EDA-TECH HUBS PHASE 2-2023
PRBio Tech Hub Phase 2: Overarching Narrative
I. Executive Summary
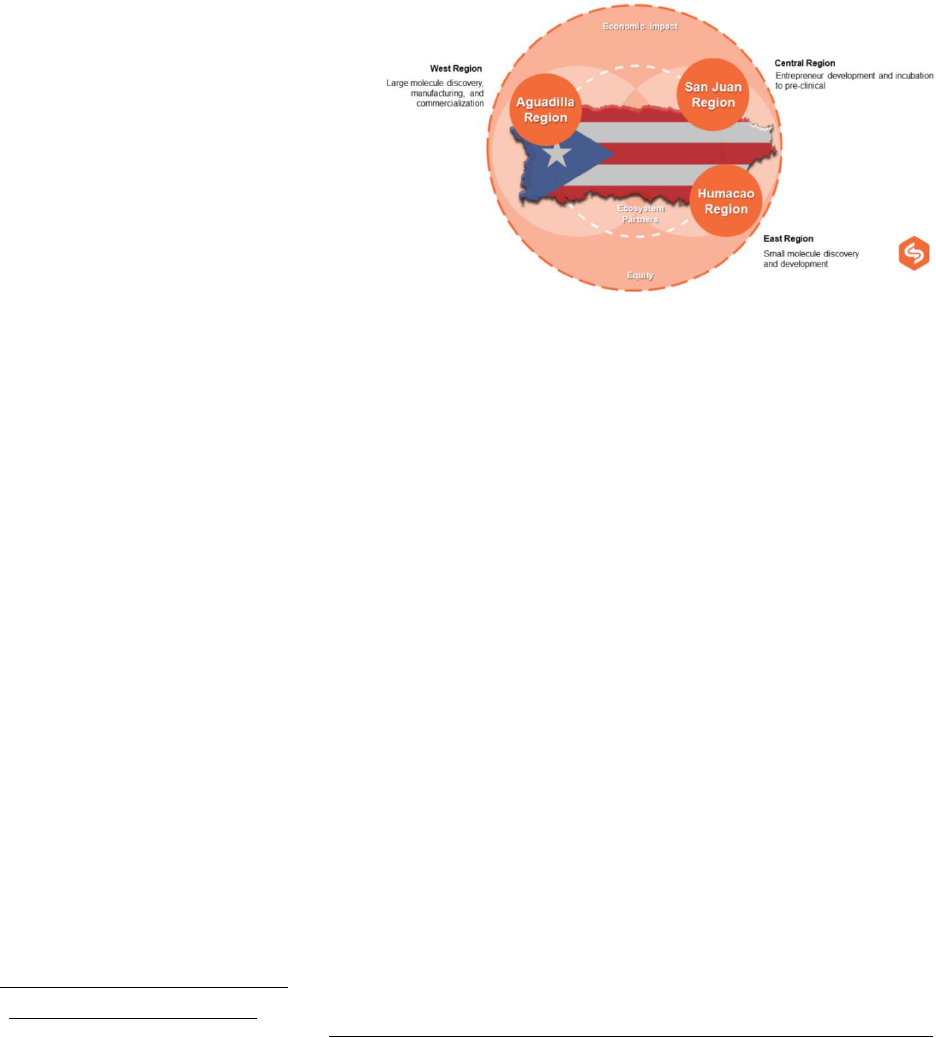
PRBio Tech Hub’s includes the full region of Puerto Rico (PR), an unincorporated,
commonwealth territory of the United States (US) with a population of ~3.3 million (2022)
American citizens, 98% Hispanic
1
. Nearly the entire region of PR is defined within the EDA’s
definition as a Metro/Micropolitan Statistical Area with a concentration of assets, capital, R&D,
labor market, and infrastructure strongly relevant to the EDA Tech Hub biotechnology key
technology focus areas. Since PR’s bioscience landscape incorporates employees from most of the
78 municipalities, the full region of PR will constitute the PRBio Tech Hub’s region for purposes
of the Tech Hub Competition.
The overall goal of the PRBio
Tech Hub (Hub) is to retain, grow, and
attract innovative companies in
biotechnology, enabling the
consortium to drive regional growth
and capacity to accelerate
development, manufacturing, and
distribution of 1
st
generation
pharmaceutical and medical products
and disruptive technology platforms.
The Hub will enable the established
ecosystem, including the coordination with the NSF Engine Development Award 2305699
Advancing Biopharmaceutical Technologies and Manufacturing Practices PR, to boldly leverage
the EDA’s key technology focus area (KTFAs) #7 including bio and medical technology, genomics,
and synthetic biology. The Hub will also intersect with KTFA #1 & #9 for advancements in medical
devices and wearable technology: artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and industrial
efficiency technologies. The Hub’s commitment to the EDA KTFAs ensures a resilient domestic
supply chain for Essential Medicines, Medical Countermeasures, and Critical Inputs capable of
meeting national security requirements for responding to threats arising from chemical, biological,
radiological, nuclear threats, and public health emergencies.
II. Vision for Regional Economic Development
The key question for the Hub’s visionary path is Why Puerto Rico? For more than six decades,
PR has been a global leader in the FDA regulated biotechnology sector, earning the reputation as
the Medicine Cabinet of the US. Beginning with the electronics and pharmaceutical industries and
then growing into medical devices, the biosciences industry reaches 75% of the FDA Class III
device manufacturers shares in 30 medical device facilities, demonstrating PR’s leadership in the
biosciences. The industry has been the anchor of PR’s economy representing 32.2% of its GDP,
33% of all manufacturing jobs, and employing over 83,500 of its total population representing
15.8% of total jobs in PR
2
. With a rich history of expertise and state-of-the-art infrastructure ready
to be utilized for the next generation of technology innovation, PR’s biotechnology industry offers
a solid foundation for innovation and growth. We believe that this moonshot opportunity will create
generational change for all of PR, while creating lasting benefits for the US and globally.
