significant improvements, measured with the Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder-
Rating Scale (ADHD-RS), an 18- item scale that measures the core symptoms of ADHD, were observed
at endpoint for all ADDERALL XR doses compared to patients who received placebo for all four weeks.
There was not adequate evidence that doses greater than 20 mg/day conferred additional benefit.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
ADDERALL XR 5 mg extended release capsules: Clear/blue (imprinted ADDERALL XR 5 mg), bottles
of 100, NDC 54092-381-01
ADDERALL XR 10 mg extended release capsules: Blue/blue (imprinted ADDERALL XR 10 mg),
bottles of 100, NDC 54092-383-01
ADDERALL XR 15 mg extended release capsules: Blue/white (imprinted ADDERALL XR 15 mg),
bottles of 100, NDC 54092-385-01
ADDERALL XR 20 mg extended release capsules: Orange/orange (imprinted ADDERALL XR 20 mg),
bottles of 100, NDC 54092-387-01
ADDERALL XR 25 mg extended release capsules: Orange/white (imprinted ADDERALL XR 25 mg),
bottles of 100, NDC 54092-389-01
ADDERALL XR 30 mg extended release capsules: Natural/orange (imprinted ADDERALL XR 30 mg),
bottles of 100, NDC 54092-391-01
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP.
Store at room temperature, 20º C to 25º C (68º F to 77º F). Excursions permitted to 15-30º C (59-86ºF)
[see USP CONTROLLED ROOM TEMPERATURE].
Disposal
Reference ID: 4943991
20
Comply with local laws and regulations on drug disposal of CNS stimulants. Dispose of remaining,
unused, or expired ADDERALL XR at authorized collection sites such as retail pharmacies, hospital or
clinic pharmacies, and law enforcement locations. If no take-back program or authorized collector is
available, mix ADDERALL XR with an undesirable, nontoxic substance to make it less appealing to
children and pets. Place the mixture in a container such as a sealed plastic bag and discard ADDERALL
XR in the household trash.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Controlled Substance Status/Potential for Abuse, Misuse, and Dependence
Advise patients that ADDERALL XR is a federally controlled substance because it can be abused or lead
to dependence. Additionally, emphasize that ADDERALL XR should be stored in a safe place to prevent
misuse and/or abuse. Evaluate patient history (including family history) of abuse or dependence on
alcohol, prescription medicines, or illicit drugs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Drug Abuse and
Dependence (9)].
Serious Cardiovascular Risks
Advise patients of serious cardiovascular risk (including sudden death, myocardial infarction, stroke, and
hypertension) with ADDERALL XR. Patients who develop symptoms such as exertional chest pain,
unexplained syncope, or other symptoms suggestive of cardiac disease during treatment should undergo a
prompt cardiac evaluation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Psychiatric Risks
Prior to initiating treatment with ADDERALL XR, adequately screen patients with comorbid depressive
symptoms to determine if they are at risk for bipolar disorder. Such screening should include a detailed
psychiatric history, including a family history of suicide, bipolar disorder, and/or depression.
Additionally, ADDERALL XR therapy at usual doses may cause treatment-emergent psychotic or manic
symptoms in patients without prior history of psychotic symptoms or mania [see Warnings and
Precautions (5.3)].
Circulation problems in fingers and toes [Peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s
phenomenon]
Instruct patients beginning treatment with ADDERALL XR about the risk of peripheral vasculopathy,
including Raynaud’s Phenomenon, and in associated signs and symptoms: fingers or toes may feel numb,
cool, painful, and/or may change color from pale, to blue, to red. Instruct patients to report to their
physician any new numbness, pain, skin color change, or sensitivity to temperature in fingers or toes.
Instruct patients to call their physician immediately with any signs of unexplained wounds appearing on
fingers or toes while taking ADDERALL XR. Further clinical evaluation (e.g., rheumatology referral)
may be appropriate for certain patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Serotonin Syndrome
Caution patients about the risk of serotonin syndrome with concomitant use of ADDERALL XR and
other serotonergic drugs including SSRIs, SNRIs, triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium,
tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, St. John’s Wort, and with drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin (in
particular MAOIs, both those intended to treat psychiatric disorders and also others such as linezolid [see
Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.7) and Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Advise patients to
contact their healthcare provider or report to the emergency room if they experience signs or symptoms of
serotonin syndrome.
Reference ID: 4943991
21
Concomitant Medications
Advise patients to notify their physicians if they are taking, or plan to take, any prescription or over-the-
counter drugs because there is a potential for interactions [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Growth
Monitor growth in children during treatment with ADDERALL XR, and patients who are not growing or
gaining weight as expected may need to have their treatment interrupted [see Warnings and Precautions
(5.4)].
Pregnancy Registry
Advise patients that there is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women
exposed to ADDERALL XR during pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy
Advise patients to notify their healthcare provider if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant
during treatment with ADDERALL XR. Advise patients of the potential fetal effects from the use of
ADDERALL XR during pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed if they are taking ADDERALL XR [see Use in Specific Populations
(8.2)].