According to the BIO National Industry Report, PR stands out as the only US jurisdiction
specialized in four of the five bioscience sub-sectors including distribution, pharmaceuticals,
1
https://www.census.gov/quickfacts/PR
2
Biopharma industry creates 87K jobs, May 2022, https://newsismybusiness.com/biopharma-industry-pumps-3b-into-economy-creates-87k-jobs/

medical devices, and research
3
. White House Executive Order 13944 supports the US’s need to
have a strong Public Health Industrial Base with a resilient domestic supply chain and states that
these chains must be capable of meeting national security requirements. This proposal seeks to
further strengthen this important Order for the national security and well-being of all US citizens.
As a Designated Hub, PR will continue to make bold impacts on the EDA’s KTFAs of
biotechnology, medical technology, genomics, and synthetic biology, strengthening PR’s
pharmaceutical industry as an asset to national security. The Hub’s vision is to develop the
necessary strategies, activities, and workforce to further strengthen PR’s focus on Technology
Readiness Levels 6 & 7 (commercialization), 8 (deployment), and 9 (manufacturing) to support
PR as a global leader in the rapid development of new products to address unmet medical needs
of patients worldwide. The Hub members listed below will strengthen PR’s capacity to
manufacture, commercialize, and deploy critical technologies to support PR’s position as a global,
leading biopharmaceutical tech hub for decades to come.
PRBio Tech Hub Consortium Members & Additional Partners
Consortium Lead – EDA Tech Hub Lead Applicant: Puerto Rico Science, Technology& Research Trust (PR Trust)
Component Project Leads
PRBio Tech Hub Governance; Access to Capital for Entrepreneurship; Advancing NextGen Workforce – PR Trust
Next-Generation Therapeutics & AI Drug Discovery – Bright Path Laboratories (BPL)
Acceleration of New Drug and Precision Medicine Laboratories – University of Puerto Rico Medical Sciences Campus
Entrepreneurship: Lab to Market – Molecular Sciences Research Center (MSRC)
Advanced Technologies Center (ATC): Pharmaceutical Manufacturing and Enabling Technologies – OcyonBio
Consortium Members
Institutions of Higher Education (all Minority Serving Institutes): University of Puerto Rico (UPR), UPR Medical Sciences
Campus, School of Pharmacy (UPR MSC SoP), UPR at Mayagüez, UPR at Aguadilla, UPR at Humacao, MSRC
Government: Puerto Rico Department of Economic Development and Commerce (DDEC)
Industry/Private Sector: OcyonBio, Dsquare Analytics, LLC, Galephar Pharmaceutical Research, Inc., CytoImmune
Therapeutics Puerto Rico, LLC, Bright Path Laboratories (BPL, venture development), PR5GZone (nonprofit), Industry
University Research Center Bioscience Cluster (INDUNIV, nonprofit)
Economic Development/Science Organizations: Invest Puerto Rico, PR Trust’s Parallel18 (venture development)
Workforce/Labor: DDEC (WIOA/Apprenticeship), PR Ready (Workforce Training Program of PR Trust), Coursera, Inc.
Committed Key Partners and Additional Partners: Pharmaceutical Industry Association, Johnson & Johnson, Bristol Myers
Squibb, Biotechnology Innovation Organization, Avara Pharmaceutical Contract Manufacturing Company, Bayer Healthcare
Pharmaceuticals LLC, North Carolina State University Biomanufacturing Training and Education Center, Lilly del Caribe,
Department of Biomedical Engineering at Georgia Tech and Emory University, Amgen Manufacturing Limited, Organon,
Sartorius, Principia, BLDM, PRO Quality Strategic, VOCES: Vaccine Coalitions, Viatris, BD Biosciences, GCM Medical
Group, SanaClis, AbbVie Biologics Ltd, 323 Family Trust, LLC.
The Hub members have developed six (6) component projects aligned with the PR Trust’s
Governance Project and supported by the overall Risk Mitigation Plan. Brief details of the Projects
and how each reinforces one another in the overall success of the Hub are listed below. The Hub
synergy briefly defines how the Projects will complementarily lead to the Hub’s global
competitiveness over the next decade. Each individual Project has detailed the constraints that its
activities and initiatives will enable the Hub to overcome (see full Component Projects).
Component Project Short Descriptions
Complementary Hub Synergy
PRBio Tech Hub Governance
Outlines the PR Trust’s comprehensive strategy for managing the
consortium, ensuring oversight, workflow management, evaluation,
reporting, communications, and sustainability, including the role of
the RIO. Aims to establish a robust framework that supports
transparent decision-making, accountability, efficient project
execution, and long-term sustainability.
Builds consensus with Hub consortium members/partners
for goal-driven strategies for Phase 2 implementation by
ensuring that the Component Projects are aligned with the
Hub’s overarching mission and vision and through the
leadership of the RIO and the overarching Risk Mitigation
Plan.
Access To Capital For Entrepreneurs
Seeks to solve PR’s biotechnology funding gap through the creation
of the PR Biotechnology Capital Network (PRBCN) through two
Industry sector attraction and retention plan for Hub to
determine the best strategy to attract, retain, and fund
3
https://go.bio.org/rs/490-EHZ-999/images/TEConomy_BIO_2022_Report.pdf
Component Project Short Descriptions
Complementary Hub Synergy
principal initiatives: i. PR Biotechnology Grant Fund; and ii. PR
Biotech Emerging Managers Program to overcome the challenges
of capital funding that local private equity & venture capital firms
encounter when investing in the PR bioscience entrepreneurs.
biopharma manufacturing businesses through leveraging
regional assets and synergistically support within Hub
component projects as the bridge to capital.
Advancing NextGen Workforce
The Hub’s Workforce Plan will harness collective learnings and
scale existing, proven approaches to education and workforce
development that are essential for biotechnology innovation
focusing on lifelong learning programs, STEM engagements,
apprenticeships, and programs that support the “cradle to career”
workforce pipeline development through various initiatives.
Industry sector workforce plan to guide the Hub to launch
and strengthen PR life sciences workforce by working
closely with a cross-section of life science employers,
academia, labor organizations, and workforce curriculum
leaders to understand industry workforce needs.
Entrepreneurship: Lab To Market
Complete the build-out of the MSRC’s EDA ASTRE project to
provide state-of-the art laboratories and pilot scale infrastructure for
small and large molecule development technologies, viral, DNA
and RNA derived immunotherapies, and gene and cell therapies for
future workforce development to accelerate benchtop to
commercialization.
Will complement the activities of the Hub’s component
projects and goals and strengthen MSRC’s
multidisciplinary ecosystem by educating new
biotechnology professionals and startups that will bolster
the biotechnology sector resulting in a more stable
pharmaceutical supply chain.
Next-Generation Therapeutics & AI Drug Discovery
Advances beyond drug manufacturing to drug development and the
go-to-market leader for biotechnology through an enabling tech-to-
chemistry capability (STT
®
) that allows therapeutics produced
through AI drug-discovery, repurposed, or reformulated drugs to be
synthesized using computer-aided synthesis, optimization, and
analysis to produce APIs.
Enables the Hub shared, tech-to-chemistry capabilities
produced through AI drug-discovery and acts as a conduit
to additional assets that include workforce talent, industrial
space, intellectual property, and access to capital
investments in AI drug discovery across the Hub.
Acceleration Of New Drug And Precision Medicine Laboratories
To catalyze the development and scale-up of new drugs and PMs
with the use of advanced manufacturing and enabling technologies,
provided by state-of-the-art equipment and instrumentation to
support existing infrastructure to close technology gaps to produce
innovative biopharma products and drive Enabling Technologies.
Identify Hub desired academic curriculum advancement
needs within pharmaceutical degree programs to support
regulatory professional development to strengthen the
knowledge transfer to the biopharmaceutical and medical
device ecosystem.
Advanced Technologies Center (ATC): Pharmaceutical Manufacturing & Enabling Technologies
Empower disadvantaged and limited educational backgrounds
through hands-on job training experience as support mechanism for
emerging biotech startups by providing critical, shared equipment,
facilities, resources, and expertise to enhance manufacturing
capabilities within the PR pharmaceutical sector to advance gene
and cell therapy, viral vectors, biologics, and small molecules.
Provide the Hub with shared facilities and equipment for
the development and utilization of advanced
pharmaceutical manufacturing technologies and provide
non-traditional students with hands-on job training
enabling them to qualify for high-demand jobs in emerging
technologies, addressing gaps in workforce readiness.
Puerto Rico provides a unique investment and policy commitment to the EDA’s funding for
the overall Hub’s sustainability for the 10-year expectation and beyond. While the PR Government
is supporting the Hub’s application through various commitments from DDEC and to specific
component projects, PR’s Act 60 and 73 are part of the economic incentive laws designed to attract
investment and promote various sectors, including research and development (R&D). Act 60 offers
tax credits to businesses that engage in eligible R&D activities in PR. The goal is to promote
innovation, technological advancement, and the development of a knowledge-based economy,
making PR a competitive jurisdiction for investment in these industries. Key benefits under Act
60 for R&D include a tax credit of up to 50% for investments in R&D activities, an additional 25%
tax credit for payments made to the PR Trust, and favorable tax rates on income generated from
intellectual property developed through R&D activities. These tax credit incentives, coupled with
the Hub’s commitments (See Section V.) act as a viable source of long-term, sustainable funding
for the Hub.
In the Hub’s Governance Project, the consortium has focused on the deliverables necessary for
Phase 2 implementation, ensuring PR’s biotechnology industry moves towards achieving its net-
zero goals and contributing to a greener, more sustainable future. PR’s industry also maintains the
highest EPA environmental standards, protecting water resources; minimizing air emissions; and
preventing land contamination including solvent elimination from chemical processing and

efficient use of water and energy, in coordination with government and regulatory agencies. The
quality of the products, protection of the environment, and preservation of life are intrinsic
elements of PR’s bioscience industry and are at the forefront of the Hub’s activities and outcomes.
The Hub will utilize the Climate and Economic Justice Screen Tool (CEJST) when accounting
for environmental and climate-related impacts and risk as activities are implemented throughout
Phase 2 and beyond. The PRBio Tech Hub and its biosciences industry is dedicated to improving
the nation’s health, food supply, and the environment through responsible biotechnological or
chemical applications meeting the highest regulatory standards. Since these products are sensitive
to environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and other conditions and contaminants,
redundant and resiliency protocols are established to maintain the business continuity during
atmospheric events that can cause power outages. The Hub will utilize the PR Trust’s disaster
preparedness plans including the Emergency Management Plan and Cyber Security Policy &
Framework of IT (see Overarching Risk Mitigation Plan) to account for weather and climate
related risks and security protections.
The Hub’s region is comprised of ~3.3 million American citizens of which, 98% are Hispanic.
The region’s communities and groups are inclusive to the definition of a SEDI (Socially and
Economically Disadvantaged Individuals) and comply with the characteristics of SEDI-owned
businesses within a Community Development Financial Institution Investment Area and
Opportunity Zone. The Hub initiatives were developed with equity in their approach to benefit the
underserved populations and communities of PR from high school and undergraduate level on-
the-job training; to apprenticeships, mentorship, and scholarship opportunities; to graduate and
post-graduate level advanced degree programs; to engaging and collaborating with STEM
underserved, minority serving institutions (MSI); to providing access to capital to Opportunity
Zone entrepreneurs. Each component project’s KPIs include measurements related to serving the
full population of the Hub and the economic growth associated with these initiatives.