Impairment in Ability to Operate Machinery or Vehicles
ADDERALL XR may impair the ability of the patient to engage in potentially hazardous activities such
as operating machinery or vehicles; the patient should therefore be cautioned accordingly.
Distributed by Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc., Lexington, MA 02421, Made in USA.
For more information call 1-800-828-2088
ADDERALL XR
®
is a registered trademark of Takeda Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc.
ADDERALL
®
is a registered trademark of Takeda Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc. under license to
Duramed Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
© 2020 Takeda Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc. All rights reserved.
Reference ID: 4943991
22

MEDICATION GUIDE
ADDERALL XR
®
(ADD-ur-all X-R) CII
Read the Medication Guide that comes with ADDERALL XR before you or your child starts taking it and
each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This Medication Guide does not take the place
of talking to your doctor about you or your child’s treatment with ADDERALL XR.
What is the most important information I
should know about ADDERALL XR?
ADDERALL XR is a stimulant medicine.
The following have been reported with use of
stimulant medicines.
1. Heart-related problems:
• sudden death in patients who have heart
problems or heart defects
• stroke and heart attack in adults
• increased blood pressure and heart rate
Tell your doctor if you or your child have any
heart problems, heart defects, high blood
pressure, or a family history of these problems.
Your doctor should check you or your child
carefully for heart problems before starting
ADDERALL XR.
Your doctor should check you or your child’s
blood pressure and heart rate regularly during
treatment with ADDERALL XR.
Call your doctor right away if you or your
child has any signs of heart problems such as
chest pain, shortness of breath, or fainting
while taking ADDERALL XR.
2. Mental (Psychiatric) problems:
All Patients
• new or worse behavior and thought
problems
• new or worse bipolar illness
• new or worse aggressive behavior or
hostility
Children and Teenagers
• new psychotic symptoms (such as hearing
voices, believing things that are not true,
are suspicious) or new manic symptoms
Tell your doctor about any mental problems you
or your child have, or about a family history of
suicide, bipolar illness, or depression.
Call your doctor right away if you or your
child have any new or worsening mental
symptoms or problems while taking
ADDERALL XR, especially seeing or hearing
things that are not real, believing things that
are not real, or are suspicious.
3. Circulation problems in fingers and toes
[Peripheral vasculopathy, including
Raynaud’s phenomenon]:
• Fingers or toes may feel numb, cool,
painful
• Fingers or toes may change from pale, to
blue, to red
Tell your doctor if you have or your child has
numbness, pain, skin color change, or sensitivity
to temperature in your fingers or toes.
Call your doctor right away if you have or
your child has any unexplained wounds
appearing on fingers or toes while taking
ADDERALL XR.
What Is ADDERALL XR?
ADDERALL XR is a once daily central nervous
system stimulant prescription medicine. It is
used for the treatment of Attention Deficit
Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD).
ADDERALL XR may help increase attention
and decrease impulsiveness and hyperactivity in
patients with ADHD.
ADDERALL XR should be used as a part of a
total treatment program for ADHD that may
include counseling or other therapies.
ADDERALL XR is a federally controlled
substance (CII) because it can be abused or
lead to dependence. Keep ADDERALL XR
in a safe place to prevent misuse and abuse.
Selling or giving away ADDERALL XR may
harm others, and is against the law.
Tell your doctor if you or your child have (or
have a family history of) ever abused or been
dependent on alcohol, prescription medicines or
Reference ID: 4943991
1

street drugs.
Who should not take ADDERALL XR?
ADDERALL XR should not be taken if you
or your child:
• have heart disease or hardening of the arteries
• have moderate to severe high blood pressure
• have hyperthyroidism
• have an eye problem called glaucoma
• are very anxious, tense, or agitated
• have a history of drug abuse
• are taking or have taken within the past 14
days an anti-depression medicine called a
monoamine oxidase inhibitor or MAOI.
• is sensitive to, allergic to, or had a reaction to
other stimulant medicines
ADDERALL XR has not been studied in
children less than 6 years old.
ADDERALL XR may not be right for you or
your child. Before starting ADDERALL XR
tell you or your child’s doctor about all health
conditions (or a family history of) including if
you or your child:
• have heart problems, heart defects, or high
blood pressure
• have mental problems including psychosis,
mania, bipolar illness, or depression
• have tics or Tourette’s syndrome
• have liver problems
• have kidney problems
• have end stage renal disease (ESRD)
• have thyroid problems
• have seizures or have had an abnormal brain
wave test (EEG)
• have circulation problems in fingers and toes
• are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is
not known if ADDERALL XR will harm
your unborn baby.
o There is a pregnancy registry for
females who are exposed to
ADDERALL XR during pregnancy. The
purpose of the registry is to collect
information about the health of females
exposed to ADDERALL XR and their
baby. If you or your child becomes
pregnant during treatment with
ADDERALL XR, talk to your
healthcare provider about registering
with the National Pregnancy Registry of
Psychostimulants at 1-866-961-2388 or
visit online at
https://womensmentalhealth.org/clinical
-and -research-
programs/pregnancyregistry/othermedic
ations/.
o are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed.