Currently PR’s biopharmaceutical sector is essential for biopharmaceutical manufacturing,
distribution, and development, and contributes 35% to PR's GDP, accounts for 45% of
manufacturing jobs, and employs over 88,000 people throughout the region. The Hub is laser
focused on the pace of change and the scale of labor market fluctuations affecting the US and the
global pharmaceutical industry. The Hub’s Projects will provide significant advancements in the
biopharmaceutical industry workforce pipeline as a global leader in advanced drug discovery and
development using emerging technologies such as generative AI, expanding production
capabilities, increasing investments, and creating new high-salary job opportunities impacting
PR’s GDP at a greater scale. While each Project has specific SMART goals and KPIs related to
the timeline of their respective activities (see Section IX), the Hub’s overarching outcomes expect
to impact PR on a larger socio-economic scale. With the Hub prioritizing closing PR’s gap in
biopharmaceutical access to capital, the project expects to impact over 10,000 individuals from the
sector, directly and indirectly, while serving entrepreneurs and R&D focused organizations. While
access to capital will provide a financial launching pad for entrepreneurs, this capital allows
companies to open and expand resulting in job creation, R&D opportunities, and indirectly fueling
the market with higher salary opportunities. During the EDA’s expected 10-year time period, the
Hub is expected to attract over 100 companies through the enrollment in the Access to Capital
Project initiatives with over $100M of raised capital, expecting to create 250+ direct jobs and ~75
new investors in PR.
The Hub has been extremely conscience of the need to make an impact starting on Day 1 to
ensure the resources necessary for biopharma companies in PR to advance globally are readily
available. With this in mind, the Hub concentrated its construction project within the Molecular
Sciences Research Center (MSRC) to complement the current EDA funded Advancing Science

and Technology Research and Entrepreneurship (ASTRE) project (EDA #01-79-14873) to
incubate and develop both new and established companies that can translate scientific discoveries
into commercial and intellectual property that can bolster PR’s economy. In addition, the Hub plans
to upskill ~2,000 PR residents through online short-form credentials provided by Coursera, Inc.
By engaging Coursera on Day 1, the Project will develop a pipeline of workers to support the Hub
activities immediately. For those completing online courses through a massive online open course
provider, 87% reported a general or tangible career benefit, ensuring increased wage growth
opportunities throughout the Hub.
III. Need for HUB
Puerto Rico’s ecosystem has been nurtured by expertise that has emanated from major
pharmaceutical companies such as Eli Lilly, Bristol Myers Squibb, Amgen, Johnson & Johnson,
and others. These companies provide many of the services needed to start a new manufacturing
operation or validate processes and complement the services offered by contract manufacturing
organizations and facilitate the implementation of a new manufacturing process. The Hub provides
a unique opportunity for new pharmaceutical companies to grow the region’s ecosystem with over
60 years of pharmaceutical manufacturing experience. With the designation of Puerto Rico’s R&D
tax credits, multiple drug development companies have begun operating within PR to expand the
ecosystem from advanced manufacturing to pharmaceutical drug development. However, these
new drug products must be approved by FDA and other regulatory agencies before they can be
available globally. Ensuring that all avenues of both advanced manufacturing and drug
development are readily available and supported by available talent, is vital to these company’s
success and PR knows that no single company or organization can ensure all elements of the
biopharmaceutical ecosystem alone. The Hub has built a growing consortium with the input and
activities of industry, private, public, academia, nonprofit, and government entities to ensure full,
wrap-around services from workforce development and on-the-job training, to regulatory and start-
up support services, to academia curriculum expansions and short-form credentialing, to access to
capital and R&D tax credits, to governance and management oversight to ensure a sustainable
ecosystem over the next 10-years.
Puerto Rico has experienced lessons learned through the cyclical closure of multiple
manufacturing plants, the Hub has used these lessons to build its goals and outcomes for the
advancement of biopharmaceutical industry, both large and small, to prevent their closure and
migration from the region. This Hub’s ecosystem will provide the foundation through matched
consortium commitments and long-term sustainability plans to ensure the longevity of the Hub as
a globally competitive powerhouse to retain, grow, and attract innovative companies in
biotechnology. The Hub has already seen a successful impact in companies such as Galephar,
Dsquare, and OcyonBio (Consortium Members), among others, as new, small pharmaceutical
companies located in the region providing new jobs opportunities.
IV. Nexus
How does the Hub fulfil this moonshot opportunity? Puerto Rico has committed to
transforming the region into a bio-manufacturing and product development hub where ideas can
flourish, and bioscience products can efficiently reach customers while creating a more resilient
supply chain to enable national security. This transformation is strongly supported by initiatives
driven by the PR Department of Economic Development and Commerce (DDEC, Consortium
Member), who in May of 2022 unveiled the strategic framework of sustainable economic
development or PR’s Comprehensive Economic Development Strategy, the PRoposito. The
strategy supports the Hub’s initiative to transform PR’s pharmaceutical manufacturing sites with
smaller, more flexible, cost-effective operations. The Hub’s directed activities within its
committed academic institutions will have students and researchers readily available to help
transform these manufacturing sites through modern manufacturing approaches. The nexus of the
Hub members is united in its collaboration with emerging, local pharmaceutical companies to
incorporate advanced pharmaceutical manufacturing and drug development based on industry-led
guidance and training within the Hub’s universities and workforce development plans. These
approaches have been presented to and accepted by the local pharmaceutical industry through
INDUNIV (Consortium Member) and PIA (Partner). The Hub already has real-time examples that
indicate a future PR-based pharmaceutical industry is a possibility through emerging companies
such as MBQ Pharma, a local company that licensed its intellectual property from UPR
(Component Lead), currently developing two drug candidates for the effective removal of pre-
existing metastases to lead to the removal of solid tumor cancer. However, companies still require
substantial financial, talent, and programmatic support, all represented in the Phase 2 Hub
activities to meet the overall Hub goal to retain, grow, and attract innovative companies in
biotechnology, enabling the consortium to drive regional growth and capacity to accelerate
development, manufacturing, and distribution of 1
st
generation products and disruptive technology
platforms. In addition, the Hub provides a governance structure and overall risk mitigation plan
aligned with the industry’s highest national and economic security at the forefront.
V. Partnership Commitments
The role of the private sector in PR’s bioscience industry plays a crucial role in its
development. PR currently hosts 12 of the world’s top 20 pharmaceutical companies including
Amgen, AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Sartorius, Boston Scientific, among others. According to
the Bureau of Labor Statistics, PR led US exports of pharmaceutical and medicine manufacturing
in 2020, accounting for 19.3% of total US exports. Therefore, the PR biopharmaceutical, medical
device, and supporting technology manufacturing sectors are a cornerstone of the US bioscience
industry and the Hub. The biotech industry encompasses a wide range of activities, and the Hub
has aligned multiple private sector entities to contribute to the Hub as Project Leads and members,
through investments, job creation, and as R&D sites to contribute to PR’s overall economic growth
while establishing PR as a global leader in biopharma advancement. The industry’s growth, driven
by private sector innovation, contributes to economic diversification making PR less reliant on
traditional industries and creating a knowledge-based economy. A full list of the Hub’s
commitments is listed below.
Commitment
Entity Type
Entity Name
Associated Component Project(s)
Value
Delivery
Cash Match
Government
DDEC
Advancing NextGen Workforce
$1,000,000
12/31/2027
Cash, In-Kind
Industry
Dsquare
Advancing NextGen Workforce
$680,000
12/31/2028
Cash Match
Industry
323 Family Trust
Next-Gen Therapeutics & AI Drug
$254,087
12/31/2028
Cash, In-Kind
Industry
OcyonBio
Advanced Technology Center (ATC)
$1,900,000
03/31/2028
Cash, In-Kind
Higher Ed
UPR MSC SoP
Acceleration of New Drug & PM Lab
$728,905
08/31/2029
Cash Match
EDO
PR Trust
PRBio Tech Hub Governance
$626,968.15
08/31/2029
Cash Match
EDO
PR Trust
Access to Capital for Entrepreneurs
$870,000
08/31/2029
Cash Match
Higher Ed
MSRC
Entrepreneurship: Lab to Market
$750,000
08/31/2029
Cash Match
Industry
BPL
Advanced Technology Center (ATC)
$90,000
12/31/2025
In-Kind, Policy
Higher Ed
UPR MSC SoP
Advancing NextGen Workforce
$310K/$1.5M
12/31/2028
In-Kind Match
Higher Ed
UPR – Mayaguez
Advanced Technology Center (ATC)
$360,000
12/31/2028
In-Kind Match
Industry
INDUNIV
Advancing NextGen Workforce,
Acceleration of New Drug & PM Lab
$640,500
08/31/2029
In-Kind Match
Industry
INDUNIV
Advancing NextGen Workforce
Invaluable
08/31/2029
In-Kind Match
Industry
BPL
Next-Gen Therapeutics & AI Drug
$572,160
08/31/2025
In-Kind Invest
Industry
BPL
Advanced Technology Center (ATC)
$2,910,000
12/31/2025
Investment
Industry
BPL
Advancing NextGen Workforce
$500,000
10/15/2025
Policy Match
Government
DDEC
All Component Projects
$4,500,000
12/31/2027
In-Kind, Invest
Workforce
Coursera, Inc.
Advancing NextGen Workforce
$300,000
12/31/2027
In-Kind Match
EDO
Invest PR
PRBio Tech Hub Governance
$100,000
08/31/2029
In-Kind Match
Nonprofit
PR5GZone
PRBio Tech Hub Governance
$250,000
08/31/2029
VI. Sustainability

PR’s existing assets are included as part of the Hub’s plan towards ensuring sustainability for
both its Component Projects and the Overarching 10-year EDA timeframe. Existing assets include
but are not limited to expertise in advanced manufacturing, partnerships in PR’s universities and
industry, research and laboratory facilities, talent in pharmaceutical science and engineering to
advance manufacturing, biopharmaceutical incubators, initiatives to enhance workforce
development, and efforts and implementation of advanced concepts such as Industry 4.0, 5G, and
IoT. Furthermore, the Hub has aligned its goals and outcomes with the PR Trust’s awarded NSF
Engine Development Award (2305699 Advancing Biopharmaceutical Technologies and
Manufacturing Practices PR) and through its EDA funded Forward Center for incubation and
acceleration capabilities for up to 60 technology-driven start-ups and early-stage companies. The
Hub will continue to leverage the PR Trust’s Technology Transfer Office (TTO) which enables
academic inventors in disclosing new discoveries by providing best-in-class technology transfer
support for PR’s scientists and researchers.