ADDERALL XR passes into breast
milk. You or your child should not
breastfeed during treatment with
ADDERALL XR.
Can ADDERALL XR be taken with other
medicines?
Tell your doctor about all of the medicines
that you or your child takes including
prescription and non-prescription medicines,
vitamins, and herbal supplements.
ADDERALL XR and some medicines may
interact with each other and cause serious side
effects. Sometimes the doses of other medicines
will need to be adjusted while taking
ADDERALL XR.
Your doctor will decide whether ADDERALL
XR can be taken with other medicines.
Especially tell your doctor if you or your
child takes:
• anti-depression medicines including MAOIs
• anti-psychotic medicines
• lithium
• narcotic pain medicines
• seizure medicines
• blood thinner medicines
• blood pressure medicines
• stomach acid medicines
• cold or allergy medicines that contain
decongestants
Know the medicines that you or your child
takes. Keep a list of your medicines with you to
show your doctor and pharmacist.
Do not start any new medicine while taking
ADDERALL XR without talking to your
doctor first.
How should ADDERALL XR be taken?
• Take ADDERALL XR exactly as
prescribed. Your doctor may adjust the dose
until it is right for you or your child.
• Take ADDERALL XR once a day in the
morning when you first wake up.
ADDERALL XR is an extended release
capsule. It releases medicine into your body
Reference ID: 4943991
2
throughout the day.
• Swallow ADDERALL XR extended release
capsules whole with water or other liquids.
If you or your child cannot swallow the
capsule, open it and sprinkle the medicine
over a spoonful of applesauce. Swallow all
of the applesauce and medicine mixture
without chewing immediately. Follow with a
drink of water or other liquid. Never chew
or crush the capsule or the medicine inside
the capsule.
• ADDERALL XR can be taken with or
without food.
• From time to time, your doctor may stop
ADDERALL XR treatment for a while to
check ADHD symptoms.
• Your doctor may do regular checks of the
heart and blood pressure while taking
ADDERALL XR. Children should have
their height and weight checked often while
taking ADDERALL XR. ADDERALL XR
treatment may be stopped if a problem is
found during these check-ups.
• If you or your child takes too much
ADDERALL XR or overdoses, call your
doctor or poison control center right away,
or get emergency treatment.
What are possible side effects of ADDERALL
XR?
See “What is the most important information
I should know about ADDERALL XR?” for
information on reported heart and mental
problems.
Other serious side effects include:
• slowing of growth (height and weight) in
children
• seizures, mainly in patients with a history of
seizures
• eyesight changes or blurred vision
Common side effects include:
• headache
● decreased appetite
• stomach ache
● nervousness
• trouble sleeping
● mood swings
• weight loss
● dizziness
• dry mouth
● fast heart beat
ADDERALL XR may affect you or your child’s
ability to drive or do other dangerous activities.
Talk to your doctor if you or your child has side
effects that are bothersome or do not go away.
This is not a complete list of possible side
effects. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more
information.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side
effects. You may report side effects to FDA at
1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store ADDERALL XR?
• Store ADDERALL XR in a safe place at
room temperature, 59 to 86° F (15 to 30° C).
• Keep ADDERALL XR and all medicines
out of the reach of children.
General information about ADDERALL XR
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for
purposes other than those listed in a Medication
Guide. Do not use ADDERALL XR for a
condition for which it was not prescribed. Do
not give ADDERALL XR to other people, even
if they have the same condition. It may harm
them and it is against the law.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most
important information about ADDERALL XR.
If you would like more information, talk with
your doctor. You can ask your doctor or
pharmacist for information about ADDERALL
XR that was written for healthcare professionals.
For more information, you may also contact
Takeda Pharmaceuticals (the maker of
ADDERALL XR) at 1-800-828-2088 or visit the
website at http://www.adderallxr.com.
What are the ingredients in ADDERALL
XR?
Active Ingredients: dextroamphetamine
saccharate, amphetamine aspartate monohydrate,
dextroamphetamine sulfate, amphetamine
sulfate
Inactive Ingredients: gelatin capsules,
hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, methacrylic
acid copolymer, opadry beige, sugar spheres,
talc, and triethyl citrate. Gelatin capsules contain
edible inks, kosher gelatin, and titanium dioxide.
The 5 mg, 10 mg, and 15 mg capsules also
contain FD&C Blue #2. The 20 mg, 25 mg, and
30 mg capsules also contain red iron oxide and
yellow iron oxide
Reference ID: 4943991
3
Distributed by:
Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.
Lexington, MA 02421
ADDERALL XR
®
is a registered trademark of
Takeda Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc.
© 2020 Takeda Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc. All
rights reserved.
Rev. 2/2022
This Medication Guide has been approved by
the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Reference ID: 4943991
4