The Hub’s ecosystem has shown its ability to continue and transform within the
biopharmaceutical sector including developing the first Industrial Biotechnology program in PR,
proving the ability to transform from small molecule tablet-based manufacturing to successfully
implementing biologic products in collaboration with Amgen, AbbVie, and Eli Lilly. These assets
have opened the door to biotechnology job development for many large pharma and small start-
ups companies providing top industry positions throughout PR. The Hub’s assets also include the
MSRC (Component Lead), funded by both EDA and NIH awards, a Ph.D. in Pharmaceutical
Sciences at the UPR MSC (Component Lead), and the collaboration of the Engineering Research
for Cell Manufacturing Technologies through the NSF Center for Structured Organic Particulate
System. The ecosystem’s sustainability is further strengthened with the mission to drive
entrepreneurship, beginning with the development of companies such as PACIV providing
computer validation services and PharmaBioServ serving multiple world-wide locations. The
ecosystem has developed logistics companies, providing indirect job opportunities, and is adapting
to contract manufacturing to focus large pharmaceutical companies on developing new products
while contracting their manufacturing with in-region companies such as ThermoFisher, Avara,
among others. Finally, the UPR-Mayagüez (Consortium Member) was recently awarded an NSF
Phase 1 EPIIC grant, ensuring best practice models and training to enhance partnership capacity-
building providing a foundation for the management of the Hub’s ecosystem. Under the EDA
Phase 2 funding, the Hub’s ability for self-sustainability increases greatly with its consortium
commitments (see Section V.). In addition, many Hub Projects are self-sustained by PY 3-5 due to
generated revenue, PR’s R&D Act 60/73 tax credits, and access to capital initiatives.
VII. Labor Union Engagement
The Hub’s Entrepreneurship: Lab To Market Project includes the MSRC construction to
complete the previously EDA-grant funded Advancing Science and Technology Research and
Entrepreneurship (ASTRE) Center. The MSRC will pursue project labor agreements (PLAs) with
bid awarded contracting entities in PR. This construction will require soliciting electricians,
plumbers, engineers, and a host of specialized trade workers. The MSRC will pursue contracts
with PLA to ensure economic benefits of this construction are equitable and local residents are
closest to their impact. And although the MSRC doesn’t have a community benefits agreement in
place, all wages for this effort will be at or above the minimum wage and comply with all
construction wages under the PLA. In addition, the Hub’s workforce plan includes supporting
existing, registered apprenticeship programs which support good quality jobs. Lastly, the Hub will
incorporate promising practices such as the AFL-CIO Technology Center which has partnered
with Microsoft to support the voice of Labor in AI development.
VIII. Equity
The Hub’s distributed manufacturing concept allows for diverse distribution of jobs, equitable
economic, and inclusive workforce development, while raising the existing footprint of the
industry in PR. Included Letters of Commitment demonstrate the Hub’s commitment to ensuring
the representation of underserved communities, businesses, and the PR workforce as they serve
the full region of PR including underserved, rural, and socioeconomically disadvantaged
populations. In addition, the PR Trust’s TTO manages a portfolio of 96 technologies from its
partner universities and diversity in inventorship is exceptional, as 42% of the inventors (76 of 179
total) are female compared to the US average of 13% female inventor-patentees. The Hub’s
workforce development commitments will also ensure that Hub benefits are equability shared
across PR since its bioscience landscape encompasses nearly a third of PR’s cities, incorporating
employees from nearly all 78 municipalities. Expanding the technology and innovation beyond
advanced manufacturing to drug discovery will only further expand the Hub’s reach, positively
impacting economic development across a historically disadvantaged region. The Hub’s focus to
expand the pharmaceutical landscape positions the Hub’s academic institutions and workforce
labor organizations to expand industry-specific course certifications and degree programs,
providing direct benefits to Minority/Hispanic Serving institutes, workplaces, and communities.
IX. Expected Outcomes
The worldwide competition in manufacturing and commercialization has been dominated by
the maturation, commoditization, and widespread application of computation in production
equipment and logistics, effectively leveling the global technological playing field. The next
generation of biotechnological competition will be dictated by inventions of new materials,
chemicals, devices, processes, and methods, among others. The Hub Component Projects have
considered bold investments to fulfil this moonshot opportunity with the fundamental R&D
required in AI, biotech, materials science, sustainability, education, and workforce development
for PR to lead globally. Upon award, the Hub will continue enhancing its leadership in
biomanufacturing, drug development, and commercialization through the joint impact its Projects’
Key Performance Indicators (KPI) per Project Year (PY) (primary KPIs represented below).
PRBio Tech Hub Component Projects: KPIs
PY1
PY2
PY3
PY4
PY5
Total
PRBio Tech Hub Governance
Number of Advisory Board meetings
4
4
4
4
4
20
Number of Steering Committee meetings
18
12
12
12
12
66
Percentage resolution of day-to-day risk & issue resolutions
70%
70%
70%
70%
70%
70%/yr
Minimum number of marketing materials for Hub use
20
20
25
25
25
115
Access To Capital For Entrepreneurs
Enrolled investors/entrepreneurs
10/5
15/10
20/10
20/10
65/35
Number of company/entrepreneur graduates
3
6
7
8
24
Total jobs created
5
10
15
25
55
Total Capital Raised by Investors
$500K
$1M
$2M
$5M
$8.5M
Total Capital Closings
1
3
5
7
16
Advancing Nextgen Workforce
Number of candidates who complete DDTC training
6
6
8
10
30
Number of participants enrolled/complete PR Integrated
Biomanufacturing STEM Program
25/20
25/20
25/20
25/20
80/100
Number of mentorships supported by PR Integrated
Biomanufacturing STEM Program
50
50
50
50
200
Apprenticeship: Number of participants
enrolled/completed/employed
10/8/8
10/8/8
10/8/8
10/8/8
40/36/36
PR Ready: Number of candidates enrolled/complete
50/25
50/25
50/45
75/70
225/165
Coursera: Number of trainings started/completed
1000/500
1000/800
1800
Entrepreneurship: Lab To Market
Number of underrepresented students served
100
100
100
100
100
500
Number of incubated companies within the space
6
6
6
18
Number of biotech/biosimilars in cGMP startups
10
20
20
25
75
Number of new incubation biotechnology companies
2
4
5
11
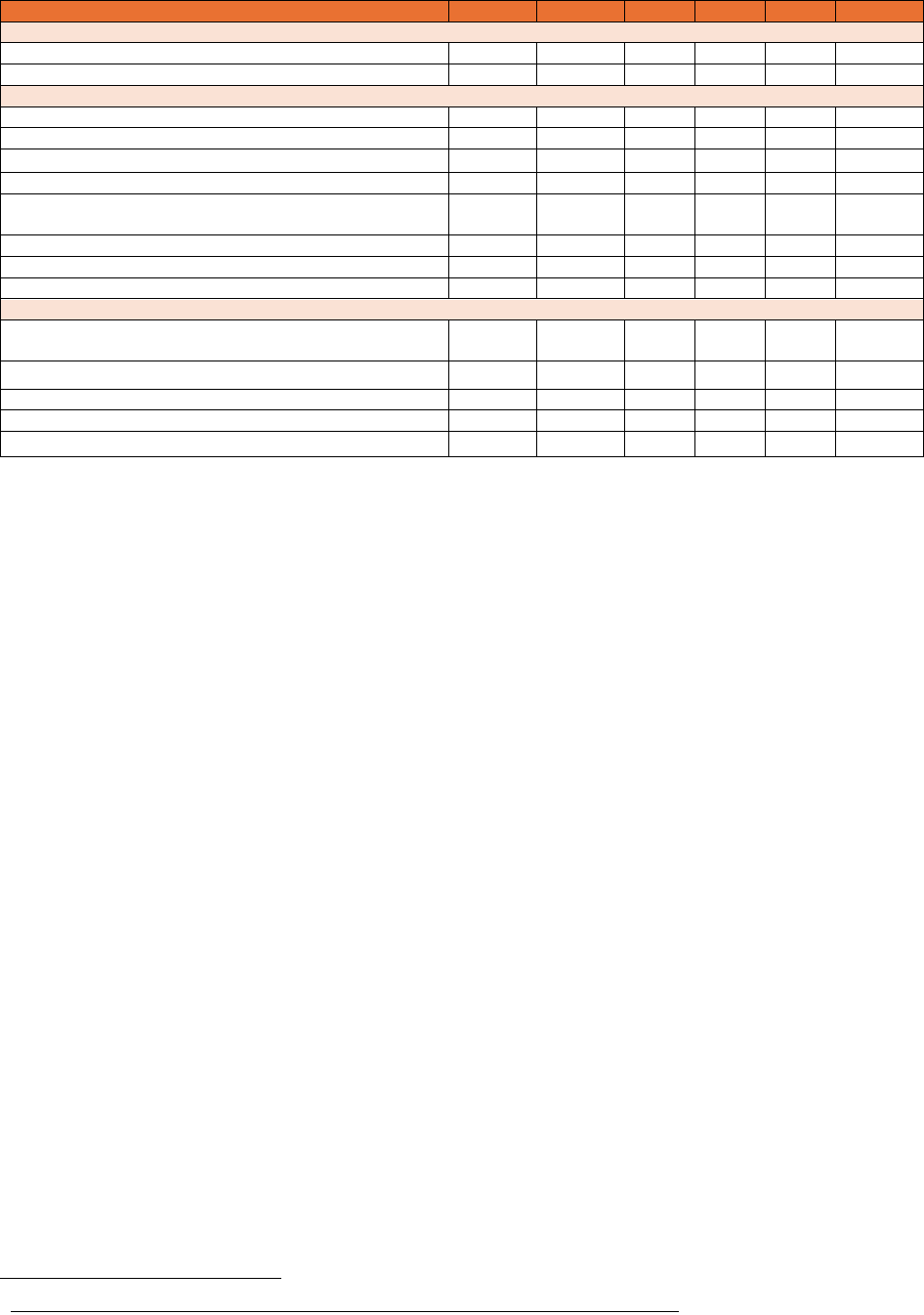
PRBio Tech Hub Component Projects: KPIs
PY1
PY2
PY3
PY4
PY5
Total
Next-Generation Therapeutics & AI Drug Discovery
Number of molecules identified/manufactured/to market
10/2/3
10/2/3
10/3/3
20/3/3
50/10/12
Total Capital Raised (Non-dilutive and dilutive)
$1M
$3M
$5M
$9M
$18M
Acceleration Of New Drug And Precision Medicine Laboratories
Broader Impact: Number of Publications
2
2
3
4
4
15
Infrastructure & Staffing: Jobs Created
5
5
5
5
5
25
Infrastructure & Staffing: Investment (capital/funds)
$5.8M
$0.3M
$0.4M
$0.3M
$0.3M
$7.1M
Project Income: New Collaborative/Partnerships
2
2
2
2
8
Project Income: Co-working space/contract income
(startups); onshoring D&D (scaleups)
1/0
1/0
1/1
1/1
4/2
Project Income: New grants (STTR/SBIR/CREST)
1
2
1
2
1
7
Number of patents granted/licensing agreements
1/1
2/2
2/2
5/5
Number of first-to-market products
2
2
4
Advanced Technologies Center: Pharmaceutical Manufacturing & Enabling Technologies
Number of drug shortage candidates selected to support
real-world process training
1
2
2
3
8
Number of sterile injectables capable of production
1
2
2
3
8
Established new startups and sponsored projects
2
3
5
5
15
Training certificates to participants
30
30
30
30
120
Number of scholarships awarded
5
10
15
20
55
These SMART PY interim goals and/or milestones will be used by the Hub to monitor the
progress of Hub activities, ultimately allowing the EDA to further monitor progress of Hub
outcomes. The goals will serve not only as the basis for determining the success of the consortium
but also as a basis for building evidence-based policies to support which strategies and approaches
work and which should be course-corrected based on the recommendations from the Hub’s
Steering, Advisory, and other overarching leadership committees. The PR Trust’s Regional
Innovation Officer (RIO) and Support Office will work with Project Leads to establish a
comprehensive framework for evaluating project outcomes, reporting progress, and maintaining
transparent communication with stakeholders. Upon Phase 2 funding, the RIO will provide a full
overview of required EDA reporting tools and ensure comprehensive tracking practices are in
place with each Lead. The evaluation plan will measure project impacts and progress towards
overall Component Project’s activities, goals, and objectives. The RIO will maintain open channels
of communication between the consortium and the EDA to proactively identify challenges and
collaborate with EDA and partners to find solutions that foster collaboration and support.
X. Expected Growth Plan
Accommodating the growth in housing demand resulting from the success of a technology
hub, while preventing displacement and ensuring access to jobs for existing low-income residents
requires a comprehensive approach that addresses supporting affordable housing development
policies, preservation and renovation of existing affordable housing, direct community
engagement, inclusive workforce development programs, and the promotion of transportation
accessibility. While the Hub cannot tackle all these areas with the EDA funding, the Hub will
actively support PR’s multifaceted approach around affordable housing development such as the
recent announcement of a FirstBank and CDBG-MIT jointly funded $30M investment for the
construction of Vista al Norte
4
, an affordable housing development that will benefit 102 low-
income renters who earn 60% or less of the median annual household income in the metropolitan
area of PR (Central Hub area). The Hub’s committees will also support local community
engagement efforts in the planning and decision-making processes of major economic and
workforce development projects via the PR government and/or public/private interest to prevent
displacement. The Hub’s activities are invested in academics, training, and research activities from
basic to advanced skill development to empower PR residents with the skills needed for entry to
4
https://newsismybusiness.com/firstbank-grants-21-5m-in-financing-for-vista-al-norte-project-in-guaynabo/

executive level biotechnology jobs creating a workforce that supports high wages to encourage
home ownership and aligns with regional rental income levels.
XI. Relevant Activities between Phase 1 & Phase 2
During Phase 1, PR Trust secured the contracted services of Accenture to provide strategic
project management for a comprehensive assessment of PR’s current biotechnology industry
through documentation review and interviews of selected stakeholders resulting in a detailed work
and resource plan to initiate Hub activity roles and responsibilities. Under Accenture, a two-day
workshop was held to inform and receive feedback and input from industry, public and private
sectors, nonprofits, government, relevant Clusters, academia, workforce industry, and others
interested in Hub participation. This ecosystem building led to meetings with government,
workforce, relevant industry operators, and academia, ultimately expanding the Hub’s consortium,
commitments, and supporting partnerships.
From the aforementioned collaborative approach, the Hub has grown and evolved from Phase
1 Designation to the Phase 2 Implementation application to ensure the catalyzation of the Hub’s
emergence over the next decade and beyond as a self-sustainable, globally competitive region. The
Hub is now positioned as an established ecosystem, including the coordination with financial and
policy commitments, collaborative partnerships, and other sources of funding, to support the
EDA’s mission to strengthen US economic and national security through EDA KTFAs 7, 9, and 1
with PR’s assets, resources, capacity, and potential to become globally competitive, within ten
years, in the biotechnology industry of the future. Over the past four months, the consortium has
executed the activities presented below to prepare for Phase 2 Implementation. The Hub and its
supporting structures under the PR Trust Governance, expects to evolve its capacity through its
members, stakeholders, advisory board, community, and industry needs and involvement to
translate innovation into equitable regional economic growth and to strengthen the overall national
security by accelerating the development, manufacturing, and distribution of new products to
address unmet medical needs of patients worldwide.
Phase 1 Goal 1 Relevant Activities from Phase 1-2: Consensus-driven Strategies for PRBio Tech Hub
- Component Projects selected through competitive abstract submissions, followed by full proposal submission.
- Secured facilitator/consultant – Accenture project management hired for Hub assessment resulting in a detailed SOW of Hub
activities through consortium agreement and a full Hub plan with roles and responsibilities.
- Cross-examined NSF Engines and existing funding sources for overlapping or duplication within Hub activities.
Phase 1 Goal 2 Relevant Activities from Phase 1-2: Industry Attraction, Retention, and Growth
- Assessment of Boston Consulting Group gaps in Hub and engagement of necessary partners for Phase 2.
- Assessed the most attractive industry sub-segments, key players, and drivers of site selection decisions and identified the
most attractive product classes that match capabilities of existing infrastructure.
Phase 1 Goal 3 Relevant Activities from Phase 1-2: Industry Future Workforce
- Post-secondary institutions aligned and defined new pathways to workforce needs.
- Planned and defined DDEC and Hub’s role in workforce development roles for the Hub.
- Defined industry needs for on-the-job training, apprenticeships, and fellowship opportunities within industry.
Phase 1 Goal 4 Relevant Activities from Phase 1-2: Regulatory Support Center
-Identified the academic curriculum and workforce training needs in regulatory professional development.
Phase 1 Goal 5 Relevant Activities from Phase 1-2: Contract Research Development and Manufacturing Organization
-Developed design estimates and budget for infrastructure and equipment for state-of-the art laboratory and pilot scale
infrastructure for small and large molecule development.
- Identified necessary initiatives for technologies, viral, DNA and RNA derived immunotherapies, and gene and cell therapies
with a parallel platform for future workforce development to complement industry capabilities.
Phase 1 Goal 6 Relevant Activities from Phase 1-2: Advanced Manufacturing and Enabling Technologies Center
-Planned a Center with platforms to deliver innovative and disruptive technologies with private industry and public university
collaboration with full workforce alignment.
XII. Statement of Consortium Member Commitment: Please see Letters of Commitment within the
submission package.
XIII. Key Partners – Letters of Commitment: Please see Letters of Commitment within the submission
package.
